Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Namie, Masanari; Saito, Junichi
Computational Materials Science, 239, p.112963_1 - 112963_7, 2024/04
 Ga K-edge XANES study of Ga-exchanged zeolites at high temperatures under different atmospheres including vacuum, CO, and pressurized H
Ga K-edge XANES study of Ga-exchanged zeolites at high temperatures under different atmospheres including vacuum, CO, and pressurized H
Huang, M.*; Kinjo, Tetsuya*; Yasumura, Shunsaku*; Toyao, Takashi*; Matsumura, Daiju; Saito, Hiroyuki*; Shimizu, Kenichi*; Namiki, Norikazu*; Maeno, Zen*
Catalysis Science & Technology, 13(23), p.6832 - 6838, 2023/12
Times Cited Count:0 Percentile:0(Chemistry, Physical)Takagi, Hirotaka*; Takagi, Rina*; Minami, Susumu*; Nomoto, Takuya*; Oishi, Kazuki*; Suzuki, Michito*; Yanagi, Yuki*; Hirayama, Motoaki*; Khanh, N.*; Karube, Kosuke*; et al.
Nature Physics, 19(7), p.961 - 968, 2023/07
Times Cited Count:8 Percentile:96.03(Physics, Multidisciplinary)Sue, Yuki*; Yotsuzuka, Mai*; Futatsukawa, Kenta*; Hasegawa, Kazuo; Iijima, Toru*; Iinuma, Hiromi*; Inami, Kenji*; Ishida, Katsuhiko*; Kawamura, Naritoshi*; Kitamura, Ryo; et al.
Physical Review Accelerators and Beams (Internet), 23(2), p.022804_1 - 022804_7, 2020/02
Times Cited Count:2 Percentile:25.94(Physics, Nuclear)A destructive monitor to measure the longitudinal bunch width of a low-energy and low-intensity muon beam was developed. This bunch-width monitor (BWM) employed microchannel plates to detect a single muon with high time resolution. In addition, constant-fraction discriminators were adopted to suppress the time-walk effect. The time resolution was measured to be 65 ps in rms using a picosecond-pulsed laser. This resolution satisfied the requirements of the muon linac of the J-PARC E34 experiment. We measured the bunch width of negative-muonium ions accelerated with a radio-frequency quadrupole using the BWM. The bunch width was successfully measured to be  54
54  11 ns, which is consistent with the simulation.
11 ns, which is consistent with the simulation.
Otani, Masashi*; Fukao, Yoshinori*; Futatsukawa, Kenta*; Kawamura, Naritoshi*; Matoba, Shiro*; Mibe, Tsutomu*; Miyake, Yasuhiro*; Shimomura, Koichiro*; Yamazaki, Takayuki*; Hasegawa, Kazuo; et al.
Journal of Physics; Conference Series, 1350, p.012067_1 - 012067_6, 2019/12
Times Cited Count:2 Percentile:73.22(Physics, Particles & Fields)Negative muonium atom ( e
e e
e , Mu
, Mu ) has unique features stimulating potential interesting for several scientific fields. Since its discovery in late 1980's in vacuum, it has been discussed that the production efficiency would be improved using a low-work function material. C12A7 was a well-known insulator as a constituent of alumina cement, but was recently confirmed to exhibit electric conductivity by electron doping. The C12A7 electride has relatively low-work function (2.9 eV). In this paper, the negative muonium production measurement with several materials including a C12A7 electride film will be presented. Measured production rate of the Mu
) has unique features stimulating potential interesting for several scientific fields. Since its discovery in late 1980's in vacuum, it has been discussed that the production efficiency would be improved using a low-work function material. C12A7 was a well-known insulator as a constituent of alumina cement, but was recently confirmed to exhibit electric conductivity by electron doping. The C12A7 electride has relatively low-work function (2.9 eV). In this paper, the negative muonium production measurement with several materials including a C12A7 electride film will be presented. Measured production rate of the Mu were 10
were 10 /s for all the Al, electride, and SUS target. Significant enhancement on electride target was not observed, thus it is presumed that the surface condition should be more carefully treated. There was no material dependence of the Mu
/s for all the Al, electride, and SUS target. Significant enhancement on electride target was not observed, thus it is presumed that the surface condition should be more carefully treated. There was no material dependence of the Mu averaged energy: it was 0.2
averaged energy: it was 0.2 0.1keV.
0.1keV.
