Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Nagai, Takayuki; Okamoto, Yoshihiro; Yamagishi, Hirona*; Shibata, Daisuke*; Kojima, Kazuo*; Hasegawa, Takehiko*; Sato, Seiichi*; Fukaya, Akane*; Hatakeyama, Kiyoshi*
JAEA-Research 2023-004, 45 Pages, 2023/09
The local structure of glass-forming elements and waste elements in borosilicate glasses varies with its chemical composition. In this study, simulated waste glass samples were prepared and the chemical state regarding boron (B), silicon (Si) and waste elements of iron (Fe), cesium (Cs) were estimated by using XAFS measurement in soft X-ray region. To understand the chemical stability of simulated waste glasses, XANES spectra of B K-edge, Fe L , L
, L -edge, and Cs M
-edge, and Cs M , M
, M -edge were measured on the glass surface exposed to the leachate. As a result, it was found that the glass surface exposed to the leachate was changed and it was difficult to obtain a clear XANES spectrum. From the B K-edge XANES spectra on glass surfaces exposed to the leachate, an increase in three-coordination of B-O (BO
-edge were measured on the glass surface exposed to the leachate. As a result, it was found that the glass surface exposed to the leachate was changed and it was difficult to obtain a clear XANES spectrum. From the B K-edge XANES spectra on glass surfaces exposed to the leachate, an increase in three-coordination of B-O (BO ) and a decrease in four-coordination of B-O (BO
) and a decrease in four-coordination of B-O (BO ) were observed compared to the glass surfaces before immersion. The XANES spectra of Fe L
) were observed compared to the glass surfaces before immersion. The XANES spectra of Fe L , L
, L -edge, and Cs M
-edge, and Cs M , M
, M -edge show that as the exposure time in the leachate increases, the Cs present on the glass surface dissolves into the leachate. The XANES spectra of Si K-edge were measured on simulated waste glass surfaces before immersion, and it was confirmed that the change in XANES spectra given by Na
-edge show that as the exposure time in the leachate increases, the Cs present on the glass surface dissolves into the leachate. The XANES spectra of Si K-edge were measured on simulated waste glass surfaces before immersion, and it was confirmed that the change in XANES spectra given by Na O concentration had a larger effect than the waste component concentration.
O concentration had a larger effect than the waste component concentration.
Oba, Yojiro; Motokawa, Ryuhei; Kaneko, Koji; Nagai, Takayuki; Tsuchikawa, Yusuke; Shinohara, Takenao; Parker, J. D.*; Okamoto, Yoshihiro
Scientific Reports (Internet), 13, p.10071_1 - 10071_8, 2023/06
Times Cited Count:1 Percentile:72.91(Multidisciplinary Sciences)Nagai, Takayuki; Tone, Masaya; Katsuoka, Nanako; Okamoto, Yoshihiro; Baba, Yuji*; Akiyama, Daisuke*
Photon Factory Activity Report 2022 (Internet), 3 Pages, 2023/00
no abstracts in English
Okamoto, Yoshihiro; Shiwaku, Hideaki; Shimamura, Keisuke*; Kobayashi, Hidekazu; Nagai, Takayuki; Inose, Takehiko*; Sato, Seiichi*; Hatakeyama, Kiyoshi*
Journal of Nuclear Materials, 570, p.153962_1 - 153962_13, 2022/11
Simulated nuclear waste glass samples containing phosphorus, which increase the solubility of molybdenum, were prepared and analyzed using synchrotron X-ray Absorption Fine Structure (XAFS) analysis for some constituent elements and Raman spectroscopic analysis of their complex structure. Changes in local structure and chemical state due to different phosphorus additions and waste loading rates were systematically studied. Consequently, no crystalline phase due to the molybdate compound was observed even at a maximum waste content of 30 wt% (corresponding to 1.87 mol% MoO ). Oxidation proceeded when the waste-loading rate was increased, whereas the reduction proceeded when phosphorus was added. In some cases, the effects of oxidation and reduction were offset. The local structure around specific elements can be classified as follows; Zn that is affected mainly by the waste-loading rate, Ce that is affected by both the waste-loading rate and phosphorus addition, and Zr element that is not affected by either of them. From the comparison between the analytical results of Mo and other elements, it was considered that the added phosphorus exists as a free PO
). Oxidation proceeded when the waste-loading rate was increased, whereas the reduction proceeded when phosphorus was added. In some cases, the effects of oxidation and reduction were offset. The local structure around specific elements can be classified as follows; Zn that is affected mainly by the waste-loading rate, Ce that is affected by both the waste-loading rate and phosphorus addition, and Zr element that is not affected by either of them. From the comparison between the analytical results of Mo and other elements, it was considered that the added phosphorus exists as a free PO structural unit and may deprive the alkali metal coordinated to the molybdate ion.
