Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
 and O
and O in a reaction cell in triple quadrupole inductively coupled plasma mass spectrometry
in a reaction cell in triple quadrupole inductively coupled plasma mass spectrometryKazama, Hiroyuki; Konashi, Kenji*; Suzuki, Tatsuya*; Koyama, Shinichi; Maeda, Koji; Sekio, Yoshihiro; Onishi, Takashi; Abe, Chikage*; Shikamori, Yasuyuki*; Nagai, Yasuyoshi*
Journal of Analytical Atomic Spectrometry, 38(8), p.1676 - 1681, 2023/07
Times Cited Count:0 Percentile:0.02(Chemistry, Analytical)Yamamoto, Kazami; Kinsho, Michikazu; Hayashi, Naoki; Saha, P. K.; Tamura, Fumihiko; Yamamoto, Masanobu; Tani, Norio; Takayanagi, Tomohiro; Kamiya, Junichiro; Shobuda, Yoshihiro; et al.
Journal of Nuclear Science and Technology, 59(9), p.1174 - 1205, 2022/09
Times Cited Count:6 Percentile:84.97(Nuclear Science & Technology)In the Japan Proton Accelerator Research Complex, the purpose of the 3 GeV rapid cycling synchrotron (RCS) is to accelerate a 1 MW, high-intensity proton beam. To achieve beam operation at a repetition rate of 25 Hz at high intensities, the RCS was elaborately designed. After starting the RCS operation, we carefully verified the validity of its design and made certain improvements to establish a reliable operation at higher power as possible. Consequently, we demonstrated beam operation at a high power, namely, 1 MW. We then summarized the design, actual performance, and improvements of the RCS to achieve a 1 MW beam.
Shimojo, Kojiro; Fujiwara, Iori*; Oshima, Tatsuya*; Yokoyama, Keiichi; Yaita, Tsuyoshi
Analytical Sciences, 38(7), p.1003 - 1006, 2022/07
Times Cited Count:0 Percentile:0(Chemistry, Analytical)Liquid-liquid extraction of lanthanide (Ln) ions was investigated using 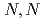 -dioctylthiodiglycolamic acid (DOTDGAA), which is a sulfur donor ligand with an amide group and a carboxyl group connected by a thioether chain. The extraction performance and selectivity of DOTDGAA for Ln ions were compared with those of
-dioctylthiodiglycolamic acid (DOTDGAA), which is a sulfur donor ligand with an amide group and a carboxyl group connected by a thioether chain. The extraction performance and selectivity of DOTDGAA for Ln ions were compared with those of 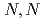 -dioctyldiglycolamic acid (DODGAA), which is also an oxygen donor ligand with a similar chemical structure, to assess the effect of the soft/hard donor atom on Ln separation. DOTDGAA quantitatively extracted all Ln ions while being selective toward light and middle Ln ions, in contrast to the selectivity of DODGAA for heavier Ln ions. Slope analysis demonstrated that the Ln
-dioctyldiglycolamic acid (DODGAA), which is also an oxygen donor ligand with a similar chemical structure, to assess the effect of the soft/hard donor atom on Ln separation. DOTDGAA quantitatively extracted all Ln ions while being selective toward light and middle Ln ions, in contrast to the selectivity of DODGAA for heavier Ln ions. Slope analysis demonstrated that the Ln transfer using DOTDGAA proceeded through a proton-exchange reaction, forming a 1:3 complex, Ln(DOTDGAA)
transfer using DOTDGAA proceeded through a proton-exchange reaction, forming a 1:3 complex, Ln(DOTDGAA) . The back-extraction of Ln ions from the extracting phase was successfully achieved under acidic conditions.
. The back-extraction of Ln ions from the extracting phase was successfully achieved under acidic conditions.
