Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
 Ni
NiShizuma, Toshiyuki*; Omer, M.; Hayakawa, Takehito*; Minato, Futoshi*; Matsuba, Shunya*; Miyamoto, Shuji*; Shimizu, Noritaka*; Utsuno, Yutaka
Physical Review C, 109(1), p.014302_1 - 014302_7, 2024/01
Times Cited Count:0 -ray elastic scattering
-ray elastic scatteringOmer, M.; Shizuma, Toshiyuki*; Koizumi, Mitsuo; Hajima, Ryoichi*; Hashimoto, Satoshi*; Miyamoto, Shuji*
LASTI Annual Report, 24, p.20 - 22, 2023/12
Omer, M.; Shizuma, Toshiyuki*; Koizumi, Mitsuo; Taira, Yoshitaka*; Zen, H.*; Ogaki, Hideaki*; Hajima, Ryoichi
UVSOR-50, P. 37, 2023/08
no abstracts in English
Taira, Yoshitaka*; Endo, Shunsuke; Kawamura, Shiori*; Nambu, Taro*; Okuizumi, Mao*; Shizuma, Toshiyuki*; Omer, M.; Zen, H.*; Okano, Yasuaki*; Kitaguchi, Masaaki*
Physical Review A, 107(6), p.063503_1 - 063503_10, 2023/06
Times Cited Count:0 Percentile:0.01(Optics)no abstracts in English
Omer, M.; Shizuma, Toshiyuki*; Hajima, Ryoichi*; Koizumi, Mitsuo
Dai-43-Kai Nihon Kaku Busshitsu Kanri Gakkai Nenji Taikai Kaigi Rombunshu (Internet), 3 Pages, 2022/11
 Pb
PbShizuma, Toshiyuki*; Endo, Shunsuke; Kimura, Atsushi; Massarczyk, R.*; Schwengner, R.*; Beyer, R.*; Hensel, T.*; Hoffmann, H.*; Junghans, A.*; R mer, K.*; et al.
mer, K.*; et al.
Physical Review C, 106(4), p.044326_1 - 044326_11, 2022/10
Times Cited Count:0 Percentile:0.02(Physics, Nuclear)no abstracts in English
Omer, M.; Shizuma, Toshiyuki*; Hajima, Ryoichi*; Koizumi, Mitsuo
Radiation Physics and Chemistry, 198, p.110241_1 - 110241_7, 2022/09
Times Cited Count:2 Percentile:53.91(Chemistry, Physical)Endo, Shunsuke; Shizuma, Toshiyuki*; Zen, H.*; Taira, Yoshitaka*; Omer, M.; Kawamura, Shiori*; Abe, Ryota*; Okudaira, Takuya*; Kitaguchi, Masaaki*; Shimizu, Hirohiko*
UVSOR-49, P. 38, 2022/08
 Pb
PbShizuma, Toshiyuki*; Minato, Futoshi; Omer, M.*; Hayakawa, Takehito*; Ogaki, Hideaki*; Miyamoto, Shuji*
Physical Review C, 103(2), p.024309_1 - 024309_8, 2021/02
Times Cited Count:4 Percentile:57.13(Physics, Nuclear)Low-lying dipole transitions in  Pb were measured via nuclear photon scattering using a quasi-monochromatic, linearly polarized photon beam. The electric (
Pb were measured via nuclear photon scattering using a quasi-monochromatic, linearly polarized photon beam. The electric ( ) and magnetic (
) and magnetic ( ) dipole strengths were extracted for excitation energies up to 6.8 MeV. The present (
) dipole strengths were extracted for excitation energies up to 6.8 MeV. The present (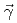 ,
,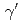 ) results, combined with (
) results, combined with ( ,
, ) data from the literature, were used to investigate the
) data from the literature, were used to investigate the  and
and  photoabsorption cross sections near the neutron separation energy by comparison with predictions of the particle-vibration coupling on top of the quasi-particle random phase approximation (PVC+QRPA).
photoabsorption cross sections near the neutron separation energy by comparison with predictions of the particle-vibration coupling on top of the quasi-particle random phase approximation (PVC+QRPA).
