Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Nishida, Akemi; Kawata, Manabu; Choi, B.; Kunitomo, Takahiro; Shiomi, Tadahiko; Iigaki, Kazuhiko; Yamakawa, Koki*
Transactions of the 27th International Conference on Structural Mechanics in Reactor Technology (SMiRT 27) (Internet), 10 Pages, 2024/03
no abstracts in English
Nishida, Akemi; Murakami, Takahiro*; Satoda, Akira*; Asano, Yuya*; Guo, Z. H.*; Oshima, Masami*; Matsukawa, Keisuke*; Nakajima, Norihiro
Transactions of the 26th International Conference on Structural Mechanics in Reactor Technology (SMiRT-26) (Internet), 10 Pages, 2022/07
no abstracts in English
Nishida, Akemi; Murakami, Takahiro*; Satoda, Akira*; Asano, Yuya*; Guo, Z.*; Matsukawa, Keisuke*; Oshima, Masami*; Nakajima, Norihiro
Transactions of the 25th International Conference on Structural Mechanics in Reactor Technology (SMiRT-25) (USB Flash Drive), 10 Pages, 2019/08
Exhaustive studies on external events that may pose a threat to the structures of nuclear facilities and evaluations of the structural integrities are critical to safety. One of the components that greatly influence the behavior of the plant structure is the connection of structural members. In particular, the modeling of the connections has relied on empirical methods, and been conservatively designed and evaluated by considering them as pinned or rigid connections. Therefore, in this research, we have aimed to develop a connection modeling method that reproduces more realistic behavior by utilizing a three-dimensional model of the connection. As the first step of this research, we planned to determine the stiffness of the connections of steel structural members. The results confirmed that the connection can be regarded as a partially-restrained connection depending on the connection specifications of the structure, and the prospects for realistic stiffness evaluation of the connection were determined.
 diffusion in cubic
diffusion in cubic  -electron compounds observed by high transverse field
-electron compounds observed by high transverse field  SR
SRIto, Takashi; Higemoto, Wataru; Oishi, Kazuki*; Nishida, Nobuhiko*; Heffner, R. H.; Aoki, Yuji*; Suzuki, Hiroyuki*; Onimaru, Takahiro*; Tanida, Hiroshi*; Takagi, Shigeru*
Journal of Physics; Conference Series, 225, p.012021_1 - 012021_6, 2010/06
Times Cited Count:2 Percentile:66.79(Physics, Applied)The diffusion of positive muon  in condensed matter has been investigated for many years by using
in condensed matter has been investigated for many years by using  spin rotation/relaxation (
spin rotation/relaxation ( SR) technique. The
SR) technique. The  SR studies have provided deep insight into quantum diffusion at low temperatures as well as hopping process at high temperatures, which are closely related to hydrogen dynamics in the dilute limit. We here report transverse field (TF)
SR studies have provided deep insight into quantum diffusion at low temperatures as well as hopping process at high temperatures, which are closely related to hydrogen dynamics in the dilute limit. We here report transverse field (TF)  SR studies of the
SR studies of the  diffusion in cubic
diffusion in cubic  -electron compounds PrPb
-electron compounds PrPb and SmAg
and SmAg In. The
In. The  site splits into two magnetically labeled sites when high TF is applied to single-crystalline specimens along the [001] direction. The
site splits into two magnetically labeled sites when high TF is applied to single-crystalline specimens along the [001] direction. The  SR lines show drastic variation according to the
SR lines show drastic variation according to the  motion between the magnetically labeled sites. From detailed analysis of the
motion between the magnetically labeled sites. From detailed analysis of the  SR lines, we deduced
SR lines, we deduced  hopping parameters for both compounds.
hopping parameters for both compounds.
Kobayashi, Yasushi; Yamada, Tsutomu; Naito, Morimasa; Yui, Mikazu; Nakayama, Masashi; Sato, Haruo; Nishida, Takahiro*; Hironaga, Michihiko*; Yamamoto, Takeshi*; Sugiyama, Daisuke*; et al.
