Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Nishino, Shohei; Motohashi, Masahiro; Nishida, Tetsuro; Kawasaki, Ichio
Nihon Hozen Gakkai Dai-19-Kai Gakujutsu Koenkai Yoshishu, p.73 - 79, 2023/08
There are 4-boiler in Nuclear fuel Cycle engineering Laboratories (NCL). These boilers have been operated in the long term over 29 years. There are many water tube as one of many identical components which together make up a boilers. The leakage from water tube have occurred four times in recently. It was presumed that sulfur acid corrosion had caused the leakage. Therefore, to reduce generation of sulfuric acid corrosion, the operation term was changed to long, and regular inspection (non-destructive testing) have been carried out.
Nishino, Saki; Okada, Jumpei; Watanabe, Kazuki; Furuuchi, Yuta; Yokota, Satoru; Yada, Yuji; Kusaka, Shota; Morokado, Shiori; Nakamura, Yoshinobu
JAEA-Technology 2023-011, 39 Pages, 2023/06
Tokai Reprocessing Plant (TRP) which shifted to decommissioning phase in 2014 had nuclear fuel materials such as the spent fuel sheared powder, the diluted plutonium solution and the uranium solution in a part of the reprocessing main equipment because TRP intended to resume reprocessing operations when it suspended the operations in 2007. Therefore, we have planned to remove these nuclear materials in sequence as Flush-out before beginning the decommissioning, and conducted removal of the spent fuel sheared powder as the first stage. The spent fuel sheared powder that had accumulated in the cell of the Main Plant (MP) as a result of the spent fuel shearing process was recovered from the cell floor, the shearing machine and the distributor between April 2016 and April 2017 as part of maintenance. Removing the recovered spent fuel sheared powder was conducted between June 2022 and September 2022. In this work, the recovered powder was dissolved in nitric acid at the dissolver in a small amount in order to remove it safely and early, and the dissolved solution was sent to the highly radioactive waste storage tanks without separating uranium and plutonium. Then, the dissolved solution transfer route was rinsed with nitric acid and water. Although about 15 years had passed since previous process operations, the removing work was successfully completed without any equipment failure because of the organization of a system that combines veterans experienced the operation with young workers, careful equipment inspections, and worker education and training. Removing this powder was conducted after revising the decommissioning project and obtaining approval from the Nuclear Regulation Authority owing to operating a part of process equipment.
Tanimura, Yoshihiko; Yoshitomi, Hiroshi; Nishino, Sho; Takahashi, Masa
Radiation Measurements, 137, p.106389_1 - 106389_5, 2020/09
Times Cited Count:0 Percentile:0.01(Nuclear Science & Technology)A portable thyroid dose monitoring system has been developed at the Japan Atomic Energy Agency (JAEA) to assess the thyroid equivalent dose for workers and members of the public in a high dose rate environment. The background (B.G.) photon correction is required for an accurate measurement in a high dose rate environment at an early stage after a nuclear accident. We developed the B.G. photon correction method using cylindrical PMMA phantoms.
Nishino, Sho; Tanimura, Yoshihiko; Yoshitomi, Hiroshi; Takahashi, Masa
Radiation Measurements, 134, p.106292_1 - 106292_5, 2020/06
Times Cited Count:4 Percentile:45.45(Nuclear Science & Technology)In the situation of a severe nuclear accident, radioiodine monitoring in thyroid should be performed for a large number of people immediately after accident. The portable thyroid dose monitoring system which can be used in a high dose rate condition is in development. In this presentation, the result of performance test using prototype model will be described.
 Cf neutron source with the spherical protection case
Cf neutron source with the spherical protection caseKowatari, Munehiko; Nishino, Sho; Romallosa, K. M. D.*; Yoshitomi, Hiroshi; Tanimura, Yoshihiko; Oishi, Tetsuya
Radiation Protection Dosimetry, 189(4), p.436 - 443, 2020/05
Times Cited Count:0 Percentile:0.01(Environmental Sciences)The anisotropic emission of neutrons from a cylindrical X1  Cf source with the spherical external casing was experimentally determined. The influence of metal materials and shapes of the external casing to the anisotropy factor,
Cf source with the spherical external casing was experimentally determined. The influence of metal materials and shapes of the external casing to the anisotropy factor, 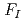 (
( ) was assessed by the Monte Carlo calculation, before performing the measurement. The results of the calculation result implied that light and spherical-shaped external casing decreases the anisotropic emission of neutrons from a cylindrical source and the nature of the material does not affect the anisotropic emission to a large extent. The experimental results obtained when a spherical-shaped aluminum protection case was employed also revealed that the anisotropy factor was close to 1.0 with a wide zenith angle range.
