Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
 C powder and B
C powder and B C pellet regarding the eutectic reaction with stainless steel
C pellet regarding the eutectic reaction with stainless steelHong, Z.*; Ahmed, Z.*; Pellegrini, M.*; Yamano, Hidemasa; Erkan, N.*; Sharma, A. K.*; Okamoto, Koji*
Progress in Nuclear Energy, 171, p.105160_1 - 105160_13, 2024/06
In this study, it is found that the eutectic reaction between B C powder and stainless steel (SS) is considerably more rapid than that between the B
C powder and stainless steel (SS) is considerably more rapid than that between the B C pellet and SS. The derived reaction rate constant values for powder and pellet cases are consistently based on the reference values. Also, a composition analysis using SEM/EDS was conducted for the detailed microstructures of the powder and pellet samples. In the powder case, only one thick layer is found as the reaction layer consisting of (Fe, Cr)B precipitate, including B
C pellet and SS. The derived reaction rate constant values for powder and pellet cases are consistently based on the reference values. Also, a composition analysis using SEM/EDS was conducted for the detailed microstructures of the powder and pellet samples. In the powder case, only one thick layer is found as the reaction layer consisting of (Fe, Cr)B precipitate, including B C powder. In the pellet case, two layers are found in the reaction layer.
C powder. In the pellet case, two layers are found in the reaction layer.
Nagai, Takayuki; Okamoto, Yoshihiro; Yamagishi, Hirona*; Shibata, Daisuke*; Kojima, Kazuo*; Hasegawa, Takehiko*; Sato, Seiichi*; Fukaya, Akane*; Hatakeyama, Kiyoshi*
JAEA-Research 2023-004, 45 Pages, 2023/09
The local structure of glass-forming elements and waste elements in borosilicate glasses varies with its chemical composition. In this study, simulated waste glass samples were prepared and the chemical state regarding boron (B), silicon (Si) and waste elements of iron (Fe), cesium (Cs) were estimated by using XAFS measurement in soft X-ray region. To understand the chemical stability of simulated waste glasses, XANES spectra of B K-edge, Fe L , L
, L -edge, and Cs M
-edge, and Cs M , M
, M -edge were measured on the glass surface exposed to the leachate. As a result, it was found that the glass surface exposed to the leachate was changed and it was difficult to obtain a clear XANES spectrum. From the B K-edge XANES spectra on glass surfaces exposed to the leachate, an increase in three-coordination of B-O (BO
-edge were measured on the glass surface exposed to the leachate. As a result, it was found that the glass surface exposed to the leachate was changed and it was difficult to obtain a clear XANES spectrum. From the B K-edge XANES spectra on glass surfaces exposed to the leachate, an increase in three-coordination of B-O (BO ) and a decrease in four-coordination of B-O (BO
) and a decrease in four-coordination of B-O (BO ) were observed compared to the glass surfaces before immersion. The XANES spectra of Fe L
) were observed compared to the glass surfaces before immersion. The XANES spectra of Fe L , L
, L -edge, and Cs M
-edge, and Cs M , M
, M -edge show that as the exposure time in the leachate increases, the Cs present on the glass surface dissolves into the leachate. The XANES spectra of Si K-edge were measured on simulated waste glass surfaces before immersion, and it was confirmed that the change in XANES spectra given by Na
-edge show that as the exposure time in the leachate increases, the Cs present on the glass surface dissolves into the leachate. The XANES spectra of Si K-edge were measured on simulated waste glass surfaces before immersion, and it was confirmed that the change in XANES spectra given by Na O concentration had a larger effect than the waste component concentration.
O concentration had a larger effect than the waste component concentration.
Machida, Masahiko; Yamada, Susumu; Kim, M.; Okumura, Masahiko; Miyamura, Hiroko; Shikaze, Yoshiaki; Sato, Tomoki*; Numata, Yoshiaki*; Tobita, Yasuhiro*; Yamaguchi, Takashi; et al.
