Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Suguro, Toshiyasu; Nishikawa, Yoshiaki*; Watahiki, Takashi*; Kagawa, Akio
JAEA-Technology 2013-023, 22 Pages, 2013/10
For safety assessment of TRU waste disposal, solubility of plutonium was investigated under hardened cement paste porewater condition. Polycarboxylic acid compound, which have the possibility to be used for the TRU waste disposal, was selected as the cement admixture for the experiment. Initial concentration of Pu was 10 M in the experiment. The porewater of hardened cement paste was obtained by squeezing out the kneading of ordinary portland cement and deionized water with the cement admixture. The porewater of hardened cement paste without cement admixture is also used for the experiment. The maximum experimental period was 154 days. The experiment was carried out at room temperature (298
M in the experiment. The porewater of hardened cement paste was obtained by squeezing out the kneading of ordinary portland cement and deionized water with the cement admixture. The porewater of hardened cement paste without cement admixture is also used for the experiment. The maximum experimental period was 154 days. The experiment was carried out at room temperature (298  5 K) under argon atmosphere, in which oxygen concentration was lower than 1 ppm. Pu concentration in the porewater of hardened cement paste with or without the cement admixture were in the order of 10
5 K) under argon atmosphere, in which oxygen concentration was lower than 1 ppm. Pu concentration in the porewater of hardened cement paste with or without the cement admixture were in the order of 10 mol/dm
mol/dm after 154 days. This value is comparable to the solubility of Pu(IV) under high pH condition, suggesting that the solubility of Pu was not affected by the cement admixture in hardened cement paste.
after 154 days. This value is comparable to the solubility of Pu(IV) under high pH condition, suggesting that the solubility of Pu was not affected by the cement admixture in hardened cement paste.
Suguro, Toshiyasu; Nishikawa, Yoshiaki*; Watahiki, Takashi*; Kagawa, Akio; Iijima, Kazuki
JAEA-Technology 2010-048, 32 Pages, 2011/03
Cementitious materials are considered to be necessary for the construction of TRU waste repository. The cement additives are used for cements and concretes in order to provide their fluidity. Many kinds of cement additives contain organic compounds which may increase radionuclide solubility by complex formation. Therefore, it is important to obtain the solubility data with cement additives for safety assessment of TRU waste disposal. In this work, two types of cement additives, such as sodium formaldehyde acid polymer and poly carboxylic acid polymer which are expected to be applied to the TRU waste disposal system, are selected. Since the chemical condition of the repository is considered to be reducing, the authors carried out batch-type experiments of plutonium solubility under reducing (Na S
S O
O added as reducant) and anoxic condition ([O
added as reducant) and anoxic condition ([O ]
]  1 ppm). Other experimental conditions are (1)initial plutonium concentration; 10
1 ppm). Other experimental conditions are (1)initial plutonium concentration; 10 M, (2) temperature; 298
M, (2) temperature; 298 5 K, (3)experimental period; 7, 14, 28 and 56 days and (4) molecular weight of cement additives; without fractionation
5 K, (3)experimental period; 7, 14, 28 and 56 days and (4) molecular weight of cement additives; without fractionation  5,000 and
5,000 and  5,000. The plutonium concentration in the absence of the cement additives was in the order of 10
5,000. The plutonium concentration in the absence of the cement additives was in the order of 10 mol dm
mol dm , while, those in the presence of cement additives were two or three orders of magnitude higher. Additionally, low molecular weight fraction of cement additives brought relatively higher plutonium concentration than high molecular weight fraction.
, while, those in the presence of cement additives were two or three orders of magnitude higher. Additionally, low molecular weight fraction of cement additives brought relatively higher plutonium concentration than high molecular weight fraction.
Suguro, Toshiyasu; Nishikawa, Yoshiaki*; Komuro, Takashi*; Kagawa, Akio; Kashiwazaki, Hiroshi; Yamada, Kazuo
JAEA-Technology 2007-058, 20 Pages, 2007/11
For safety assessment of TRU waste disposal, data on sorption data of plutonium on Tuff have been obtained by a static batch-type experiment. Because the repository condition will be reducing and be affected by considerable amount of nitrate in waste, the authors carried out the experiments using Tuff under the reducing (Na S
S O
O as added as reductant) and anoxic condition (O
as added as reductant) and anoxic condition (O
 1 ppm) and solution of 0 to 0.5 M NaNO
1 ppm) and solution of 0 to 0.5 M NaNO . The experimental results suggest that distribution coefficient (Kd) ranges 0.2 to 0.7 m
. The experimental results suggest that distribution coefficient (Kd) ranges 0.2 to 0.7 m kg
kg in case of L/S=0.1 m
in case of L/S=0.1 m kg
kg . Similarly the Kd ranges, 1 to 7 m
. Similarly the Kd ranges, 1 to 7 m kg
kg at L/S=1 m
at L/S=1 m kg
kg . However, almost samples of the solution after experiments were plutonium solubility less than detection limit(10
. However, almost samples of the solution after experiments were plutonium solubility less than detection limit(10 mol/dm
mol/dm ) of alpha spectrometer. The reason, it is guessed plutonium coprecipitation with calcium hydroxide, because experiments using saturated calcium hydroxide in the liquid.