) was assessed by the Monte Carlo calculation, before performing the measurement. The results of the calculation result implied that light and spherical-shaped external casing decreases the anisotropic emission of neutrons from a cylindrical source and the nature of the material does not affect the anisotropic emission to a large extent. The experimental results obtained when a spherical-shaped aluminum protection case was employed also revealed that the anisotropy factor was close to 1.0 with a wide zenith angle range.
Yoshitomi, Hiroshi; Nishino, Sho; Tanimura, Yoshihiko; Takahashi, Masa
Radiation Measurements, 133, p.106279_1 - 106279_6, 2020/04
Times Cited Count:5 Percentile:53.85(Nuclear Science & Technology)Uncertainty of the body size on the counting efficiency of a newly developed thyroid monitor was estimated by Monte Carlo simulations using several voxel phantoms. Overlying tissue thickness was a major impact factor on the counting efficiency. As a result, uncertainty related to the body size of the monitored subject was found to be 25%.
Kowatari, Munehiko; Yoshitomi, Hiroshi; Nishino, Sho; Tanimura, Yoshihiko; Oishi, Tetsuya; Kessler, P.*; Neumaier, S.*; R ttger, A.*
ttger, A.*
Radiation Protection Dosimetry, 187(1), p.61 - 68, 2019/12
Times Cited Count:2 Percentile:21.58(Environmental Sciences)Kowatari, Munehiko; Yoshitomi, Hiroshi; Nishino, Sho; Tanimura, Yoshihiko; Oishi, Tetsuya; Kessler, P.*; Neumaier, S.*; R ttger, A.*
ttger, A.*
Radiation Protection Dosimetry, 186(4), P. 538, 2019/12
Times Cited Count:0 Percentile:1.45(Environmental Sciences)In the original version of this article an error occurred in Table 5. In section (b), the unit  Sv h
Sv h has been amended to nSv h
has been amended to nSv h . The corrected table appears below. The author apologises for this error.
. The corrected table appears below. The author apologises for this error.
 Am-Li sources
Am-Li sourcesHoshi, Katsuya; Nishino, Sho; Yoshida, Tadayoshi; Tsujimura, Norio
JPS Conference Proceedings (Internet), 24, p.011020_1 - 011020_6, 2019/01
We studied the application of AmLi interrogation neutron sources, which originally deployed in non-destructive assay apparatus for nuclear safeguard, to calibration work. To determine the emission rate, the angular distribution of neutron fluence was measured by a potable long counter. The emission rate at the date of measurement (October 23rd, 2015) was determined to be 1.00 10
10 n/s (
n/s ( 4.1% (
4.1% ( = 2)).
= 2)).
Tanimura, Yoshihiko; Nishino, Sho; Yoshitomi, Hiroshi; Kowatari, Munehiko; Oishi, Tetsuya
Progress in Nuclear Science and Technology (Internet), 6, p.134 - 138, 2019/01
At the severe nuclear accidents like the Fukushima Daiichi Nuclear Power Plant, various radionuclides will be dispersed into the environment and raise the dose rate. The 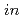 -
-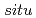 measurements of
measurements of  ray spectra and identifying radionuclides using the results are important for the radiological protection from both external and internal exposure. For this application a commercially available CdZnTe spectrometer (Kromek GR-1) was characterized at the calibration fields of FRS/JAEA. The angular dependence of the detection efficiency was studied and the efficiency was kept within 15 % degradation in
ray spectra and identifying radionuclides using the results are important for the radiological protection from both external and internal exposure. For this application a commercially available CdZnTe spectrometer (Kromek GR-1) was characterized at the calibration fields of FRS/JAEA. The angular dependence of the detection efficiency was studied and the efficiency was kept within 15 % degradation in  135 degree incident angle, which covers 85 % of all. The usable dose range was evaluated and the spectrometer could correctly measure the
135 degree incident angle, which covers 85 % of all. The usable dose range was evaluated and the spectrometer could correctly measure the  ray spectra below 200
ray spectra below 200  Gy/h.
Gy/h.
Nishino, Sho; Hoshi, Katsuya; Tsujimura, Norio; Kowatari, Munehiko; Yoshida, Tadayoshi
Proceedings of 14th International Congress of the International Radiation Protection Association (IRPA-14), Vol.3 (Internet), p.1258 - 1263, 2017/11
In order to investigate how neutron dosimeters respond in the continuous neutron fields in workplaces, we performed performance tests of four widely-used neutron survey meters in various simulated workplace neutron calibration fields established in two calibration facilities (FRS and ICF) in JAEA. As a result, we found that survey meters significantly over or underestimate neutron dose in the fields which have spectral components only in the energy range below 1 MeV, while those show good performance in the fields which have spectral components in the energy range above 1 MeV.