JAEA-Research 2009-013, 70 Pages, 2009/06
Cementitious materials will be used to ensure construction and operational safety and work efficiency in a deep geological repository. The low alkaline cement has been developed to reduce uncertainties due to hyper alkaline for the long-term safety performance of the repository system. Functions of cementitious material required in each phase of repository construction, operation and closure were summarized in a separate report entitled "Application Study on Low Alkaline Cementitious Materials for Deep Geological Repository of High Level Radioactive Wastes (Phase I) "In this report, properties of low alkaline cement/concrete which have been developed both at home and abroad, and recipes of the low alkaline concrete taken account of application to the repository component have been investigated. Fresh and hardened properties of the low alkaline cement are equivalent to the OPC and the low alkaline cement has an advantage over OPC in terms of leaching resistance. The HFSC developed by JAEA, which belongs to a pozzolanic type low alkaline cement will be able to apply to the shotcrete and the lining concrete by choosing an adequate recipe. Clarification of influences of the chemical composition of groundwater on leachate properties of the hydrates, examination of pH measurement of cement leachate, evaluation of corrosion behavior of rebar embedded in the HFSC concrete are raised as open questions for future activities.
Nishida, Akemi; Suzuki, Yoshio; Hayashi, Sachiko; Kunitomo, Takahiro*; Kumazawa, Mineo*; Hasada, Yoko*
Dai-58-Kai Riron Oyo Rikigaku Koenkai Koen Rombunshu (CD-ROM), 2 Pages, 2009/06
ACROSS (Accurately Controlled, Routinely Operated, Signal System) is such a precise metrology of frequency response characteristics that the accurately controlled sinusoidal waves (acoustic comb) is used as an input to the linear dynamic system, and induced vibration as an output is measured by the accelerometers synchronized accurately to input. This technology has been developed to be used on a routine basis for the subsurface structural analysis and state-monitoring of the geological targets. We discuss the theoretical background and the related subjects of applying this method to the artificial structures. Further we report the preliminary test experiments and results on the steel beam structure installed at TGC, JAEA.
Nishida, Akemi; Suzuki, Yoshio; Hayashi, Sachiko; Kunitomo, Takahiro*; Kumazawa, Mineo*; Hasada, Yoko*
Dai-58-Kai Riron Oyo Rikigaku Koenkai Koen Rombunshu (CD-ROM), 2 Pages, 2009/06
The transfer function data in frequency domain acquired by ACROSS is analyzed by SOMPI method, which is based essentially on AR model as a discrete equivalent of linear dynamic system. The analysis is made in two steps, time domain analysis and space-wave number domain both in a consistent way as a linear dynamic system. We have derived an accurate set of vibration characteristics including attenuation and also the local characteristics such as wave propagation within the structural units and their interactions. Detection of small change in the structure is demonstrated by introduction of very precise measurement by ACROSS combined with the data analysis by SOMPI method.
Nishida, Akemi; Suzuki, Yoshio; Hayashi, Sachiko; Kunitomo, Takahiro*; Kumazawa, Mineo*; Hasada, Yoko*
Dai-58-Kai Riron Oyo Rikigaku Koenkai Koen Rombunshu (CD-ROM), 2 Pages, 2009/06
Reliable and strict evaluation is demanded to guarantee the safety of nuclear facilities against earthquake vibrations, in particular. Usually the necessary data have been acquired by determining the natural frequency and attenuation characteristics by utilizing microseisms as an excitation agent of the vibration. The presence of measurement errors and estimation bias has been inherent and problematic in this approach. Here we try to make a break through by introducing ACROSS technology, which have been providing very accurate and reliable data on subsurface, i.e., geologic targets. In this paper, we report the relevant strategy, general concept of this approach. The technical subjects on measurement system and also a potential method of analyzing data are reported in the subsequent two papers.
