Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
 muon spin relaxation method and first-principles calculations
muon spin relaxation method and first-principles calculationsTsuru, Tomohito; Nishimura, Katsuhiko*; Matsuda, Kenji*; Nunomura, Norio*; Namiki, Takahiro*; Lee, S.*; Higemoto, Wataru; Matsuzaki, Teiichiro*; Yamaguchi, Masatake; Ebihara, Kenichi; et al.
Metallurgical and Materials Transactions A, 54(6), p.2374 - 2383, 2023/06
Times Cited Count:0 Percentile:0(Materials Science, Multidisciplinary)Although hydrogen embrittlement susceptibility of high-strength Al alloys is recognized as a critical issue in the practical use of Al alloys, identifying the hydrogen trapping or distribution has been challenging. In the present study, an effective approach based on experiment and simulation is proposed to explore the potential trap sites in Al alloys. Zero-field muon spin relaxation experiments were carried out for Al-0.5%Mg, Al-0.2%Cu, Al-0.15%Ti, Al-0.011%Ti, Al-0.28%V, and Al-0.015%V (at.%) in the temperature range from 5 to 300 K. The temperature variations of the dipole field widths have revealed three peaks for Al-0.5%Mg, four peaks for Al-0.2%Cu, three peaks for Al-0.011%Ti and Al-0.015%V. Atomic configurations of the muon trapping sites corresponding to the observed  peaks are well assigned using the first-principles calculations for the trap energies of hydrogen around a solute and solute-vacancy pair. The extracted linear relationship between the muon
peaks are well assigned using the first-principles calculations for the trap energies of hydrogen around a solute and solute-vacancy pair. The extracted linear relationship between the muon  peak temperature and the trap energy enables us to explore the potential alloying elements and their complex that have strong binding energies with hydrogen in Al alloys.
peak temperature and the trap energy enables us to explore the potential alloying elements and their complex that have strong binding energies with hydrogen in Al alloys.
Sakasegawa, Hideo; Nomura, Mitsuo; Sawayama, Kengo; Nakayama, Takuya; Yaita, Yumi*; Yonekawa, Hitoshi*; Kobayashi, Noboru*; Arima, Tatsumi*; Hiyama, Toshiaki*; Murata, Eiichi*
Progress in Nuclear Energy, 153, p.104396_1 - 104396_9, 2022/11
Times Cited Count:0 Percentile:0.01(Nuclear Science & Technology)When dismantling centrifuges in uranium-enrichment facilities, decontamination techniques must be developed to remove uranium-contaminated surfaces of dismantled parts selectively. Dismantled uranium-contaminated parts can be disposed of as nonradioactive wastes or recycled after decontamination appropriate for clearance. previously, we developed a liquid decontamination technique using acidic electrolyzed water to remove uranium-contaminated surfaces. However, further developments are still needed for its actual application. Dismantled parts have various uranium-contaminated surface features due to varied operational conditions, inhomogeneous decontamination using iodine heptafluoride gas, and changes in long-term storage conditions after dismantling. Here, we performed liquid decontamination on specimens with varying uranium-contaminated surfaces cut from a centrifuge made of low-carbon steel. From the results, the liquid decontamination can effectively remove the uranium-contaminated surfaces, and radioactive concentrations fell below the target value within twenty minutes. Although the required time should also depend on dismantled parts' sizes and shapes in their actual application, we demonstrated that it could be an effective decontamination technique for uranium-contaminated steels of dismantled centrifuges.
Yamamoto, Kazami; Kinsho, Michikazu; Hayashi, Naoki; Saha, P. K.; Tamura, Fumihiko; Yamamoto, Masanobu; Tani, Norio; Takayanagi, Tomohiro; Kamiya, Junichiro; Shobuda, Yoshihiro; et al.
Journal of Nuclear Science and Technology, 59(9), p.1174 - 1205, 2022/09
Times Cited Count:6 Percentile:84.97(Nuclear Science & Technology)In the Japan Proton Accelerator Research Complex, the purpose of the 3 GeV rapid cycling synchrotron (RCS) is to accelerate a 1 MW, high-intensity proton beam. To achieve beam operation at a repetition rate of 25 Hz at high intensities, the RCS was elaborately designed. After starting the RCS operation, we carefully verified the validity of its design and made certain improvements to establish a reliable operation at higher power as possible. Consequently, we demonstrated beam operation at a high power, namely, 1 MW. We then summarized the design, actual performance, and improvements of the RCS to achieve a 1 MW beam.