Yoshitomi, Hiroshi; Hagiwara, Masayuki*; Kowatari, Munehiko; Nishino, Sho; Sanami, Toshiya*; Iwase, Hiroshi*
Proceedings of 14th International Congress of the International Radiation Protection Association (IRPA-14), Vol.3 (Internet), p.1188 - 1195, 2017/11
The equivalent doses to the lens of the eye and extremities for radiation workers should be assessed properly to ensure that the dose limits are not exceeded. Recently, the following two issues has pressed demand on more appropriate evaluation of the equivalent doses of the lens of the eye and extremity. One is the new occupational dose limit for the lens of the eye the ICRP recommended. The other is growing demand on handling of highly activated materials in the maintenance works of an accelerator and contaminated materials during the decommissioning works of nuclear facility, which increases the potential exposure risk to the extremities to a wider variety of radio-nuclides. Since the points to be assessed for the exposures to the lens of the eye and the extremities are apart from the trunk, the homogeneity of the radiation fields would be significantly impact on the assessment of these equivalent doses. However, there has been no sufficient and available method to identify the nonhomogeneous situations systematically in terms of the eye lens or extremity monitoring. The goal of this study is to provide the framework to identify the nonhomogeneous exposure situations. In order to fulfil this purpose, newly proposed indices to represent the homogeneity were calculated by Monte Carlo simulation incorporated with mathematical phantom, verifying the benchmark measurements. Important parameters that significantly impact on these indices were also shown from the various trials of calculations of homogeneity indices.
Kowatari, Munehiko; Yoshitomi, Hiroshi; Nishino, Sho; Tanimura, Yoshihiko; Oishi, Tetsuya; Yoshizawa, Michio
Proceedings of 14th International Congress of the International Radiation Protection Association (IRPA-14), Vol.3 (Internet), p.1230 - 1238, 2017/11
The Facility of Radiation Standards (FRS) of the Japan Atomic Energy Agency (JAEA) offers various kinds of radiation calibration fields for calibration and testing for over three decades. The FRS-JAEA offers reliable X-ray,  -ray, beta-ray and neutron calibration fields with a vast range of variety. The quality and a set of neutron calibration fields are particularly mentioned. Neutron calibration fields with energies ranging between 0.025 eV and 19 MeV enable users to check the whole items for performance test. Two different sets of beta-ray calibration fields were established and served for regular calibration of dosimeters mainly used in nuclear industries. Resent research accomplishments on
-ray, beta-ray and neutron calibration fields with a vast range of variety. The quality and a set of neutron calibration fields are particularly mentioned. Neutron calibration fields with energies ranging between 0.025 eV and 19 MeV enable users to check the whole items for performance test. Two different sets of beta-ray calibration fields were established and served for regular calibration of dosimeters mainly used in nuclear industries. Resent research accomplishments on  -ray calibration fields can extend the upper limit of the energy up to 6 MeV. In addition to them, a simulated workplace neutron calibration field has been newly established for calibration of neutron dosimeters used inside the nuclear reactors.
-ray calibration fields can extend the upper limit of the energy up to 6 MeV. In addition to them, a simulated workplace neutron calibration field has been newly established for calibration of neutron dosimeters used inside the nuclear reactors.
Kawasaki, Masatsugu; Nakajima, Junya; Yoshida, Keisuke; Kato, Saori; Nishino, Sho; Nozaki, Teo; Nakagawa, Masahiro; Tsunoda, Junichi; Sugaya, Yuki; Hasegawa, Rie; et al.
JAEA-Data/Code 2017-004, 57 Pages, 2017/03
In emergency situation of nuclear facilities, we need to estimate the radiation dose due to radiation and radioactivity to grasp the influence range of the accident in the early stage. Therefore, we prepare the case studies of dose assessment for public exposure dose and personal exposure dose and contribute them to emergency procedures. This document covers about accidents of nuclear facilities in Nuclear Science Research Institute and past accident of nuclear power plant, and it can be used for inheritance of techniques of emergency dose assessment.
