Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Omer, M.; Shizuma, Toshiyuki*; Koizumi, Mitsuo; Taira, Yoshitaka*; Zen, H.*; Ogaki, Hideaki*; Hajima, Ryoichi
UVSOR-50, P. 37, 2023/08
no abstracts in English
 Pb
PbShizuma, Toshiyuki*; Minato, Futoshi; Omer, M.*; Hayakawa, Takehito*; Ogaki, Hideaki*; Miyamoto, Shuji*
Physical Review C, 103(2), p.024309_1 - 024309_8, 2021/02
Times Cited Count:4 Percentile:57.13(Physics, Nuclear)Low-lying dipole transitions in  Pb were measured via nuclear photon scattering using a quasi-monochromatic, linearly polarized photon beam. The electric (
Pb were measured via nuclear photon scattering using a quasi-monochromatic, linearly polarized photon beam. The electric ( ) and magnetic (
) and magnetic ( ) dipole strengths were extracted for excitation energies up to 6.8 MeV. The present (
) dipole strengths were extracted for excitation energies up to 6.8 MeV. The present (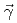 ,
,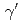 ) results, combined with (
) results, combined with ( ,
, ) data from the literature, were used to investigate the
) data from the literature, were used to investigate the  and
and  photoabsorption cross sections near the neutron separation energy by comparison with predictions of the particle-vibration coupling on top of the quasi-particle random phase approximation (PVC+QRPA).
photoabsorption cross sections near the neutron separation energy by comparison with predictions of the particle-vibration coupling on top of the quasi-particle random phase approximation (PVC+QRPA).
 Cr
CrShizuma, Toshiyuki*; Hayakawa, Takehito*; Daito, Izuru*; Ogaki, Hideaki*; Miyamoto, Shuji*; Minato, Futoshi
Physical Review C, 96(4), p.044316_1 - 044316_10, 2017/10
Times Cited Count:9 Percentile:55.37(Physics, Nuclear)The low-lying dipole strength in  Cr was measured in nuclear resonance fluorescence experiments using a quasi-monochromatic, linearly polarized photon beam. The parities of the excited dipole states were determined by the intensity asymmetry of resonantly scattered
Cr was measured in nuclear resonance fluorescence experiments using a quasi-monochromatic, linearly polarized photon beam. The parities of the excited dipole states were determined by the intensity asymmetry of resonantly scattered  -rays with respect to the polarization plane of the incident photon beam. The summed magnetic dipole (M1) strength was determined as
-rays with respect to the polarization plane of the incident photon beam. The summed magnetic dipole (M1) strength was determined as 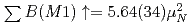 at excitation energies between 7.5 and 12.1 MeV; the summed electric dipole (E1) strength was obtained as
at excitation energies between 7.5 and 12.1 MeV; the summed electric dipole (E1) strength was obtained as 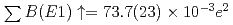 fm
fm . The observed M1 and E1 strengths were compared via random phase approximation calculations using the Skyrme interaction. The effects of 2 particle-2 hole configuration mixing and tensor force on dipole strength distributions were investigated.
. The observed M1 and E1 strengths were compared via random phase approximation calculations using the Skyrme interaction. The effects of 2 particle-2 hole configuration mixing and tensor force on dipole strength distributions were investigated.
 ,
,  ') reaction of
') reaction of  U on the target thickness
U on the target thicknessNegm, H.*; Ogaki, Hideaki*; Daito, Izuru*; Hayakawa, Takehito; Zen, H.*; Kii, Toshiteru*; Masuda, Kai*; Hori, Toshitada*; Hajima, Ryoichi; Shizuma, Toshiyuki; et al.
Journal of Nuclear Science and Technology, 52(6), p.811 - 820, 2015/06
Times Cited Count:4 Percentile:33.25(Nuclear Science & Technology)The dependence of the nuclear resonance fluorescence (NRF) yield on the target thickness was studied. To this end, an NRF experiment was performed on  U using a laser Compton back-scattering (LCS)
U using a laser Compton back-scattering (LCS)  -ray beam at the High Intensity
-ray beam at the High Intensity  -ray Source facility at Duke University.
