Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Yamaguchi, Takashi*; Katata, Genki; Noguchi, Izumi*; Sakai, Shigekatsu*; Watanabe, Yoko*; Uematsu, Mitsuo*; Furutani, Hiroshi*
Atmospheric Research, 151, p.82 - 92, 2015/01
Times Cited Count:18 Percentile:48.9(Meteorology & Atmospheric Sciences)To evaluate water and nitrogen input via fog water deposition, fog chemistry and deposition around a crater lake (Mashu) in northern Japan were investigated in the growing seasons of trees in 2006-2012. The fog samples were collected using an active fog collector and droplet size distribution was measured by a droplet size spectrometer. Compared to previous iterature of exposure experiments of acid mist on plants, fog acidity in this study did not seem to injure plant leaves. The visibility (VIS)-liquid water content of fog (LWC) relationship differed between summer and autumn. Fog water deposition was calculated from LWC empirically derived from past VIS data and deposition velocity estimated using wind speed and vegetation parameters. The water and nitrogen inputs via fog water deposition accumulated for each growing season were estimated as 107-161 mm and 20-41 meq m , respectively.
, respectively.
Katata, Genki; Yamaguchi, Takashi*; Sato, Haruna*; Watanabe, Yoko*; Noguchi, Izumi*; Hara, Hiroshi*; Nagai, Haruyasu
Asian Journal of Atmospheric Environment, 7(1), p.17 - 24, 2013/03
Fog deposition onto the cool-temperate deciduous forest in northern Japan was estimated by the inferential method using the parameterizations of deposition velocity and liquid water content of fog (LWC). Two parameterizations of fog deposition velocity derived from the field experiments and numerical simulations were tested. The empirical function between horizontal visibility (VIS) and LWC was applied to produce hourly LWC as input data of the inferential method. Weekly mean LWC computed from VIS had a good correlation with the one sampled by an active string-fog collector. Fog deposition calculated by the inferential method agreed with that computed from thorough fall data within the factors of 2 to 3. The results indicated that the inferential method using the current parameterizations of deposition velocity and LWC can provide a rough estimation of water input due to fog deposition onto cool-temperature deciduous forests.
Yamaguchi, Takashi*; Noguchi, Izumi*; Watanabe, Yoko*; Katata, Genki; Sato, Haruna*; Hara, Hiroshi*
Asian Journal of Atmospheric Environment, 7(1), p.8 - 16, 2013/03
Fog water chemistry was measured and the fog water deposition rate was estimated by a throughfall method at Lake Mashu, northern Japan, from May to November, 2010. NH
 and SO
and SO
 were the most abundant cation and anion, respectively. The fog water pH ranged from 4.2 to 6.4 (mean value: 5.1). The [NH
were the most abundant cation and anion, respectively. The fog water pH ranged from 4.2 to 6.4 (mean value: 5.1). The [NH
 ]/[SO
]/[SO
 ] equivalent ratio in fog water was more than 1.0 throughout the measuring period, indicating that NH
] equivalent ratio in fog water was more than 1.0 throughout the measuring period, indicating that NH
 was the major factor in the neutralization of fog water. The estimated fog water deposition rate and fog water deposition were 0.11
was the major factor in the neutralization of fog water. The estimated fog water deposition rate and fog water deposition were 0.11 0.22 mm h
0.22 mm h and 117.0 mm, respectively. The estimated seasonal deposition of nitrogen in fog water, 26.1 meq m
and 117.0 mm, respectively. The estimated seasonal deposition of nitrogen in fog water, 26.1 meq m , was considerable amount compared to that of reported nitrogen deposition in rainfall.
, was considerable amount compared to that of reported nitrogen deposition in rainfall.
Watanabe, Yoko*; Yamaguchi, Takashi*; Katata, Genki; Noguchi, Izumi*
Asian Journal of Atmospheric Environment, 7(1), p.1 - 7, 2013/03
SEM-EDX analysis was performed using birch leaves collected from urban area and suburb area in northern Japan. Collected leaves were divided into three treatments: (1) untreated, (2) wash leaf surface (adaxial side) with deionized water, and (3) wipe leaf surface with Kimwipes. In untreated samples, many various-shaped particles including soil particles and organic debris were deposited on the surface. Sulfur (S) particles were observed on the surface of samples collected from urban area. After treatments of (2), soil particles and S particles were washed off by water, although coarse particles still remained on the leaf surface. Although treatment of (3) removed almost all particles from surface, NaCl particles were found in both urban area and suburb area. Our study revealed that the behavior of particles depends on environmental conditions such as rain.
