Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Oizumi, Akito; Sagara, Hiroshi*
Dai-44-Kai Nihon Kaku Busshitsu Kanri Gakkai Nenji Taikai Kaigi Rombunshu (Internet), 4 Pages, 2023/11
Research and development of transuranium (TRU) fuel cycles with accelerator drive systems (ADSs) transmuting minor actinides separated from the commercial cycles has been continuously conducted to reduce the high-level radioactive waste contained in spent fuel discharged from nuclear power plants. Since ADS could be misused to illegally produce Pu by using neutrons generated by the accelerator, a different approach from a conventional nuclear reactor would be needed. In this study, we have analyzed possible misuse scenarios of ADS quantitatively evaluated Pu that can be illegally produced within the design tolerance of ADS, and evaluated the effects of the Dual Containment and Surveillance(C/S) and the design information verification methods. As a result, it was quantitatively clarified that 10-60 kg of Pu could be generated clandestinely, and the dual C/S and design information verification with monitoring of the operation history of both accelerators and reactors could detect and prevent all the misuse scenarios effectively.
Nagatani, Taketeru; Sagara, Hiroshi*; Kosuge, Yoshihiro*; Nomi, Takayoshi; Okumura, Keisuke
Journal of Nuclear Science and Technology, 60(4), p.460 - 472, 2023/04
Times Cited Count:1 Percentile:31.61(Nuclear Science & Technology)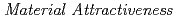 evaluation for TRU fuel cycle
evaluation for TRU fuel cycleOizumi, Akito; Sagara, Hiroshi*
Dai-43-Kai Nihon Kaku Busshitsu Kanri Gakkai Nenji Taikai Kaigi Rombunshu (Internet), 4 Pages, 2022/11
Research and development of partitioning and transmutation cycle with accelerator drive systems (ADSs) transmuting minor actinides separated from the commercial cycles has been continuously conducted to reduce the high-level radioactive waste contained in spent fuel discharged from nuclear power plants. Since the chemical form and composition of the fuels are different from those of the current commercial cycles, it is necessary to examine the inspection goal of the safeguards and the design level of physical protections which are required for the partitioning and transmutation (P&T) cycle. In previous studies, the 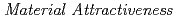 (
(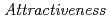 ) of the uranium (U) in the ADS fuel with a unique isotopic composition was evaluated as 2, the second highest on a 4-point scale, assuming state actors. In this study, reduction methods of potential nuclear proliferation were examined for the rationalization of the P&T cycle design considering nuclear non-proliferation. The amount of recovered U (RepU) added to the ADS fuel, which was required to increase the bare critical mass of U, was quantitatively evaluated as one of the reduction methods of potential nuclear proliferation risk. As a result, the addition of RepU, which was about 1.3- 2.7 times U in the ADS fuel, lowered the
) of the uranium (U) in the ADS fuel with a unique isotopic composition was evaluated as 2, the second highest on a 4-point scale, assuming state actors. In this study, reduction methods of potential nuclear proliferation were examined for the rationalization of the P&T cycle design considering nuclear non-proliferation. The amount of recovered U (RepU) added to the ADS fuel, which was required to increase the bare critical mass of U, was quantitatively evaluated as one of the reduction methods of potential nuclear proliferation risk. As a result, the addition of RepU, which was about 1.3- 2.7 times U in the ADS fuel, lowered the 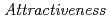 to 3 - 4. The rationalization of the P&T cycle design based on the safeguards by design can be expected by reviewing the U decontamination standards in the reprocessing steps of the commercial cycle based on these quantitative data.
to 3 - 4. The rationalization of the P&T cycle design based on the safeguards by design can be expected by reviewing the U decontamination standards in the reprocessing steps of the commercial cycle based on these quantitative data.