structural unit and may deprive the alkali metal coordinated to the molybdate ion.
Nagai, Takayuki; Okamoto, Yoshihiro; Yamagishi, Hirona*; Kojima, Kazuo*; Inose, Takehiko*; Sato, Seiichi*; Hatakeyama, Kiyoshi*
JAEA-Research 2022-008, 37 Pages, 2022/10
The local structure of glass-forming elements and waste elements in borosilicate glasses varies with its chemical composition. In this study, borosilicate glass frit and simulated waste glass samples were prepared and the chemical state regarding boron (B), silicon (Si) and waste elements of iron (Fe), cesium (Cs) were estimated by using XAFS measurement in soft X-ray region. Following results were obtained by XAFS measurements of simulated waste glass surfaces after immersion test to investigate the long chemical stability. (1) As the leaching time of glass samples in immersion test passed, the Cs M , M
, M -edge XANES spectra disappeared and the Fe L
-edge XANES spectra disappeared and the Fe L , L
, L -edge spectra changed. (2) A new compound was formed on the sample surface after the immersion test, and these changes in the surface state were confirmed by Raman spectroscopy. However, it became difficult to obtain a clear B K-edge XANES spectrum by forming a compound on glass surfaces. The Si K-edge XANES spectra of borosilicate glass frits with different Na
-edge spectra changed. (2) A new compound was formed on the sample surface after the immersion test, and these changes in the surface state were confirmed by Raman spectroscopy. However, it became difficult to obtain a clear B K-edge XANES spectrum by forming a compound on glass surfaces. The Si K-edge XANES spectra of borosilicate glass frits with different Na O content were measured, and following was confirmed. (1) As the Na
O content were measured, and following was confirmed. (1) As the Na O concentration increases in borosilicate glass frit, the K-edge peak of Si shifts to the low energy side. (2) The intensity of the Si K-edge peak is maximum when the Na
O concentration increases in borosilicate glass frit, the K-edge peak of Si shifts to the low energy side. (2) The intensity of the Si K-edge peak is maximum when the Na O content in glass frits was about 7wt%.
O content in glass frits was about 7wt%.
Iwase, Akihiro*; Fukuda, Kengo*; Saito, Yuichi*; Okamoto, Yoshihiro; Semboshi, Satoshi*; Amekura, Hiroshi*; Matsui, Toshiyuki*
Journal of Applied Physics, 132(16), p.163902_1 - 163902_10, 2022/10
Times Cited Count:0 Percentile:0(Physics, Applied)Amorphous SiO samples were implanted with 380 keV Fe ions at room temperature. After implantation, some of the samples were irradiated with 16 MeV Au ions. magnetic properties were investigated using a SQUID magnetometer, and the morphology of the Fe-implanted SiO
samples were implanted with 380 keV Fe ions at room temperature. After implantation, some of the samples were irradiated with 16 MeV Au ions. magnetic properties were investigated using a SQUID magnetometer, and the morphology of the Fe-implanted SiO samples was examined using transmission electron microscopy and X-ray absorption spectroscopy (EXAFS and XANES), which showed that the size of Fe nanoparticles was increasing The size of Fe nanoparticles increased with increasing Fe implantation amount; some of the Fe nanoparticles consisted of Fe oxides, and the valence and structure of Fe atoms became closer to that of metallic
samples was examined using transmission electron microscopy and X-ray absorption spectroscopy (EXAFS and XANES), which showed that the size of Fe nanoparticles was increasing The size of Fe nanoparticles increased with increasing Fe implantation amount; some of the Fe nanoparticles consisted of Fe oxides, and the valence and structure of Fe atoms became closer to that of metallic  -Fe with increasing Fe injection amount. The magnetization-field curve of the sample implanted with a small amount of Fe was reproduced by Langevin's equation, suggesting that the Fe nanoparticles behave in a superparamagnetic manner. In addition, when a large amount of Fe was implanted, the magnetization-magnetic field curve shows a ferromagnetic state. These magnetic property results are consistent with the X-ray absorption results. Subsequent 16 MeV Au irradiation crushed the Fe nanoparticles, resulting in a decrease in magnetization.
