Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Igarashi, Takahiro; Otani, Kyohei; Kato, Chiaki; Sakairi, Masatoshi*; Togashi, Yusuke*; Baba, Kazuhiko*; Takagi, Shusaku*
ISIJ International, 61(4), p.1085 - 1090, 2021/04
Times Cited Count:1 Percentile:8.06(Metallurgy & Metallurgical Engineering)In order to clarify the effect of metal cations (Zn , Mg
, Mg , Na
, Na ) in aqueous solution on hydrogen permeation into iron, the amount of hydrogen permeation from iron surface was measured by electrochemical tests with a laser ablation. Moreover, in order to obtain the basic mechanism of hydrogen permeation with metal cation, first-principles calculations were used to acquire the adsorption potential of the metal cation and the electronic state around iron surface. By Zn
) in aqueous solution on hydrogen permeation into iron, the amount of hydrogen permeation from iron surface was measured by electrochemical tests with a laser ablation. Moreover, in order to obtain the basic mechanism of hydrogen permeation with metal cation, first-principles calculations were used to acquire the adsorption potential of the metal cation and the electronic state around iron surface. By Zn in solution, anodic reaction on ablated surface by laser irradiation was suppressed. Also, by quantum analysis Zn atoms were chemically bonded stronger than Na and Mg atoms to iron surface. It was suggested that the dissolution reaction of iron was suppressed by the formation of the Zn layer, and that lead suppression of hydrogen permeation into iron.
in solution, anodic reaction on ablated surface by laser irradiation was suppressed. Also, by quantum analysis Zn atoms were chemically bonded stronger than Na and Mg atoms to iron surface. It was suggested that the dissolution reaction of iron was suppressed by the formation of the Zn layer, and that lead suppression of hydrogen permeation into iron.
Sue, Yuki*; Yotsuzuka, Mai*; Futatsukawa, Kenta*; Hasegawa, Kazuo; Iijima, Toru*; Iinuma, Hiromi*; Inami, Kenji*; Ishida, Katsuhiko*; Kawamura, Naritoshi*; Kitamura, Ryo; et al.
Physical Review Accelerators and Beams (Internet), 23(2), p.022804_1 - 022804_7, 2020/02
Times Cited Count:2 Percentile:25.94(Physics, Nuclear)A destructive monitor to measure the longitudinal bunch width of a low-energy and low-intensity muon beam was developed. This bunch-width monitor (BWM) employed microchannel plates to detect a single muon with high time resolution. In addition, constant-fraction discriminators were adopted to suppress the time-walk effect. The time resolution was measured to be 65 ps in rms using a picosecond-pulsed laser. This resolution satisfied the requirements of the muon linac of the J-PARC E34 experiment. We measured the bunch width of negative-muonium ions accelerated with a radio-frequency quadrupole using the BWM. The bunch width was successfully measured to be  54
54  11 ns, which is consistent with the simulation.
11 ns, which is consistent with the simulation.
Sue, Yuki*; Iijima, Toru*; Inami, Kenji*; Yotsuzuka, Mai*; Iinuma, Hiromi*; Nakazawa, Yuga*; Otani, Masashi*; Kawamura, Naritoshi*; Shimomura, Koichiro*; Futatsukawa, Kenta*; et al.
Proceedings of 16th Annual Meeting of Particle Accelerator Society of Japan (Internet), p.55 - 60, 2019/07
The result of bunch size measurement of muon accelerated by RFQ up to 89 keV is presented in this paper. A four-stage muon linac for precise measurement of muon property is under construction in the J-PARC. The demonstration of the first muon RF acceleration with an RFQ linac was conducted and the transverse profile of the accelerated muons was measured in 2017. As one of the remaining issues for the beam diagnostic system, the longitudinal beam profile after the RFQ should be measured to match the profile to the designed acceptance of the subsequent accelerator. For this purpose, the new longitudinal beam monitor using the microchannel plate is under development. The time resolution of the monitor aims to be around 30 to 40 ps corresponding to 1% of a period of an operating frequency of the accelerator, which is 324 MHz. On November 2018, the bunch size of accelerated negative muonium ion of 89 keV with the RFQ was measured using this monitor at the J-PARC MLF. The measured bunch width is 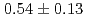 ns, which is consistent with the simulation.
ns, which is consistent with the simulation.
Sue, Yuki*; Iijima, Toru*; Inami, Kenji*; Yotsuzuka, Mai*; Futatsukawa, Kenta*; Kawamura, Naritoshi*; Mibe, Tsutomu*; Miyake, Yasuhiro*; Otani, Masashi*; Hasegawa, Kazuo; et al.
Proceedings of 10th International Particle Accelerator Conference (IPAC '19) (Internet), p.37 - 40, 2019/06
The result of bunch size measurement of muon accelerated by RFQ up to 89 keV is presented in this paper. A four-stage muon linac for precise measurement of muon property is under construction in the J-PARC. The demonstration of the first muon RF acceleration with an RFQ linac was conducted and the transverse profile of the accelerated muons was measured in 2017. As one of the remaining issues for the beam diagnostic system, the longitudinal beam profile after the RFQ should be measured to match the profile to the designed acceptance of the subsequent accelerator. For this purpose, the new longitudinal beam monitor using the microchannel plate is under development. The time resolution of the monitor aims to be around 30 to 40 ps corresponding to 1% of a period of an operating frequency of the accelerator, which is 324 MHz. On November 2018, the bunch size of accelerated negative muonium ion of 89 keV with the RFQ was measured using this monitor at the J-PARC MLF. The measured bunch width is 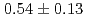 ns, which is consistent with the simulation.
ns, which is consistent with the simulation.
Chino, Daisuke*; Sato, Tsutomu*; Otani, Yusuke*; Nakabayashi, Ryo*; Oda, Chie; Yoneda, Tetsuro*
no journal, ,
Steady-state dissolution rates of smectite were determined as function of aqueous Al and Si concentrations using a stirred-flow-through reactor at 70 degrees in 0.3M-NaOH solution to obtain the reliable dissolution rates of smectite at hyperalkaline condition and to formulate the effect of deviation from equilibrium on smectite dissolution rate. The dissolution rates were calculated based from the dissolved Si or Al concentrations of the output solutions or from ex situ AFM observations. Results of the flow-through dissolution experiments and ex situ AFM observations suggest that the dissolved Si and Al concentrations in the solutions appear to be retarding the dissolution rate of smectite. If we assume the decrease is attributed by the effect of deviation from equilibrium on dissolution rate, the dissolution rate of smectite can be expressed in a non-linear function of the Gibbs free energy. This non-liner relationship is nearly same as that obtained by Cama, et al. (2000).