Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Ishidera, Takamitsu; Okazaki, Mitsuhiro*; Yamada, Yoshihide*; Tomura, Tsutomu*; Shibutani, Sanae*
Journal of Nuclear Science and Technology, 60(5), p.536 - 546, 2023/05
The distribution coefficient ( ) value of radionuclides is an important parameter in the radionuclide migration analysis in the safety assessment of the geological disposal of high-level radioactive waste. The
) value of radionuclides is an important parameter in the radionuclide migration analysis in the safety assessment of the geological disposal of high-level radioactive waste. The  values must be extensively evaluated especially under conditions where they might be decreased to improve the reliability of safety assessment. In this study, the pH dependence of the
values must be extensively evaluated especially under conditions where they might be decreased to improve the reliability of safety assessment. In this study, the pH dependence of the  values for Sn and Nb on montmorillonite was evaluated using batch sorption experiments at neutral to alkaline pH, which might be caused by the leaching of cementitious materials and the corrosion of carbon steel. The
values for Sn and Nb on montmorillonite was evaluated using batch sorption experiments at neutral to alkaline pH, which might be caused by the leaching of cementitious materials and the corrosion of carbon steel. The  values were determined in the range 8
values were determined in the range 8  pH
pH  12 by the experiments and were found to decrease with increasing pH. A model calculation using a thermodynamic sorption model was conducted on the measured pH dependence of the
12 by the experiments and were found to decrease with increasing pH. A model calculation using a thermodynamic sorption model was conducted on the measured pH dependence of the  values. Two different sorption sites were required to describe the pH dependence of the
values. Two different sorption sites were required to describe the pH dependence of the  values of Sn in the model calculation, whereas one sorption site was considered predominant in the sorption of Nb.
values of Sn in the model calculation, whereas one sorption site was considered predominant in the sorption of Nb.
Kuroda, Kenta*; Arai, Yosuke*; Rezaei, N.*; Kunisada, So*; Sakuragi, Shunsuke*; Alaei, M.*; Kinoshita, Yuto*; Bareille, C.*; Noguchi, Ryo*; Nakayama, Mitsuhiro*; et al.
Nature Communications (Internet), 11, p.2888_1 - 2888_9, 2020/06
Times Cited Count:21 Percentile:74.83(Multidisciplinary Sciences)Okazaki, Hiro; Sumi, Mika; Sato, Mitsuhiro; Kayano, Masashi; Kageyama, Tomio; Martinez, P.*; Xu, N.*; Thomas, M.*; Porterfield, D.*; Colletti, L.*; et al.
Kaku Busshitsu Kanri Gakkai (INMM) Nihon Shibu Dai-35-Kai Nenji Taikai Rombunshu (Internet), 9 Pages, 2015/01
The quality control section of Plutonium Fuel Development Center (PFDC) in Japan Atomic Energy Agency has been analyzing isotopic compositions and content of plutonium and uranium as well as impurity and physics of nuclear materials in the process of MOX fuel fabrication for accountancy purpose as well as process control purposes. These analytical techniques are also effective for nuclear forensics to identify the source, history, and route of the material by determining a composition and chemical property of it. Therefore, PFDC cooperates with Los Alamos National Laboratory which has broad experience and established measurement skill for nuclear forensics, and evaluates the each method, procedure, and analytical data toward R&D of characterizing a nuclear fuel for forensics purposes. This paper describes the approaches to develop characterization techniques of nuclear fuel for nuclear forensic purpose at PFDC.
Okazaki, Hiro; Sumi, Mika; Abe, Katsuo; Sato, Mitsuhiro; Kageyama, Tomio
Kaku Busshitsu Kanri Gakkai (INMM) Nihon Shibu Dai-34-Kai Nenji Taikai Rombunshu (Internet), 9 Pages, 2013/10
The quality control section of Plutonium Fuel Development Center (PFDC) has been analyzing isotopic compositions by Mass Spectrometry as well as content by Isotope Dilution Mass Spectrometry (IDMS) of plutonium and uranium in nuclear materials. Along with establishing and managing the quality assurance system, ensuring the reliability of the analysis data is important. PFDC has been establishing the quality management system with ISO 9001. We addressed technical improvement to improve further reliability of analysis quality, and accredited for ISO/IEC 17025 in March 2010. While ISO 9001 consists of management requirements for quality system of organizations, ISO/IEC 17025 consists of technical requirements for the competence of testing and calibration laboratories in addition to the management requirements. In this presentation, we report our approaches to have accreditation and operation status for isotopic compositions and content of plutonium and uranium in nuclear materials.