) of alpha spectrometer. The reason, it is guessed plutonium coprecipitation with calcium hydroxide, because experiments using saturated calcium hydroxide in the liquid.
Toshiyasu, Suguro,; Notoya, Shin; Nishikawa, Yoshiaki*; Nakamura, Ryosuke*; Shibutani, Tomoki; Kuroha, Mitsuhiko; Kamei, Gento
JNC TN8430 2004-004, 27 Pages, 2005/01
In terms of safety assessment of TRU waste disposal, data on plutonium sorption on cementitious materials have been obtained by means of a static batch-type experiment. Because the repository condition will be reducing and be affected by considerable amount of nitrate, the authors carried out the experiments using ordinary portland cement (OPC) under the reducing (Na S
S O
O as added as reductant) and anoxic condition (O
as added as reductant) and anoxic condition (O
 1ppm) and solution of 0 to 0.5 M NaNO
1ppm) and solution of 0 to 0.5 M NaNO . Other experimental conditions are : liquid/solid (L/S) ratios ; 100 and 1000 mL g
. Other experimental conditions are : liquid/solid (L/S) ratios ; 100 and 1000 mL g , Initially aaded plutonium; 2.84
, Initially aaded plutonium; 2.84 10
10 M, Temperature; 25
M, Temperature; 25 5
5 C and Reaction times; 7, 14 and 28 days. The experimental results suggest that distribution coefficient (
C and Reaction times; 7, 14 and 28 days. The experimental results suggest that distribution coefficient (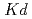 ) ranges 50 to 1000 mL g
) ranges 50 to 1000 mL g in case of L/S=100mL g
in case of L/S=100mL g . Similarly the
. Similarly the 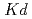 ranges, 100 to 10000 mL g
ranges, 100 to 10000 mL g at L/S=1000mL g
at L/S=1000mL g . These
. These 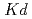 values tend to increase with lapsing reaction time. On the basis of these results, we recommend 50mL g
values tend to increase with lapsing reaction time. On the basis of these results, we recommend 50mL g as a conservative
as a conservative 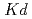 value of plutonium on OPC in a TRU waste repository condition.
value of plutonium on OPC in a TRU waste repository condition.
Sakamoto, Yoshihiko; Sakamoto, Yoshihiko; Enuma, Yasuhiro; Ando, Masato; Nishikawa, Akira; Kotake, Shoji; Ieda, Yoshiaki
Dai-14-Kai Kantaiheiyo Genshiryoku Kaigi (2004-Nen 3-Gatsu 21-Nichi 25-Nichi), 0 Pages, 2003/00
25-Nichi), 0 Pages, 2003/00
This paper describes the summary of an interim report of phase II of the Feasibility Study on Commercialized FR Cycle Systems, related to reactor systems. Promising plant concepts (sodium-, lead-bismuth-, helium-, and water-cooled fast reactor) and reactor core concepts are presented. These concepts are quantitatively evaluated from the viewpoint of the suitability to the development targets, such as economic competitiveness, efficient utilization of resources and reduction of environmental burden, with securing safety. As results, sodium cooled fast reactor is well suited to the development targets. LBE cooled fast rector would have a potential to attain the development targets. Helium gas cooled fast reactor would have the great potential for high thermal efficiency and multipurpose energy system. And water cooled fast reactor has the advantage that there are many experiences with LWR. Furthermore the crucial issues for technical feasibility are also clarified as road map of key technology development for each concept.