Onoue, Tetsuji*; Sato, Honami*; Nakamura, Tomoki*; Noguchi, Takaaki*; Hidaka, Yoshihiro*; Shirai, Naoki*; Ebihara, Mitsuru*; Osawa, Takahito; Hatsukawa, Yuichi; Toh, Yosuke; et al.
Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America, 109(47), p.19134 - 19139, 2012/11
Times Cited Count:40 Percentile:72.81(Multidisciplinary Sciences)The 34 million year (My) interval of the Late Triassic is marked by the formation of several large impact structures on Earth. As with the Chicxulub impact event at the Cretaceous/Paleogene boudary, the Late Triassic impact events have been considered a factor in biotic extinction events in the Late Triassic (e.g., the Triassic/Jurassic boundary). However, the causal link between these impact events and a mass extinction event in the Late Triassic remains controversial because of a lack of stratigraphic records of their ejecta deposits. Here we report evidence for an impact event (platinum group elements anomaly, nickel-rich magnetite and microspherules) deposited within a Paleo-Pacific basin in the middle Norian (Upper Triassic) deep-sea sediment in Japan. This includes anomalously high abundances of iridium, up to 41.5 parts per billion (ppb), in the ejecta deposit, which suggests that the iridium anomaly may be found on a global scale. The middle Norian age of the ejecta deposit suggests that the impact event that produced the 100-km-wide Manicouagan crater in Canada8 is most likely related to its deposition. Our analysis of siliceous microfossils shows no evidence of a mass extinction event across the impact event horizon, and no contemporaneous faunal turnover is seen in other marine fossils. However, such an event has been reported among terrestrial tetrapods and floras in North America. We therefore hypothesize that the Manicouagan impact caused the catastrophic collapse of terrestrial ecosystems near the impact site, but not within the marine realm.
 substrate co-implanted with Si and C ions
substrate co-implanted with Si and C ionsKikuchi, Shusuke*; Umenyi, A. V.*; Inada, Kazuki*; Kawashima, Akihiro*; Noguchi, Katsuya*; Sasaki, Tomoyuki*; Miura, Kenta*; Hanaizumi, Osamu*; Yamamoto, Shunya; Kawaguchi, Kazuhiro; et al.
no journal, ,
Light emission around a wavelength ( ) of 500 nm from SiO
) of 500 nm from SiO substrates implanted with Si and C ions and annealed at 1100
substrates implanted with Si and C ions and annealed at 1100 C has been reported. In this report, we investigated photoluminescence (PL) properties of SiO
C has been reported. In this report, we investigated photoluminescence (PL) properties of SiO substrates implanted with Si and C ions and annealed at the lower temperature of 700
substrates implanted with Si and C ions and annealed at the lower temperature of 700 C. PL peaks by Si-ion implantation were observed around
C. PL peaks by Si-ion implantation were observed around  = 650 nm, and PL peaks by C-ion implantation were observed around
= 650 nm, and PL peaks by C-ion implantation were observed around  = 450 nm from SiO
= 450 nm from SiO substrates annealed at 700
substrates annealed at 700 C. The PL peak wavelength became shorter by increasing the ratio of C to Si ions. Consequently, it was confirmed that it is possible to control the emission wavelength by the ratio of C to Si ions. Our samples showed typical light-emission though the annealing temperature was lower than the temperature reported by other groups.
C. The PL peak wavelength became shorter by increasing the ratio of C to Si ions. Consequently, it was confirmed that it is possible to control the emission wavelength by the ratio of C to Si ions. Our samples showed typical light-emission though the annealing temperature was lower than the temperature reported by other groups.
Sato, Honami*; Onoue, Tetsuji*; Nakamura, Tomoki*; Noguchi, Takaaki*; Hatsukawa, Yuichi; Osawa, Takahito; Toh, Yosuke; Koizumi, Mitsuo
no journal, ,
Microspherules were discovered from a claystone layer (5 cm thick) in an Upper Triassic bedded chert succession of the Sakahogi section, Mino Terrane, Japan. An analysis of radiolarian fossils reveals that the claystone layer is correlated with the early to middle Norian stage of the Upper Triassic. The base of the layer contains 10-15% (by rock volume) green microspherules. Microspherules range in size from 200 to 300 microns. Synchrotron X-ray diffraction analysis indicates that the microspherules are composed mainly of clinoclore. Some microspherules contain a high proportion of small, euhedral to subhedral crystals of oxidized Ni-rich spinels. They are distinguished from typical igneous spinels by high contents of NiO and Fe . The geochemical signals of extraterrestrial impact are recorded in the claystone layer. Examination of the clay layer using a multiple
. The geochemical signals of extraterrestrial impact are recorded in the claystone layer. Examination of the clay layer using a multiple  -ray analysis system after neutron activation reveals that microspherules and Ni-rich spinels occur associated with an iridium anomaly, which levels comparable with those at the Cretaceous-Paleogene boudary. A scanning X-ray analytical microscope analysis shows high concentrations of siderophile elements such as nickel and cobalt, which would be expected from an extraterrestrial source.
