Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Kitazato, Kohei*; Milliken, R. E.*; Iwata, Takahiro*; Abe, Masanao*; Otake, Makiko*; Matsuura, Shuji*; Takagi, Yasuhiko*; Nakamura, Tomoki*; Hiroi, Takahiro*; Matsuoka, Moe*; et al.
Nature Astronomy (Internet), 5(3), p.246 - 250, 2021/03
Times Cited Count:43 Percentile:96.93(Astronomy & Astrophysics)Here we report observations of Ryugu's subsurface material by the Near-Infrared Spectrometer (NIRS3) on the Hayabusa2 spacecraft. Reflectance spectra of excavated material exhibit a hydroxyl (OH) absorption feature that is slightly stronger and peak-shifted compared with that observed for the surface, indicating that space weathering and/or radiative heating have caused subtle spectral changes in the uppermost surface. However, the strength and shape of the OH feature still suggests that the subsurface material experienced heating above 300  C, similar to the surface. In contrast, thermophysical modeling indicates that radiative heating does not increase the temperature above 200
C, similar to the surface. In contrast, thermophysical modeling indicates that radiative heating does not increase the temperature above 200  C at the estimated excavation depth of 1 m, even if the semimajor axis is reduced to 0.344 au. This supports the hypothesis that primary thermal alteration occurred due to radiogenic and/or impact heating on Ryugu's parent body.
C at the estimated excavation depth of 1 m, even if the semimajor axis is reduced to 0.344 au. This supports the hypothesis that primary thermal alteration occurred due to radiogenic and/or impact heating on Ryugu's parent body.
 O in the film on Fe oxidized at high temperature in air
O in the film on Fe oxidized at high temperature in airHaruna, Takumi*; Yamamoto, Tatsuya*; Miyairi, Yoji*; Shibata, Toshio*; Taniguchi, Naoki; Sakamaki, Keiko; Tachikawa, Hirokazu*
Zairyo To Kankyo, 64(5), p.201 - 206, 2015/05
Diffusion coefficients of D O in the films was determined in order to estimate corrosion rate of carbon steel for the overpack in ground water. Fe plates were heated to form oxide films. The films were characterized with XRD and SEM. After that, the specimen was contacted with D
O in the films was determined in order to estimate corrosion rate of carbon steel for the overpack in ground water. Fe plates were heated to form oxide films. The films were characterized with XRD and SEM. After that, the specimen was contacted with D O for 5184 ks, followed by subjected to TDS to obtain an amount of D
O for 5184 ks, followed by subjected to TDS to obtain an amount of D O absorbing into the film. As a result, single-layered film of Fe
O absorbing into the film. As a result, single-layered film of Fe O
O was formed at 573 and 723 K, and double-layered film of Fe
was formed at 573 and 723 K, and double-layered film of Fe O
O and Fe
and Fe O
O was formed at 873 K. It was found that an amount of D
was formed at 873 K. It was found that an amount of D O in the film correlated linearly with a square root of the absorption period, and that the amount was steady for a long period. From the results and Fick's second law, diffusion coefficients of D
O in the film correlated linearly with a square root of the absorption period, and that the amount was steady for a long period. From the results and Fick's second law, diffusion coefficients of D O was determined as 9.7
O was determined as 9.7 10
10 cm
cm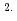 s
s for the Fe
for the Fe O
O film, and 5.5
film, and 5.5 10
10 cm
cm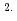 s
s to 2.2
to 2.2 10
10 cm
cm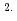 s
s for Fe
for Fe O
O film.
film.