Wang, J.*; Hatano, Yuji*; Toyama, Takeshi*; Suzudo, Tomoaki; Hinoki, Tatsuya*; Alimov, V. Kh.*; Schwarz-Selinger, T.*
Journal of Nuclear Materials, 559, p.153449_1 - 153449_7, 2022/02
Times Cited Count:3 Percentile:68.71(Materials Science, Multidisciplinary)To study the effect of the content of chromium (Cr) in the tungsten (W) matrix on the vacancy formation and retention of hydrogen isotopes, the samples of the W-0.3Cr alloy were irradiated with 6.4 MeV Fe ions in the temperature range of 523-1273 K. These displacement-damaged samples were exposed to D gas at a temperature of 673 K. The addition of 0.3% Cr into the W matrix resulted in a significant decrease in the retention of deuterium compared to pure W after irradiation especially at high temperature. Positron lifetime for W-0.3Cr alloy irradiated at 1073 K was almost similar to that for non-irradiated one. These facts indicate the suppression of the formation of vacancy-type defects by 0.3% Cr addition.
gas at a temperature of 673 K. The addition of 0.3% Cr into the W matrix resulted in a significant decrease in the retention of deuterium compared to pure W after irradiation especially at high temperature. Positron lifetime for W-0.3Cr alloy irradiated at 1073 K was almost similar to that for non-irradiated one. These facts indicate the suppression of the formation of vacancy-type defects by 0.3% Cr addition.
Kikuchi, Tatsuya*; Nakajima, Kenji; Kawamura, Seiko; Inamura, Yasuhiro; Nakamura, Mitsutaka; Wakai, Daisuke*; Aoyama, Kazuhiro*; Iwahashi, Takaaki*; Kambara, Wataru*
Physica B; Condensed Matter, 564, p.45 - 53, 2019/07
Times Cited Count:1 Percentile:4.76(Physics, Condensed Matter)Details of the background, that is, unwanted signals accumulated by the data acquisition system of neutron instruments, observed by the cold-neutron chopper spectrometer AMATERAS installed at the Materials and Life Science Experimental Facility at J-PARC are reported. In the design phase of AMATERAS, we carefully considered the achievement of high signal-to-noise ratio, and possible countermeasures were implemented. Actually, recent scientific outputs from AMATERAS indicates that the spectrometer is one of excellent neutron instruments with low background. In spite of that, in nine years of AMATERAS operation, we have encountered unwanted signals due to various reasons, including gamma-rays emitted at materials on or near the beam line including the sample itself, scattered neutrons from the beam line devices, air scattering, electronic noise in data acquisition system, cosmic rays, T0 burst, and other unknown sources. In this report, we discuss the background observed by AMATERAS, especially in the conditions of without samples, comprehensively. The possible sources of these signals and the countermeasures considered against the above sources are discussed, which may be helpful to those who are engaged in other existing or planned neutron-scattering instruments.
Nakajima, Kenji; Kawamura, Seiko; Kikuchi, Tatsuya*; Kofu, Maiko; Kawakita, Yukinobu; Inamura, Yasuhiro; Kambara, Wataru*; Aoyama, Kazuhiro*; Wakai, Daisuke*; Harada, Masahide; et al.
Journal of Physics; Conference Series, 1021(1), p.012031_1 - 012031_5, 2018/06
Times Cited Count:5 Percentile:94.52(Nuclear Science & Technology)Sakasai, Kaoru; Sato, Setsuo*; Seya, Tomohiro*; Nakamura, Tatsuya; To, Kentaro; Yamagishi, Hideshi*; Soyama, Kazuhiko; Yamazaki, Dai; Maruyama, Ryuji; Oku, Takayuki; et al.
Quantum Beam Science (Internet), 1(2), p.10_1 - 10_35, 2017/09
Neutron devices such as neutron detectors, optical devices including supermirror devices and  He neutron spin filters, and choppers are successfully developed and installed at the Materials Life Science Facility (MLF) of the Japan Proton Accelerator Research Complex (J-PARC), Tokai, Japan. Four software components of MLF computational environment, instrument control, data acquisition, data analysis, and a database, have been developed and equipped at MLF. MLF also provides a wide variety of sample environment options including high and low temperatures, high magnetic fields, and high pressures. This paper describes the current status of neutron devices, computational and sample environments at MLF.