RIST News, (69), p.2 - 18, 2023/09
The contamination of radioactive materials leaked from the reactor has resulted in numerous hot spots in the Fukushima Daiichi Nuclear Power Station (1F) building, posing obstacles to its decommissioning. In order to solve this problem, JAEA has conducted research and development of the digital technique for inverse estimation of radiation source distribution and countermeasures against the estimated source in virtual space for two years from 2021 based on the subsidy program "Project of Decommissioning and Contaminated Water Management" performed by the funds from the Ministry of Economy, Trade and Industry. In this article, we introduce the results of the project and the plan of the renewal project started in April 2023. For the former project, we report the derivative method for LASSO method considering the complex structure inside the building and the character of the source and show the result of the inverse estimation using the method in the real reactor building. Moreover, we explain the platform software "3D-ADRES-Indoor" which integrates these achievements. Finally, we introduce the plan of the latter project.
Shi, W.*; Machida, Masahiko; Yamada, Susumu; Yoshida, Toru*; Hasegawa, Yukihiro*; Okamoto, Koji*
Progress in Nuclear Energy, 162, p.104792_1 - 104792_19, 2023/08
Times Cited Count:0 Percentile:0.01(Nuclear Science & Technology)Predicting radioactive source distributions inside reactor building rooms based on monitoring air dose rates is one of the most essential steps towards decommissioning of nuclear power plants. However, the attempt is rather a difficult task, because it can be generally mapped onto mathematically ill-posed problem. Then, in order to successfully perform the inverse estimations on radioactive source distributions even in such ill-posed conditions, we suggest that a machine learning method, least absolute shrinkage and selection operator (LASSO) minimizing the loss function, 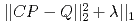 is a promising scheme. For the purpose of its feasibility demonstrations in real building rooms, we employ PHITS code to make LASSO input as the above matrix C connecting the radioactive source vector P defined on surface meshes of structural materials with the air dose rate vector Q measured at internal positions inside the rooms. We develop a mathematical criterion on the number of monitoring points to correctly predict source distributions based on the theory of Candes and Tao. Then, we confirm that LASSO actually shows extremely high possibility for source distribution reconstructions as far as the number of detection points satisfies our criterion. Moreover, we verify that radioactive hot spots can be truly reconstructed in an experiment setup. At last, we examine an influence factor like detector-source distance to enhance the predicting possibility in the inverse estimation. From the above demonstrations, we propose that LASSO scheme is a quite useful way to explore hot spots as seen in damaged nuclear power plants like Fukushima Daiichi nuclear power plants.
is a promising scheme. For the purpose of its feasibility demonstrations in real building rooms, we employ PHITS code to make LASSO input as the above matrix C connecting the radioactive source vector P defined on surface meshes of structural materials with the air dose rate vector Q measured at internal positions inside the rooms. We develop a mathematical criterion on the number of monitoring points to correctly predict source distributions based on the theory of Candes and Tao. Then, we confirm that LASSO actually shows extremely high possibility for source distribution reconstructions as far as the number of detection points satisfies our criterion. Moreover, we verify that radioactive hot spots can be truly reconstructed in an experiment setup. At last, we examine an influence factor like detector-source distance to enhance the predicting possibility in the inverse estimation. From the above demonstrations, we propose that LASSO scheme is a quite useful way to explore hot spots as seen in damaged nuclear power plants like Fukushima Daiichi nuclear power plants.
