Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Tamura, Jun; Kondo, Yasuhiro; Yee-Rendon, B.; Meigo, Shinichiro; Maekawa, Fujio; Kako, Eiji*; Umemori, Kensei*; Sakai, Hiroshi*; Domae, Takeshi*
Proceedings of 32nd Linear Accelerator Conference (LINAC 2024) (Internet), p.496 - 498, 2024/10
Tamura, Jun; Kondo, Yasuhiro; Yee-Rendon, B.; Meigo, Shinichiro; Maekawa, Fujio; Kako, Eiji*; Umemori, Kensei*; Sakai, Hiroshi*; Domae, Takeshi*
Journal of Physics; Conference Series, 2687(5), p.052008_1 - 052008_6, 2024/01
Times Cited Count:0 Percentile:0.00(Physics, Atomic, Molecular & Chemical)Kondo, Yasuhiro; Tamura, Jun; Yee-Rendon, B.; Meigo, Shinichiro; Maekawa, Fujio; Kako, Eiji*; Umemori, Kensei*; Sakai, Hiroshi*; Domae, Takeshi*
Proceedings of 21st International Conference on Radio-Frequency Superconductivity (SRF 2023), p.947 - 951, 2023/07
Japan Atomic Energy Agency (JAEA) has been proposing an accelerator-driven system (ADS) as a future nuclear system to efficiently reduce the high-level radioactive waste generated at nuclear power plants. As the first step toward the full-scale CW proton linac for the JAEA-ADS, we are now prototyping a low-beta (around 0.2) single-spoke cavity. Because there is no experience in manufacturing super-conducting spoke cavities in Japan, prototyping and performance testing of the cavity are essential to ensure the feasibility of the JAEA-ADS. The dimensional parameters of the prototype spoke cavity were optimized to obtain higher cavity performance. The actual cavity fabrication started in 2020. Most of the cavity parts were fabricated in fiscal year 2020 by press-forming and machining. In 2021, we started welding the cavity parts together. After investigating the optimum welding conditions using mock-up test pieces, each cavity part was joined with smooth welding beads. Currently, the cavity's body section and the beam port sections have been assembled. This paper presents the current status of the JAEA-ADS and it's cavity prototyping.
Yamashita, Takuya; Honda, Takeshi*; Mizokami, Masato*; Nozaki, Kenichiro*; Suzuki, Hiroyuki*; Pellegrini, M.*; Sakai, Takeshi*; Sato, Ikken; Mizokami, Shinya*
Nuclear Technology, 209(6), p.902 - 927, 2023/06
Times Cited Count:5 Percentile:80.64(Nuclear Science & Technology)Tamura, Jun; Kondo, Yasuhiro; Yee-Rendon, B.; Meigo, Shinichiro; Maekawa, Fujio; Kako, Eiji*; Umemori, Kensei*; Sakai, Hiroshi*; Domae, Takeshi*
Proceedings of 31st International Linear Accelerator Conference (LINAC 2022) (Internet), p.180 - 183, 2022/09
The Japan Atomic Energy Agency (JAEA) has proposed an accelerator-driven subcritical system (ADS) to efficiently reduce high-level radioactive waste generated at nuclear power plants. One of the challenging R&D aspects of ADS is the reliability of the accelerator. In preparation for the full-scale design of the CW proton linac for the JAEA-ADS, we are now prototyping a low-beta (around 0.2) single spoke cavity. Since there is no experience in Japan in manufacturing a superconducting spoke cavity, prototyping and performance testing of the cavity is essential to ensure the feasibility of the JAEA-ADS linac. In the Japanese fiscal year 2021, we have started welding cavity parts together. By preliminarily examining the electron beam welding conditions, each press-formed niobium part was joined with a smooth welding bead. At present, we have fabricated the cavity's body part.
Kondo, Yasuhiro; Harada, Hiroyuki; Kabumoto, Hiroshi; Kamiya, Junichiro; Matsuda, Makoto; Moriya, Katsuhiro; Tamura, Jun; Kako, Eiji*; Domae, Takeshi*; Sakai, Hiroshi*; et al.