Watanabe, Jin*; Araki, Yasufumi; Kobayashi, Koji*; Ozawa, Akihiro*; Nomura, Kentaro*
Journal of the Physical Society of Japan, 91(8), p.083702_1 - 083702_5, 2022/08
Times Cited Count:3 Percentile:58.88(Physics, Multidisciplinary)We investigate magnetic orderings on kagome lattice numerically from the tight-binding Hamiltonian of electrons, governed by the filling factor and spin-orbit coupling (SOC) of electrons. We find that even a simple kagome lattice model can host both ferromagnetic and noncollinear antiferromagnetic orderings depending on the electron filling, reflecting gap structures in the Dirac and flat bands characteristic to the kagome lattice. Kane-Mele- or Rashba-type SOC tends to stabilize noncollinear orderings, such a magnetic spirals and 120-degree antiferromagnetic orderings, due to the effective Dzyaloshinskii-Moriya interaction from SOC. The obtained phase structure helps qualitative understanding of magnetic orderings in various kagome-layered materials with Weyl or Dirac electrons.
Yamane, Ikumi; Takahashi, Nobuo; Sawayama, Kengo; Nishiwaki, Hiroki; Matsumoto, Takashi; Ogawa, Jumpei; Nomura, Mitsuo; Arima, Tatsumi*
JAEA-Technology 2021-038, 18 Pages, 2022/02
We have dismantled uranium enrichment facilities in Ningyo-toge Environmental Engineering Center since their operation finished in 2001, and the total amount of metallic wastes is estimated to be about 130 thousand tons. Eighty percent of them can be disposed as nonradioactive waste (NR), but there are some steel parts possibly uranium-contaminated. We need removing painted surface of such steels and radiologically surveying to dispose them as NRs. Though painted surfaces have been conventionally removed through hand working with grinders, this manual work requires installation of green house, protective clothing, and full-face mask, in order to prevent dispersion and inhalation of airborne dusts. We desire further developments of surface cleaning techniques to reduce time, cost, workload, and secondary waste generation caused by excessive grinding. Therefore, in this study, we focused on the laser cleaning technology used for the separation and removal of paint films at construction sites. In order to improve the coating separation and removal technology for NR objects, we evaluated the coating separation and removal performance of NR steel surface by laser cleaning system, observed the coating scattering behavior by high-speed camera and investigated the coating recovery method, evaluated the laser separation and removal performance of steel surface powder, and thermodynamically evaluated the uranium compounds on steel surface. We additionally evaluated the feasibility of laser cleaning techniques in our works basing on these results, and discussed future work plans for further developments of laser cleaning techniques.
Araki, Yasufumi; Watanabe, Jin*; Nomura, Kentaro*
Journal of the Physical Society of Japan, 90(9), p.094702_1 - 094702_9, 2021/09
Times Cited Count:1 Percentile:16.57(Physics, Multidisciplinary)While nodal-line semimetals with magnetism have been theoretically predicted and experimentally observed in a few compounds, idea on the relation between the magnetic order and the electronic structure is still limited. We theoretically explore the electronic structure in bulk and boundary of such a magnetic nodal-line state by introducing magnetism in topological Dirac semimetal (TDSM). TDSMs, such as 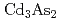 and
and 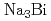 ,are characterized by a pair of spin-degenerate Dirac points protected by rotational symmetries of crystals. By introducing local magnetic moments coupled to the electron spins in the lattice model of TDSM, we show that the TDSM can turn into either a Weyl semimetal or a nodal-line semimetal, which is determined by the orbital dependence in the exchange coupling and the direction of magnetization formed by the magnetic moments. In this magnetic nodal-line semimetal state, we find zero modes with drumhead-like band structure at the boundary that are characterized by the topological number of
,are characterized by a pair of spin-degenerate Dirac points protected by rotational symmetries of crystals. By introducing local magnetic moments coupled to the electron spins in the lattice model of TDSM, we show that the TDSM can turn into either a Weyl semimetal or a nodal-line semimetal, which is determined by the orbital dependence in the exchange coupling and the direction of magnetization formed by the magnetic moments. In this magnetic nodal-line semimetal state, we find zero modes with drumhead-like band structure at the boundary that are characterized by the topological number of 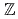 . Those zero modes are numerically demonstrated by introducing magnetic domain walls in the lattice model.