Li, C.-Y.; Wang, K.*; Uchibori, Akihiro; Okano, Yasushi; Pellegrini, M.*; Erkan, N.*; Takata, Takashi*; Okamoto, Koji*
Applied Sciences (Internet), 13(13), p.7705_1 - 7705_29, 2023/07
Times Cited Count:1 Percentile:0(Chemistry, Multidisciplinary)Nanjo, Kotaro; Shiotsu, Hiroyuki; Maruyama, Yu; Sugiyama, Tomoyuki; Okamoto, Koji*
Journal of Nuclear Science and Technology, 60(7), p.816 - 823, 2023/07
Times Cited Count:0 Percentile:0.01(Nuclear Science & Technology)Oba, Yojiro; Motokawa, Ryuhei; Kaneko, Koji; Nagai, Takayuki; Tsuchikawa, Yusuke; Shinohara, Takenao; Parker, J. D.*; Okamoto, Yoshihiro
Scientific Reports (Internet), 13, p.10071_1 - 10071_8, 2023/06
Times Cited Count:1 Percentile:72.91(Multidisciplinary Sciences)Shi, W.*; Machida, Masahiko; Yamada, Susumu; Yoshida, Toru*; Hasegawa, Yukihiro*; Okamoto, Koji*
Annals of Nuclear Energy, 184, p.109686_1 - 109686_12, 2023/05
Times Cited Count:1 Percentile:72.91(Nuclear Science & Technology)Okita, Shoichiro; Mizuta, Naoki; Takamatsu, Kuniyoshi; Goto, Minoru; Yoshida, Katsumi*; Nishimura, Yosuke*; Okamoto, Koji*
Proceedings of 30th International Conference on Nuclear Engineering (ICONE30) (Internet), 10 Pages, 2023/05
Shi, W.*; Machida, Masahiko; Yamada, Susumu; Yoshida, Toru*; Hasegawa, Yukihiro*; Okamoto, Koji*
Proceedings of Waste Management Symposia 2023 (WM2023) (Internet), 8 Pages, 2023/02
Machida, Masahiko; Shi, W.*; Yamada, Susumu; Miyamura, Hiroko; Yoshida, Toru*; Hasegawa, Yukihiro*; Okamoto, Koji; Aoki, Yuto; Ito, Rintaro; Yamaguchi, Takashi; et al.
Proceedings of Waste Management Symposia 2023 (WM2023) (Internet), 11 Pages, 2023/02
Hong, Z.*; Pellegrini, M.*; Erkan, N.*; Liao, H.*; Yang, H.*; Yamano, Hidemasa; Okamoto, Koji*
Annals of Nuclear Energy, 180, p.109462_1 - 109462_9, 2023/01
Times Cited Count:0 Percentile:0.01(Nuclear Science & Technology)A series of experiments were conducted using B C material and SUS304 tubes as a simulant of the real control rods. Reaction rate constant data in the 1450K-1500K range were obtained, and are consistent with the reference values. The reaction layer microstructure observation and the associated chemical composition analysis were also carried onto the experiment samples.
C material and SUS304 tubes as a simulant of the real control rods. Reaction rate constant data in the 1450K-1500K range were obtained, and are consistent with the reference values. The reaction layer microstructure observation and the associated chemical composition analysis were also carried onto the experiment samples.
Nanjo, Kotaro; Ishikawa, Jun; Sugiyama, Tomoyuki; Pellegrini, M.*; Okamoto, Koji*
Journal of Nuclear Science and Technology, 59(11), p.1407 - 1416, 2022/11
Times Cited Count:7 Percentile:88.9(Nuclear Science & Technology)Nagai, Takayuki; Okamoto, Yoshihiro; Yamagishi, Hirona*; Kojima, Kazuo*; Inose, Takehiko*; Sato, Seiichi*; Hatakeyama, Kiyoshi*
JAEA-Research 2022-008, 37 Pages, 2022/10
The local structure of glass-forming elements and waste elements in borosilicate glasses varies with its chemical composition. In this study, borosilicate glass frit and simulated waste glass samples were prepared and the chemical state regarding boron (B), silicon (Si) and waste elements of iron (Fe), cesium (Cs) were estimated by using XAFS measurement in soft X-ray region. Following results were obtained by XAFS measurements of simulated waste glass surfaces after immersion test to investigate the long chemical stability. (1) As the leaching time of glass samples in immersion test passed, the Cs M , M
, M -edge XANES spectra disappeared and the Fe L
-edge XANES spectra disappeared and the Fe L , L
, L -edge spectra changed. (2) A new compound was formed on the sample surface after the immersion test, and these changes in the surface state were confirmed by Raman spectroscopy. However, it became difficult to obtain a clear B K-edge XANES spectrum by forming a compound on glass surfaces. The Si K-edge XANES spectra of borosilicate glass frits with different Na
-edge spectra changed. (2) A new compound was formed on the sample surface after the immersion test, and these changes in the surface state were confirmed by Raman spectroscopy. However, it became difficult to obtain a clear B K-edge XANES spectrum by forming a compound on glass surfaces. The Si K-edge XANES spectra of borosilicate glass frits with different Na O content were measured, and following was confirmed. (1) As the Na
O content were measured, and following was confirmed. (1) As the Na O concentration increases in borosilicate glass frit, the K-edge peak of Si shifts to the low energy side. (2) The intensity of the Si K-edge peak is maximum when the Na
O concentration increases in borosilicate glass frit, the K-edge peak of Si shifts to the low energy side. (2) The intensity of the Si K-edge peak is maximum when the Na O content in glass frits was about 7wt%.