-Fe with increasing Fe injection amount. The magnetization-field curve of the sample implanted with a small amount of Fe was reproduced by Langevin's equation, suggesting that the Fe nanoparticles behave in a superparamagnetic manner. In addition, when a large amount of Fe was implanted, the magnetization-magnetic field curve shows a ferromagnetic state. These magnetic property results are consistent with the X-ray absorption results. Subsequent 16 MeV Au irradiation crushed the Fe nanoparticles, resulting in a decrease in magnetization.
 and CrUO
and CrUO
Akiyama, Daisuke*; Kusaka, Ryoji; Kumagai, Yuta; Nakada, Masami; Watanabe, Masayuki; Okamoto, Yoshihiro; Nagai, Takayuki; Sato, Nobuaki*; Kirishima, Akira*
Journal of Nuclear Materials, 568, p.153847_1 - 153847_10, 2022/09
Times Cited Count:3 Percentile:68.71(Materials Science, Multidisciplinary)FeUO , CrUO
, CrUO , and Fe
, and Fe Cr
Cr UO
UO are monouranates containing pentavalent U. Even though these compounds have similar crystal structures, their formation conditions and thermal stability are significantly different. To determine the factors causing the difference in thermal stability between FeUO
are monouranates containing pentavalent U. Even though these compounds have similar crystal structures, their formation conditions and thermal stability are significantly different. To determine the factors causing the difference in thermal stability between FeUO and CrUO
and CrUO , their crystal structures were evaluated in detail. A Raman band was observed at 700 cm
, their crystal structures were evaluated in detail. A Raman band was observed at 700 cm in all the samples. This Raman band was derived from the stretching vibration of the O-U-O axis band, indicating that Fe
in all the samples. This Raman band was derived from the stretching vibration of the O-U-O axis band, indicating that Fe Cr
Cr UO
UO was composed of a uranyl-like structure in its lattice regardless of its "x"' value. M
was composed of a uranyl-like structure in its lattice regardless of its "x"' value. M ssbauer measurements indicated that the Fe in FeUO
ssbauer measurements indicated that the Fe in FeUO and Fe
and Fe Cr
Cr UO
UO were trivalent. Furthermore, Fe
were trivalent. Furthermore, Fe Cr
Cr UO
UO lost its symmetry around Fe
lost its symmetry around Fe with increasing electron densities around Fe
with increasing electron densities around Fe , as the abundance of Cr increased. These results suggested no significant structural differences between FeUO
, as the abundance of Cr increased. These results suggested no significant structural differences between FeUO and CrUO
and CrUO . Thermogravimetric measurements for UO
. Thermogravimetric measurements for UO , FeUO
, FeUO , and CrUO
, and CrUO showed that the temperature at which FeUO
showed that the temperature at which FeUO decomposed under an oxidizing condition (approximately 800
decomposed under an oxidizing condition (approximately 800  C) was significantly lower than the temperature at which the decomposition of CrUO
C) was significantly lower than the temperature at which the decomposition of CrUO started (approximately 1250
started (approximately 1250  C). Based on these results, we concluded that the decomposition of FeUO
C). Based on these results, we concluded that the decomposition of FeUO was triggered by an "in-crystal" redox reaction, i.e., Fe
was triggered by an "in-crystal" redox reaction, i.e., Fe
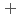 U
U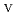
 Fe
Fe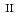
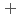 U
U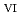 , which would not occur in the CrUO
, which would not occur in the CrUO lattice because Cr
lattice because Cr could never be reduced under the investigated condition. Finally, the existence of Cr
could never be reduced under the investigated condition. Finally, the existence of Cr in FexCr
in FexCr UO
UO effectively suppressed the decomposition of the Fe
effectively suppressed the decomposition of the Fe Cr
Cr UO
UO crystal, even at a very low Cr content.
crystal, even at a very low Cr content.