Nagatani, Taketeru; Sagara, Hiroshi*; Kosuge, Yoshihiro*; Nakaguki, Sho; Nomi, Takayoshi; Okumura, Keisuke
Dai-43-Kai Nihon Kaku Busshitsu Kanri Gakkai Nenji Taikai Kaigi Rombunshu (Internet), 3 Pages, 2022/11
Oizumi, Akito; Sugawara, Takanori; Sagara, Hiroshi*
Annals of Nuclear Energy, 169, p.108951_1 - 108951_9, 2022/05
Times Cited Count:0 Percentile:0.01(Nuclear Science & Technology)Research and development of the partitioning and transmutation (P&T) cycle with accelerator-drive systems (ADSs) transmuting minor actinides separated from the commercial cycles have been continuously conducted to reduce the amount of high-level radioactive waste contained in spent fuel discharged from nuclear power plants. Because the chemical form and composition of the fuels are different from those of the current commercial cycles, it is necessary to examine the inspection goal of the safeguards (SGs) and the design level of physical protections (PPs) that are required for the P&T cycle. In this study, the material attractiveness was evaluated assuming the theft or diversion of fuel assemblies from the fuel storage pool of the ADS facility in terms of nuclear security and non-proliferation. According to the results, quantitative components based on the fundamental fuel property were created as an important factor to decide the inspection goal for SGs and the design level for PPs required for the ADS facility. Additionally, the attractiveness of mixed oxide (MOX) fuel assemblies stored in the commercial boiling water reactor (BWR) facility was compared with that of the ADS. With regard to nuclear security, the ADS fuel was less attractive than the BWR MOX in every cycle. Regarding nuclear non-proliferation, the ADS fuel assembly had less attractive plutonium (Pu) than the BWR MOX, and the uranium (U) in the ADS fuel assembly was as attractive as (or slightly more attractive than) that of the BWR MOX owing to low spontaneous fission neutron. Furthermore, new issues were identified through this evaluation. With the current regulations, it was difficult to decide whether the ADS fuel before irradiation should be treated as fresh or spent, because the ADS fresh fuel contained more transuranium and rare earth than U and contained U whose main component was U-234 instead of U-238.
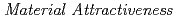 of uranium in ADS fuel assembly
of uranium in ADS fuel assemblyOizumi, Akito; Sugawara, Takanori; Sagara, Hiroshi*
Dai-42-Kai Nihon Kaku Busshitsu Kanri Gakkai Nenji Taikai Kaigi Rombunshu (Internet), 4 Pages, 2021/11
Research and development of partitioning and transmutation cycle with accelerator drive systems (ADSs) transmuting minor actinides (MAs) separated from the commercial cycles has been continuously conducted to reduce the high-level radioactive waste (HLW) contained in spent fuel discharged from nuclear power plants. Since the chemical form and composition of the fuels are different from those of the current commercial cycles, it is necessary to examine the inspection goal of the safeguards (SGs) and the design level of physical protections (PPs) which are required for the partitioning and transmutation cycle. In this study, 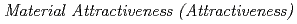 of the uranium (U) in the fuel assembly in the fuel storage pool in the ADS facility was evaluated and it was compared with the plutonium (Pu) in the MOX fuel assembly for a general boiling water reactor (BWR). As a result, it made clear that the U in the ADS fuel assembly had equal to or less attractive than the Pu in the BWR MOX fuel assembly. Moreover, a new issue has been extracted. It is difficult to determine whether the ADS fresh fuel should be considered as non-irradiated or irradiated fuel under the current regulatory standards because the ADS fresh fuel contains many MAs, rare-earths, and
of the uranium (U) in the fuel assembly in the fuel storage pool in the ADS facility was evaluated and it was compared with the plutonium (Pu) in the MOX fuel assembly for a general boiling water reactor (BWR). As a result, it made clear that the U in the ADS fuel assembly had equal to or less attractive than the Pu in the BWR MOX fuel assembly. Moreover, a new issue has been extracted. It is difficult to determine whether the ADS fresh fuel should be considered as non-irradiated or irradiated fuel under the current regulatory standards because the ADS fresh fuel contains many MAs, rare-earths, and  U rich U.
U rich U.