He neutron spin filters, and choppers are successfully developed and installed at the Materials Life Science Facility (MLF) of the Japan Proton Accelerator Research Complex (J-PARC), Tokai, Japan. Four software components of MLF computational environment, instrument control, data acquisition, data analysis, and a database, have been developed and equipped at MLF. MLF also provides a wide variety of sample environment options including high and low temperatures, high magnetic fields, and high pressures. This paper describes the current status of neutron devices, computational and sample environments at MLF.
Ogoshi, Yurie; Satoyama, Tomonori; Kishimoto, Katsumi; Nanri, Tomohiro; Suzuki, Takeshi; Tomioka, Osamu; Takaizumi, Hirohide*; Kanno, Tomoyuki*; Maruyama, Tatsuya*
JAEA-Technology 2017-017, 152 Pages, 2017/08
At Nuclear Science Research Institute, clearance works for about 4,000 tons of extremely low-level radioactive concrete debris, which were generated from the modification activities of JRR-3 from FY 1985 to FY 1989 and stored in the waste storage facility NL, carried out. First of this clearance works, method for measuring and evaluating radioactivity concentration was approved by Minister of MEXT on July 25, 2008. And then, clearance works were started from FY 2009. Measuring and evaluating radioactivity concentration was achieved by using the approved method, and was confirmed by government. And then, clearance works were completed in FY 2014. The clearance concrete was recycled as a material for restoration works of the 2011 off the Pacific coast of Tohoku Earthquake. This report summarizes the results of measuring and evaluating radioactivity concentration, achievement of confirmation by government, recycling of cleared concrete and cost for clearance works.
Sako, Hiroyuki; Harada, Hiroyuki; Sakaguchi, Takao*; Chujo, Tatsuya*; Esumi, Shinichi*; Gunji, Taku*; Hasegawa, Shoichi; Hwang, S.; Ichikawa, Yudai; Imai, Kenichi; et al.
Nuclear Physics A, 956, p.850 - 853, 2016/12
Times Cited Count:12 Percentile:65.66(Physics, Nuclear)Nakamura, Tatsuya; To, Kentaro; Sakasai, Kaoru; Honda, Katsunori; Soyama, Kazuhiko; Katagiri, Masaki*
JAEA-Conf 2015-002, p.391 - 398, 2016/02
Development of position-sensitive scintillator detectors at the J-PARC/MLF is briefly reviewed. The detector development for the neutron scattering instruments in the J-PARC/MLF initiated back in 2001. After the basic experiments and design study we have produced first beam line detectors in 2008 both with the one and two-dimensional position-sensitivity. With an extension of the fiber detector technology the detector that has an active area of 256  256 mm
256 mm with a 4-mm spatial resolution was designed and made for the single crystal diffractometer, SENJU, in 2011. In the presentation recent development work including the alternative detectors to
with a 4-mm spatial resolution was designed and made for the single crystal diffractometer, SENJU, in 2011. In the presentation recent development work including the alternative detectors to  He gas is also introduced as well as the new detector development for the nextiBIX instrument.
He gas is also introduced as well as the new detector development for the nextiBIX instrument.
Ozu, Akira; Takase, Misao*; Haruyama, Mitsuo; Kurata, Noritaka*; Kobayashi, Nozomi*; Kureta, Masatoshi; Nakamura, Tatsuya; To, Kentaro; Sakasai, Kaoru; Suzuki, Hiroyuki; et al.
Nuclear Instruments and Methods in Physics Research A, 798, p.62 - 69, 2015/10
Times Cited Count:2 Percentile:17.57(Instruments & Instrumentation)The light transport properties of scintillator light inside alternative He-3 neutron detector modules using scintillator sheets have been investigated by a ray-tracing simulation code. The detector module consists of a light-reflecting tube, a thin rectangular ceramic scintillator sheet laminated on a glass plate, and two photo-multiplier tubes (PMTs) mounted at both ends of the detector tube. The light induced on the surface of the scintillator sheet via nuclear interaction between the scintillator and neutrons are detected by the two PMTs. The light output of various detector modules in which the scintillator sheets are installed with several different arrangements were examined and evaluated in comparison with experimental results. The results derived from the simulation reveal that the light transport property is strongly dependent on the arrangement of the scintillator sheet inside the tube and the shape of the tube.