 -ray beam
-ray beamOmer, M.; Shizuma, Toshiyuki*; Hajima, Ryoichi*
Nuclear Instruments and Methods in Physics Research A, 951, p.162998_1 - 162998_6, 2020/01
Times Cited Count:1 Percentile:13.56(Instruments & Instrumentation) -rays elastic scattering by Monte Carlo simulation
-rays elastic scattering by Monte Carlo simulationOmer, M.; Hajima, Ryoichi*
New Journal of Physics (Internet), 21(11), p.113006_1 - 113006_10, 2019/11
Times Cited Count:5 Percentile:42.69(Physics, Multidisciplinary)Omer, M.; Shizuma, Toshiyuki*; Hajima, Ryoichi*; Koizumi, Mitsuo
Nihon Kaku Busshitsu Kanri Gakkai Dai-40-Kai Nenji Taikai Puroshidhingusushu, p.59 - 62, 2019/11
 Al; Its low-lying multiplet structure
Al; Its low-lying multiplet structureShizuma, Toshiyuki*; Omer, M.; Hajima, Ryoichi*; Shimizu, Noritaka*; Utsuno, Yutaka
Physical Review C, 100(1), p.014307_1 - 014307_6, 2019/07
Times Cited Count:7 Percentile:59.68(Physics, Nuclear) -rays
-raysOmer, M.; Hajima, Ryoichi*
JAEA-Data/Code 2018-007, 32 Pages, 2018/06
Nuclear resonance fluorescence (NRF) is a promising technique for the non-destructive assay (NDA) of nuclear materials. Its powerfulness is apparent in the highly penetrative  -rays emitted in an isotopic fingerprint of the NRF interactions. However; there exist other interactions that may interfere with the NRF and hence, may limit its accuracy. Of these interactions is the elastic scattering of
-rays emitted in an isotopic fingerprint of the NRF interactions. However; there exist other interactions that may interfere with the NRF and hence, may limit its accuracy. Of these interactions is the elastic scattering of  -rays by atoms which needs further investigation and testing. Japan Atomic Energy Agency started in 2015 to develop a NDA system based on the NRF for nuclear non-proliferation and nuclear security purposes. One of the tasks of the current development is assessing the effect of the elastic scattering of
-rays by atoms which needs further investigation and testing. Japan Atomic Energy Agency started in 2015 to develop a NDA system based on the NRF for nuclear non-proliferation and nuclear security purposes. One of the tasks of the current development is assessing the effect of the elastic scattering of  -rays on NRF measurement. A new simulation code for the elastic scattering of
-rays on NRF measurement. A new simulation code for the elastic scattering of  -rays has recently been developed in the Geant4 environment. The present JAEA-Data/Code report provides a more detailed description of the simulation code as well as an elaborated illustration of the elastic scattering of
-rays has recently been developed in the Geant4 environment. The present JAEA-Data/Code report provides a more detailed description of the simulation code as well as an elaborated illustration of the elastic scattering of  -rays and its interaction cross sections. This report facilitates user feedback of the simulation code which is indispensable for reaching a stable and reliable simulation. The current report would contribute to better understanding of the elastic scattering of
-rays and its interaction cross sections. This report facilitates user feedback of the simulation code which is indispensable for reaching a stable and reliable simulation. The current report would contribute to better understanding of the elastic scattering of  -rays. This research was implemented under the subsidiary for nuclear security promotion of MEXT.
-rays. This research was implemented under the subsidiary for nuclear security promotion of MEXT.