Kobayashi, Yasushi; Yamada, Tsutomu; Naito, Morimasa; Yui, Mikazu; Nakayama, Masashi; Sato, Haruo; Nishida, Takahiro*; Hironaga, Michihiko*; Yamamoto, Takeshi*; Sugiyama, Daisuke*; et al.
JAEA-Research 2008-112, 43 Pages, 2009/03
In deep geological repository, use of cementitious material for rock support, lining, and grouting is essential for construction and operation and possibly raises in groundwater pH due to leachate from the cements. Since this hyperalkaline condition may lead to degradation of barriers, there is concern that it gives significant impact on long-term safety performance of the repository system. Because of these backgrounds, developments of low alkaline cement have been conducted both at home and abroad. JAEA is now planning to conduct an in-situ test for shotcreting using low alkaline cement at the Horonobe URL. On the other hand, CRIEPI has studied and developed cementitious materials for disposal of radioactive wastes. This joint research report summarizes requirements and expected performance of cementitious materials in repository taking account of surrounding conditions in each stage of the repository program so as to reflect them to further development of the low alkaline cement.
 site in PrPb
site in PrPb ; Interplay between localized
; Interplay between localized  electrons and an interstitial charged particle
electrons and an interstitial charged particleIto, Takashi; Higemoto, Wataru; Oishi, Kazuki*; Nishida, Nobuhiko*; Heffner, R. H.; Aoki, Yuji*; Amato, A.*; Onimaru, Takahiro*; Suzuki, Hiroyuki*
Physical Review Letters, 102(9), p.096403_1 - 096403_4, 2009/03
Times Cited Count:14 Percentile:62.63(Physics, Multidisciplinary) in paraquadrupolar state
in paraquadrupolar stateIto, Takashi; Higemoto, Wataru; Oishi, Kazuki; Heffner, R. H.; Nishida, Nobuhiko*; Aoki, Yuji*; Onimaru, Takahiro*; Suzuki, Hiroyuki*
Journal of Magnetism and Magnetic Materials, 310(2, Part1), p.743 - 745, 2007/03
PrPb exhibits antiferroquadrupole ordering at T
exhibits antiferroquadrupole ordering at T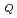 = 0.4 K. In the ordering phase, incommensurate structure of quadruple was found from recent experimental study and much attention is paid to this compound. We performed muon spin rotation and relaxation measurements on a single crystalline sample of PrPb
= 0.4 K. In the ordering phase, incommensurate structure of quadruple was found from recent experimental study and much attention is paid to this compound. We performed muon spin rotation and relaxation measurements on a single crystalline sample of PrPb . A quite anisotropic contact-coupling constant was extracted from the muon Knight shift, possibly concerned with nonspherical distribution of 4
. A quite anisotropic contact-coupling constant was extracted from the muon Knight shift, possibly concerned with nonspherical distribution of 4 -electron at low temperature. The contact and dipole coupling constants are of comparable magnitudes, suggesting significance of strong hybridization between the
-electron at low temperature. The contact and dipole coupling constants are of comparable magnitudes, suggesting significance of strong hybridization between the 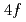 electrons of Pr and the conduction electrons for incommensurate structure.
electrons of Pr and the conduction electrons for incommensurate structure.
Matsubara, Hitoshi; Minami, Takahiro; Hazama, Osamu; Nishida, Akemi; Tian, R.; Nakajima, Norihiro; Tani, Masayuki
no journal, ,
A nuclear power plant is made up of numerous components. In previous techniques, structural analyses of entire nuclear power plant have not been achieved because it is assumed to be united structure. In this work, through our new model approach called the assembled-structure analysis, simulation of an entire nuclear power plant by assembling of individual components was made possible.