Kirishima, Akira*; Terasaki, Mariko*; Miyakawa, Kazuya; Okamoto, Yoshihiro; Akiyama, Daisuke*
Chemosphere, 289, p.133181_1 - 133181_12, 2022/04
Times Cited Count:1 Percentile:6.09(Environmental Sciences)no abstracts in English
Motokawa, Ryuhei; Kaneko, Koji; Oba, Yojiro; Nagai, Takayuki; Okamoto, Yoshihiro; Kobayashi, Taishi*; Kumada, Takayuki; Heller, W. T.*
Journal of Non-Crystalline Solids, 578, p.121352_1 - 121352_7, 2022/02
Times Cited Count:3 Percentile:22.84(Materials Science, Ceramics)Nagai, Takayuki; Okamoto, Yoshihiro; Yamagishi, Hirona*; Ota, Toshiaki*; Kojima, Kazuo*; Inose, Takehiko*; Sato, Seiichi*; Hatakeyama, Kiyoshi*
JAEA-Research 2021-010, 62 Pages, 2022/01
The local structure of glass-forming elements and waste elements in borosilicate glasses varies with its chemical composition. In this study, borosilicate glass frit and simulated waste glass samples were prepared and the local structure and chemical state regarding boron(B), oxygen(O), silicon(Si) and waste elements of iron(Fe), cesium(Cs) were estimated by using XAFS measurement in soft X-ray region. Following results were obtained by XAFS measurements of prepared glass frit and simulated waste glass samples: (1) The effect of Na O concentration on B-O coordination structure is greater than that of the waste elements concentration. (2) The height of pre-edge by O K-edge spectrum depends on the concentration of first transition elements such as Fe in glass samples. Following results were obtained by XAFS measurements of simulated waste glass samples after immersion test to investigate the long chemical stability. (1) A new compound was formed on the sample surface after the immersion test, and changes in the surface state were confirmed by Raman spectroscopy. (2) Cs on the sample surface after immersion test dissolves into the leaching solution. The Si K-edge XANES spectra of borosilicate glass frits and simulated waste glass samples included lanthanides oxide were measured, and following was confirmed. (1) As the Na
O concentration on B-O coordination structure is greater than that of the waste elements concentration. (2) The height of pre-edge by O K-edge spectrum depends on the concentration of first transition elements such as Fe in glass samples. Following results were obtained by XAFS measurements of simulated waste glass samples after immersion test to investigate the long chemical stability. (1) A new compound was formed on the sample surface after the immersion test, and changes in the surface state were confirmed by Raman spectroscopy. (2) Cs on the sample surface after immersion test dissolves into the leaching solution. The Si K-edge XANES spectra of borosilicate glass frits and simulated waste glass samples included lanthanides oxide were measured, and following was confirmed. (1) As the Na O concentration increases in borosilicate glass frit, the K-edge peak of Si shifts to the low energy side. (2) The peak height of the K-edge of Si differs depending on the kind of lanthanide.
O concentration increases in borosilicate glass frit, the K-edge peak of Si shifts to the low energy side. (2) The peak height of the K-edge of Si differs depending on the kind of lanthanide.