Proceedings of 20th International Conference on RF Superconductivity (SRF 2021) (Internet), p.299 - 302, 2021/10
The Japan Atomic Energy Agency (JAEA) tandem booster is one of the pioneering superconducting heavy ion linac in the world. It consists of 40 QWRs with an operation frequency of 130 MHz and 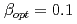 , and has potential to accelerate various ions up to Au to 10 MeV/u. The user operation was started in 1994, however, it has been suspended since the Great East Japan Earthquake in 2011. Recently, in addition to the efforts to restart the tandem booster, activities to develop new lower-beta cavities to improve the acceleration efficiency of heavier ions such as Uranium has been launched. In this work, the current status of the design study of the QWRS for the JAEA tandem facility is presented. Electro-magnetic design using simulation code was performed and acceleration gradient of 5.7 MV/m and 6.6 MV/m was obtained for 130-MHz and 65-MHz QWRs, respectively.
, and has potential to accelerate various ions up to Au to 10 MeV/u. The user operation was started in 1994, however, it has been suspended since the Great East Japan Earthquake in 2011. Recently, in addition to the efforts to restart the tandem booster, activities to develop new lower-beta cavities to improve the acceleration efficiency of heavier ions such as Uranium has been launched. In this work, the current status of the design study of the QWRS for the JAEA tandem facility is presented. Electro-magnetic design using simulation code was performed and acceleration gradient of 5.7 MV/m and 6.6 MV/m was obtained for 130-MHz and 65-MHz QWRs, respectively.
Tamura, Jun; Kondo, Yasuhiro; Maekawa, Fujio; Meigo, Shinichiro; Yee-Rendon, B.; Domae, Takeshi*; Kako, Eiji*; Sakai, Hiroshi*; Umemori, Kensei*
Proceedings of 20th International Conference on RF Superconductivity (SRF 2021) (Internet), p.612 - 615, 2021/06
Sakai, Kenji; Oi, Motoki; Haga, Katsuhiro; Kai, Tetsuya; Nakatani, Takeshi; Kobayashi, Yasuo*; Watanabe, Akihiko*
JPS Conference Proceedings (Internet), 33, p.011151_1 - 011151_6, 2021/03
For safely and efficiently operating a spallation neutron source and a muon target, a general control system (GCS) operates within Materials and Life Science Experimental Facility (MLF), GCS administers operation processes and interlocks of many instruments for various operation statuses. It consists of several subsystems such as an integral control system (ICS), interlock systems (ILS), shared servers, network system, and timing distribution system (TDS). Although GCS is an independent system that controls the target stations, it works closely with the control systems of other facilities in J-PARC. Since the first beam injection in 2008, GCS has operated stably without any serious troubles after modification based on commissioning for operation and control. Then, significant improvements in GCS such as upgrade of ICS by changing its framework software and function enhancement of ILS were proceeded until 2015, in considering sustainable long-term operation and maintenance. In recent years, many instruments in GCS have replaced due to end of production and support of them. In this way, many modifications have been proceeded in the entire GCS after start of beam operation. Under these situation, it is important to comprehend upgrade history and present status of GCS in order to decide its upgrade plan for the coming ten years. This report will mention upgrade history, present status and future agenda of GCS.
Yamashita, Takuya; Sato, Ikken; Honda, Takeshi*; Nozaki, Kenichiro*; Suzuki, Hiroyuki*; Pellegrini, M.*; Sakai, Takeshi*; Mizokami, Shinya*
Nuclear Technology, 206(10), p.1517 - 1537, 2020/10
Times Cited Count:22 Percentile:91.04(Nuclear Science & Technology)Wada, Yuki*; Enoto, Teruaki*; Nakamura, Yoshitaka*; Morimoto, Takeshi*; Sato, Mitsuteru*; Ushio, Tomoo*; Nakazawa, Kazuhiro*; Yuasa, Takayuki*; Yonetoku, Daisuke*; Sawano, Tatsuya*; et al.
Journal of Geophysical Research; Atmospheres, 125(4), p.e2019JD031730_1 - e2019JD031730_11, 2020/02
Times Cited Count:28 Percentile:78.32(Meteorology & Atmospheric Sciences)Wada, Yuki*; Enoto, Teruaki*; Nakamura, Yoshitaka*; Furuta, Yoshihiro; Yuasa, Takayuki*; Nakazawa, Kazuhiro*; Morimoto, Takeshi*; Sato, Mitsuteru*; Matsumoto, Takahiro*; Yonetoku, Daisuke*; et al.