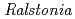 sp. A-471 reveals a unique arrangement of the catalytic residues for inverting chitin hydrolysis
sp. A-471 reveals a unique arrangement of the catalytic residues for inverting chitin hydrolysisArimori, Takao*; Kawamoto, Noriko*; Shinya, Shoko*; Okazaki, Nobuo*; Nakazawa, Masami*; Miyatake, Kazutaka*; Fukamizo, Tamo*; Ueda, Mitsuhiro*; Tamada, Taro
Journal of Biological Chemistry, 288(26), p.18696 - 18706, 2013/07
Times Cited Count:31 Percentile:64.14(Biochemistry & Molecular Biology)Chitinase C from 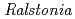 sp. A-471 (Ra-ChiC) has a catalytic domain sequence similar to goose type (G-type) lysozymes and, unlike other chitinases, belongs to glycohydrolase (GH) family 23. Using NMR spectroscopy, however, Ra-ChiC was found to interact only with the chitin dimer but not with the peptideglycan fragment. Here we report the crystal structures of wild-type, E141Q, and E162Q of the catalytic domain of Ra-ChiC with or without chitin oligosaccharides. Ra-ChiC has a substrate-binding site including a tunnel-shaped cavity, which determines the substrate specificity. Mutation analyses based on this structural information indicated that a highly conserved Glu141 acts as a catalytic acid, and that Asp226 located at the roof of the tunnel activates a water molecule as a catalytic base. The unique arrangement of the catalytic residues makes a clear contrast to the other GH23 members and also to inverting GH19 chitinases.
sp. A-471 (Ra-ChiC) has a catalytic domain sequence similar to goose type (G-type) lysozymes and, unlike other chitinases, belongs to glycohydrolase (GH) family 23. Using NMR spectroscopy, however, Ra-ChiC was found to interact only with the chitin dimer but not with the peptideglycan fragment. Here we report the crystal structures of wild-type, E141Q, and E162Q of the catalytic domain of Ra-ChiC with or without chitin oligosaccharides. Ra-ChiC has a substrate-binding site including a tunnel-shaped cavity, which determines the substrate specificity. Mutation analyses based on this structural information indicated that a highly conserved Glu141 acts as a catalytic acid, and that Asp226 located at the roof of the tunnel activates a water molecule as a catalytic base. The unique arrangement of the catalytic residues makes a clear contrast to the other GH23 members and also to inverting GH19 chitinases.
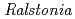 sp. A-471
sp. A-471Okazaki, Nobuo; Arimori, Takao; Nakazawa, Masami*; Miyatake, Kazutaka*; Ueda, Mitsuhiro*; Tamada, Taro
Acta Crystallographica Section F, 67(4), p.494 - 497, 2011/04
Times Cited Count:3 Percentile:41.25(Biochemical Research Methods)Fujiwara, Kenso; Kohara, Yukitoshi*; Okazaki, Mitsuhiro*; Suzuki, Yasuyuki*
no journal, ,
The stability constants of Np(IV) with Ca and Si are measured by solubility method. In the case of coexistence of Ca or Si under high pH region, the solubility of tetravalent actinide was higher than the case of without Ca or Si in a recent study. However, in the case of Np(IV), the experiment was not measured. Therefore, the solubility of Np(IV) was measured with Ca or Si in the high pH region, the stability constants of (Ca Np(OH)
Np(OH)
 ) and Si of Ca and the Np and complex (Np(OH)nSi
) and Si of Ca and the Np and complex (Np(OH)nSi O
O (OH)
(OH) etc) was calculated by solubility of Np(IV).
etc) was calculated by solubility of Np(IV).