Iwata, Keiko; Takamizawa, Hisashi; Ha, Yoosung; Shimodaira, Masaki; Okamoto, Yoshihiro; Honda, Mitsunori; Katsuyama, Jinya; Nishiyama, Yutaka
Nuclear Instruments and Methods in Physics Research B, 511, p.143 - 152, 2022/01
Times Cited Count:1 Percentile:33.4(Instruments & Instrumentation)Nagai, Takayuki; Okamoto, Yoshihiro; Baba, Yuji*; Akiyama, Daisuke*; Arima, Tatsumi*
Photon Factory Activity Report 2021 (Internet), 2 Pages, 2022/00
no abstracts in English
 Ln
Ln O
O (Ln = Gd, Er) solid solution
(Ln = Gd, Er) solid solutionPham, V. M.*; Arima, Tatsumi*; Inagaki, Yaohiro*; Idemitsu, Kazuya*; Akiyama, Daisuke*; Nagai, Takayuki; Okamoto, Yoshihiro
Journal of Nuclear Materials, 556, p.153189_1 - 153189_9, 2021/12
Times Cited Count:1 Percentile:16.35(Materials Science, Multidisciplinary)The crystal structure change was evaluated for (1-x)UO -xLnO
-xLnO (Ln=Gd or Er; x = 0 to 0.4) samples sintered at 1973 K for 8 h under Ar and Ar-10%H
(Ln=Gd or Er; x = 0 to 0.4) samples sintered at 1973 K for 8 h under Ar and Ar-10%H atmospheres. The effect of LnO
atmospheres. The effect of LnO doping on the crystal structure of UO
doping on the crystal structure of UO was investigated by X-ray diffraction (XRD) and X-ray absorption fine structure (XAFS). LnO
was investigated by X-ray diffraction (XRD) and X-ray absorption fine structure (XAFS). LnO doping into UO
doping into UO reduced the lattice parameter of UO
reduced the lattice parameter of UO -LnO
-LnO solid solutions up to 40mol% LnO
solid solutions up to 40mol% LnO . The lattice parameters of these samples were comparable to those of stoichiometric (U,Ln)O
. The lattice parameters of these samples were comparable to those of stoichiometric (U,Ln)O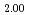 solid solutions, that is, the O/M ratios were close to 2.00. The U L
solid solutions, that is, the O/M ratios were close to 2.00. The U L -edge XANES analysis showed that higher U oxidation states of +5 or +6 formed, in addition to + 4. The EXAFS analysis indicated that the interatomic distances of U-O and Gd-O decreased with increasing x, whereas those of Er-O may not decrease monotonically.
-edge XANES analysis showed that higher U oxidation states of +5 or +6 formed, in addition to + 4. The EXAFS analysis indicated that the interatomic distances of U-O and Gd-O decreased with increasing x, whereas those of Er-O may not decrease monotonically.
Nagai, Takayuki; Akiyama, Daisuke*; Kirishima, Akira*; Sato, Nobuaki*; Okamoto, Yoshihiro
2020-Nendo "Busshitsu, Debaisu Ryoiki Kyodo Kenkyu Kyoten" Oyobi "Hito, Kankyo To Busshitsu O Tsunagu Inobeshion Soshutsu Dainamikku, Araiansu" Kenkyu Seika, Katsudo Hokokusho (CD-ROM), 1 Pages, 2021/11
no abstracts in English
Okamoto, Yoshihiro; Osugi, Takeshi; Shiwaku, Hideaki; Akabori, Mitsuo*
Insights Concerning the Fukushima Daiichi Nuclear Accident, Vol.4; Endeavors by Scientists, p.285 - 294, 2021/10
The transfer behavior of cesium adsorbed on some clay minerals in aqueous solution was investigated by X-ray absorption fine structure (XAFS) analysis of the Cs K-edge. The sample was prepared by mixing Cs-adsorbed mineral with a different pure clay mineral in water. The XAFS results of the dried mixture powder were compared with those obtained before mixing. It was recognized from the XAFS analysis for three kinds of clay minerals illite, kaolinite and vermiculite, that cesium was transferred from kaolinite to illite and vermiculite, and from illite to vermiculite. It can be concluded that cesium is transferred to and accumulated in vermiculite.
Tanida, Hajime; Okamoto, Yoshihiro
Advances in X-Ray Chemical Analysis, Japan, 52, p.69 - 80, 2021/03
In the two-dimensional imaging XAFS method using an X-ray CCD detector, a transmission method has been applied to heavy elements with absorption edges at relatively high energies. Although the transmission method requires the sample to be an optimal thickness, the high-energy X-rays have high transmission capability, and can be applied to relatively thick samples. In this study, we attempted to develop a fluorescence method for fast screening of transition metal elements with the low energy X-ray absorption edges and their valence distribution in the samples such as glass materials, which are difficult to make thin. In order to obtain XAFS spectra with high sensitivity and positional resolution, a direct imaging detector without a scintillator and a pinhole were used. The results were demonstrated with a highly brilliant synchrotron radiation undulator X-ray with variable incident energy.