-ray Source facility at Duke University.
 -ray source at JAEA 150-MeV microtron
-ray source at JAEA 150-MeV microtronHajima, Ryoichi; Ferdows, M.; Hayakawa, Takehito; Shizuma, Toshiyuki; Kando, Masaki; Daito, Izuru*; Negm, H.*; Ogaki, Hideaki*
Proceedings of 5th International Particle Accelerator Conference (IPAC '14) (Internet), p.1943 - 1945, 2014/07
 (Ce) detectors near 2 MeV
(Ce) detectors near 2 MeVOmer, M.*; Negm, H.*; Ogaki, Hideaki*; Daito, Izuru*; Hayakawa, Takehito; Bakr, M.*; Zen, H.*; Hori, Toshitada*; Kii, Toshiteru*; Masuda, Kai*; et al.
Nuclear Instruments and Methods in Physics Research A, 729, p.102 - 107, 2013/11
Times Cited Count:6 Percentile:44.02(Instruments & Instrumentation)The performance of LaBr (Ce) to measure nuclear resonance fluorescence (NRF) excitations is discussedin terms of limits of detection and in comparison with high-purity germanium (HPGe)detectors near the 2 MeV region where many NRF excitation levels from special nuclear materials are located. The NRF experiment was performed at the High Intensity Gamma-ray Source (HIGS) facility of Duke University. The incident
(Ce) to measure nuclear resonance fluorescence (NRF) excitations is discussedin terms of limits of detection and in comparison with high-purity germanium (HPGe)detectors near the 2 MeV region where many NRF excitation levels from special nuclear materials are located. The NRF experiment was performed at the High Intensity Gamma-ray Source (HIGS) facility of Duke University. The incident  -rays, of 2.12 MeV energy, hit a B
-rays, of 2.12 MeV energy, hit a B C target to excite the
C target to excite the  B nuclei to the first excitation level. The statistical-sensitive non-linear peak clipping (SNIP) algorithm was implemented to eliminate theback ground and enhance the limits of detection for the spectra measured with LaBr
B nuclei to the first excitation level. The statistical-sensitive non-linear peak clipping (SNIP) algorithm was implemented to eliminate theback ground and enhance the limits of detection for the spectra measured with LaBr (Ce). Both detection and determination limits were deduced from the experimental data.
(Ce). Both detection and determination limits were deduced from the experimental data.
 U measured with high-resolution LaBr
U measured with high-resolution LaBr (Ce) scintillation detectors
(Ce) scintillation detectorsOmer, M.*; Negm, H.*; Zen, H.*; Daito, Izuru*; Kii, Toshiteru*; Masuda, Kai*; Ogaki, Hideaki*; Hajima, Ryoichi; Shizuma, Toshiyuki; Hayakawa, Takehito; et al.
Japanese Journal of Applied Physics, 52(10), p.106401_1 - 106401_4, 2013/10
Times Cited Count:7 Percentile:30.71(Physics, Applied)A nuclear resonance fluorescence (NRF) experiment was performed on a  U target with quasi-monochromatic
U target with quasi-monochromatic  -rays at the High Intensity Gamma-ray Source (HIGS) facility of Duke University using a 1733 keV resonant energy. A LaBr
-rays at the High Intensity Gamma-ray Source (HIGS) facility of Duke University using a 1733 keV resonant energy. A LaBr (Ce) detector array consisting of eight cylindrical detectors, each with a length of 7.62 cm and a diameter of 3.81 cm, was implemented in this measurement. Moreover, a high-purity germanium (HPGe) detector array consisting of four detectors, each of which has a relative efficiency of 60%, was used as the benchmark for the measurement taken using the LaBr
(Ce) detector array consisting of eight cylindrical detectors, each with a length of 7.62 cm and a diameter of 3.81 cm, was implemented in this measurement. Moreover, a high-purity germanium (HPGe) detector array consisting of four detectors, each of which has a relative efficiency of 60%, was used as the benchmark for the measurement taken using the LaBr (Ce) detector array. The integrated cross section of the NRF level, measured with LaBr
(Ce) detector array. The integrated cross section of the NRF level, measured with LaBr (Ce) detectors, showed good agreement with the available data.