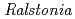 sp. A-471
sp. A-471Tamada, Taro; Okazaki, Nobuo; Ueda, Mitsuhiro*; Nakazawa, Masami*; Miyatake, Kazutaka*; Kuroki, Ryota
no journal, ,
Crystal structure of a novel chitinase (Ra-ChiC), a member of GH family 23, from the moderately thermophilic bacterium 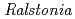 sp. A-471 has been solved in the active site to 1.9
sp. A-471 has been solved in the active site to 1.9  resolution. Crystal structure of Ra-ChiC was resemble to that of g-type lysozyme. It is well known that the residues involved in catalysis of the g-type lysozymes are Glu73, Asp90, and Asp101. The Glu73 (proton donor) in g-type lysozymes was conserved as Glu141 in the catalytic domain of Ra-ChiC.
resolution. Crystal structure of Ra-ChiC was resemble to that of g-type lysozyme. It is well known that the residues involved in catalysis of the g-type lysozymes are Glu73, Asp90, and Asp101. The Glu73 (proton donor) in g-type lysozymes was conserved as Glu141 in the catalytic domain of Ra-ChiC.
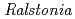 sp. A-471
sp. A-471Ueda, Mitsuhiro*; Nakazawa, Masami*; Miyatake, Kazutaka*; Okazaki, Nobuo; Kuroki, Ryota; Tamada, Taro
no journal, ,
Crystal structure of a novel chitinase (Ra-ChiC), a member of GH family 23, from the moderately thermophilic bacterium 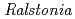 sp. A-471 has been solved in the active site to 1.9
sp. A-471 has been solved in the active site to 1.9  resolution. Crystal structure of Ra-ChiC was resemble to that of g-type lysozyme. It is well known that the residues involved in catalysis of the g-type lysozymes are Glu73, Asp90, and Asp101. The Glu73 (proton donor) in g-type lysozymes was conserved as Glu141 in the catalytic domain of Ra-ChiC.
resolution. Crystal structure of Ra-ChiC was resemble to that of g-type lysozyme. It is well known that the residues involved in catalysis of the g-type lysozymes are Glu73, Asp90, and Asp101. The Glu73 (proton donor) in g-type lysozymes was conserved as Glu141 in the catalytic domain of Ra-ChiC.
Ishii, Yasuo; Seida, Yoshimi*; Tachi, Yukio; Okazaki, Mitsuhiro*; Kurosawa, Seiichi*
no journal, ,
We developed the Sorption/diffusion data acquisition method for high sorbing nuclides using trivalent actinide Am.
Terashima, Motoki; Seida, Yoshimi*; Okazaki, Mitsuhiro; Iwatsuki, Teruki; Iijima, Kazuki; Yui, Mikazu
no journal, ,
no abstracts in English
Ishii, Yasuo; Takahashi, Hiroaki; Seida, Yoshimi*; Tachi, Yukio; Nakazawa, Toshiyuki*; Kurosawa, Seiichi*; Okazaki, Mitsuhiro*
no journal, ,
We have developed Sorption/Diffusion Data Acquisition Method for High Sorbiong Am and Th in Horonobe Sedimentary Rock.
Ishii, Yasuo; Takahashi, Hiroaki; Tachi, Yukio; Tomura, Tsutomu*; Nemoto, Kazuaki*; Okazaki, Mitsuhiro*
no journal, ,
Am(III) diffusion experiment were performed by reservoir depletion (RD) test method coupled with thin layer ID profile fitting in 0.1 or 0.5M NaCl / 0.05M NaHCO - bentonite (kunipia-F) system. The Kd values were also measured using batch technique in the same experimental conditions. In an ordinary ID profile acquisition cutting the bentonite by scraper, the compacted bentonite sample can be cut into 100
- bentonite (kunipia-F) system. The Kd values were also measured using batch technique in the same experimental conditions. In an ordinary ID profile acquisition cutting the bentonite by scraper, the compacted bentonite sample can be cut into 100  m thick slices. Using this technique, it was possible to divide the ID profile into 10
m thick slices. Using this technique, it was possible to divide the ID profile into 10  m and therefore, to analyze diffusion distance layer larger than 50
m and therefore, to analyze diffusion distance layer larger than 50  m.
m.
Terashima, Motoki; Okazaki, Mitsuhiro; Iijima, Kazuki; Yui, Mikazu
no journal, ,
no abstracts in English
Arimori, Takao; Okazaki, Nobuo; Nakazawa, Masami*; Miyatake, Kazutaka*; Ueda, Mitsuhiro*; Tamada, Taro
no journal, ,
no abstracts in English
Terashima, Motoki; Okazaki, Mitsuhiro; Iijima, Kazuki; Yoshikawa, Hideki
no journal, ,
no abstracts in English
Arimori, Takao; Kawamoto, Noriko*; Okazaki, Nobuo; Nakazawa, Masami*; Miyatake, Kazutaka*; Ueda, Mitsuhiro*; Tamada, Taro
no journal, ,
no abstracts in English
Ishii, Yasuo; Tomura, Tsutomu; Nemoto, Kazuaki; Okazaki, Mitsuhiro; Tachi, Yukio
no journal, ,
Am(III) diffusion experiment were performed by reservoir depletion (RD) test method coupled with thin layer ID profile fitting.