Nakamura, Mitsutaka; Kawakita, Yukinobu; Kambara, Wataru; Aoyama, Kazuhiro; Kajimoto, Ryoichi; Nakajima, Kenji; Kawamura, Seiko; Ikeuchi, Kazuhiko*; Kikuchi, Tatsuya; Inamura, Yasuhiro; et al.
JPS Conference Proceedings (Internet), 8, p.036011_1 - 036011_6, 2015/09
The needs for inelastic neutron scattering experiments under the special sample environment such as strong magnetic field and high temperature are recently increasing. However, the unwanted scatterings originating from these devices affect the detection of weak inelastic signals. In order to overcome this problem we have developed an oscillating radial collimator specialized for the chopper spectrometer at Materials and Life Science Experimental Facility (MLF) in J-PARC. In this study, we will report the performances of newly-developed oscillating radial collimators both for 4SEASONS and AMATERAS.
To, Kentaro; Nakamura, Tatsuya; Sakasai, Kaoru; Soyama, Kazuhiko; Yamagishi, Hideshi*
Nuclear Instruments and Methods in Physics Research A, 784, p.194 - 197, 2015/06
Times Cited Count:1 Percentile:9.74(Instruments & Instrumentation)A novel ceramics insulated detector element was developed for neutron measurement. The developed detector element consists of a ceramics insulator, cathode lines on the insulator, and ball-shaped anodes. The incident neutrons are usually scattered by the detector element itself because it acts as scatterer. To estimate the effects of scattering, we calculated the amount of neutrons scattered by the developed element. By the calculation results by a Monte Carlo simulation using PHITS, it is found that the developed element is effective to reduce the scattered neutrons. The number of scattered neutrons of the developed element is 40% smaller than that of polymer insulated element, which is widely used in micro-pattern element. Finally, neutron-induced signals were clearly observed using the developed detector element.
Nakamura, Tatsuya; To, Kentaro; Kawasaki, Takuro; Ebine, Masumi; Birumachi, Atsushi; Sakasai, Kaoru; Soyama, Kazuhiko
Nuclear Instruments and Methods in Physics Research A, 784, p.202 - 207, 2015/06
Times Cited Count:2 Percentile:17.57(Instruments & Instrumentation)A two-dimensional scintillation neutron detector incorporating an interpolation method readout by wavelength-shifting (WLS) fiber was developed to make an effective pixel size smaller than the physical pitch of the WLS fibre array. The detector that was made with the crossed arranged WLS fiber arrays where the fibers were placed in a regular pitch of 2.5 mm in  and
and  directions. The dedicated signal processing algorithms that calculated an incident position of neutron with a base length of the same, half and quarter of the physical WLS fiber pitch were developed for the detector operated in a photon-counting method. The paper demonstrated the feasibility of the developed interpolation method using a collimated neutron beam.
directions. The dedicated signal processing algorithms that calculated an incident position of neutron with a base length of the same, half and quarter of the physical WLS fiber pitch were developed for the detector operated in a photon-counting method. The paper demonstrated the feasibility of the developed interpolation method using a collimated neutron beam.