Maeda, Toshikatsu; Watanabe, Koichi; Omori, Hiroyuki*; Sakamaki, Keiko; Inagaki, Yaohiro*; Idemitsu, Kazuya*
Genshiryoku Bakkuendo Kenkyu (CD-ROM), 21(2), p.63 - 74, 2014/12
Static leach tests were conducted for simulated HLW glass in CaCl /Ca(OH)
/Ca(OH) solutions to investigate the corrosion behavior of HLW glass under calcium-rich environments induced by cement based materials in geological repositories. Another series of leach tests were conducted in deionized water in the presence of iron to investigate the effects of iron over-pack on the glass corrosion. In Ca solutions, corrosion of the glass was inhibited during the test period compared to that in deionized water, while the corrosion was enhanced at the presence of iron. The enhancement of the glass corrosion was assumed to be accompanied with transformation of silica, a glass network former, into iron silicates.
solutions to investigate the corrosion behavior of HLW glass under calcium-rich environments induced by cement based materials in geological repositories. Another series of leach tests were conducted in deionized water in the presence of iron to investigate the effects of iron over-pack on the glass corrosion. In Ca solutions, corrosion of the glass was inhibited during the test period compared to that in deionized water, while the corrosion was enhanced at the presence of iron. The enhancement of the glass corrosion was assumed to be accompanied with transformation of silica, a glass network former, into iron silicates.
Ishimori, Yuu; Sakoda, Akihiro; Tanaka, Hiroshi; Mitsunobu, Fumihiro*; Yamaoka, Kiyonori*; Kataoka, Takahiro*; Yamato, Keiko*; Nishiyama, Yuichi*
JAEA-Research 2013-005, 60 Pages, 2013/06
Okayama University and the Japan Atomic Energy Agency (JAEA) have carried out the collaborative study of physiological effects of inhaled radon for the low-dose range. From 2007 to 2011, the following results were obtained. (1) Literature on effects of radon for the low-dose range was surveyed to determine the present tasks. (2) The first Japanese large-scale facility was developed for radon inhalation experiments with small animals. (3) Relationships between radon concentration and inhalation time were widely examined to understand the change in antioxidative functions due to radon, which are the most basic parameters. (4) Inhibitory effects of radon on oxidative damages were observed using model mice with reactive oxygen- or free radical-related diseases like alcohol-induced oxidative damages and type I diabetes. (5) In order to discuss biological responses quantitatively following radon inhalation, the biokinetics of inhaled radon was examined and the model for calculation of absorbed doses for organs and tissues was obtained.
Ohgama, Kazuya; Ando, Yoko; Yamaguchi, Mika; Ikuta, Yuko; Shinohara, Nobuo; Murakami, Hiroyuki; Yamashita, Kiyonobu; Uesaka, Mitsuru*; Demachi, Kazuyuki*; Komiyama, Ryoichi*; et al.
JAEA-Review 2013-004, 76 Pages, 2013/05
JAEA together with the Japan Nuclear Human Resource Development Network (JN-HRD Net), the University of Tokyo (UT) and the Japan Atomic Industrial Forum (JAIF) cohosted the IAEA-Nuclear Energy Management School in Tokai Village, aiming that Japan will be the center of nuclear HRD in the Asian region. In the school, not only lectures by IAEA experts, but also lectures by Japanese experts and technical visits were included for foreign participants. The school contributed to the internationalization of Japanese young professionals, development of nuclear human resource of other countries, and enhancement of cooperation between IAEA and Japan. Additionally, collaborative relationship within JN-HRD Net was strengthened by the school. In this report, findings obtained during the preparatory work and the school period are reported for future international nuclear HRD activities in Japan.
Kataoka, Takahiro*; Sakoda, Akihiro*; Yoshimoto, Masaaki*; Nakagawa, Shinya*; Toyota, Teruaki*; Nishiyama, Yuichi*; Yamato, Keiko*; Ishimori, Yuu; Kawabe, Atsushi*; Hanamoto, Katsumi*; et al.