Communications Physics (Internet), 2(1), p.67_1 - 67_9, 2019/06
Times Cited Count:58 Percentile:92.61(Physics, Multidisciplinary)Sakai, Kenji; Oi, Motoki; Takada, Hiroshi; Kai, Tetsuya; Nakatani, Takeshi; Kobayashi, Yasuo*; Watanabe, Akihiko*
JAEA-Technology 2018-011, 57 Pages, 2019/01
For safely and efficiently operating a spallation neutron source and a muon target, a general control system (GCS) operates within Materials and Life Science Experimental Facility (MLF). GCS administers operation processes and interlocks of many instruments. It consists of several subsystems such as an integral control system (ICS), interlock systems (ILS), shared servers, network system, and timing distribution system (TDS). Although GCS is an independent system that controls the target stations, it works closely with the control systems of the accelerators and other facilities in J-PARC. Since the first beam injection, GCS has operated stably without any serious troubles after modification based on commissioning for operation and control. Then, significant improvements in GCS such as upgrade of ICS by changing its framework software and function enhancement of ILS were proceeded until 2015. In this way, many modifications have been proceeded in the entire GCS during a period of approximately ten years after start of beam operation. Under these situation, it is important to comprehend upgrade history and present status of GCS in order to decide its upgrade plan. This report summarizes outline, structure, roles and functions of GCS in 2017.
 Fe and
Fe and  Co nuclear magnetic resonance studies
Co nuclear magnetic resonance studiesSakai, Hironori; Hattori, Taisuke; Tokunaga, Yo; Kambe, Shinsaku; Ueda, Hiroaki*; Tanioku, Yasuaki*; Michioka, Chishiro*; Yoshimura, Kazuyoshi*; Takao, Kenta*; Shimoda, Aiko*; et al.
Physical Review B, 98(6), p.064403_1 - 064403_10, 2018/08
Times Cited Count:15 Percentile:54.26(Materials Science, Multidisciplinary)To specify preferential occupation sites of Co substituents and to clarify charge and spin states of Co ions in (La, Co)-cosubstituted hexagonal magnetoplumbite-type (M-type) Sr ferrite,  Fe and
Fe and  Co nuclear magnetic resonance (NMR) spectra are measured under zero and external magnetic fields using powdered and single crystalline specimens. To a considerable degree, the charge compensation between La
Co nuclear magnetic resonance (NMR) spectra are measured under zero and external magnetic fields using powdered and single crystalline specimens. To a considerable degree, the charge compensation between La and Co
and Co works in the equal (La, Co)-codoped case, where more than half of the Co ions are considered to be present in the minority spin
works in the equal (La, Co)-codoped case, where more than half of the Co ions are considered to be present in the minority spin 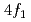 sites at the center of the oxygen tetrahedra, with the
sites at the center of the oxygen tetrahedra, with the  = 3/2 state carrying a small orbital moment owing to spin-orbit interaction. The remaining small number of high-spin Co
= 3/2 state carrying a small orbital moment owing to spin-orbit interaction. The remaining small number of high-spin Co (
( = 3/2,
= 3/2,  = 1) ions with unquenched orbital moments would be distributed to the other octahedral
= 1) ions with unquenched orbital moments would be distributed to the other octahedral 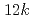 ,
, 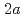 , and
, and 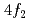 sites.
sites.
Sakasai, Kaoru; Sato, Setsuo*; Seya, Tomohiro*; Nakamura, Tatsuya; To, Kentaro; Yamagishi, Hideshi*; Soyama, Kazuhiko; Yamazaki, Dai; Maruyama, Ryuji; Oku, Takayuki; et al.
Quantum Beam Science (Internet), 1(2), p.10_1 - 10_35, 2017/09
Neutron devices such as neutron detectors, optical devices including supermirror devices and  He neutron spin filters, and choppers are successfully developed and installed at the Materials Life Science Facility (MLF) of the Japan Proton Accelerator Research Complex (J-PARC), Tokai, Japan. Four software components of MLF computational environment, instrument control, data acquisition, data analysis, and a database, have been developed and equipped at MLF. MLF also provides a wide variety of sample environment options including high and low temperatures, high magnetic fields, and high pressures. This paper describes the current status of neutron devices, computational and sample environments at MLF.
He neutron spin filters, and choppers are successfully developed and installed at the Materials Life Science Facility (MLF) of the Japan Proton Accelerator Research Complex (J-PARC), Tokai, Japan. Four software components of MLF computational environment, instrument control, data acquisition, data analysis, and a database, have been developed and equipped at MLF. MLF also provides a wide variety of sample environment options including high and low temperatures, high magnetic fields, and high pressures. This paper describes the current status of neutron devices, computational and sample environments at MLF.
