Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Kato, Masato; Oki, Takumi; Watanabe, Masashi; Hirooka, Shun; Vauchy, R.; Ozawa, Takayuki; Uwaba, Tomoyuki; Ikusawa, Yoshihisa; Nakamura, Hiroki; Machida, Masahiko
Journal of the American Ceramic Society, 107(5), p.2998 - 3011, 2024/05
Times Cited Count:0 Percentile:0.01(Materials Science, Ceramics)Sakakibara, Hiroshi; Aoki, Nobuhiro; Muto, Masahiro; Otabe, Jun; Takahashi, Kenji*; Fujita, Naoyuki*; Hiyama, Kazuhiko*; Suzuki, Hirokazu*; Kamogawa, Toshiyuki*; Yokosuka, Toru*; et al.
JAEA-Technology 2020-020, 73 Pages, 2021/03
The decommissioning is currently in progress at the prototype fast breeder reactor Monju. Fuel assemblies will be taken out of its core for the first step of the great task. Fuel assemblies stand on their own spike plugged into a socket on the core support plate and support with adjacent assemblies through their housing pads each other, resulting in steady core structure. For this reason, some substitutive assemblies are necessary for the purpose of discharging the fuel assemblies of the core. Monju side commissioned, therefore, Plutonium Fuel Development Center to manufacture the substitutive assemblies and the Center accepted it. This report gives descriptions of design, manufacture, and shipment in regard to the substitutive assemblies.
Aoki, Tomoyuki*; Tani, Takuya*; Sakai, Kazuo*; Koga, Yoshihisa*; Aoyagi, Kazuhei; Ishii, Eiichi
JAEA-Research 2020-002, 83 Pages, 2020/06
The Japan Atomic Energy Agency (JAEA) has conducted with the Horonobe Underground Research Project in Horonobe, Teshio-gun, Hokkaido for the purpose of research and development related to geological disposal technology for high-level radioactive wastes in sedimentary soft rocks. The geology around the Horonobe Underground Research Laboratory (HURL) is composed of the Koetoi diatomaceous mudstone layer and the Wakkanai siliceous layer, both of which contain a large amount of diatom fossils. Since these rocks exhibit relatively high porosity but low permeability, it is important to investigate the poro-elastic characteristics of the rock mass. For this objective, it is necessary to measure parameters based on the poro-elastic theory. However, there are few measurement results of the poro-elastic parameters for the geology around HURL, and the characteristics such as dependence on confining pressure are not clearly understood. One of the reasons is that the rocks show low permeability and the pressure control during testing is difficult. Therefore, a poro-elastic parameter measurement test was conducted on the siliceous mudstone of the Wakkanai formation to accumulate measurement results on the poro-elastic parameters and to examine the dependence of the parameters on confining pressure. As a result, some dependency of the poro-elastic parameters on confining pressure was observed. Among the measured or calculated poro-elastic parameters, the drained bulk modulus increased, while the Skempton's pressure coefficient, and the Biot-Wills coefficient in the elastic region decreased with the increase in confining pressure. The measurement results also inferred that the foliation observed in the rock specimens might impact a degree of dependency of those parameters on confining pressure.
Nakajima, Kenji; Kawakita, Yukinobu; Ito, Shinichi*; Abe, Jun*; Aizawa, Kazuya; Aoki, Hiroyuki; Endo, Hitoshi*; Fujita, Masaki*; Funakoshi, Kenichi*; Gong, W.*; et al.
Quantum Beam Science (Internet), 1(3), p.9_1 - 9_59, 2017/12
The neutron instruments suite, installed at the spallation neutron source of the Materials and Life Science Experimental Facility (MLF) at the Japan Proton Accelerator Research Complex (J-PARC), is reviewed. MLF has 23 neutron beam ports and 21 instruments are in operation for user programs or are under commissioning. A unique and challenging instrumental suite in MLF has been realized via combination of a high-performance neutron source, optimized for neutron scattering, and unique instruments using cutting-edge technologies. All instruments are/will serve in world-leading investigations in a broad range of fields, from fundamental physics to industrial applications. In this review, overviews, characteristic features, and typical applications of the individual instruments are mentioned.