Radiation Protection Dosimetry, 146(1-3), p.360 - 363, 2011/07
Times Cited Count:6 Percentile:44.28(Environmental Sciences)Our previous studies showed the possibility that activation of the antioxidative function alleviates various oxidative damages, which are related to lifestyle diseases. Results showed that, low-dose X-ray irradiation activated superoxide dismutase and inhibits oedema following ischaemia-reperfusion. To alleviate ischaemia-reperfusion injury with transplantation, the changes of the antioxidative function in liver graft using low-dose X-ray irradiation immediately after exenteration were examined. Results showed that liver grafts activate the antioxidative function as a result of irradiation. In addition, radon inhalation enhances the antioxidative function in some organs, and alleviates alcohol-induced oxidative damage of mouse liver. Moreover, in order to determine the most effective condition of radon inhalation, mice inhaled radon before or after carbon tetrachloride (CCl ) administration. Results showed that radon inhalation alleviates CCl
) administration. Results showed that radon inhalation alleviates CCl -induced hepatopathy, especially prior inhalation. It is highly possible that adequate activation of antioxidative functions induced by low-dose irradiation can contribute to preventing or reducing oxidative damages, which are related to lifestyle diseases.
-induced hepatopathy, especially prior inhalation. It is highly possible that adequate activation of antioxidative functions induced by low-dose irradiation can contribute to preventing or reducing oxidative damages, which are related to lifestyle diseases.
Sano, Tadashi*; Wada, Seiichi*; Suzuki, Keiko*; Natsuhori, Masahiro*; Kakizaki, Takehiko; Ito, Takashi*; Nakazawa, Konomi*; Kobayashi, Yasuhiko; Ito, Nobuhiko*
JAEA-Review 2006-042, JAEA Takasaki Annual Report 2005, P. 115, 2007/02
Kobayashi, Takatoshi*; Yokobori, Hitoshi*; Sasaki, Makoto*; Tada, Keiko*
PNC TJ206 73-07, 228 Pages, 1973/04
no abstracts in English
Sano, Tadashi*; Suzuki, Keiko*; Natsuhori, Masahiro*; Kakizaki, Takehiko; Ito, Nao*; Nakazawa, Konomi*; Ito, Nobuhiko*; Wada, Seiichi*; Kobayashi, Yasuhiko
no journal, ,
no abstracts in English
Ishino, Masahiko; Kado, Masataka; Tamotsu, Satoshi*; Yasuda, Keiko*; Shinohara, Kunio*; Mikata, Yuji*; Kishimoto, Maki; Nishikino, Masaharu; Oba, Toshiyuki; Kaihori, Takeshi; et al.
no journal, ,
no abstracts in English
 Li+
Li+ Pb reaction and simple chemical separation of astatine
Pb reaction and simple chemical separation of astatineNishinaka, Ichiro; Yokoyama, Akihiko*; Washiyama, Koshin*; Amano, Ryohei*; Ri, Keiko*; Yamada, Norihiro*; Ishiguro, Rika*; Maeda, Eita*; Makii, Hiroyuki; Hashimoto, Kazuyuki; et al.
no journal, ,
We have started to study production and utilization of an  radioactive nuclide
radioactive nuclide  At which is a prospective candidate for targeted alpha radiotherapy. We determined production cross sections of astatine radioisotopes in the reaction of 29-48 MeV
At which is a prospective candidate for targeted alpha radiotherapy. We determined production cross sections of astatine radioisotopes in the reaction of 29-48 MeV  Li+
Li+ Pb by
Pb by  -ray and
-ray and  -ray spectrometry at the tandem accelerator of JAEA-Tokai. Besides, we developed a simple dry-chemical method for separation of astatine.
-ray spectrometry at the tandem accelerator of JAEA-Tokai. Besides, we developed a simple dry-chemical method for separation of astatine.
Maeda, Toshikatsu; Omori, Hiroyuki; Sakamaki, Keiko
no journal, ,
no abstracts in English
Habe, Hiroshi*; Inaba, Tomohiro*; Aoyagi, Tomo*; Aizawa, Hidenobu*; Sato, Yuya*; Hori, Tomoyuki*; Yamaji, Keiko*; Ohara, Yoshiyuki; Fukuyama, Kenjin; Cai, H.*; et al.
no journal, ,
no abstracts in English