Arimori, Takao*; Kawamoto, Noriko*; Okazaki, Nobuo*; Nakazawa, Masami*; Miyatake, Kazutaka*; Fukamizo, Tamo*; Ueda, Mitsuhiro*; Tamada, Taro
no journal, ,
Chitin, linear  -1,4-linked polymer of
-1,4-linked polymer of  -acetyl-D-glucosamine (NAG), is the second abundant biopolymer in nature next to cellulose. Hydrolysis of chitin provides useful products,
-acetyl-D-glucosamine (NAG), is the second abundant biopolymer in nature next to cellulose. Hydrolysis of chitin provides useful products,  -acetyl-chitooligosaccharides [(NAG)
-acetyl-chitooligosaccharides [(NAG) ] and chitooligosaccharides, which have a variety of biological functions including antibacterial activity and antitumor activity. We have previously cloned a novel chitinase gene from a moderate thermophilic strain
] and chitooligosaccharides, which have a variety of biological functions including antibacterial activity and antitumor activity. We have previously cloned a novel chitinase gene from a moderate thermophilic strain 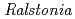 sp. A-471 (Ra-ChiC). Ra-ChiC comprises a signal peptide, a chitin-binding domain, an interdomain linker, and a catalytic domain. The catalytic domain shares amino acid sequence homology with goose type (G-type) lysozymes and, unlike other chitinases, Ra-ChiC belongs to glycohydrolase (GH) family 23. However, Ra-ChiC does not exhibit lysozyme activity, but only chitinase activity. In this study, we aim to reveal how Ra-ChiC catalyzes the hydrolysis of chitin and why Ra-ChiC exhibits chitinase activity instead of lysozyme activity. We determined the crystal structures of the catalytic domain of Ra-ChiC (Ra-ChiC
sp. A-471 (Ra-ChiC). Ra-ChiC comprises a signal peptide, a chitin-binding domain, an interdomain linker, and a catalytic domain. The catalytic domain shares amino acid sequence homology with goose type (G-type) lysozymes and, unlike other chitinases, Ra-ChiC belongs to glycohydrolase (GH) family 23. However, Ra-ChiC does not exhibit lysozyme activity, but only chitinase activity. In this study, we aim to reveal how Ra-ChiC catalyzes the hydrolysis of chitin and why Ra-ChiC exhibits chitinase activity instead of lysozyme activity. We determined the crystal structures of the catalytic domain of Ra-ChiC (Ra-ChiC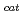 ), Ra-ChiC
), Ra-ChiC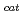 complexed with (NAG)
complexed with (NAG) , E141Q mutant of Ra-ChiC
, E141Q mutant of Ra-ChiC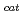 complexed with (NAG)
complexed with (NAG) , E162Q mutant of Ra-ChiC
, E162Q mutant of Ra-ChiC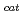 , and E162Q mutant of Ra-ChiC
, and E162Q mutant of Ra-ChiC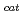 complexed with (NAG)
complexed with (NAG) . These structures provided us structural basis of substrate recognition mechanism and revealed that Ra-ChiC has a unique substrate-binding site including a tunnel-shaped cavity, which determines the substrate specificity. In addition, we also carried out a mutation analysis of acidic amino acid residues located at the active site. As a result, we found that not only a highly conserved Glu141 but also Asp226 located at the roof of the tunnel have quite important roles in catalysis.
. These structures provided us structural basis of substrate recognition mechanism and revealed that Ra-ChiC has a unique substrate-binding site including a tunnel-shaped cavity, which determines the substrate specificity. In addition, we also carried out a mutation analysis of acidic amino acid residues located at the active site. As a result, we found that not only a highly conserved Glu141 but also Asp226 located at the roof of the tunnel have quite important roles in catalysis.
Terashima, Motoki; Saito, Takumi*; Okazaki, Mitsuhiro*; Tachi, Yukio; Iijima, Kazuki
no journal, ,
no abstracts in English