Akagi, Hiroshi; Kasajima, Tatsuya*; Kumada, Takayuki; Itakura, Ryuji; Yokoyama, Atsushi; Hasegawa, Hirokazu*; Oshima, Yasuhiro*
Physical Review A, 91(6), p.063416_1 - 063416_7, 2015/06
Times Cited Count:7 Percentile:38.91(Optics)We propose a strategy of isotope-selective ionization for a binary mixture of isotopologues of homonuclear diatomic molecules, utilizing field-free alignment with a train of femtosecond laser pulses. Field-free alignment can be achieved simultaneously for two isotopologues consisting of two atoms with the same atomic mass number  or
or  , utilizing a pulse train with their time interval of T
, utilizing a pulse train with their time interval of T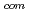 =
=  T(
T( ) =
) =  T(
T( ), where T(
), where T( ) and T(
) and T( ) are the rotational revival times of the isotopologues. We demonstrate experimentally that a train of four alignment pulses with their interval of T
) are the rotational revival times of the isotopologues. We demonstrate experimentally that a train of four alignment pulses with their interval of T (
( = 14,
= 14,  = 15) creates transiently aligned
= 15) creates transiently aligned  N
N and anti-aligned
and anti-aligned  N
N just before T
just before T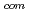 /2 after the last pulse, and vice versa just after T
/2 after the last pulse, and vice versa just after T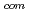 /2. Highly isotope-selective N
/2. Highly isotope-selective N ionization is achieved at these timings with another femtosecond laser pulse, which induces the non-resonant multiphoton ionization with the cross section remarkably depending on the angle between the molecular axis and the laser electric field direction. The ion yield ratio I(
ionization is achieved at these timings with another femtosecond laser pulse, which induces the non-resonant multiphoton ionization with the cross section remarkably depending on the angle between the molecular axis and the laser electric field direction. The ion yield ratio I( N
N
 )/I(
)/I( N
N
 ) ranges from 0.49 to 2.00, which is wider than the range obtained with single alignment pulse.
) ranges from 0.49 to 2.00, which is wider than the range obtained with single alignment pulse.
Nakajima, Kenji; Kawamura, Seiko; Kikuchi, Tatsuya; Kajimoto, Ryoichi; Takahashi, Nobuaki*; Nakamura, Mitsutaka; Soyama, Kazuhiko; Osakabe, Toyotaka
EPJ Web of Conferences, 83, p.03011_1 - 03011_5, 2015/01
Times Cited Count:3 Percentile:72.17(Physics, Multidisciplinary)We report the design of the beam-transport system (especially the vertical geometry) for a cold-neutron disk-chopper spectrometer AMATERAS at J-PARC. Based on the elliptical shape, which is one of the most effective geometries for a ballistic mirror, the design was optimized to obtain, at the sample position, a neutron beam with high flux without serious degrading in divergence and spacial homogeneity within the boundary conditions required from actual spectrometer construction. The optimum focal point was examined. An ideal elliptical shape was modified to reduce its height without serious loss of transmission. The final result was adapted to the construction requirements of AMATERAS. Although the ideas studied in this paper are considered for the AMATERAS case, they can be useful also to other spectrometers in similar situations.
To, Kentaro; Nakamura, Tatsuya; Sakasai, Kaoru; Soyama, Kazuhiko; Yamagishi, Hideshi*
Journal of Instrumentation (Internet), 9(11), p.C11019_1 - C11019_9, 2014/11
Times Cited Count:3 Percentile:16.04(Instruments & Instrumentation)A multiwire-type two-dimensional neutron detector system using individual line readout and optical signal transmission method is developed for use in the Materials and Life Science Experimental Facility (MLF) at the Japan Proton Accelerator Research Complex (J-PARC). The sensitive area was 128  128 mm
128 mm with a pitch of 1 mm in both directions (x and y), and the 256 signal lines are individually readout by signal-processing electronics. First irradiation experiments using pulsed neutrons are performed at the J-PARC/MLF. The developed detector could determine time-of-flight spectra and time-resolved two-dimensional images accurately with time range from 0 to 40 ms that arise from 25-Hz pulsed neutrons. Finally, the validity of the detector system is confirmed by a neutron reflectometry using Ni/Ti multilayer.
with a pitch of 1 mm in both directions (x and y), and the 256 signal lines are individually readout by signal-processing electronics. First irradiation experiments using pulsed neutrons are performed at the J-PARC/MLF. The developed detector could determine time-of-flight spectra and time-resolved two-dimensional images accurately with time range from 0 to 40 ms that arise from 25-Hz pulsed neutrons. Finally, the validity of the detector system is confirmed by a neutron reflectometry using Ni/Ti multilayer.