Oizumi, Akito; Sagara, Hiroshi*
Proceedings of INMM & ESARDA Joint Virtual Annual Meeting (Internet), 7 Pages, 2021/08
Research and development of partitioning and transmutation (P&T) cycle with accelerator-drive systems (ADSs) transmuting minor actinides (MAs) separated from the commercial cycles has been continuously conducted to reduce the high-level radioactive waste (HLW) contained in spent fuel discharged from nuclear power plants. The Japan Atomic Energy Agency has proposed a pyrochemical process for reprocessing ADS spent fuel with high decay heat and radioactivity due to the large amount of MA. Since the chemical form and composition of the fuels are different from those of the current commercial cycles, it is necessary to examine the inspection goal of the safeguards (SGs) and the design level of physical protections (PPs) which are required for the P&T cycle. In this study, the material attractiveness was evaluated assuming the diversion of the Cd cathode and the nitride powder from the pyroprocessing in terms of non-proliferation. Additionally, they were compared with the material attractiveness of the MOX fuel assemblies (fresh and spent fuels) for a conventional boiling water reactor (BWR). The Cd cathode used to recover actinides from ADS spent fuel by molten salt electrolysis in the pyroprocessing facility of P&T cycle was less attractive than the MOX fuel assembly for the BWR because the Cd cathode included  Pu having high decay heat. The nitride powder electrorefined from the ADS spent fuel was also less attractiveness than the MOX fuel assembly for the BWR because of the same reasons of the Cd cathode.
Pu having high decay heat. The nitride powder electrorefined from the ADS spent fuel was also less attractiveness than the MOX fuel assembly for the BWR because of the same reasons of the Cd cathode.
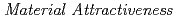 of fuel assembly in early period of burnup cycle
of fuel assembly in early period of burnup cycleOizumi, Akito; Sugawara, Takanori; Sagara, Hiroshi*
Dai-41-Kai Nihon Kaku Busshitsu Kanri Gakkai Nenji Taikai Kaigi Rombunshu (Internet), 4 Pages, 2020/11
Research and development of partitioning and transmutation cycle with accelerator drive systems (ADSs) transmuting minor actinides (MAs) separated from the commercial cycles has been continuously conducted to reduce the high-level radioactive waste (HLW) contained in spent fuel discharged from nuclear power plants. Since the chemical form and composition of the fuels are different from those of the current commercial cycles, it is necessary to examine the accuracy of the safeguards (SGs) and the level of physical protections (PPs) which are required for the partitioning and transmutation cycle. In this study, 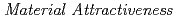 of the first cycle fuel assemblies (fresh and spent fuels) in the fuel storage pool in the ADS facility was evaluated and it was compared with that of the MOX fuel assemblies (fresh and spent fuels) for a general boiling water reactor (BWR). As a result, it made clear that the fuel storage pool in the ADS facility storing the first cycle fuel assemblies were required the SG detection accuracy and PP level equal to or lower than the MOX fuel assembly of the BWR since the ADS fuel assembly in the first cycle was less attractive than the MOX fuel assembly for the BWR.
of the first cycle fuel assemblies (fresh and spent fuels) in the fuel storage pool in the ADS facility was evaluated and it was compared with that of the MOX fuel assemblies (fresh and spent fuels) for a general boiling water reactor (BWR). As a result, it made clear that the fuel storage pool in the ADS facility storing the first cycle fuel assemblies were required the SG detection accuracy and PP level equal to or lower than the MOX fuel assembly of the BWR since the ADS fuel assembly in the first cycle was less attractive than the MOX fuel assembly for the BWR.
El-Asaad, H.*; Nagai, Haruyasu; Sagara, Hiroshi*; Han, C. Y.*
Annals of Nuclear Energy, 141, p.107292_1 - 107292_9, 2020/06
Times Cited Count:0 Percentile:0.01(Nuclear Science & Technology)Atmospheric dispersion simulations can provide crucial information to assess radioactive plumes in the environment for nuclear emergency preparedness. However, it is a difficult and time-consuming task to make simulations assuming many possible scenarios and to derive data from a vast number of results. Therefore, an interface was developed to assist users in conveying characteristics of plumes from simulation results. The interface uses a large database that contains WSPEEDI-II simulations for the first 20-days of radioactive release from the Fukushima Daiichi Nuclear Power Plant, and it displays essential quantitative data to the user from the database. The user may conduct sensitivity analysis with the help of the interface by changing release condition to generate many different case scenarios.