 Am-Be sources in JAEA-FRS
Am-Be sources in JAEA-FRSNishino, Sho; Tanimura, Yoshihiko; Ebata, Yoshiaki*; Yoshizawa, Michio
Journal of Radiation Protection and Research, 41(3), p.211 - 215, 2016/09
We developed the graphite-moderated neutron calibration fields using  Am-Be sources at the Facility of Radiation Standard in the Japan Atomic Energy Agency. The neutron spectra of the fields were evaluated by Monte-Carlo calculation and measurements using the Bonner Multi-sphere Spectrometer. Reference values of fluence rates and dose equivalent rates of H
Am-Be sources at the Facility of Radiation Standard in the Japan Atomic Energy Agency. The neutron spectra of the fields were evaluated by Monte-Carlo calculation and measurements using the Bonner Multi-sphere Spectrometer. Reference values of fluence rates and dose equivalent rates of H (10) and H
(10) and H (10) were determined from neutron spectra by measurements. Currently, our fields are available for calibration or performance test of neutron measuring instruments.
(10) were determined from neutron spectra by measurements. Currently, our fields are available for calibration or performance test of neutron measuring instruments.
Watanabe, Hitoshi; Nakano, Masanao; Fujita, Hiroki; Kono, Takahiko; Inoue, Kazumi; Yoshii, Hideki*; Otani, Kazunori*; Hiyama, Yoshinori*; Kikuchi, Masaaki*; Sakauchi, Nobuyuki*; et al.
JAEA-Review 2015-030, 115 Pages, 2015/12
Based on the regulations (the safety regulation of Tokai reprocessing plant, the safety regulation of nuclear fuel material usage facilities, the radiation safety rule, the regulation about prevention from radiation hazards due to radioisotopes, which are related with the nuclear regulatory acts, the local agreement concerning with safety and environment conservation around nuclear facilities, the water pollution control law, and bylaw of Ibaraki prefecture), the effluent control of liquid waste discharged from the Nuclear Fuel Cycle Engineering Laboratories of Japan Atomic Energy Agency has been performed. This report describes the effluent control results of the liquid waste in the fiscal year 2014. In this period, the concentrations and the quantities of the radioactivity in liquid waste discharged from the reprocessing plant, the plutonium fuel fabrication facilities, and the other nuclear fuel material usage facilities were much lower than the limits authorized by the above regulations.
Nakashima, Yosuke*; Takeda, Hisahito*; Ichimura, Kazuya*; Hosoi, Katsuhiro*; Oki, Kensuke*; Sakamoto, Mizuki*; Hirata, Mafumi*; Ichimura, Makoto*; Ikezoe, Ryuya*; Imai, Tsuyoshi*; et al.
Journal of Nuclear Materials, 463, p.537 - 540, 2015/08
Times Cited Count:19 Percentile:82.55(Materials Science, Multidisciplinary)Kawasaki, Ichio; Ishiyama, Toru; Nishino, Shohei; Aoki, Masaru*
Boira Kenkyu, (391), p.8 - 14, 2015/06
no abstracts in English
Watanabe, Hitoshi; Nakano, Masanao; Fujita, Hiroki; Kono, Takahiko; Inoue, Kazumi; Yoshii, Hideki*; Otani, Kazunori*; Hiyama, Yoshinori*; Goto, Ichiro*; Kibe, Satoshi*; et al.
JAEA-Review 2014-040, 115 Pages, 2015/01
Based on the regulations (the safety regulation of Tokai reprocessing plant, the safety regulation of nuclear fuel material usage facilities, the radiation safety rule, the regulation about prevention from radiation hazards due to radioisotopes, which are related with the nuclear regulatory acts, the local agreement concerning with safety and environment conservation around nuclear facilities, the water pollution control law, and bylaw of Ibaraki prefecture), the effluent control of liquid waste discharged from the Nuclear Fuel Cycle Engineering Laboratories of Japan Atomic Energy Agency has been performed. This report describes the effluent control results of the liquid waste in the fiscal year 2013. In this period, the concentrations and the quantities of the radioactivity in liquid waste discharged from the reprocessing plant, the plutonium fuel fabrication facilities, and the other nuclear fuel material usage facilities were much lower than the limits authorized by the above regulations.
Nakashima, Yosuke*; Sakamoto, Mizuki*; Yoshikawa, Masayuki*; Oki, Kensuke*; Takeda, Hisahito*; Ichimura, Kazuya*; Hosoi, Katsuhiro*; Hirata, Mafumi*; Ichimura, Makoto*; Ikezoe, Ryuya*; et al.
Proceedings of 25th IAEA Fusion Energy Conference (FEC 2014) (CD-ROM), 8 Pages, 2014/10