. Those zero modes are numerically demonstrated by introducing magnetic domain walls in the lattice model.
Kurebayashi, Daichi*; Araki, Yasufumi; Nomura, Kentaro*
Journal of the Physical Society of Japan, 90(8), p.084702_1 - 084702_9, 2021/08
Times Cited Count:8 Percentile:61.42(Physics, Multidisciplinary)We theoretically study current- and charge-induced spin torque in magnetic Weyl semimetals. In magnetic Weyl semimetals (WSM), topologically nontrivial band structure mediates anomalous coupling between magnetization and transport, making WSMs preferable for spintronics systems. In this paper, we determine all current-induced spin torques including spin-orbit torque and spin-transfer torque, up to first order with respect to spatial and temporal derivatives and electrical currents. We also calculate the charge-induced spin torque microscopically. We find the charge-induced spin torque originates from the chiral anomaly due to the correspondence between spin operators and axial current operators in our model.
Araki, Yasufumi; Misawa, Takahiro*; Nomura, Kentaro*
Physical Review Research (Internet), 3(2), p.023219_1 - 023219_15, 2021/06
We theoretically propose the long-range spin transport mediated by the gapless surface states of topological Dirac semimetal (TDSM). Low-dissipation spin current is a building block of next-generation spintronics devices. While conduction electrons in metals and spin waves in ferromagnetic insulators (FMIs) are the major carriers of spin current, their propagation length is inevitably limited due to the Joule heating or the Gilbert damping. In order to suppress dissipation and realize long-range spin transport, we here make use of the spin-helical surface states of TDSMs, such as Cd As
As and Na
and Na Bi, which are robust against disorder. Based on a junction of two FMIs connected by a TDSM, we demonstrate that the magnetization dynamics in one FMI induces a spin current on the TDSM surface flowing to the other FMI. By both the analytical transport theory on the surface and the numerical simulation of real-time evolution in the bulk, we find that the induced spin current takes a universal semi-quantized value that is insensitive to the microscopic coupling structure between the FMI and the TDSM. We show that this surface spin current is robust against disorder over a long range, which indicates that the TDSM surface serves as a promising system for realizing spintronics devices.
Bi, which are robust against disorder. Based on a junction of two FMIs connected by a TDSM, we demonstrate that the magnetization dynamics in one FMI induces a spin current on the TDSM surface flowing to the other FMI. By both the analytical transport theory on the surface and the numerical simulation of real-time evolution in the bulk, we find that the induced spin current takes a universal semi-quantized value that is insensitive to the microscopic coupling structure between the FMI and the TDSM. We show that this surface spin current is robust against disorder over a long range, which indicates that the TDSM surface serves as a promising system for realizing spintronics devices.
Bendo, A.*; Matsuda, Kenji*; Nishimura, Katsuhiko*; Nunomura, Norio*; Tsuchiya, Taiki*; Lee, S.*; Marioara, C. D.*; Tsuru, Tomohito; Yamaguchi, Masatake; Shimizu, Kazuyuki*; et al.
Materials Science and Technology, 36(15), p.1621 - 1627, 2020/09
Times Cited Count:8 Percentile:47.13(Materials Science, Multidisciplinary)Metastable phases in aluminum alloys are the primary nano-scale precipitates which have the biggest contribution to the increase in the tangible mechanical properties. The continuous increase in hardness in the 7xxx aluminum alloys is associated with the phase transformation from clusters or GP-zones to the metastable  phase. The transformation which is structural and compositional should occur following the path of the lowest activation energy. This work is an attempt to gain insight into how the structural transformation may occur based on the shortest route of diffusion for the eventual structure to result in that of
phase. The transformation which is structural and compositional should occur following the path of the lowest activation energy. This work is an attempt to gain insight into how the structural transformation may occur based on the shortest route of diffusion for the eventual structure to result in that of  phase. However, for the compositional transformation to occur, the proposed mechanism may not stand, since it is a prerequisite for the atoms to be at very precise positions in the aluminum lattice, at the very beginning of structural transformation, which may completely differ from that of the GP-zones atomic arrangements.
phase. However, for the compositional transformation to occur, the proposed mechanism may not stand, since it is a prerequisite for the atoms to be at very precise positions in the aluminum lattice, at the very beginning of structural transformation, which may completely differ from that of the GP-zones atomic arrangements.