 ck scattering in GEANT4
ck scattering in GEANT4Omer, M.; Hajima, Ryoichi*
Nuclear Instruments and Methods in Physics Research B, 405, p.43 - 49, 2017/08
Times Cited Count:8 Percentile:61.27(Instruments & Instrumentation)Elastic scattering of  -rays by an atom nearly associates all their interactions with matter. Therefore, the planning of experiments, involving measurements of
-rays by an atom nearly associates all their interactions with matter. Therefore, the planning of experiments, involving measurements of  -rays, using Monte Carlo simulations usually includes the elastic scattering. However, current simulation tools do not provide a complete picture of the elastic scattering. The majority of these tools assume Rayleigh scattering is the primary contributor to the elastic scattering and neglect other elastic scattering processes, such as nuclear Thomson and Delbr
-rays, using Monte Carlo simulations usually includes the elastic scattering. However, current simulation tools do not provide a complete picture of the elastic scattering. The majority of these tools assume Rayleigh scattering is the primary contributor to the elastic scattering and neglect other elastic scattering processes, such as nuclear Thomson and Delbr ck scattering. Here, we develop a tabulation-based method to simulate elastic scattering in one of the most common open-source Monte Carlo simulation toolkits, GEANT4. We collectively include three processes, Rayleigh scattering, nuclear Thomson scattering, and Delbr
ck scattering. Here, we develop a tabulation-based method to simulate elastic scattering in one of the most common open-source Monte Carlo simulation toolkits, GEANT4. We collectively include three processes, Rayleigh scattering, nuclear Thomson scattering, and Delbr ck scattering. Our simulation more appropriately uses differential cross sections based on the second-order scattering matrix instead of current data, which is based on the form factor approximation. Moreover, the superposition of these processes is carefully taken into account emphasizing the complex nature of the scattering amplitudes. The simulation covers an energy range of 0.01 MeV
ck scattering. Our simulation more appropriately uses differential cross sections based on the second-order scattering matrix instead of current data, which is based on the form factor approximation. Moreover, the superposition of these processes is carefully taken into account emphasizing the complex nature of the scattering amplitudes. The simulation covers an energy range of 0.01 MeV E
E  3 MeV and all elements with the atomic numbers of 1
3 MeV and all elements with the atomic numbers of 1  Z
Z  99. In addition, we verified our simulation by comparing the differential cross section measured in earlier experiments to those extracted from the simulations. We find that the simulations are in good agreement with the experimental measurements. Differences between the experiments and the simulations are 21% for uranium, 24% for lead, 3% for tantalum, and 8% for cerium at 2.754 MeV. Coulomb corrections to the Delbr
99. In addition, we verified our simulation by comparing the differential cross section measured in earlier experiments to those extracted from the simulations. We find that the simulations are in good agreement with the experimental measurements. Differences between the experiments and the simulations are 21% for uranium, 24% for lead, 3% for tantalum, and 8% for cerium at 2.754 MeV. Coulomb corrections to the Delbr ck amplitudes may account for the relatively large differences that appear at higher Z values.
ck amplitudes may account for the relatively large differences that appear at higher Z values.
 -ray polarization in NRF-based nondestructive assay of nuclear materials
-ray polarization in NRF-based nondestructive assay of nuclear materialsOmer, M.; Hajima, Ryoichi*; Shizuma, Toshiyuki*; Koizumi, Mitsuo
Proceedings of INMM 58th Annual Meeting (Internet), 7 Pages, 2017/07
Nuclear resonance fluorescence (NRF) is a process in which the electric and/or the magnetic dipole excitations of the nucleus take place. Since these excitations are unique signatures of each nucleus, the NRF provides a practical tool for a non-destructive detection and assay of nuclear materials. Using a polarized  -ray beam, distinguishing the nature of the excitation is straightforward. At a scattering angle of 90
-ray beam, distinguishing the nature of the excitation is straightforward. At a scattering angle of 90 , the electric dipole excitations are radiated normal to the polarization plane whereas the magnetic dipole excitations are radiated in the same plane as the incident beam polarization. By contrast, other
, the electric dipole excitations are radiated normal to the polarization plane whereas the magnetic dipole excitations are radiated in the same plane as the incident beam polarization. By contrast, other  -ray interactions with the atom may exhibit different responses regarding the polarization of the incident beam. For example, the elastic scattering is expected to give approximately 60% lower yield in the direction of the incident beam polarization than the other direction. This fact significantly affects the sensitivity of the NRF technique because it is not possible to separate the NRF and the elastic scattering on the basis of the photon energy. We report the results of a photon scattering experiment on
-ray interactions with the atom may exhibit different responses regarding the polarization of the incident beam. For example, the elastic scattering is expected to give approximately 60% lower yield in the direction of the incident beam polarization than the other direction. This fact significantly affects the sensitivity of the NRF technique because it is not possible to separate the NRF and the elastic scattering on the basis of the photon energy. We report the results of a photon scattering experiment on  U using a 100% linearly polarized
U using a 100% linearly polarized  -ray beam with an energy of 2.04 MeV. We demonstrate how the elastic scattering responds to the polarization of the incident beam. Accordingly, we are able to resolve the effects of the polarization of incident photon in an NRF measurement.