Ohgama, Kazuya; Ota, Hirokazu*; Ikusawa, Yoshihisa; Oki, Shigeo; Ogata, Takanari*
Proceedings of 2017 International Congress on Advances in Nuclear Power Plants (ICAPP 2017) (CD-ROM), 6 Pages, 2017/04
Niwa, Hideharu*; Saito, Makoto*; Kobayashi, Masaki*; Harada, Yoshihisa*; Oshima, Masaharu*; Moriya, Shogo*; Matsubayashi, Katsuyuki*; Nabae, Yuta*; Kuroki, Shigeki*; Ikeda, Takashi; et al.
Journal of Power Sources, 223, p.30 - 35, 2013/02
Times Cited Count:18 Percentile:50.94(Chemistry, Physical)To design non-platinum, inexpensive, but high performance carbon-based cathode catalysts for polymer electrolyte fuel cells, it is important to elucidate the active site for oxygen reduction reaction (ORR). However, it is difficult to directly identify the active site by applying conventional structural or electronic probes to such complex systems. Here, we used C 1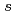 X-ray absorption spectroscopy (XAS) to observe electronic structure of carbon in iron phthalocyanine-based catalysts, and found a signature of edge exposure below the
X-ray absorption spectroscopy (XAS) to observe electronic structure of carbon in iron phthalocyanine-based catalysts, and found a signature of edge exposure below the 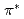 edge, whose intensity is well correlated with the ORR activity. These results demonstrate that C 1
edge, whose intensity is well correlated with the ORR activity. These results demonstrate that C 1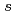 XAS can be used to characterize the ORR activity of carbon-based cathode catalysts in terms of the edge exposure.
XAS can be used to characterize the ORR activity of carbon-based cathode catalysts in terms of the edge exposure.
Kiuchi, Hisao*; Niwa, Hideharu*; Kobayashi, Masaki*; Harada, Yoshihisa*; Oshima, Masaharu*; Chokai, Masayuki*; Nabae, Yuta*; Kuroki, Shigeki*; Kakimoto, Masaaki*; Ikeda, Takashi; et al.
Electrochimica Acta, 82(1), p.291 - 295, 2012/10
Times Cited Count:14 Percentile:34.42(Electrochemistry)We study the characteristics of oxygen adsorption on metal-free carbon-based cathode catalysts derived from nitrogen-containing polyamide (PA) and nitrogen-free phenolic resin (PhRs). Electrochemical analysis and Raman spectroscopy showed higher 2-electron oxygen reduction reaction (ORR) activity and more defect sites in PA than PhRs. The increase in the amount of adsorbed oxygen in PA was also identified by oxygen adsorption isotherms.  X-ray photoelectron spectroscopy reveals that graphite-like nitrogen contributes to oxygen adsorption and C=O components are dominant in PA. These experimental results indicate that the adsorbed C=O components near the graphite-like nitrogen can be assigned as active sites for 2-electron ORR.
X-ray photoelectron spectroscopy reveals that graphite-like nitrogen contributes to oxygen adsorption and C=O components are dominant in PA. These experimental results indicate that the adsorbed C=O components near the graphite-like nitrogen can be assigned as active sites for 2-electron ORR.
Fujii, Tadashi; ; ; Sakai, Takaaki; ; Oki, Yoshihisa;
JNC TN9400 2002-049, 78 Pages, 2002/09
The conceptual design study of the large-scale sodium-cooled reactor is in progress in the "Feasibility Study on Commercialized Fast Reactor Cycle Systems (F/S)". The direct water pool storage system is being examined as a candidate concept to simplify the fuel handling facility for the sodium-cooled reactor. In this concept, the decay heat of a fuel subassembly is relatively higher (18kW which is about 4.5 times of the Ex-vessel Storage Tank system in the demonstration FBR). Therefore, the information about the cooling characteristics of the fuel subassembly are lacking in cases of submergence process at a normal operation and cooling water injection process from upper part of the subassembly at a transfer accident. Accordingly, the understanding of the cooling characteristics of the fuel subassembly in higher decay heat condition was pointed out as one of the thermal hydraulic problems which influence the realization of the plant concept. Using the single heater pin equipment, fundamental tests were conducted with the parameters of the thermal conditions of a fuel pin, the outlet shapes of it, the submergence speeds and so on. Then, following basic data were acquired to be reflected in the actual plant design. (1)Cooling modes of the normally submergence tests and water injection tests were identified by visualization of the boiling behavior in the test section and the temperature change of the heater pin. (2)The initial temperature of the heater surface and the blockage size of the outlet of test section were dominating factors to the cooling completion time. (3)Maximum temperature rise of the heater surface was about 4K in normally submergence tests and 6K in water injection tests, respectively. Therefore, the heater was well cooled without significant temperature rise.(4)In the normally submergence tests, the pressure of the upper part of the test section did not exceed the lower part pressure and a water level rise in the test section was not obstructed ...