; Nishikawa, Yoshiaki*; Kagawa, Akio
JNC TN8410 2002-009, 191 Pages, 2002/11
Organic TRU waste form (organic matrix and/or organic matter in waste) seems to be decomposed in the repository in long term by the reaction with water, radiation and by effect of microorganisms. Groundwater intruded into the repository dissolves soluble organic components as degradation products from the waste form. It is possible that complexation of transuranic elements with soluble organic component makes solubility higher and makes sorption coefficient of days and rocks lower. These phenomena may affect the performance assessment of the TRU waste repository. This paper reports the chemical degradation of asphalt as a material of organic TRU waste form by contacting water under reducing condition. The chemical degradation tests by contacting water in reducing condition were conducted in (1)asphalt +water +iron powder system (AH) (2)asphalt +calcium hydroxide +sodium nitrate water +ion powder system (ACNH) (3)asphalt +sodium hydroxide +water +iron powder system (AOH). The test result of TOC of leachant shows TOC does not increase by time in AH and ACNH case, but TOC of leachant increases in AOH case. In previous research, TOC in high alkaline (10M-NaOH) system in aerobic condition showed high value. Chemical degradation mechanism of asphalt seems to be mainly oxidative decomposition, but even under reducing condition it is possible that soluble organic components are formed by alkaline hydrolysis.
Fukumoto, Masahiro; Nishikawa, Yoshiaki*
JNC TN8400 2001-017, 355 Pages, 2001/03
The alkali hydrolysis experiments which seem to be important from the view point of the alteration mechanism using the following seven organic materials was performed as a part of the evaluation of the influence on the disposal of the organic materials contained in the TRU wastes. As a result of the alkali hydrolysis experiments (90 C and 91d), each organic materials became those of lower molecular weight. The degradation products were able to be detected in the solution. The organic materials seem to be degraded to the organic matters which were confirmed in this study in a long term of disposal. The degradation products were shown below. Therefore, the evaluation of the influence on the migration of radionuclides by degradation products becomes important in the future. (1)Cement additives of Naphthalenesulfonic acid and Ligninsulfonic acid (
C and 91d), each organic materials became those of lower molecular weight. The degradation products were able to be detected in the solution. The organic materials seem to be degraded to the organic matters which were confirmed in this study in a long term of disposal. The degradation products were shown below. Therefore, the evaluation of the influence on the migration of radionuclides by degradation products becomes important in the future. (1)Cement additives of Naphthalenesulfonic acid and Ligninsulfonic acid ( Naphthalenedisulfonic acid etc.) (2)Cement additives of polycarboxylic acid (
Naphthalenedisulfonic acid etc.) (2)Cement additives of polycarboxylic acid ( Oligomer of distal methoxypoly ethylene glycol.) (3)Ethylenediamine-N,N,N',N'-tetraacetic acid disodium salt (
Oligomer of distal methoxypoly ethylene glycol.) (3)Ethylenediamine-N,N,N',N'-tetraacetic acid disodium salt ( Acetic acid desorped and cyclized organic matters from EDTA.) (4)Tributyl phosphate (
Acetic acid desorped and cyclized organic matters from EDTA.) (4)Tributyl phosphate ( Dibutyl phthalate, n-butanol) (5)Poly vinyl acetate (
Dibutyl phthalate, n-butanol) (5)Poly vinyl acetate ( Acetic acid) (6)Nylon66 (
Acetic acid) (6)Nylon66 ( Adipic acid, Hexamethylenediamine) (7)Cured epoxy resin (
Adipic acid, Hexamethylenediamine) (7)Cured epoxy resin ( Glycerol poly glycidyl ether, Carboxylic acid)
Glycerol poly glycidyl ether, Carboxylic acid)
Fukumoto, Masahiro; Nishikawa, Yoshiaki*; Kagawa, Akio; Kawamura, Kazuhiro
JNC TN8400 2001-002, 23 Pages, 2000/12
The soluble organic compounds generated by radiological degradation of asphalt ( ray) were confirmed as a part of influence of the bituminized waste degradation in the TRU waste repository. Especially, the influence of the nitrate was focused on. As a result, the concentration of the soluble organic compounds generated by radiological degradation of asphalt (10MGy,
ray) were confirmed as a part of influence of the bituminized waste degradation in the TRU waste repository. Especially, the influence of the nitrate was focused on. As a result, the concentration of the soluble organic compounds generated by radiological degradation of asphalt (10MGy,  ray which is correspond to absorbed dose of asphalt for 1,000,000 years) were lower (each formic acid : about 50mg/dm
ray which is correspond to absorbed dose of asphalt for 1,000,000 years) were lower (each formic acid : about 50mg/dm , acetic acid : about 30mg/dm
, acetic acid : about 30mg/dm and oxalic acid : about 2mg/dm
and oxalic acid : about 2mg/dm ) than that of the formic acid, the acetic acid and the oxalic acid which Valcke et al. had shown (the influence of the organic at the solubility examination which uses Pu and Am). Moreover, the change in the concentration of TOC and the soluble organic compounds (formic acid, acetic acid and oxalic acid) is little under the existence of nitrate ion. That is, the formic acid and acetic acid which can be organic ligands were generated little by oxidative decomposition of asphalt in the process that nitrate ion becomes nitrite ion by radiation. The influence of the soluble organic compounds by the radiological degradation of the asphalt (
) than that of the formic acid, the acetic acid and the oxalic acid which Valcke et al. had shown (the influence of the organic at the solubility examination which uses Pu and Am). Moreover, the change in the concentration of TOC and the soluble organic compounds (formic acid, acetic acid and oxalic acid) is little under the existence of nitrate ion. That is, the formic acid and acetic acid which can be organic ligands were generated little by oxidative decomposition of asphalt in the process that nitrate ion becomes nitrite ion by radiation. The influence of the soluble organic compounds by the radiological degradation of the asphalt ( ray) on adsorption and solubility by the complexation of radionuclides in the performance assessment can be limited.