-ray beam with an energy of 2.04 MeV. We demonstrate how the elastic scattering responds to the polarization of the incident beam. Accordingly, we are able to resolve the effects of the polarization of incident photon in an NRF measurement.
Omer, M.; Hajima, Ryoichi*; Angell, C.*; Shizuma, Toshiyuki*; Hayakawa, Takehito*; Seya, Michio; Koizumi, Mitsuo
Proceedings of INMM 57th Annual Meeting (Internet), 9 Pages, 2016/07
Isotope-specific  -rays emitted in the nuclear resonance fluorescence (NRF) process provide a good technique for a non-destructive detection and assay of nuclear materials. We are developing technologies relevant to
-rays emitted in the nuclear resonance fluorescence (NRF) process provide a good technique for a non-destructive detection and assay of nuclear materials. We are developing technologies relevant to  -ray nondestructive detection and assay utilizing NRF. A Monte Carlo code to simulate NRF process is necessary for design and evaluation of NDA systems. We are developing NRFGeant4, a Geant4-based simulation code, for this purpose. In NRF experiments, highly-enriched targets are generally used such that the NRF signals are dominant and easily measured. In contrast, a real situation may involve very small contents of isotopes of interest. This results in a difficulty in measuring NRF signals because of the interference with other interactions, e.g. elastic scattering. For example, a typical nuclear fuel pellet contains about 90% of
-ray nondestructive detection and assay utilizing NRF. A Monte Carlo code to simulate NRF process is necessary for design and evaluation of NDA systems. We are developing NRFGeant4, a Geant4-based simulation code, for this purpose. In NRF experiments, highly-enriched targets are generally used such that the NRF signals are dominant and easily measured. In contrast, a real situation may involve very small contents of isotopes of interest. This results in a difficulty in measuring NRF signals because of the interference with other interactions, e.g. elastic scattering. For example, a typical nuclear fuel pellet contains about 90% of  U as a host material and less than 1% of
U as a host material and less than 1% of  Pu as an isotope of interest. When measuring NRF of
Pu as an isotope of interest. When measuring NRF of  Pu, there would be a huge background coming from the elastic scattering of
Pu, there would be a huge background coming from the elastic scattering of  U. Therefore, an estimation of the elastic scattering with the host material is essential for precise determination of isotope of interest. Satisfying estimation of elastic scattering is currently not available except for some calculations. In the present study, we upgrade our simulation code to include the calculation of elastic scattering events.
U. Therefore, an estimation of the elastic scattering with the host material is essential for precise determination of isotope of interest. Satisfying estimation of elastic scattering is currently not available except for some calculations. In the present study, we upgrade our simulation code to include the calculation of elastic scattering events.
 (Ce) detectors near 2 MeV
(Ce) detectors near 2 MeVOmer, M.*; Negm, H.*; Ogaki, Hideaki*; Daito, Izuru*; Hayakawa, Takehito; Bakr, M.*; Zen, H.*; Hori, Toshitada*; Kii, Toshiteru*; Masuda, Kai*; et al.