Iitsuka, Toru; Oki, Yoshihisa; Kawashima, Shigeyo*; Nishimura, Motohiko; Isozaki, Tadashi; Kamide, Hideki
PNC TN9410 98-022, 58 Pages, 1998/03
Assessment of the maximum temperature and the position of the hot spot is the most important issues on the reactor safety when the local subchannel porous blockage is occurred. From these background, authors are going to perform a sodium experiment with 37-pin bundle test rig simulating the porous blockage, to understand the phenomena and acquire data for thermal-hydraulic analysis code validation. Before the execution of sodium test, one basic experiment and some using subchannel analysis code ASFRE-III had been done. The basic experiment was a water test to examine the pressure loss characteristics of the porous blockage. The pressure loss correlation derived from the water test was applied to the subsequent subchannel analysis of the 37-pin bundle sodium test rig. The analysis such predicted that the difference between the maximum temperature and the inlet temperature would be in propotion to the power to flow rate ratio, within the condition of the power=100 400 W/cm and the flow rate =200
400 W/cm and the flow rate =200 480
480  /min. And it was also shown that the maximum subchannel temperature would not over the operational limit temperature 650
/min. And it was also shown that the maximum subchannel temperature would not over the operational limit temperature 650  C, if the power to flow rate ratio were kept lower than 0.75(W/cm)/
C, if the power to flow rate ratio were kept lower than 0.75(W/cm)/ /min). The map was made to predict the maximum temperature from the experimental conditions.
/min). The map was made to predict the maximum temperature from the experimental conditions.
Hirabayashi, Masaru; Kobayashi, Jun; Tokuhiro, Akira; Oki, Yoshihisa; ;
PNC TN9430 98-002, 29 Pages, 1998/01
no abstracts in English
Tokuhiro, Akira; Hishida, Koichi; Oki, Yoshihisa
PNC TN9410 96-275, 59 Pages, 1996/10
Particle Image Velocimetry (PIV) describes a velocity measurement technique for gas and liquid flows whereby, as the name implies, movement of tracer particles in motion with the flow are recorded as images. The particles are framr-to-frame "tracked by one of several correlation techniques from which a 2D vector field can be generated. A 3D vector field is also possible. The measurement method takes advantage of current computer, CCD camera and laser light technologies for its image processing needs. A laser light sheet is typically used to illuminate the tracer particles in the flow field of interest and when implemented accentuates the constrast between the particle and the transparent medium. One can also apply Laser Induced Fluorescence (LIF) in order to further distinguish the tracer particles, the transparent, continuous medium and any light reflecting surfaces in the flow field such as the interface of a gas bubble rising in a liquid. It is also possible to deduce the temperature field from LIF images. In the present work an introduction to PIV is given by way of an example. The selected flow configuration is that of wake-flow behind a bubble and its solid equivalent. By solid equivalent we mean a solid model with approximately the equivalent bubble breadth and volume. This two-component, two-phase flow aptly demonstrates the applicability of PIV to spatio-temporal flows. Use was additionally made of an Infrared Shadow Technique (IST) in order to capture the unlit image (shadow) of the bubble or solid within the flow field. By triggering both the laser and infrared light sources with the CCD camera, the shape of the object as well as the flow field was simultaneously recorded. Besides the 2D vector field, calculations of the vorticity, Reynolds stress and turbulent kinetic energy (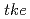 ) distributions were made. The results indicate that for counter-current flow (U
) distributions were made. The results indicate that for counter-current flow (U sim$0.245 m/s) of water in a square channel (100 mm) with a single air bubble of ...
sim$0.245 m/s) of water in a square channel (100 mm) with a single air bubble of ...
*; *; *; Oki, Yoshihisa*
PNC TJ9214 88-007, 119 Pages, 1988/12
Pressure drop characteristics and possible cavitation occurrence have been investigated on the Joyo receptacles and nosepieces as part of the Joyo Advanced Core Study. The occurrence of cavitation is of particular important on the part of non-replaceable components. Thus, visual observation was made with particular emphasis on cavitation on the receptacle side. Fixed-type of cavitation has been observed on the receptacle wall of Zone-5. In order to suppress this type of cavitation, flow testing has been made using a nosepiece with a large orifice diameter on the second stage. For this case, no cavitation has been observed on the receptacle wall, thereby demonstrating one possible cure for cavitation on the Zone-5 receptacle.