Aoki, Takeshi; Chirayath, S. S.*; Sagara, Hiroshi*
Annals of Nuclear Energy, 141, p.107325_1 - 107325_7, 2020/06
Times Cited Count:2 Percentile:24.28(Nuclear Science & Technology)The proliferation resistance (PR) of an inert matrix fuel (IMF) in the transuranic nuclear fuel cycle (NFC) of a high temperature gas cooled reactor is evaluated relative to the uranium and plutonium mixed-oxide (MOX) NFC of a light water reactor using PRAETOR code and sixty-eight input attributes. The objective is to determine the impacts of chemical stability of IMF and fuel irradiation on the PR. Specific material properties of the IMF, such as lower plutonium content, carbide ceramics coating, and absence of  U, contribute to enhance its relative PR compared to MOX fuel. The overall PR value of the fresh IMF (an unirradiated direct use material with a one-month diversion detection timeliness goal) is nearly equal to that of the spent MOX fuel (an irradiated direct use nuclear material with a three-month diversion detection timeliness goal). Final results suggest a reduced safeguards inspection frequency to manage the IMF.
U, contribute to enhance its relative PR compared to MOX fuel. The overall PR value of the fresh IMF (an unirradiated direct use material with a one-month diversion detection timeliness goal) is nearly equal to that of the spent MOX fuel (an irradiated direct use nuclear material with a three-month diversion detection timeliness goal). Final results suggest a reduced safeguards inspection frequency to manage the IMF.
Hamuza, E.-A.; Nagai, Haruyasu; Sagara, Hiroshi*
Energy Procedia, 131, p.279 - 284, 2017/12
Times Cited Count:1 Percentile:61.21(Energy & Fuels)In this study we would like to propose a method to use atmospheric dispersion simulations by WSPEEDI for consideration of crisis management on radionuclide dispersion from a nuclear power plant. WSPEEDI can simulate and output crucial information regarding environmental distribution of radionuclides and weather pattern for nuclear emergency countermeasures, thus this study will make use of its output to display the effective information for evacuation planning from a radionuclide dispersion. We will be assembling database of atmospheric dispersion outputs for one year by using WSPEEDI for a nuclear facility, then the database will be analysed to make the summary that has useful information for nuclear emergency managements. WSPEEDI outputs are converted into numeric information showing dispersion characteristics so that users can understand WSPEEDI predictions easily.
Shiba, Tomooki; Maeda, Shigetaka; Sagara, Hiroshi*; Ishimi, Akihiro; Tomikawa, Hirofumi
Energy Procedia, 131, p.250 - 257, 2017/12
Times Cited Count:0 Percentile:0.03(Energy & Fuels)In the present paper, the  ray source data was developed for the debris composition based on "best estimates", and the subsequent photon transportation calculation was performed to evaluate the leakage
ray source data was developed for the debris composition based on "best estimates", and the subsequent photon transportation calculation was performed to evaluate the leakage  ray spectra according to the fuel debris. Since the creation of the line spectrum source requires a great deal, we have developed the relatively simple but accurate enough method to build up
ray spectra according to the fuel debris. Since the creation of the line spectrum source requires a great deal, we have developed the relatively simple but accurate enough method to build up  ray source, coupling of baseline spectra evaluated by ORIGEN2 code and several line spectra of interest. One of the advantages of the method is taking bremsstrahlung X rays into consideration by utilizing the bremsstrahlung libraries of ORIGEN2. The new
ray source, coupling of baseline spectra evaluated by ORIGEN2 code and several line spectra of interest. One of the advantages of the method is taking bremsstrahlung X rays into consideration by utilizing the bremsstrahlung libraries of ORIGEN2. The new  ray source was used to calculate the detector response of HPGe detector and the results was compared as a benchmark with experimental measurement results of irradiated fuel pins. As the result, the simulated
ray source was used to calculate the detector response of HPGe detector and the results was compared as a benchmark with experimental measurement results of irradiated fuel pins. As the result, the simulated  ray spectrum shape agreed well with the shape of
ray spectrum shape agreed well with the shape of  ray spectrum obtained by the experiment.
ray spectrum obtained by the experiment.
Nagatani, Taketeru; Komeda, Masao; Shiba, Tomooki; Nauchi, Yasushi*; Maeda, Makoto; Sagara, Hiroshi*; Kosuge, Yoshihiro*; Kureta, Masatoshi; Tomikawa, Hirofumi; Okumura, Keisuke; et al.