(Ce) detectors, showed good agreement with the available data.
 -rays from a 150-MeV microtron
-rays from a 150-MeV microtronHajima, Ryoichi; Hayakawa, Takehito; Shizuma, Toshiyuki; Angell, C.; Daito, Izuru; Kando, Masaki; Ogaki, Hideaki*
Proceedings of 4th International Particle Accelerator Conference (IPAC '13) (Internet), p.3645 - 3647, 2013/05
 Fe
FeShizuma, Toshiyuki; Hayakawa, Takehito; Ogaki, Hideaki; Toyokawa, Hiroyuki*; Komatsubara, Tetsuro*; Kikuzawa, Nobuhiro; Inakura, Tsunenori*; Homma, Michio*; Nakada, Hitoshi*
Physical Review C, 87(2), p.024301_1 - 024301_7, 2013/02
Times Cited Count:16 Percentile:68.29(Physics, Nuclear)Electro-magnetic dipole transitions in  Fe were measured in photon scattering experiments with a linearly polarized photon beam. The parity quantum numbers of the excited dipole states were determined by the intensity asymmetry of resonantly scattered
Fe were measured in photon scattering experiments with a linearly polarized photon beam. The parity quantum numbers of the excited dipole states were determined by the intensity asymmetry of resonantly scattered  -rays with respect to the polarization plane of the incident photon beam. While the summed magnetic dipole (
-rays with respect to the polarization plane of the incident photon beam. While the summed magnetic dipole ( ) strength was determined as
) strength was determined as 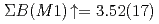
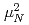 at excitation energies between 7 and 10 MeV, the summed electric dipole (
at excitation energies between 7 and 10 MeV, the summed electric dipole ( ) strength below 10 MeV was obtained as
) strength below 10 MeV was obtained as 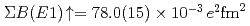 . The observed
. The observed  strength was compared with shell-model predictions in the
strength was compared with shell-model predictions in the 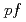 -shell using the GXPF1J and KB3G effective interactions. In addition, the
-shell using the GXPF1J and KB3G effective interactions. In addition, the  strength was compared with random-phase approximation calculations with the Skyrme interaction.
strength was compared with random-phase approximation calculations with the Skyrme interaction.
 -ray source by SBS pulse compressed laser
-ray source by SBS pulse compressed laserDaito, Izuru; Kando, Masaki; Shizuma, Toshiyuki; Hayakawa, Takehito; Angell, C.; Hajima, Ryoichi; Ogaki, Hideaki*
Purazuma, Kaku Yugo Gakkai-Shi, 88(10), p.553 - 554, 2012/10
no abstracts in English
 -ray source by compressed Nd:YAG laser pulse
-ray source by compressed Nd:YAG laser pulseDaito, Izuru; Kando, Masaki; Kotaki, Hideyuki; Hayashi, Yukio; Shizuma, Toshiyuki; Hayakawa, Takehito; Hajima, Ryoichi; Ogaki, Hideaki*
Proceedings of 3rd International Particle Accelerator Conference (IPAC '12) (Internet), p.4124 - 4126, 2012/05
A non-destructive detection system of nuclear material hidden in cargo containers is under development in JAEA and Kyoto University. The system is able to detect and identify isotopes of special nuclear material in a container by employing Nuclear Resonance Fluorescence triggered by mono-energetic laser Compton scattered  -ray. One of the most important technologies for such system is generation of
-ray. One of the most important technologies for such system is generation of  -rays at a flux of 3
-rays at a flux of 3 10
10 photon/s. In order to achieve this
photon/s. In order to achieve this  -ray flux with a compact system, a pulse compression system for Nd:YAG laser by using stimulated brillouin scattering has been developed. The laser pulse with a duration of 10 ns from a Nd:YAG laser is compressed down to 200 ps. As a feasibility study of the proposed system 400 keV
-ray flux with a compact system, a pulse compression system for Nd:YAG laser by using stimulated brillouin scattering has been developed. The laser pulse with a duration of 10 ns from a Nd:YAG laser is compressed down to 200 ps. As a feasibility study of the proposed system 400 keV  -ray generation is performed at KPSI by using 150 MeV electron beam from microtron accelerator and compressed Nd:YAG laser. Experimental results of pulse compression and
-ray generation is performed at KPSI by using 150 MeV electron beam from microtron accelerator and compressed Nd:YAG laser. Experimental results of pulse compression and  -ray generation are presented.