 LiF scintillator for detecting thermal neutrons
LiF scintillator for detecting thermal neutronsNakamura, Tatsuya; To, Kentaro; Honda, Katsunori; Sakasai, Kaoru; Soyama, Kazuhiko; Katagiri, Masaki*
Journal of Instrumentation (Internet), 9(11), p.C11020_1 - C11020_7, 2014/11
Times Cited Count:0 Percentile:0.01(Instruments & Instrumentation)An empirical formula that predicts a spatial resolution of a thermal neutron detector comprising wavelength-shifting (WLS) fibre arrays coupled with a ZnS/ LiF scintillator screen was derived based on the experimental results. The spatial resolutions of the test detectors were measured separately to evaluate the contributions due to light spread within the part of the scintillator and the part of the WLS fibres layres. The calculated results by using the derived formula reproduced the results with the test detectors, demonstrating the feasibility of the formula for designing a neutron-detecting head of this type detector.
LiF scintillator screen was derived based on the experimental results. The spatial resolutions of the test detectors were measured separately to evaluate the contributions due to light spread within the part of the scintillator and the part of the WLS fibres layres. The calculated results by using the derived formula reproduced the results with the test detectors, demonstrating the feasibility of the formula for designing a neutron-detecting head of this type detector.
To, Kentaro; Nakamura, Tatsuya; Sakasai, Kaoru; Soyama, Kazuhiko; Yamagishi, Hideshi*
Journal of Physics; Conference Series, 528, p.012045_1 - 012045_6, 2014/07
Times Cited Count:2 Percentile:69.29(Optics)A multiwire proportional chamber (MWPC) neutron detector system is developed for use in the Materials and Life Science Experimental Facility at the Japan Proton Accelerator Research Complex. In the developed MWPC system, a short response time and high spatial resolution can be obtained through the use of an individual line readout method. The developed system consists of a 256 channel detector element (x: 128 lines, y: 128 lines) equipped with a pressure vessel, amplifier-shaper-discriminator (ASD) boards, optical signal transmission devices, position encoders with field-programmable gate arrays (FPGAs), and a data acquisition device. The measured uniformity of all pixels in the two-dimensional image was 7.9%. The average intrinsic spatial resolution was 1.55 mm full width at half-maximum in the sensitive region calculated by taking into account measured track lengths of secondary particles.
 He at J-PARC/MLF
He at J-PARC/MLFNakamura, Tatsuya; To, Kentaro; Honda, Katsunori; Birumachi, Atsushi; Ebine, Masumi; Sakasai, Kaoru; Soyama, Kazuhiko; Katagiri, Masaki*
Journal of Physics; Conference Series, 528, p.012042_1 - 012042_7, 2014/07
Times Cited Count:5 Percentile:87.86(Optics)A wavelength-shifting fiber based scintillator detector has been developed as a helium-3 alternative detector in J-PARC/MLF. The detector is aimed at using for an inelastic neutron scattering instrument in a pulsed neutron source. The detector should have a capability to have a large-area coverage with a moderate pixel size as well as high detector efficiency, low  sensitivity, and a low background rate. We have developed a detector that has a larger neutron-sensitive area with a moderate pixel size based on the detector implemented in the SENJU instrument in the J-PARC/MLF. The prototype detector has a pixel size of 20
sensitivity, and a low background rate. We have developed a detector that has a larger neutron-sensitive area with a moderate pixel size based on the detector implemented in the SENJU instrument in the J-PARC/MLF. The prototype detector has a pixel size of 20  20 mm with a neutron-sensitive area of 320
20 mm with a neutron-sensitive area of 320  320 mm. In the presentation detailed detector performances are presented in comparison to those measured by an original SENJU detector.
320 mm. In the presentation detailed detector performances are presented in comparison to those measured by an original SENJU detector.