Sue, Yuki*; Iijima, Toru*; Inami, Kenji*; Yotsuzuka, Mai*; Iinuma, Hiromi*; Nakazawa, Yuga*; Otani, Masashi*; Kawamura, Naritoshi*; Shimomura, Koichiro*; Futatsukawa, Kenta*; et al.
Proceedings of 16th Annual Meeting of Particle Accelerator Society of Japan (Internet), p.55 - 60, 2019/07
The result of bunch size measurement of muon accelerated by RFQ up to 89 keV is presented in this paper. A four-stage muon linac for precise measurement of muon property is under construction in the J-PARC. The demonstration of the first muon RF acceleration with an RFQ linac was conducted and the transverse profile of the accelerated muons was measured in 2017. As one of the remaining issues for the beam diagnostic system, the longitudinal beam profile after the RFQ should be measured to match the profile to the designed acceptance of the subsequent accelerator. For this purpose, the new longitudinal beam monitor using the microchannel plate is under development. The time resolution of the monitor aims to be around 30 to 40 ps corresponding to 1% of a period of an operating frequency of the accelerator, which is 324 MHz. On November 2018, the bunch size of accelerated negative muonium ion of 89 keV with the RFQ was measured using this monitor at the J-PARC MLF. The measured bunch width is 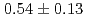 ns, which is consistent with the simulation.
ns, which is consistent with the simulation.
Yotsuzuka, Mai*; Iijima, Toru*; Iinuma, Hiromi*; Inami, Kenji*; Otani, Masashi*; Kawamura, Naritoshi*; Kitamura, Ryo; Kondo, Yasuhiro; Saito, Naohito; Shimomura, Koichiro*; et al.
Proceedings of 16th Annual Meeting of Particle Accelerator Society of Japan (Internet), p.814 - 817, 2019/07
The J-PARC E34 experiment aims to measure the muon anomalous magnetic moment and the electric dipole moment with a high precision. In this experiment, thermal muonium is produced and ionized by laser resonance to generate ultra-slow muons, which are then accelerated in a multistage muon linac. In order to satisfy the experimental requirements, suppression of the emittance growth during the acceleration is necessary. Because the main cause of the emittance growth is beam mismatching between the accelerating stages, the transverse and longitudinal beam monitoring is important. The longitudinal beam monitor has to measure the bunch length with the resolution equivalent to tens of picoseconds, which is 1% of the acceleration phase of 324 MHz. In addition, it should be sensitive to single muon because the beam intensity is limited during the commissioning phase. To realize above requirements, we are developing a longitudinal beam monitor with a micro channel plate, and the test bench to evaluate the monitor performance. So far, the time resolution of the beam monitor was obtained to be 65 ps in RMS including the jitter on the test bench. We also succeeded in measuring the longitudinal bunch size of the muon beam accelerated by RFQ using the beam monitor. In this paper, the results of the performance evaluation for this beam monitor are reported.
Yotsuzuka, Mai*; Iijima, Toru*; Inami, Kenji*; Sue, Yuki*; Iinuma, Hiromi*; Nakazawa, Yuga*; Saito, Naohito; Hasegawa, Kazuo; Kondo, Yasuhiro; Kitamura, Ryo; et al.
Proceedings of 10th International Particle Accelerator Conference (IPAC '19) (Internet), p.2571 - 2574, 2019/06
The J-PARC E34 experiment aims to measure the muon anomalous magnetic moment and the electric dipole moment with a high precision. In this experiment, thermal muonium is produced and ionized by laser resonance to generate ultra-slow muons, which are then accelerated in a multistage muon linac. In order to satisfy the experimental requirements, suppression of the emittance growth during the acceleration is necessary. Because the main cause of the emittance growth is beam mismatching between the accelerating stages, the transverse and longitudinal beam monitoring is important. The longitudinal beam monitor has to measure the bunch length with the resolution equivalent to tens of picoseconds, which is 1% of the acceleration phase of 324 MHz. In addition, it should be sensitive to single muon because the beam intensity is limited during the commissioning phase. To realize above requirements, we are developing a longitudinal beam monitor with a micro channel plate, and the test bench to evaluate the monitor performance. So far, the time resolution of the beam monitor was obtained to be 65 ps in RMS including the jitter on the test bench. We also succeeded in measuring the longitudinal bunch size of the muon beam accelerated by RFQ using the beam monitor. Further improvement of the measurement system is needed to guarantee the required accuracy. In this paper, the results of the performance evaluation for this beam monitor are reported.
Sue, Yuki*; Iijima, Toru*; Inami, Kenji*; Yotsuzuka, Mai*; Futatsukawa, Kenta*; Kawamura, Naritoshi*; Mibe, Tsutomu*; Miyake, Yasuhiro*; Otani, Masashi*; Hasegawa, Kazuo; et al.