-ray generation are presented.
Shizuma, Toshiyuki; Hayakawa, Takehito; Hajima, Ryoichi; Kikuzawa, Nobuhiro; Ogaki, Hideaki; Toyokawa, Hiroyuki*
Review of Scientific Instruments, 83(1), p.015103_1 - 015103_4, 2012/01
Times Cited Count:8 Percentile:37.67(Instruments & Instrumentation)Nondestructive identification of heavy isotopes concealed in a thick iron box has been demonstrated by using nuclear resonance fluorescence. A quasi-monochromatic photon beam produced by the collision of laser quanta with high energy electrons was used for resonant excitation of nuclear levels in  Pb and
Pb and  Pb. By measuring the resonant
Pb. By measuring the resonant  rays emitted from
rays emitted from  Pb and
Pb and  Pb, each of these isotopes were clearly identified. The ratio of the effective thickness, i.e., concentration distribution, of these isotopes was deduced from the relative intensities of the measured NRF strengths.
Pb, each of these isotopes were clearly identified. The ratio of the effective thickness, i.e., concentration distribution, of these isotopes was deduced from the relative intensities of the measured NRF strengths.
Hayakawa, Takehito; Hajima, Ryoichi; Toyokawa, Hiroyuki*; Ogaki, Hideaki*
Kensa Gijutsu, 15(3), p.47 - 50, 2010/03
no abstracts in English
 rays
raysHayakawa, Takehito; Ogaki, Hideaki*; Shizuma, Toshiyuki; Hajima, Ryoichi; Kikuzawa, Nobuhiro; Minehara, Eisuke; Kii, Toshiteru*; Toyokawa, Hiroyuki*
Review of Scientific Instruments, 80(4), p.045110_1 - 045110_5, 2009/04
Times Cited Count:27 Percentile:71.5(Instruments & Instrumentation)A non-destructive assay method for measuring a shielded chemical compound has been proposed. The chemical compound is measured by using a nuclear resonance fluorescence (NRF) measurement technique with an energy tunable laser Compton scattering (LCS)  -ray source. This method has an advantage that hidden materials can be detected through heavy shields such as iron plates of a thickness of several centimeters. A detection of a chemical compound of melamine, C
-ray source. This method has an advantage that hidden materials can be detected through heavy shields such as iron plates of a thickness of several centimeters. A detection of a chemical compound of melamine, C H
H N
N , shielded by 15-mm-thick iron and 4-mm-thick lead plates is demonstrated. The NRF
, shielded by 15-mm-thick iron and 4-mm-thick lead plates is demonstrated. The NRF  -rays of
-rays of  C and
C and  N of the melamine are measured by using the LCS
N of the melamine are measured by using the LCS  -rays of the energies of up to 5.0 MeV. The observed ratio (
-rays of the energies of up to 5.0 MeV. The observed ratio ( C/
C/ N)
N)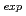 = 0.39
= 0.39  0.12 is consistent with (C/N)
0.12 is consistent with (C/N)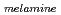 = 0.5.
= 0.5.