ray) on adsorption and solubility by the complexation of radionuclides in the performance assessment can be limited.
; Nishikawa, Yoshiaki*; Kagawa, Akio;
JNC TN8400 2000-017, 30 Pages, 2000/03
The influence of the cement additives on the distribution coefficients of americium-241 to the Ca-bentonite was confirmed. The adsorption experiment of americium-241 to Ca-bentonite with cement additives was performed by the batch method, as a part of the influence evaluation of the organic in the research of TRU waste disposal. As a result, the distribution coefficient of americium-241 to the Ca-bentonite was over 1.2E+3m /kg in the condition of the absence of cement additives. In the case of low concentration (0.3g/kg) of the naphthalenesulfonic acid type cement additives, the distribution coefficient was 5.2E+2m
/kg in the condition of the absence of cement additives. In the case of low concentration (0.3g/kg) of the naphthalenesulfonic acid type cement additives, the distribution coefficient was 5.2E+2m kg. And, in the case of high concentration (30g/kg) of the same cement additives, the distribution coefficients was 2.0E-1m
kg. And, in the case of high concentration (30g/kg) of the same cement additives, the distribution coefficients was 2.0E-1m /kg. On the other hand in the case of flow concentration (0.5g/kg) of the polycarboxylic acid type cement additives, the distribution coefficients was over 1.3E+3m
/kg. On the other hand in the case of flow concentration (0.5g/kg) of the polycarboxylic acid type cement additives, the distribution coefficients was over 1.3E+3m /kg. And, in the case of high concentration (50g/kg) of the same cement additives, the distribution coefficient was 1.8E-1m
/kg. And, in the case of high concentration (50g/kg) of the same cement additives, the distribution coefficient was 1.8E-1m /kg. Here, selected cement additives concentrations were based on a standard concentration of 10g/kg when the ratio of water:cement is about one. From these results, the distribution coefficient of americium-241 to the Ca-bentonite decreases according cement additive concentration. The distribution coefficients were similar on different kinds of cement additives. The cement additives concentration influences the distribution coefficient. The distribution coefficient was small in the case of high concentration of the cement additives. That is, it is thought that the cement additives have small influences on the distribution coefficient of americium-241 to the Ca-bentonite in the case of low concentration, though the cement additives have influences on the distribution coefficient of americium-241 to the Ca-bentonite in the case of high concentration.
/kg. Here, selected cement additives concentrations were based on a standard concentration of 10g/kg when the ratio of water:cement is about one. From these results, the distribution coefficient of americium-241 to the Ca-bentonite decreases according cement additive concentration. The distribution coefficients were similar on different kinds of cement additives. The cement additives concentration influences the distribution coefficient. The distribution coefficient was small in the case of high concentration of the cement additives. That is, it is thought that the cement additives have small influences on the distribution coefficient of americium-241 to the Ca-bentonite in the case of low concentration, though the cement additives have influences on the distribution coefficient of americium-241 to the Ca-bentonite in the case of high concentration.
Shibutani, Tomoki; Nishikawa, Yoshiaki*; Inui, Shinichi*; Uchidate, Nobuyuki*; Yui, Mikazu
PNC TN8410 94-395, 41 Pages, 1994/10
None
Yoshikawa, Hideki; Oda, Chie; Yui, Mikazu; Nishikawa, Yoshiaki*
International Proceading workshop on Research and, ,
None
Suguro, Toshiyasu; Kagawa, Akio; Nishikawa, Yoshiaki*; Watahiki, Takashi*; Mihara, Morihiro; Iijima, Kazuki
no journal, ,
no abstracts in English
Kimuro, Shingo; Iwata, Hajime; Eguchi, Ayano; Nishikawa, Yoshiaki*; Tachi, Yukio
no journal, ,
no abstracts in English