Energy Procedia, 131, p.258 - 263, 2017/12
Times Cited Count:10 Percentile:98.3(Energy & Fuels)Shiba, Tomooki; Sagara, Hiroshi*; Tomikawa, Hirofumi
Proceedings of International Nuclear Fuel Cycle Conference (GLOBAL 2017) (USB Flash Drive), 3 Pages, 2017/09
Since the removal of fuel debris from the Fukushima Daiichi Nuclear Power Plant is planned to commence in 2021, measurement technologies for quantification of the nuclear material in fuel debris will be required for appropriate nuclear material management. In this paper, an outline of a passive gamma technique as one of the measurement technologies is briefly described, and the results of phase 1 and 2 of the so-called common set of simulation models for fuel debris and canisters are reported. The newly developed coupling method is applied to produce a gamma ray source for simulation. As the result of phase 1, it is revealed that the variation in the composition of fuel debris does not affect the gamma ray leakage behavior from canisters. According to the result of phase 2, the primary peak of Eu-154 at 1.27 MeV is clearly observable, although the debris is centrally located in canister. In addition, rotational scanning is effective for correcting the deviation in detection efficiency due to debris located off-center in canisters.
Shiba, Tomooki; Tomikawa, Hirofumi; Sagara, Hiroshi*; Ishimi, Akihiro
57th Annual Meeting of the Institute of Nuclear Materials Management (INMM 2016), Vol.1, p.365 - 374, 2017/02
Fission products (FPs) such as Ce and Eu seem to be very low volatile even in high temperature environment in the severe accident of nuclear reactors. They are supposed to chemically coexist with nuclear fuel. In our passive gamma ray spectroscopy, gamma rays from such FPs are measured and their amount and burnup are estimated. Then we multiply the mass ratio of the FPs and nuclear materials, and we obtain the mass of nuclear material of interest. According to hypothetical fuel debris and canister models, we performed simulation of leakage gamma rays from canister of debris. gamma ray source spectra were derived from the composition of the hypothetical fuel debris and the photon transport calculation was carried out. In addition, we conducted experiments of gamma ray measurement from intact spent fuels irradiated in the Experimental Fast Reactor Joyo in order to validate the prediction performance of the simulation by the comparison of the experiments and simulation.
Nagatani, Taketeru; Komeda, Masao; Shiba, Tomooki; Maeda, Makoto; Nauchi, Yasushi*; Sagara, Hiroshi*; Kosuge, Yoshihiro*; Kureta, Masatoshi; Tomikawa, Hirofumi; Okumura, Keisuke; et al.
Proceedings of INMM 57th Annual Meeting (Internet), 10 Pages, 2016/07
Shiba, Tomooki; Sagara, Hiroshi*; Tomikawa, Hirofumi
56th Annual Meeting of the Institute of Nuclear Materials Management (INMM 2015), Vol.3, p.1735 - 1741, 2016/00
In response to the accident at Fukushima Daiichi Nuclear Power Station, passive gamma spectrometry is being researched and developed as one of the candidates of a mass measurement method for the special nuclear materials in molten core material. Among Fission Products (FPs) accompanied in molten core materials, some of them are very low-volatile and emit high-energy gamma rays, which enable us to derive the mass of those FPs by passive gamma spectrometry. Using the mass ratio of the FPs and nuclear materials, this technique provides the mass estimation of nuclear materials. This technique is relatively simple and was applied to the analysis of nuclear materials in the clean-up process of damaged Three Mile Island unit-2 (TMI-2) reactor. In this paper, we show the characteristics of leakage gamma rays from removed fuel canisters simulated by MCNP. Different detector responses to gamma rays from fuel debris are also evaluated supposing NaI, LaBr and HPGe.
and HPGe.
Sagara, Hiroshi; Kawakubo, Yoko; Inoue, Naoko
JAEA-Review 2013-011, 54 Pages, 2014/01
The Generation IV (GEN IV) International Forum Proliferation Resistance and Physical Protection (PR & PP) Working Group is in charge of developing a methodology for evaluating PR & PP of potential GEN IV options. The present report, published in Oct. 2009, was used as a supporting study for development of the evaluation methodology for PR & PP, summarizing the case study of the PR & PP evaluation of Example Sodium Fast Reactor (ESFR) co located with a dry fuel storage facility and a pyrochemical spent-fuel reprocessing facility, a hypothetical nuclear energy system, consisting of nine main system elements, and it provides for designers the practical experience of applying the PR&PP evaluation methodology to a nuclear energy system. The development of the future nuclear fuel cycle system with sufficient PR & PP features is a crucial task in Japan. With the usefulness the report, it was translated and published here as a Japanese-language edition with the concurrence of the OECD-NEA.