Suzuki, Yoshio; Kushida, Noriyuki; Yamagishi, Nobuhiro; Minami, Takahiro; Matsumoto, Nobuko; Nakajima, Kohei; Nishida, Akemi; Matsubara, Hitoshi; Tian, R.; Hazama, Osamu; et al.
no journal, ,
no abstracts in English
 SR study on multipolar ordering in PrPb
SR study on multipolar ordering in PrPb , 2
, 2Ito, Takashi; Higemoto, Wataru; Oishi, Kazuki; Heffner, R. H.; Nishida, Nobuhiko*; Aoki, Yuji*; Onimaru, Takahiro*; Suzuki, Hiroyuki*
no journal, ,
no abstracts in English
Ito, Takashi; Higemoto, Wataru; Oishi, Kazuki*; Nishida, Nobuhiko*; Aoki, Yuji*; Onimaru, Takahiro*; Suzuki, Hiroyuki*
no journal, ,
no abstracts in English
Nishida, Akemi; Suzuki, Yoshio; Hasegawa, Ken; Hayashi, Sachiko; Kunitomo, Takahiro*; Kumazawa, Mineo*; Hasada, Yoko*
no journal, ,
Reliable and strict evaluation is demanded to guarantee the safety of nuclear facilities against earthquake vibrations, in particular. Usually the necessary data have been acquired by determining the natural frequency, the natural mode and attenuation characteristics by utilizing microseisms as an excitation agent of the vibration. The presence of measurement errors and estimation bias has been inherent and problematic in this approach. Here we try to make a break through by introducing ACROSS technology, which have been providing very accurate and reliable data on subsurface, i.e., geologic targets. In this presentation, we present the relevant strategy, general concept of this approach. The technical subjects on measurement system and also a potential method of analyzing data are presented, too. Some parts of this research result were obtained as the results of the JAEA director's fund for research and development in 2008.
 -Pr in PrPb
-Pr in PrPb
Ito, Takashi; Higemoto, Wataru; Oishi, Kazuki*; Nishida, Nobuhiko*; Heffner, R. H.; Aoki, Yuji*; Amato, A.*; Onimaru, Takahiro*; Suzuki, Hiroyuki*
no journal, ,
An isolated few-spin system including a  spin
spin  is usually unlikely to be realized in metal. Contrary to the expectation, we actually found an isolated three-spin system
is usually unlikely to be realized in metal. Contrary to the expectation, we actually found an isolated three-spin system 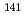 Pr-
Pr- -
-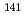 Pr in a rare-earth intermetallic compound PrPb
Pr in a rare-earth intermetallic compound PrPb . This system results in
. This system results in  spin precession with six frequencies at regular intervals. Such harmonic frequencies cannot be obtained only from dipolar interactions between
spin precession with six frequencies at regular intervals. Such harmonic frequencies cannot be obtained only from dipolar interactions between  and bare
and bare 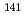 Pr nuclear spins
Pr nuclear spins 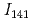 . Extremely anisotropic enhancement of the
. Extremely anisotropic enhancement of the  -
-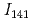 coupling is required. This enhancement can be explained by mechanism of the
coupling is required. This enhancement can be explained by mechanism of the 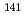 Pr hyperfine-enhanced nuclear magnetism and
Pr hyperfine-enhanced nuclear magnetism and  -induced perturbation on 4f-electronic state of two Pr ions next to the
-induced perturbation on 4f-electronic state of two Pr ions next to the  .
.
Kumazawa, Mineo*; Kunitomo, Takahiro*; Nishida, Akemi
no journal, ,
ACROSS (Accurately Controlled, Routinely Operated, Signal System) is such a precise metrology of frequency response characteristics that the accurately controlled sinusoidal waves (acoustic comb) is used as an input to the linear dynamic system, and induced vibration as an output is measured by the accelerometers synchronized accurately to input. This technology has been developed to be used on a routine basis for the subsurface structural analysis and state-monitoring of the geological targets. We discuss the theoretical background and the related subjects of applying this method to the artificial structures. The transfer function data in frequency domain acquired by ACROSS is analyzed by SOMPI method, which is based essentially on AR model as a discrete equivalent of linear dynamic system. Detection of small change in the structure is demonstrated by introduction of very precise measurement by ACROSS combined with the data analysis by SOMPI method.