Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
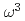 scaling of the vibrational density of states in quasi-2D nanoconfined solids
scaling of the vibrational density of states in quasi-2D nanoconfined solidsYu, Y.*; Yang, C.*; Baggioli, M.*; Phillips, A. E.*; Zaccone, A.*; Zhang, L.*; Kajimoto, Ryoichi; Nakamura, Mitsutaka; Yu, D.*; Hong, L.*
Nature Communications (Internet), 13, p.3649_1 - 3649_10, 2022/06
Times Cited Count:8 Percentile:81.66(Multidisciplinary Sciences)Okumura, Yoshikazu; Gobin, R.*; Knaster, J.*; Heidinger, R.*; Ayala, J.-M.*; Bolzon, B.*; Cara, P.*; Chauvin, N.*; Chel, S.*; Gex, D.*; et al.
Review of Scientific Instruments, 87(2), p.02A739_1 - 02A739_3, 2016/02
Times Cited Count:7 Percentile:35.23(Instruments & Instrumentation)IFMIF is an accelerator based neutron facility having two set of linear accelerators each producing 125mA/CW deuterium ion beams (250mA in total) at 40MeV. The LIPAc (Linear IFMIF Prototype Accelerator) being developed in the IFMIF-EVEDA project consists of an injector, a RFQ accelerator, and a part of superconducting Linac, whose target is to demonstrate 125mA/CW deuterium ion beam acceleration up to 9MeV. The injector has been developed in CEA Saclay and already demonstrated 140mA/100keV deuterium beam. The injector was disassembled and delivered to the International Fusion Energy Research Center (IFERC) in Rokkasho, Japan, and the commissioning has started after its reassembly 2014; the first beam production has been achieved in November 2014. Up to now, 100keV/120mA/CW hydrogen ion beam has been produced with a low beam emittance of 0.2  .mm.mrad (rms, normalized).
.mm.mrad (rms, normalized).
Okumura, Yoshikazu; Ayala, J.-M.*; Bolzon, B.*; Cara, P.*; Chauvin, N.*; Chel, S.*; Gex, D.*; Gobin, R.*; Harrault, F.*; Heidinger, R.*; et al.
Proceedings of 12th Annual Meeting of Particle Accelerator Society of Japan (Internet), p.203 - 205, 2015/09
Under the framework of Broader Approach (BA) agreement between Japan and Euratom, IFMIF/EVEDA project was launched in 2007 to validate the key technologies to realize IFMIF. The most crucial technology to realize IFMIF is two set of linear accelerator each producing 125mA/CW deuterium ion beams up to 40MeV. The prototype accelerator, whose target is 125mA/CW deuterium ion beam acceleration up to 9MeV, is being developed in International Fusion Research Energy Center (IFERC) in Rokkasho, Japan. The injector developed in CEA Saclay was delivered in Rokkasho in 2014, and is under commissioning. Up to now, 100keV/120mA/CW hydrogen ion beams and 100keV/90mA/CW duty deuterium ion beams are successfully produced with a low beam emittance of 0.21  .mm.mrad (rms, normalized). Delivery of RFQ components will start in 2015, followed by the installation of RF power supplies in 2015.
.mm.mrad (rms, normalized). Delivery of RFQ components will start in 2015, followed by the installation of RF power supplies in 2015.
Koide, Yoshihiko; Yoshida, Kiyoshi; Wanner, M.*; Barabaschi, P.*; Cucchiaro, A.*; Davis, S.*; Decool, P.*; Di Pietro, E.*; Disset, G.*; Genini, L.*; et al.
Nuclear Fusion, 55(8), p.086001_1 - 086001_7, 2015/08
Times Cited Count:31 Percentile:83.35(Physics, Fluids & Plasmas)The most distinctive feature of the superconducting magnet system for JT-60SA is the optimized coil structure in terms of the space utilization as well as the highly accurate coil manufacturing, thus meeting the requirements for the steady-state tokamak research: A conceptually new outer inter-coil structure separated from the casing is introduced to the toroidal field coils to realize their slender shape, allowing large-bore diagnostic ports for detailed plasma measurements. A method to minimize the manufacturing error of the equilibrium-field coils has been established, aiming at the precise plasma shape/position control. A compact butt-joint has been successfully developed for the Central Solenoid, which allows an optimized utilization of the limited space for the Central Solenoid to extend the duration of the plasma pulse.