 -ray source
-ray sourceKikuzawa, Nobuhiro; Hajima, Ryoichi; Nishimori, Nobuyuki; Minehara, Eisuke; Hayakawa, Takehito; Shizuma, Toshiyuki; Toyokawa, Hiroyuki*; Ogaki, Hideaki*
Applied Physics Express, 2(3), p.036502_1 - 036502_3, 2009/03
Times Cited Count:56 Percentile:86.56(Physics, Applied) Pb
PbShizuma, Toshiyuki; Hayakawa, Takehito; Ogaki, Hideaki*; Toyokawa, Hiroyuki*; Komatsubara, Tetsuro*; Kikuzawa, Nobuhiro; Tamii, Atsushi*; Nakada, Hitoshi*
Physical Review C, 78(6), p.061303_1 - 061303_4, 2008/12
Times Cited Count:77 Percentile:95.33(Physics, Nuclear)Spin-flip  strength in
strength in  Pb has been measured in photon scattering experiments with a quasi-monochromatic, linearly polarized photon beam. The data resolve an
Pb has been measured in photon scattering experiments with a quasi-monochromatic, linearly polarized photon beam. The data resolve an  giant resonance into at least seven, possibly eight, discrete transitions at excitation energies between 7.1 and 7.4 MeV below the neutron separation energy. The measured
giant resonance into at least seven, possibly eight, discrete transitions at excitation energies between 7.1 and 7.4 MeV below the neutron separation energy. The measured  strength in this region is found to be larger than the previous report. The experimental results are compared with an estimation of self-consistent random phase approximation using a semi-realistic interaction.
strength in this region is found to be larger than the previous report. The experimental results are compared with an estimation of self-consistent random phase approximation using a semi-realistic interaction.
Kikuzawa, Nobuhiro; Hajima, Ryoichi; Hayakawa, Takehito; Shizuma, Toshiyuki; Toyokawa, Hiroyuki*; Ogaki, Hideaki*; Minehara, Eisuke
Proceedings of 5th Annual Meeting of Particle Accelerator Society of Japan and 33rd Linear Accelerator Meeting in Japan (CD-ROM), p.598 - 600, 2008/00
Laser-Compton-backscattered photons from an energy-recovery linac (ERL) and a high power laser realize a high-efficiency, high-flux and tunable monochromatic  -ray source. A nondestructive assay method by using the monoenegetic
-ray source. A nondestructive assay method by using the monoenegetic  -rays and nuclear resonance fluorescence (NRF) make possible to isotope imaging. The purpose of our work is to demonstrate of the NRF-based isotope imaging system. For this evaluation, we are developing a GEANT4-based Monte Carlo simulation code. In the simulation, we assume metal cubes (4
-rays and nuclear resonance fluorescence (NRF) make possible to isotope imaging. The purpose of our work is to demonstrate of the NRF-based isotope imaging system. For this evaluation, we are developing a GEANT4-based Monte Carlo simulation code. In the simulation, we assume metal cubes (4 4
4 4 mm) of U238 and lead are contained in a concrete block of 5 cm thickness. The simulation results indicate that the nondestructive
4 mm) of U238 and lead are contained in a concrete block of 5 cm thickness. The simulation results indicate that the nondestructive  spectrometric method can be applicable in the isotope imaging.
spectrometric method can be applicable in the isotope imaging.
 W,
W,  Re and
Re and  Os; Implications for the Re-Os cosmochronology
Os; Implications for the Re-Os cosmochronologyShizuma, Toshiyuki; Utsunomiya, Hiroaki*; Mohr, P.*; Hayakawa, Takehito; Goko, Shinji*; Makinaga, Ayano*; Akimune, Hidetoshi*; Yamagata, Tamio*; Ota, Masahisa*; Ogaki, Hideaki*; et al.