Araki, Yasufumi; Misawa, Takahiro*; Nomura, Kentaro*
Physical Review Research (Internet), 2(2), p.023195_1 - 023195_11, 2020/05
 S
S
Nomura, Takuji*; Yamamoto, Yuji*; Yoshii, Kenji
Journal of the Physical Society of Japan, 89(2), p.024704_1 - 024704_10, 2020/02
Times Cited Count:0 Percentile:0(Physics, Multidisciplinary)We report a mean-field theoretical study of a triangular magnet NiGa S
S . Using the localized Wannier functions obtained from a band calculation, the most stable magnetic state was found to be spiral with the incommensurate structure, consistent with the result from neutron diffraction. The Ni-site Coulomb interaction was not strong (U about 2 eV). The spin value at the Ni site was also not so large about 1.1 mb. These results mean that the hybridization between Ni and S may play an important role. The dynamical spin correlation function was found to in accord with the results from neutron scattering.
. Using the localized Wannier functions obtained from a band calculation, the most stable magnetic state was found to be spiral with the incommensurate structure, consistent with the result from neutron diffraction. The Ni-site Coulomb interaction was not strong (U about 2 eV). The spin value at the Ni site was also not so large about 1.1 mb. These results mean that the hybridization between Ni and S may play an important role. The dynamical spin correlation function was found to in accord with the results from neutron scattering.
Bendo, A.*; Matsuda, Kenji*; Lervik, A.*; Tsuru, Tomohito; Nishimura, Katsuhiko*; Nunomura, Norio*; Holmestad, R.*; Marioara, C. D.*; Shimizu, Kazuyuki*; Toda, Hiroyuki*; et al.
Materials Characterization, 158, p.109958_1 - 109958_7, 2019/12
Times Cited Count:19 Percentile:78.27(Materials Science, Multidisciplinary)Characterization of precipitates in Al-Zn-Mg alloys, using a combination of electron diffraction, bright field transmission electron microscopy and atomic scale scanning transmission electron microscopy imaging revealed the presence of an unreported 
 orientation relationship between the
orientation relationship between the  -MgZn
-MgZn phase and the Al lattice with the following orientation relationship (0001)
phase and the Al lattice with the following orientation relationship (0001)
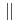 (120)
(120)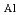 and (
and (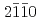 )
)
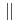 (001)
(001)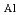 , plate on (120)
, plate on (120)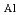 . The precipitate interfaces were observed and analyzed along two projections 90
. The precipitate interfaces were observed and analyzed along two projections 90 to one-another. The precipitate coarsening was through the common thickening ledge mechanism. The ledges were significantly stepped along one lateral direction. An interface relaxation model using density functional theory was carried out to explain the precipitate behavior.
to one-another. The precipitate coarsening was through the common thickening ledge mechanism. The ledges were significantly stepped along one lateral direction. An interface relaxation model using density functional theory was carried out to explain the precipitate behavior.
Matsuda, Kenji*; Yasumoto, Toru*; Bendo, A.*; Tsuchiya, Taiki*; Lee, S.*; Nishimura, Katsuhiko*; Nunomura, Norio*; Marioara, C. D.*; Lervik, A.*; Holmestad, R.*; et al.
Materials Transactions, 60(8), p.1688 - 1696, 2019/08
Times Cited Count:14 Percentile:63.04(Materials Science, Multidisciplinary)no abstracts in English
Bendo, A.*; Maeda, Tomoyoshi*; Matsuda, Kenji*; Lervik, A.*; Holmestad, R.*; Marioara, C. D.*; Nishimura, Katsuhiko*; Nunomura, Norio*; Toda, Hiroyuki*; Yamaguchi, Masatake; et al.