Yoshida, Kiyoshi; Murakami, Haruyuki; Kizu, Kaname; Tsuchiya, Katsuhiko; Kamiya, Koji; Koide, Yoshihiko; Phillips, G.*; Zani, L.*; Wanner, M.*; Barabaschi, P.*; et al.
IEEE Transactions on Applied Superconductivity, 24(3), p.4200806_1 - 4200806_6, 2014/06
Times Cited Count:13 Percentile:56.48(Engineering, Electrical & Electronic)The upgrade of the JT-60U magnet system to the superconducting coils (JT-60SA) is progressing as a satellite facility for ITER by Japan and EU in the BA agreement. All components of magnet system are now under manufacturing in mass production. The first superconducting EF conductor was manufactured in 2010 in Japan. First superconducting coil EF4 was manufactured in 2012. Other EF5 and EF6 coils shall be manufactured by 2013 to install temporally on the cryostat base before the assembly of the plasma vacuum vessel. CS model coil is fabricated to qualify all manufacturing process of Nb Sn conductor. The first TF conductor was manufactured in 2012. The cryogenic requirements for JT-60SA are about 9 kW at 4.5K. Each coil is connected through an in-cryostat feeder to the current leads located outside the cryostat in the CTB. A total of 26 HTS current leads are installed in the CTB. The manufacturing of the magnet system is in progress to provide components to assembly the Tokamak machine.
Sn conductor. The first TF conductor was manufactured in 2012. The cryogenic requirements for JT-60SA are about 9 kW at 4.5K. Each coil is connected through an in-cryostat feeder to the current leads located outside the cryostat in the CTB. A total of 26 HTS current leads are installed in the CTB. The manufacturing of the magnet system is in progress to provide components to assembly the Tokamak machine.
Shibanuma, Kiyoshi; Arai, Takashi; Hasegawa, Koichi; Hoshi, Ryo; Kamiya, Koji; Kawashima, Hisato; Kubo, Hirotaka; Masaki, Kei; Saeki, Hisashi; Sakurai, Shinji; et al.
Fusion Engineering and Design, 88(6-8), p.705 - 710, 2013/10
Times Cited Count:10 Percentile:61.16(Nuclear Science & Technology)Shibanuma, Kiyoshi; Arai, Takashi; Kawashima, Hisato; Hoshino, Katsumichi; Hoshi, Ryo; Kobayashi, Kaoru; Sawai, Hiroaki; Masaki, Kei; Sakurai, Shinji; Shibama, Yusuke; et al.
Journal of Plasma and Fusion Research SERIES, Vol.9, p.276 - 281, 2010/08
The JT-60 SA project is a combined project of JA-EU satellite tokamak program under the Broader Approach (BA) agreement and JA domestic program. Major components of JT-60SA for assembly are vacuum vessel (VV), superconducting coils (TF coils, EF coils and CS coil), in-vessel components such as divertor, thermal shield and cryostat. An assembly frame (with the dedicated cranes), which is located around the tokamak, is adopted to carry out effectively the assembly of tokamak components in the tokamak hall, independently of the facility cranes in the building. The assembly frame also provides assembly tools and jigs with jacks to support temporarily the components as well as to adjust the components at right positions. In this paper, the assembly scenario and scequence of the major components such as VV and TFC and the concept of the assembly frame including special jigs and fixtures are discussed.
Gormezano, C.*; Sips, A. C. C.*; Luce, T. C.*; Ide, Shunsuke; Becoulet, A.*; Litaudon, X.*; Isayama, Akihiko; Hobirk, J.*; Wade, M. R.*; Oikawa, Toshihiro; et al.
Nuclear Fusion, 47(6), p.S285 - S336, 2007/06
Times Cited Count:315 Percentile:75.44(Physics, Fluids & Plasmas)This paper reviews recent world-wide progress in physics research towards International Thermonuclear Reactor (ITER). This chaper descrives on steady state operation with emphasis on: integrated scenarios, review of presently developed experimental scenarios, actuators for steady state operation, specific control issues to steady state operation, simulation of ITER steady-state and hybrid scenarios.