Physical Review C, 72(2), p.025808_1 - 025808_9, 2005/08
Times Cited Count:43 Percentile:90.03(Physics, Nuclear)Cross sections of the  W,
W,  Re,
Re,  Os(
Os(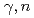 ) reactions were measured using quasi-monochromatic photon beams from laser Compton scattering (LCS) with average energies from 7.3 to 10.9 MeV. The results are compared with the predictions of Hauser-Feshbach statistical calculations using four different sets of input parameters. In addition, the inverse neutron capture cross sections were evaluated by constraining the model parameters, especially the
) reactions were measured using quasi-monochromatic photon beams from laser Compton scattering (LCS) with average energies from 7.3 to 10.9 MeV. The results are compared with the predictions of Hauser-Feshbach statistical calculations using four different sets of input parameters. In addition, the inverse neutron capture cross sections were evaluated by constraining the model parameters, especially the  strength function, on the basis of the experimental data. The present experiment helps to further constrain the correction factor
strength function, on the basis of the experimental data. The present experiment helps to further constrain the correction factor 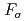 for the neutron capture on the 9.75 keV state in
for the neutron capture on the 9.75 keV state in  Os. Implications of
Os. Implications of 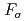 to the Re-Os cosmochronology are discussed with a focus on the uncertainty in the estimate of the age of the Galaxy.
to the Re-Os cosmochronology are discussed with a focus on the uncertainty in the estimate of the age of the Galaxy.
 W,
W,  Re and
Re and  Os for cosmochronology
Os for cosmochronologyShizuma, Toshiyuki; Utsunomiya, Hiroaki*; Goko, Shinji*; Mohr, P.*; Hayakawa, Takehito; Makinaga, Ayano*; Hara, Kaoru*; Ogaki, Hideaki*; Lui, Y.-W.*; Goriely, S.*
Nuclear Physics A, 758, p.561c - 564c, 2005/07
Photodisintegration experiments were carried out for  W,
W,  Re, and
Re, and  Os using quasi-monochromatic
Os using quasi-monochromatic  -ray beams from laser Compton scattering (LCS) at the National Institute of Advanced Industrial Science and Technology. The excitation function of (
-ray beams from laser Compton scattering (LCS) at the National Institute of Advanced Industrial Science and Technology. The excitation function of ( ,n) cross sections was measured for the three nuclei near neutron thresholds, taking advantage of the intense peaking of the energy-tunable LCS beam in the energy region of astrophysical importance. Neutron capture cross sections for
,n) cross sections was measured for the three nuclei near neutron thresholds, taking advantage of the intense peaking of the energy-tunable LCS beam in the energy region of astrophysical importance. Neutron capture cross sections for  W,
W,  Re, and
Re, and  Os are evaluated from the photodisintegration data with the Hauser-Feshbach statistical model. We quantitatively discuss the two corrections factors for the s-process branchings and the neutron capture on the 9.75 keV state.
Os are evaluated from the photodisintegration data with the Hauser-Feshbach statistical model. We quantitatively discuss the two corrections factors for the s-process branchings and the neutron capture on the 9.75 keV state.
 -process branching at
-process branching at  W revised
W revisedMohr, P.*; Shizuma, Toshiyuki; Ueda, Hiroyasu*; Goko, Shinji*; Makinaga, Ayano*; Hara, Kaoru*; Hayakawa, Takehito; Lui, Y.-W.*; Ogaki, Hideaki*; Utsunomiya, Hiroaki*
Physical Review C, 69(3), p.032801_1 - 032801_4, 2004/03
Times Cited Count:35 Percentile:84.6(Physics, Nuclear)The neutron capture cross section of the unstable s-process branching nucleus  W has been derived from experimental data of the inverse
W has been derived from experimental data of the inverse  W(
W( ,n)
,n) W photodisintegration taken with monochromatic photon beams from laser Compton scattering. The result of
W photodisintegration taken with monochromatic photon beams from laser Compton scattering. The result of 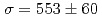 mb at
mb at 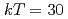 keV leads to a relatively high effective neutron density in the classical s process of
keV leads to a relatively high effective neutron density in the classical s process of 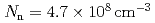 . A realistic model for the s process in thermally pulsing AGB stars overestimates the abundance of
. A realistic model for the s process in thermally pulsing AGB stars overestimates the abundance of  Os significantly because of the relatively small neutron capture cross section of
Os significantly because of the relatively small neutron capture cross section of  W.
W.