Proceedings of 10th International Particle Accelerator Conference (IPAC '19) (Internet), p.37 - 40, 2019/06
The result of bunch size measurement of muon accelerated by RFQ up to 89 keV is presented in this paper. A four-stage muon linac for precise measurement of muon property is under construction in the J-PARC. The demonstration of the first muon RF acceleration with an RFQ linac was conducted and the transverse profile of the accelerated muons was measured in 2017. As one of the remaining issues for the beam diagnostic system, the longitudinal beam profile after the RFQ should be measured to match the profile to the designed acceptance of the subsequent accelerator. For this purpose, the new longitudinal beam monitor using the microchannel plate is under development. The time resolution of the monitor aims to be around 30 to 40 ps corresponding to 1% of a period of an operating frequency of the accelerator, which is 324 MHz. On November 2018, the bunch size of accelerated negative muonium ion of 89 keV with the RFQ was measured using this monitor at the J-PARC MLF. The measured bunch width is 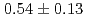 ns, which is consistent with the simulation.
ns, which is consistent with the simulation.
 VFeAsO
VFeAsO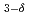 studied by X-ray magnetic circular dichroism
studied by X-ray magnetic circular dichroismHorio, Masafumi*; Takeda, Yukiharu; Namiki, Hiromasa*; Katagiri, Takao*; Wakabayashi, Yuki*; Sakamoto, Shoya*; Nonaka, Yosuke*; Shibata, Goro*; Ikeda, Keisuke*; Saito, Yuji; et al.
Journal of the Physical Society of Japan, 87(10), p.105001_1 - 105001_2, 2018/10
Times Cited Count:2 Percentile:21.2(Physics, Multidisciplinary)Sakamoto, Hiroyuki*; Akagi, Yosuke*; Yamada, Kazuo*; Tachi, Yukio; Fukuda, Daisuke*; Ishimatsu, Koichi*; Matsuda, Mikiya*; Saito, Nozomi*; Uemura, Jitsuya*; Namihira, Takao*; et al.
Nihon Genshiryoku Gakkai Wabun Rombunshi, 17(2), p.57 - 66, 2018/05
Concrete debris contaminated with radioactive cesium and other nuclides have been generated from the accident in the Fukushima Dai-ichi Nuclear Power Plant and there will be generated due to the decommissioning of nuclear power plants in the future. Although conventional decontamination techniques are effective for flat concrete surfaces such as floors and walls, it is not clear what techniques to apply for decontaminating radioactive concrete debris. In this study, focusing on a pulsed power discharge technique, fundamental experimental works were carried out. Decontamination of concrete by applying the aggregate recycling technique using the pulsed power discharge technique was evaluated by measuring radioactivity of aggregate and sludge separated from the contaminated concrete. The results suggest that the separation into aggregate and sludge of the contaminated concrete debris could achieve decontamination and volume reduction of the radioactive concrete debris.
 and their Zr-O surface modified electrodes
and their Zr-O surface modified electrodesAbe, Machiko*; Iba, Hideki*; Suzuki, Kota*; Minamishima, Hiroaki*; Hirayama, Masaaki*; Tamura, Kazuhisa; Mizuki, Junichiro*; Saito, Tomohiro*; Ikuhara, Yuichi*; Kanno, Ryoji*
Journal of Power Sources, 345, p.108 - 119, 2017/03
Times Cited Count:11 Percentile:38.74(Chemistry, Physical)The surface structure of the Li(Ni, Co, Mn)O electrode was studied during charge/discharge process using electrochemical methods and X-ray/Neutron scattering techniques. It was found that during charge/discharge process the coverage of spinel structure increased. The spinel structure has low electrochemical activity and is not involved in Li insertion/extraction. After the surface modification, it was found that the coverage of the spinel structure did not increase. Further, it was also found out that the Li concentration at the electrode/electrolyte interface increased.
electrode was studied during charge/discharge process using electrochemical methods and X-ray/Neutron scattering techniques. It was found that during charge/discharge process the coverage of spinel structure increased. The spinel structure has low electrochemical activity and is not involved in Li insertion/extraction. After the surface modification, it was found that the coverage of the spinel structure did not increase. Further, it was also found out that the Li concentration at the electrode/electrolyte interface increased.