Nakai, Satoru; Nishio, Ryuichi; Uchihashi, Masaya; Kaneko, Yoshihisa; Yamashita, Hironobu*; Yamaguchi, Atsunori*; Aoki, Takayuki*
no journal, ,
A sodium cooled fast breeder reactor (FBR) has unique systems and components and different degradation mechanism from light water reactor (LWR) so that need to establish maintenance technology in accordance with its features. The examination of the FBR maintenance technology is carried out in the special committee for considering the maintenance for Monju established in the Japan Society of Maintenology (JSM). As a result of the study such as extraction of Monju maintenance feature, maintenance technology benchmark between Monju and LWR components and survey of LWR maintenance experience, it is clear that principles of maintenance are same as LWR, necessity of LWR maintenance experience reflection and points to be considered in Monju maintenance. The road map to establish a FBR maintenance technology in the technical aspect became clear and it is vital to acquire operation and maintenance experience of the plant to implement this road map, and to establish a fast reactor maintenance.
Ohgama, Kazuya; Ota, Hirokazu*; Ikusawa, Yoshihisa; Oki, Shigeo; Ogata, Takanari*
no journal, ,
no abstracts in English
Ota, Hirokazu*; Ohgama, Kazuya; Ogata, Takanari*; Ikusawa, Yoshihisa; Oki, Shigeo
no journal, ,
no abstracts in English
Taniguchi, Takumi; Imaizumi, Ken*; Namiki, Masahiro*; Osugi, Takeshi; Kuroki, Ryoichiro; Kikuchi, Michio*; Yamamoto, Takeshi*; Kaneda, Yoshihisa*; Haga, Kazuko*
no journal, ,
It is important to understand fundamental solidification characteristics of contaminated water management waste at Fukushima Daiichi Nuclear Power Station. The Solidified bodies are fabricated with cementitious material and Alkali Activated Material, and are irradiated with Gamma-ray.
Hiraki, Yoshihisa; Terasawa, Toshiharu*; Imaizumi, Ken*; Taniguchi, Takumi; Kato, Jun; Osugi, Takeshi; Sone, Tomoyuki; Nakazawa, Osamu; Kuroki, Ryoichiro
no journal, ,
The relationship between the amount of radionuclide to be solidified and the solidified body temperature was analyzed, when solidify contaminated water management waste at Fukushima Daiichi Nuclear Power Station with cement etc. at low temperature. The analysis code used the radiation transport code and the thermal analysis code. Thus, the limit value by radionuclide concentration during solidification process are evaluated. The summary of the test and some of the obtained results are introduced.
Kaneda, Yoshihisa*; Haga, Kazuko*; Shibata, Masahito*; Kuranaga, Mebae*; Kikuchi, Michio*; Yamamoto, Takeshi*; Kato, Jun; Osugi, Takeshi; Kuroki, Ryoichiro
no journal, ,
Solidified cement and alkali activated materials was made, and used for dissolution test to obtain basic data of solidification on the waste caused by the contaminated water treatment at Fukushima Daiichi Nuclear Power Station.
Kikuchi, Michio*; Yamamoto, Takeshi*; Otsuka, Taku*; Kawato, Takaya*; Kaneda, Yoshihisa*; Shibata, Masahito*; Haga, Kazuko*; Taniguchi, Takumi; Osugi, Takeshi; Kuroki, Ryoichiro
no journal, ,
Summary of the study which is for characterization of Solidified cement and alkali activated materials was carried out due to obtain the data available for applicability evaluation low-temperature solidification on the waste caused by the contaminated water treatment at Fukushima Daiichi Nuclear Power Station.
Hiraki, Yoshihisa; Enomoto, Mayu*; Terasawa, Toshiharu*; Imaizumi, Ken*; Kato, Jun; Osugi, Takeshi; Sone, Tomoyuki; Kuroki, Ryoichiro
no journal, ,
Evaluate the maximum temperature of solidified body, when Secondary Waste Produced from Contaminated Water Treatment at Fukushima Daiichi NPP is solidified with cement etc. Simulate various container shapes, and analysis using the radiation transport code and the thermal analysis code was performed. The summary of the test and some of the obtained results are introduced.