O content in glass frits was about 7wt%.
Rizaal, M.; Nakajima, Kunihisa; Saito, Takumi*; Osaka, Masahiko; Okamoto, Koji*
ACS Omega (Internet), 7(33), p.29326 - 29336, 2022/08
Times Cited Count:2 Percentile:29.84(Chemistry, Multidisciplinary) ambient on threshold voltage stability in 4H-SiC metal-oxide-semiconductor field-effect transistors
ambient on threshold voltage stability in 4H-SiC metal-oxide-semiconductor field-effect transistorsHosoi, Takuji*; Osako, Momoe*; Moges, K.*; Ito, Koji*; Kimoto, Tsunenobu*; Sometani, Mitsuru*; Okamoto, Mitsuo*; Yoshigoe, Akitaka; Shimura, Takayoshi*; Watanabe, Heiji*
Applied Physics Express, 15(6), p.061003_1 - 061003_5, 2022/06
Times Cited Count:2 Percentile:34.67(Physics, Applied)The combination of NO annealing and subsequent post-nitridation annealing (PNA) in CO ambient for SiO
ambient for SiO /SiC structures has been demonstrated to be effective in obtaining both high channel mobility and superior threshold voltage stability in SiC-based metal-oxide-semiconductor field-effect transistors (MOSFETs). N atoms on the SiO
/SiC structures has been demonstrated to be effective in obtaining both high channel mobility and superior threshold voltage stability in SiC-based metal-oxide-semiconductor field-effect transistors (MOSFETs). N atoms on the SiO side of the SiO
side of the SiO /SiC interface incorporated by NO annealing, which are plausible cause of charge trapping sites, could be selectively removed by CO
/SiC interface incorporated by NO annealing, which are plausible cause of charge trapping sites, could be selectively removed by CO -PNA at 1300
-PNA at 1300 C without oxidizing the SiC. CO
C without oxidizing the SiC. CO -PNA was also effective in compensating oxygen vacancies in SiO
-PNA was also effective in compensating oxygen vacancies in SiO , resulting high immunity against both positive and negative bias-temperature stresses.
, resulting high immunity against both positive and negative bias-temperature stresses.
Motokawa, Ryuhei; Kaneko, Koji; Oba, Yojiro; Nagai, Takayuki; Okamoto, Yoshihiro; Kobayashi, Taishi*; Kumada, Takayuki; Heller, W. T.*
Journal of Non-Crystalline Solids, 578, p.121352_1 - 121352_7, 2022/02
Times Cited Count:3 Percentile:22.84(Materials Science, Ceramics)Nagai, Takayuki; Okamoto, Yoshihiro; Yamagishi, Hirona*; Ota, Toshiaki*; Kojima, Kazuo*; Inose, Takehiko*; Sato, Seiichi*; Hatakeyama, Kiyoshi*
JAEA-Research 2021-010, 62 Pages, 2022/01
The local structure of glass-forming elements and waste elements in borosilicate glasses varies with its chemical composition. In this study, borosilicate glass frit and simulated waste glass samples were prepared and the local structure and chemical state regarding boron(B), oxygen(O), silicon(Si) and waste elements of iron(Fe), cesium(Cs) were estimated by using XAFS measurement in soft X-ray region. Following results were obtained by XAFS measurements of prepared glass frit and simulated waste glass samples: (1) The effect of Na O concentration on B-O coordination structure is greater than that of the waste elements concentration. (2) The height of pre-edge by O K-edge spectrum depends on the concentration of first transition elements such as Fe in glass samples. Following results were obtained by XAFS measurements of simulated waste glass samples after immersion test to investigate the long chemical stability. (1) A new compound was formed on the sample surface after the immersion test, and changes in the surface state were confirmed by Raman spectroscopy. (2) Cs on the sample surface after immersion test dissolves into the leaching solution. The Si K-edge XANES spectra of borosilicate glass frits and simulated waste glass samples included lanthanides oxide were measured, and following was confirmed. (1) As the Na
O concentration on B-O coordination structure is greater than that of the waste elements concentration. (2) The height of pre-edge by O K-edge spectrum depends on the concentration of first transition elements such as Fe in glass samples. Following results were obtained by XAFS measurements of simulated waste glass samples after immersion test to investigate the long chemical stability. (1) A new compound was formed on the sample surface after the immersion test, and changes in the surface state were confirmed by Raman spectroscopy. (2) Cs on the sample surface after immersion test dissolves into the leaching solution. The Si K-edge XANES spectra of borosilicate glass frits and simulated waste glass samples included lanthanides oxide were measured, and following was confirmed. (1) As the Na O concentration increases in borosilicate glass frit, the K-edge peak of Si shifts to the low energy side. (2) The peak height of the K-edge of Si differs depending on the kind of lanthanide.