-ray analysis system after neutron activation reveals that microspherules and Ni-rich spinels occur associated with an iridium anomaly, which levels comparable with those at the Cretaceous-Paleogene boudary. A scanning X-ray analytical microscope analysis shows high concentrations of siderophile elements such as nickel and cobalt, which would be expected from an extraterrestrial source.
Watanabe, Yoko*; Yamaguchi, Takashi*; Noguchi, Izumi*; Katata, Genki
no journal, ,
no abstracts in English
Ozawa, Yusuke*; Kubota, Hitoshi*; Miura, Kenta*; Hanaizumi, Osamu*; Noguchi, Katsuya*; Sato, Takahiro; Ishii, Yasuyuki; Koka, Masashi; Takano, Katsuyoshi*; Okubo, Takeru; et al.
no journal, ,
 substrates implanted with Si and C ions
substrates implanted with Si and C ionsInada, Kazuki*; Kawashima, Akihiro*; Kano, Keisuke*; Noguchi, Katsuya*; Miura, Kenta*; Hanaizumi, Osamu*; Yamamoto, Shunya; Kawaguchi, Kazuhiro*; Yoshikawa, Masahito
no journal, ,
It is reported that Si and C ions implanted SiO substrates emit blue light. In this paper, we are studying photoluminescence (PL) properties of SiO
substrates emit blue light. In this paper, we are studying photoluminescence (PL) properties of SiO substrates implanted with Si and C ions on various conditions. Si and C ions were implanted into an SiO
substrates implanted with Si and C ions on various conditions. Si and C ions were implanted into an SiO substrate by using a 400-kV ion implanter at JAEA/Takasaki. The Si-ion implantation energy was 150 keV, and the implantation dose was
substrate by using a 400-kV ion implanter at JAEA/Takasaki. The Si-ion implantation energy was 150 keV, and the implantation dose was  5.0
5.0 10
10 ions/cm
ions/cm . The C-ion implantation energy was 75 keV, and the implantation dose was
. The C-ion implantation energy was 75 keV, and the implantation dose was  3.0
3.0 10
10 ions/cm
ions/cm . The samples were subsequently annealed at 700
. The samples were subsequently annealed at 700 C for 25 min in air, after 1000
C for 25 min in air, after 1000 C for 25 min in air. The results of PL measurements show that the PL peak wavelength became shorter by increasing the ratio of C ions to Si ions. Consequently, it was confirmed that the emission wavelength can be controlled by hanging the ratio of C and Si.
C for 25 min in air. The results of PL measurements show that the PL peak wavelength became shorter by increasing the ratio of C ions to Si ions. Consequently, it was confirmed that the emission wavelength can be controlled by hanging the ratio of C and Si.
Yamaguchi, Takashi*; Watanabe, Yoko*; Katata, Genki; Noguchi, Izumi*
no journal, ,
The fog chemistry and droplet size distributions were observed at the somma of Lake Mashu during the summertime in 2012. Daily fogwater sample were collected by using an active string fog collector. Rainwater was collected for a week using bulk samplers. Both samlples were analyzed by an ion chromatography. During the midnight, fog droplet size distribution was also observed using an optical droplet monitor from 0:00 to 4:00 in local time. The mean concentration of total nitrogen ion in fogwater (NO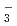 +NH
+NH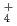 ) was 5.4 times higher than that of rainwater. Observed highly acidified fog events suggested the effects of anthropogenic air pollution and volcanoes. In October, liquid water content of large fog droplets was clearly less than other months. This may be explained by the increase of sea salt particles transported from the Japan sea.
) was 5.4 times higher than that of rainwater. Observed highly acidified fog events suggested the effects of anthropogenic air pollution and volcanoes. In October, liquid water content of large fog droplets was clearly less than other months. This may be explained by the increase of sea salt particles transported from the Japan sea.
Yamaguchi, Takashi*; Katata, Genki; Noguchi, Izumi*; Watanabe, Yoko*; Furutani, Hiroshi*; Uematsu, Mitsuo*
no journal, ,
no abstracts in English
Kano, Keisuke*; Saruya, Ryota*; Kawabata, Shunsuke*; Araki, Jun*; Noguchi, Katsuya*; Kada, Wataru*; Miura, Kenta*; Kato, Hijiri*; Sato, Takahiro; Koka, Masashi; et al.
no journal, ,