Shimada, Hiroyuki*; Minami, Hirotake*; Okuizumi, Naoto*; Sakuma, Ichiro*; Ukai, Masatoshi*; Fujii, Kentaro; Yokoya, Akinari; Fukuda, Yoshihiro*; Saito, Yuji
Journal of Chemical Physics, 142(17), p.175102_1 - 175102_9, 2015/05
Times Cited Count:10 Percentile:38.6(Chemistry, Physical)Shimada, Hiroyuki*; Fukao, Taishi*; Minami, Hirotake*; Ukai, Masatoshi*; Fujii, Kentaro; Yokoya, Akinari; Fukuda, Yoshihiro*; Saito, Yuji
Journal of Chemical Physics, 141(5), p.055102_1 - 055102_8, 2014/08
Times Cited Count:16 Percentile:53.96(Chemistry, Physical)Ozeki, Hidemasa; Hamada, Kazuya; Takahashi, Yoshikazu; Nunoya, Yoshihiko; Kawano, Katsumi; Oshikiri, Masayuki; Saito, Toru; Teshima, Osamu*; Matsunami, Masahiro*
IEEE Transactions on Applied Superconductivity, 24(3), p.4800604_1 - 4800604_4, 2014/06
Times Cited Count:16 Percentile:62.24(Engineering, Electrical & Electronic)Shimada, Hiroyuki*; Fukao, Taishi*; Minami, Hirotake*; Ukai, Masatoshi*; Fujii, Kentaro; Yokoya, Akinari; Fukuda, Yoshihiro*; Saito, Yuji
Chemical Physics Letters, 591, p.137 - 141, 2014/01
Times Cited Count:9 Percentile:33.36(Chemistry, Physical)Tsuda, Shuichi; Sato, Tatsuhiko; Satoh, Daiki; Takahashi, Fumiaki; Sasaki, Shinichi*; Namito, Yoshihito*; Sanami, Toshiya*; Saito, Kiwamu*; Takada, Masashi*
HIMAC-136, p.219 - 220, 2011/11
Measurements of lineal energy distribution were employed using 160 MeV proton and 490 MeV/u Si. The calculated 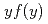 by PHITS and
by PHITS and 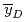 agree fairly well with those measured. The LET dependence of
agree fairly well with those measured. The LET dependence of 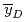 was obtained from 3 to 300 keV/um in this project.
was obtained from 3 to 300 keV/um in this project.
Tsuda, Shuichi; Sato, Tatsuhiko; Satoh, Daiki; Takahashi, Fumiaki; Endo, Akira; Sasaki, Shinichi*; Namito, Yoshihito*; Sanami, Toshiya*; Saito, Kiwamu*; Takada, Masashi*
HIMAC-134 (CD-ROM), p.227 - 228, 2010/06
no abstracts in English
Tsuda, Shuichi; Sato, Tatsuhiko; Satoh, Daiki; Takahashi, Fumiaki; Endo, Akira; Sasaki, Shinichi*; Namito, Yoshihito*; Sanami, Toshiya*; Saito, Kiwamu*; Takada, Masashi*
NIRS-M-226, HIMAC-132, p.264 - 265, 2009/06
A wall-less tissue equivalent proportional counter was designed and applied to measuring deposit energy distribution of heavy ion beams, including the contribution of delta-rays produced along heavy ion tracks. Lineal energy distributions were obtained for 400 MeV/u carbon and 490 MeV/u silicon beams.
Ito, Kenji*; Oka, Toshitaka*; Kobayashi, Yoshinori*; Shirai, Yasuharu*; Wada, Kenichiro*; Matsumoto, Masataka*; Fujinami, Masanori*; Hirade, Tetsuya; Honda, Yoshihide*; Hosomi, Hiroyuki*; et al.
Materials Science Forum, 607, p.248 - 250, 2009/00
So far no standard procedure for the positron annihilation lifetime (PAL) technique has been established. A lack of the standards has led to difficulty in ensuring the equivalency and reliability of data from different laboratories. As a first, we conducted an interlaboratory comparison of PAL measurements for metal, polymer and silica glass with agreed procedures for data recording and analysis. The PAL data recorded at different laboratories were analyzed with a single lifetime component for the metal sample and with three components for the others, respectively. Based on the results of the reported positron and ortho-positronium lifetimes, the possible sources of the uncertainties in the PAL measurements are discussed. To reduce the effect of scattered  rays, a lead shield was placed between the detectors. The uncertainty was significantly decreased, signifying that placing lead shields between the detectors effectively reduced the false signals due to the scattered
rays, a lead shield was placed between the detectors. The uncertainty was significantly decreased, signifying that placing lead shields between the detectors effectively reduced the false signals due to the scattered  rays.
rays.