 -bearing Mg-perovskite and its crystal chemistry at high pressure
-bearing Mg-perovskite and its crystal chemistry at high pressureMashimo, Izumi*; Otani, Eiji*; Hirao, Naohisa*; Mitsui, Takaya; Masuda, Ryo*; Seto, Makoto*; Sakai, Takeshi*; Takahashi, Suguru*; Nakano, Satoshi*
American Mineralogist, 99(8-9), p.1555 - 1561, 2014/08
Times Cited Count:7 Percentile:22.25(Geochemistry & Geophysics)Sakai, Kenji; Kai, Tetsuya; Oi, Motoki; Watanabe, Akihiko; Nakatani, Takeshi; Higemoto, Wataru; Meigo, Shinichiro; Sakamoto, Shinichi; Takada, Hiroshi; Futakawa, Masatoshi
Progress in Nuclear Science and Technology (Internet), 4, p.264 - 267, 2014/04
no abstracts in English
 -Co compound/Ni bilayer structure
-Co compound/Ni bilayer structureMatsumoto, Yoshihiro; Sakai, Seiji; Entani, Shiro; Takagi, Yasumasa*; Nakagawa, Takeshi*; Naramoto, Hiroshi*; Avramov, P.; Yokoyama, Toshihiko*
Chemical Physics Letters, 511(1-3), p.68 - 72, 2011/07
Times Cited Count:5 Percentile:15.54(Chemistry, Physical)X-ray magnetic circular dichroism (XMCD) spectroscopy was employed to investigate the electronic and magnetic structures of the bilayers of a C -Co compound and Ni. A few -several nm thick C
-Co compound and Ni. A few -several nm thick C -Co compound layers on the Ni(111) surface are found to show intense XMCD signals attributed to the localized Co d-spins only with the remanent magnetization of Ni layer. It is suggested that the region of the C
-Co compound layers on the Ni(111) surface are found to show intense XMCD signals attributed to the localized Co d-spins only with the remanent magnetization of Ni layer. It is suggested that the region of the C -Co compound within 3 nm from the interface is ferromagnetically coupled with Ni due to the indirect exchange interaction mediated by C
-Co compound within 3 nm from the interface is ferromagnetically coupled with Ni due to the indirect exchange interaction mediated by C , probably relevant to the interlayer charge transfer.
, probably relevant to the interlayer charge transfer.
Tanaka, Momoko; Nakazato, Tomoharu*; Shimizu, Toshihiko*; Yamanoi, Kohei*; Sakai, Kohei*; Sarukura, Nobuhiko*; Nishikino, Masaharu; Oba, Toshiyuki; Kaihori, Takeshi; Ochi, Yoshihiro; et al.
JAEA-Conf 2011-001, p.126 - 128, 2011/03
The spatial resolution of hydrothermal method grown zinc oxide (ZnO) scintillator was evaluated using X-ray laser focused with Fresnel zone plate. The fluorescence image of the ZnO scintillator was measured to be less than 10um using CCD camera coupled with a Schbartzchild expander mirror. The availability of large size ZnO crystal up to 3-inch is quite attractive for future lithography and imaging applications.
Umemori, Kensei*; Furuya, Takaaki*; Sakai, Hiroshi*; Takahashi, Takeshi*; Shinoe, Kenji*; Sawamura, Masaru
Proceedings of 25th International Linear Accelerator Conference (LINAC 2010) (CD-ROM), p.404 - 406, 2010/09
In order to obtain technology needed for construction of the ERL main linac cryomodule, several developments have been performed. A prototype of 9-cell superconducting cavity was fabricated. Its performance was confirmed through vertical tests. Prototypes of coupler components were also fabricated and tested at the high power test stand. They could successfully pass the specified RF power. A prototype of HOM absorber without ferrite was made. It is under cooling tests. Design work of cryomodule is in progress.
Sakai, Hiroshi*; Umemori, Kensei*; Takahashi, Takeshi*; Furuya, Takaaki*; Shinoe, Kenji*; Ishii, Atsushi*; Sawamura, Masaru; Muto, Toshiya*
Proceedings of 7th Annual Meeting of Particle Accelerator Society of Japan (DVD-ROM), p.173 - 176, 2010/08
We are developing the superconducting (SC) cavity for Energy Recovery Linac (ERL) in Japan. In order to survey the electron emission and the heating spot of the cavity inner surface in detail, cavity diagnostics with the rotating mapping system was applied. Two types of sensors, one of which was the carbon resistor and the other was the Si PIN photo diode, were set to detect the temperature rise and electron emission. By rotating the sensor arrays around the cavity axis, a lot of information was obtained all over the cavity surface in detail. This paper reports the results of vertical tests by using this rotating mapping system with the single-cell and 9-cell Nb ERL cavity.