Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
 F from
F from  O
O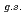 ?
?Tang, T. L.*; Uesaka, Tomohiro*; Kawase, Shoichiro; Beaumel, D.*; Dozono, Masanori*; Fujii, Toshihiko*; Fukuda, Naoki*; Fukunaga, Taku*; Galindo-Uribarri, A.*; Hwang, S. H.*; et al.
Physical Review Letters, 124(21), p.212502_1 - 212502_6, 2020/05
Times Cited Count:14 Percentile:74.18(Physics, Multidisciplinary)The structure of a neutron-rich  F nucleus is investigated by a quasifree (
F nucleus is investigated by a quasifree ( ) knockout reaction. The sum of spectroscopic factors of
) knockout reaction. The sum of spectroscopic factors of 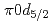 orbital is found to be 1.0
orbital is found to be 1.0  0.3. The result shows that the
0.3. The result shows that the  O core of
O core of  F nucleus significantly differs from a free
F nucleus significantly differs from a free  O nucleus, and the core consists of
O nucleus, and the core consists of  35%
35%  O
O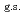 , and
, and  65% excited
65% excited  O. The result shows that the
O. The result shows that the  O core of
O core of  F nucleus significantly differs from a free
F nucleus significantly differs from a free  O nucleus. The result may infer that the addition of the
O nucleus. The result may infer that the addition of the  proton considerably changes the neutron structure in
proton considerably changes the neutron structure in  F from that in
F from that in  O, which could be a possible mechanism responsible for the oxygen dripline anomaly.
O, which could be a possible mechanism responsible for the oxygen dripline anomaly.
Okajima, Satoshi*; Honda, Kei*; Sakai, Shinsuke*; Izumi, Satoshi*; Oishi, Kunio*; Kasahara, Naoto
Nihon Kikai Gakkai M&M 2007 Zairyo Rikigaku Kanfarensu Koen Rombunshu (CD-ROM), p.262 - 263, 2007/10
It is well known that fatigue damage accumulates around T-junctions of piping system where two kinds of fluid with different temperatures are mixed. Kasahara et al. have proposed the thermal fatigue evaluation method based on power spectrum density (PSD). However, this method is too complex to practical use in the design stage. In this paper, a simplified damage evaluation guideline is proposed based on the Kasahara et al. method. The damage evaluation procedure from stress PSD is simplified in this guideline.
Kasahara, Naoto; Kawasaki, Nobuchika; Kamide, Hideki; Sakai, Shinsuke*; Okajima, Satoshi*
Proceedings of International Symposium on Research for Aging Management of Light Water Reactors and Its Future Trend, p.23_1 - 23_16, 2007/10
Fluid temperature fluctuates at an incomplete mixing area of high and low temperature fluids in nuclear components. It induces random variations of local temperature gradients in structural walls, which lead to cyclic thermal stresses. When thermal stresses and cycle numbers are large, there are possibilities of fatigue crack initiations and propagations. It is recognized that there are attenuation factors depending on fluctuation frequency in the transfer process from fluid temperature to thermal stresses. Considering above fluid-structure interaction against fluid temperature fluctuation, authors has proposed a fatigue evaluation method related to frequencies. JAEA has the plan to develop thermal load modeling guidelines, which has consistency with JSME guidelines for light water reactors.
Sakai, Shinsuke*; Honda, Kei*; Okajima, Satoshi*; Izumi, Satoshi*; Kasahara, Naoto
Proceedings of 2007 ASME Pressure Vessels and Piping Division Conference/8th International Conference on Creep and Fatigue at Elevated Temperatures (PVP 2007/CREEP-8) (CD-ROM), 7 Pages, 2007/07
At an incomplete mixing area of high and low temperature fluids, fluid temperature fluctuation often occurs. It induces cyclic thermal stresses in the wall, which may result in fatigue crack initiation. Kasahara et al. proposed the thermal fatigue evaluation method based on power spectrum density (PSD). This method generalizes the evaluation procedure by preparing PSD charts of fluid and frequency transfer functions of stress for various kinds of plant components. From design point of view, however, this method is too complicated due to the inverse Fourier transform and wave decomposition procedures named Rain Flow Cycle Counting (RFC). In this paper, simplified damage evaluation method for thermal fatigue is proposed by directly evaluating fatigue damage from PSD of stress.
Okajima, Satoshi*; Sakai, Shinsuke*; Izumi, Satoshi*; Kasahara, Naoto
Nihon Zairyo Gakkai Dai-21-Kai Zairyo, Kozo Shinraisei Shimpojiumu Koen Rombunshu, p.132 - 137, 2005/12
no abstracts in English
Okajima, Satoshi*; Sakai, Shinsuke*; Izumi, Satoshi*; Kasahara, Naoto
no journal, ,
no abstracts in English
Honda, Kei*; Sakai, Shinsuke*; Izumi, Satoshi*; Okajima, Satoshi*; Kasahara, Naoto
no journal, ,
no abstracts in English