Philosophical Magazine, 99(21), p.2619 - 2635, 2019/07
Times Cited Count:26 Percentile:82.72(Materials Science, Multidisciplinary)Nishimura, Katsuhiko*; Matsuda, Kenji*; Lee, S.*; Nunomura, Norio*; Shimano, Tomoki*; Bendo, A.*; Watanabe, Katsumi*; Tsuchiya, Taiki*; Namiki, Takahiro*; Toda, Hiroyuki*; et al.
Journal of Alloys and Compounds, 774, p.405 - 409, 2019/02
Times Cited Count:3 Percentile:17.96(Chemistry, Physical) hydrogen partitioning control
hydrogen partitioning controlToda, Hiroyuki*; Yamaguchi, Masatake; Matsuda, Kenji*; Shimizu, Kazuyuki*; Hirayama, Kyosuke*; Su, H.*; Fujihara, Hiro*; Ebihara, Kenichi; Itakura, Mitsuhiro; Tsuru, Tomohito; et al.
Tetsu To Hagane, 105(2), p.240 - 253, 2019/02
Times Cited Count:0 Percentile:0(Metallurgy & Metallurgical Engineering)no abstracts in English
Nomura, Katsuhiro; Tanikawa, Shinichi*; Amamiya, Hiroki; Yasue, Kenichi
JAEA-Data/Code 2016-015, 49 Pages, 2017/03
The uplift of the last hundred thousand years in the Japanese Islands has been acquired mainly using marine and river terraces. We arranged information regarding the uplift in a table. This data is one of the useful information for the development of the investigation technology of uplift and for the research of the landform evolution in Japanese islands.

Nomura, Takuji*; Harada, Yoshihisa*; Niwa, Hideharu*; Ishii, Kenji*; Ishikado, Motoyuki*; Shamoto, Shinichi; Jarrige, I.*
Physical Review B, 94(3), p.035134_1 - 035134_9, 2016/07
Times Cited Count:11 Percentile:47.12(Materials Science, Multidisciplinary)Low-energy electron excitation spectra were measured on a single crystal of a typical iron-based superconductor PrFeAsO using resonant inelastic X-ray scattering (RIXS) at the Fe-
using resonant inelastic X-ray scattering (RIXS) at the Fe-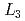 edge.
edge.
Shiomi, Yuki*; Nomura, Kentaro*; Kajiwara, Yosuke*; Eto, Kazuma*; Novak, M.*; Segawa, Koji*; Ando, Yoichi*; Saito, Eiji
Physical Review Letters, 113(19), p.196601_1 - 196601_5, 2014/11
Times Cited Count:272 Percentile:99.03(Physics, Multidisciplinary)
Jarrige, I.*; Nomura, Takuji; Ishii, Kenji; Gretarsson, H.*; Kim, Y.-J.*; Kim, J.*; Upton, M.*; Casa, D.*; Gog, T.*; Ishikado, Motoyuki*; et al.
Physical Review B, 86(11), p.115104_1 - 115104_4, 2012/09
Times Cited Count:8 Percentile:35.38(Materials Science, Multidisciplinary)We report the first observation by momentum-resolved resonant inelastic X-ray scattering of charge excitations in an iron-based superconductor and its parent compound, PrFeAsO and PrFeAsO respectively, with two main results. First, using calculations based on a 16 band
and PrFeAsO respectively, with two main results. First, using calculations based on a 16 band 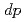 model, we show that the energy of the lowest-lying excitations, identified as
model, we show that the energy of the lowest-lying excitations, identified as 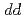 interband transitions of dominant
interband transitions of dominant 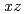 ,
, 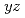 orbital character, exhibits a dramatic dependence on electron correlation. This enables us to estimate the Coulomb repulsion
orbital character, exhibits a dramatic dependence on electron correlation. This enables us to estimate the Coulomb repulsion  and Hund's coupling
and Hund's coupling  , and to highlight the role played by
, and to highlight the role played by  in these peculiar orbital-dependent electron correlation effects. Second, we show that short-range antiferromagnetic correlations, which are a prerequisite to the occurrence of these excitations at the
in these peculiar orbital-dependent electron correlation effects. Second, we show that short-range antiferromagnetic correlations, which are a prerequisite to the occurrence of these excitations at the  point, are still present in the superconducting state.
point, are still present in the superconducting state.