Nuclear Instruments and Methods in Physics Research A, 729, p.102 - 107, 2013/11
Times Cited Count:6 Percentile:44.02(Instruments & Instrumentation)The performance of LaBr (Ce) to measure nuclear resonance fluorescence (NRF) excitations is discussedin terms of limits of detection and in comparison with high-purity germanium (HPGe)detectors near the 2 MeV region where many NRF excitation levels from special nuclear materials are located. The NRF experiment was performed at the High Intensity Gamma-ray Source (HIGS) facility of Duke University. The incident
(Ce) to measure nuclear resonance fluorescence (NRF) excitations is discussedin terms of limits of detection and in comparison with high-purity germanium (HPGe)detectors near the 2 MeV region where many NRF excitation levels from special nuclear materials are located. The NRF experiment was performed at the High Intensity Gamma-ray Source (HIGS) facility of Duke University. The incident  -rays, of 2.12 MeV energy, hit a B
-rays, of 2.12 MeV energy, hit a B C target to excite the
C target to excite the  B nuclei to the first excitation level. The statistical-sensitive non-linear peak clipping (SNIP) algorithm was implemented to eliminate theback ground and enhance the limits of detection for the spectra measured with LaBr
B nuclei to the first excitation level. The statistical-sensitive non-linear peak clipping (SNIP) algorithm was implemented to eliminate theback ground and enhance the limits of detection for the spectra measured with LaBr (Ce). Both detection and determination limits were deduced from the experimental data.
(Ce). Both detection and determination limits were deduced from the experimental data.
 U measured with high-resolution LaBr
U measured with high-resolution LaBr (Ce) scintillation detectors
(Ce) scintillation detectorsOmer, M.*; Negm, H.*; Zen, H.*; Daito, Izuru*; Kii, Toshiteru*; Masuda, Kai*; Ogaki, Hideaki*; Hajima, Ryoichi; Shizuma, Toshiyuki; Hayakawa, Takehito; et al.
Japanese Journal of Applied Physics, 52(10), p.106401_1 - 106401_4, 2013/10
Times Cited Count:7 Percentile:30.71(Physics, Applied)A nuclear resonance fluorescence (NRF) experiment was performed on a  U target with quasi-monochromatic
U target with quasi-monochromatic  -rays at the High Intensity Gamma-ray Source (HIGS) facility of Duke University using a 1733 keV resonant energy. A LaBr
-rays at the High Intensity Gamma-ray Source (HIGS) facility of Duke University using a 1733 keV resonant energy. A LaBr (Ce) detector array consisting of eight cylindrical detectors, each with a length of 7.62 cm and a diameter of 3.81 cm, was implemented in this measurement. Moreover, a high-purity germanium (HPGe) detector array consisting of four detectors, each of which has a relative efficiency of 60%, was used as the benchmark for the measurement taken using the LaBr
(Ce) detector array consisting of eight cylindrical detectors, each with a length of 7.62 cm and a diameter of 3.81 cm, was implemented in this measurement. Moreover, a high-purity germanium (HPGe) detector array consisting of four detectors, each of which has a relative efficiency of 60%, was used as the benchmark for the measurement taken using the LaBr (Ce) detector array. The integrated cross section of the NRF level, measured with LaBr
(Ce) detector array. The integrated cross section of the NRF level, measured with LaBr (Ce) detectors, showed good agreement with the available data.
(Ce) detectors, showed good agreement with the available data.
Kameda, Jun*; Nishiyama, Yutaka; Bloomer, T. E.*
Surface and Interface Analysis, 31(7), p.522 - 531, 2001/07
Times Cited Count:10 Percentile:28.89(Chemistry, Physical)This study describes intergranular segregation and embrittlement in several model ferritic alloys doped with Mn, P, S and/or Cu subjected to neutron irradiation, irradiation-equivalent thermal ageing (ETA) and post-irradiation annealing (PIA). Neutron irradiation produced a larger amount of intergranular P segregation than S segregation. Intergranular C segregation remained small in all the as-irradiated alloys. A PIA study has shown that the P segregation in P-doped alloys subjected to lower temperature PIA proceeds via mobile P-interstitial complexes while the S segregation is controlled by vacancy-enhanced diffusion. The mechanisms of non-equilibrium intergranular segregation induced by neutron irradiation are discussed in light of coupled fluxes of point defects and impurities, and changes in the segregation capacity of grain boundaries. Small punch tests demonstrated how the impurity segregation or desegregation and hardening or softening induced by the irradiation, ETA and PIA influence intergranular embrittlement in the various ferritic alloys.