Okamoto, Yoshihiro; Kobayashi, Hidekazu; Shiwaku, Hideaki; Sasage, Kenichi; Hatakeyama, Kiyoshi*; Nagai, Takayuki
Journal of Non-Crystalline Solids, 551, p.120393_1 - 120393_8, 2021/01
Times Cited Count:5 Percentile:30.89(Materials Science, Ceramics)The chemical state of ruthenium in simulated iron phosphate radioactive waste glass was investigated by conventional X-ray absorption fine structure (XAFS) and imaging XAFS analyses. The EXAFS analysis suggested that ruthenium was contained as glass phase when content of the waste components was less than 10wt.% in 30 mol%Fe O
O -P
-P O
O base glass. In other samples, crystalline RuO
base glass. In other samples, crystalline RuO was predominant. According to the imaging XAFS analysis, RuO
was predominant. According to the imaging XAFS analysis, RuO particles in all samples had length smaller than 50
particles in all samples had length smaller than 50 m. Aggregations of RuO
m. Aggregations of RuO , which are found in nuclear waste borosilicate glass, were not seen in any of the iron phosphate glass samples.
, which are found in nuclear waste borosilicate glass, were not seen in any of the iron phosphate glass samples.
Nagai, Takayuki; Akiyama, Daisuke*; Kirishima, Akira*; Sato, Nobuaki*; Okamoto, Yoshihiro
2019-Nendo "Busshitsu, Debaisu Ryoiki Kyodo Kenkyu Kyoten" Oyobi "Hito, Kankyo To Busshitsu O Tsunagu Inobeshion Soshutsu Dainamikku, Araiansu" Kenkyu Seika, Katsudo Hokokusho (CD-ROM), P. 20191107_1, 2020/11
no abstracts in English
Nagai, Takayuki; Okamoto, Yoshihiro; Yamagishi, Hirona*; Ota, Toshiaki*; Kojima, Kazuo*; Inose, Takehiko*; Sato, Seiichi*; Hatakeyama, Kiyoshi*
JAEA-Research 2020-009, 48 Pages, 2020/09
The local structure of glass-forming elements and waste elements in waste glass varies with its chemical composition. In this study, borosilicate glass frit and simulated waste glass samples were prepared and the local structure and chemical state regarding boron (B), oxygen (O), and waste elements of cerium (Ce), cesium (Cs) were estimated by using XAFS measurement in soft X-ray region. Following results were obtained by XAFS measurements of prepared glass frit and simulated waste glass samples: (1) The existence ratio of four coordinate sp structure (BO
structure (BO ) tends to increase with increasing Na
) tends to increase with increasing Na O content in glass samples. (2) The height of a pre-edge which appears by K-edge XANES spectrum of O is so high that the Fe content in glass samples. Following results were obtained by XAFS measurements of simulated waste glass samples after immersion test to investigate long chemical stability. (1) The existence ratio of four coordinate sp
O content in glass samples. (2) The height of a pre-edge which appears by K-edge XANES spectrum of O is so high that the Fe content in glass samples. Following results were obtained by XAFS measurements of simulated waste glass samples after immersion test to investigate long chemical stability. (1) The existence ratio of four coordinate sp structure (BO
structure (BO ) increases by immersion test. (2) Ce which exists in the surface layer is oxidized by immersion test, and much of Cs in surface layer is lost after leach testing. Even if the glass frit form (fiber cartridge or beads) and manufacturing method were changed and a glass sample of the similar chemical composition was prepared, these observed Raman spectra of samples were different.
) increases by immersion test. (2) Ce which exists in the surface layer is oxidized by immersion test, and much of Cs in surface layer is lost after leach testing. Even if the glass frit form (fiber cartridge or beads) and manufacturing method were changed and a glass sample of the similar chemical composition was prepared, these observed Raman spectra of samples were different.
Nagai, Takayuki; Okamoto, Yoshihiro; Akiyama, Daisuke*; Uehara, Akihiro*; Fujii, Toshiyuki*; Sekimoto, Shun*
KURNS Progress Report 2019, P. 257, 2020/08
To understand the influence of glass structural change by neutron irradiation and boron isotope composition, glass samples were made from enrichment boric acid reagents and neutron irradiation of those samples was carried out in Pn-2 of KUR. The structural change of glass sample after the irradiation will be estimated in 2020FY. Before neutron irradiation test of glass samples, the Si-O bridging structure difference by boron isotope composition compared by using a Raman spectrometry.