 spectrometry of molten core material from Fukushima Daiichi Nuclear Power Station unit 1, 2 and 3 cores for special nuclear material accountancy; Low-volatile FP and special nuclear material inventory analysis and fundamental characteristics of
spectrometry of molten core material from Fukushima Daiichi Nuclear Power Station unit 1, 2 and 3 cores for special nuclear material accountancy; Low-volatile FP and special nuclear material inventory analysis and fundamental characteristics of  -rays from fuel debris
-rays from fuel debrisSagara, Hiroshi; Tomikawa, Hirofumi; Watahiki, Masaru; Kuno, Yusuke
Journal of Nuclear Science and Technology, 51(1), p.1 - 23, 2014/01
Times Cited Count:9 Percentile:57.19(Nuclear Science & Technology)Feasibility study of  spectrometry of molten core material from Fukushima Daiichi Nuclear Power Station Unit 1, 2 and 3 cores for special nuclear material accountancy has been performed, focusing on the low-volatile fission product and heavy metal inventory analysis, and fundamental characteristics of
spectrometry of molten core material from Fukushima Daiichi Nuclear Power Station Unit 1, 2 and 3 cores for special nuclear material accountancy has been performed, focusing on the low-volatile fission product and heavy metal inventory analysis, and fundamental characteristics of  -ray from fuel debris for passive measurement. The inventory ratio of low-volatile lanthanides,
-ray from fuel debris for passive measurement. The inventory ratio of low-volatile lanthanides,  Eu and
Eu and  Ce, to special nuclear material were evaluated by whole core inventory in unit 1, 2 and 3 cores as reference value for homogenized molten fuel material, and also as a function of burnup for specific fuel debris, considering the sensitivity of enrichment, specific power, water void fraction, cooling time, calculation tool accuracy and release ratio. The same indices could be applied to unit 3, while the uncertainty of specific fuel debris of separated MOX fuel would be increased significantly. Source photon spectrum results showed the detectability of low-volatile high energy
Ce, to special nuclear material were evaluated by whole core inventory in unit 1, 2 and 3 cores as reference value for homogenized molten fuel material, and also as a function of burnup for specific fuel debris, considering the sensitivity of enrichment, specific power, water void fraction, cooling time, calculation tool accuracy and release ratio. The same indices could be applied to unit 3, while the uncertainty of specific fuel debris of separated MOX fuel would be increased significantly. Source photon spectrum results showed the detectability of low-volatile high energy  -rays emitted from
-rays emitted from  Eu at least in 20 years after the accident, that from Ce/
Eu at least in 20 years after the accident, that from Ce/ Pr in 10 years, and volatile
Pr in 10 years, and volatile  Cs and
Cs and  Cs at least in 20 years with 99% or more release ratio. Mass attenuation coefficients of fuel debris was evaluated to be insensitive to its compositions in high energy region. Leakage photon ratio was evaluated with variety of parameters and significant impact was confirmed with certain size of fuel debris, its correlation was summarized with respect to the photopeak ratio of source
Cs at least in 20 years with 99% or more release ratio. Mass attenuation coefficients of fuel debris was evaluated to be insensitive to its compositions in high energy region. Leakage photon ratio was evaluated with variety of parameters and significant impact was confirmed with certain size of fuel debris, its correlation was summarized with respect to the photopeak ratio of source  Eu. Finally, preliminary study with hypothetical canister model of fuel debris based on TMI-2 experience, and future plan were introduced.
Eu. Finally, preliminary study with hypothetical canister model of fuel debris based on TMI-2 experience, and future plan were introduced.
Ismailov, K.*; Nishihara, Kenji; Saito, Masaki*; Sagara, Hiroshi*
Annals of Nuclear Energy, 56, p.136 - 142, 2013/06
Times Cited Count:6 Percentile:44.02(Nuclear Science & Technology)The transmutation of iodine-129 in accelerator driven system (ADS) is studied. The sodium iodide assembly loadings inside the core of ADS and in the surrounding core region are considered. The introduced concept of ADS with a power of 800 MWt is able to transmute 250 kg/y of minor actinides (MAs) and 46 kg/y of Iodine-129 that supports ten PWRs. The initial loading masses of MAs and I-129 in ADS were equal to 3810 kg and 824 kg, respectively.