O concentration increases in borosilicate glass frit, the K-edge peak of Si shifts to the low energy side. (2) The peak height of the K-edge of Si differs depending on the kind of lanthanide.
Li, C.-Y.; Uchibori, Akihiro; Takata, Takashi; Pellegrini, M.*; Erkan, N.*; Okamoto, Koji*
Dai-25-Kai Doryoku, Enerugi Gijutsu Shimpojiumu Koen Rombunshu (Internet), 4 Pages, 2021/07
The capability of stable cooling and avoiding re-criticality on the debris bed are the main issues for achieving IVR (In-Vessel Retention). In the actual situation, the debris bed is composed of mixed-density debris particles. Hence, when these mixed-density debris particles were launched to re-distribute, the debris bed would possibly form a density-stratified distribution. For the proper evaluation of this scenario, the multi-physics model of CFD-DEM-Monte-Carlo based neutronics is established to investigate the coolability and re-criticality on the heterogeneous density-stratified debris bed with considering the particle relocation. The CFD-DEM model has been verified by utilizing water injection experiments on the mixed-density particle bed in the first portion of this research. In the second portion, the coupled system of the CFD-DEM-Monte-Carlo based neutronics model is applied to reactor cases. Afterward, the debris particles' movement, debris particles' and coolant's temperature, and the k-eff eigenvalue are successfully tracked. Ultimately, the relocation and stratification effects on debris bed's coolability and re-criticality had been quantitatively confirmed.
Kitazato, Kohei*; Milliken, R. E.*; Iwata, Takahiro*; Abe, Masanao*; Otake, Makiko*; Matsuura, Shuji*; Takagi, Yasuhiko*; Nakamura, Tomoki*; Hiroi, Takahiro*; Matsuoka, Moe*; et al.
Nature Astronomy (Internet), 5(3), p.246 - 250, 2021/03
Times Cited Count:43 Percentile:96.93(Astronomy & Astrophysics)Here we report observations of Ryugu's subsurface material by the Near-Infrared Spectrometer (NIRS3) on the Hayabusa2 spacecraft. Reflectance spectra of excavated material exhibit a hydroxyl (OH) absorption feature that is slightly stronger and peak-shifted compared with that observed for the surface, indicating that space weathering and/or radiative heating have caused subtle spectral changes in the uppermost surface. However, the strength and shape of the OH feature still suggests that the subsurface material experienced heating above 300  C, similar to the surface. In contrast, thermophysical modeling indicates that radiative heating does not increase the temperature above 200
C, similar to the surface. In contrast, thermophysical modeling indicates that radiative heating does not increase the temperature above 200  C at the estimated excavation depth of 1 m, even if the semimajor axis is reduced to 0.344 au. This supports the hypothesis that primary thermal alteration occurred due to radiogenic and/or impact heating on Ryugu's parent body.
C at the estimated excavation depth of 1 m, even if the semimajor axis is reduced to 0.344 au. This supports the hypothesis that primary thermal alteration occurred due to radiogenic and/or impact heating on Ryugu's parent body.