Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Urano, Hajime; Saibene, G.*; Oyama, Naoyuki; Parail, V.*; de Vries, P.*; Sartori, R.*; Kamada, Yutaka; Kamiya, Kensaku; Loarte, A.*; L nnroth, J.*; et al.
nnroth, J.*; et al.
Nuclear Fusion, 51(11), p.113004_1 - 113004_10, 2011/11
Times Cited Count:10 Percentile:41.01(Physics, Fluids & Plasmas)The effect of TF ripple on the edge pedestal characteristics are examined in JET and JT-60U. By the installation of ferritic inserts, TF ripple was reduced from 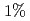 to
to 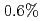 in JT-60U. In JET, TF ripple was varied from
in JT-60U. In JET, TF ripple was varied from 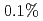 to
to 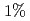 by feeding different currents to TF coils. The pedestal pressure was similar with reduced ripple in JT-60U. In JET, no clear difference of the pedestal characteristics was also observed. The edge toroidal rotation clearly decreased in counter direction by increased TF ripple. However, in JT-60U, the ELM frequency decreased by
by feeding different currents to TF coils. The pedestal pressure was similar with reduced ripple in JT-60U. In JET, no clear difference of the pedestal characteristics was also observed. The edge toroidal rotation clearly decreased in counter direction by increased TF ripple. However, in JT-60U, the ELM frequency decreased by 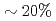 and the increased ELM loss power by
and the increased ELM loss power by 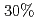 with reduced ripple. In JET, ELM frequency increases only slightly with increased TF ripple. From this inter-machine experiment, TF ripple less than
with reduced ripple. In JET, ELM frequency increases only slightly with increased TF ripple. From this inter-machine experiment, TF ripple less than 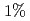 does not strongly affect the pedestal pressure. The effect of TF ripple on pedestal characteristics at lower collisionality close to ITER should be investigated as a next step study.
does not strongly affect the pedestal pressure. The effect of TF ripple on pedestal characteristics at lower collisionality close to ITER should be investigated as a next step study.
Sips, A. C. C.*; Casper, T.*; Doyle, E. J.*; Giruzzi, G.*; Gribov, Y.*; Hobirk, J.*; Hogeweij, G. M. D.*; Horton, L. D.*; Hubbard, A. E.*; Hutchinson, I.*; et al.
Nuclear Fusion, 49(8), p.085015_1 - 085015_11, 2009/08
Times Cited Count:53 Percentile:87.31(Physics, Fluids & Plasmas)Key parts of the ITER scenarios are determined by the capability of the proposed poloidal field (PF) coil set. They include the plasma breakdown at low loop voltage, the current rise phase, the performance during the flat top (FT) phase and a ramp down of the plasma. The ITER discharge evolution has been verified in dedicated experiments. New data are obtained from C-Mod, ASDEX Upgrade, DIII-D, JT-60U and JET. Results show that breakdown for 
 0.23-0.33 V m
0.23-0.33 V m is possible unassisted (ohmic) for large devices like JET and attainable in devices with a capability of using ECRH assist. For the current ramp up, good control of the plasma inductance is obtained using a full bore plasma shape with early X-point formation. This allows optimization of the flux usage from the PF set. Additional heating keeps
is possible unassisted (ohmic) for large devices like JET and attainable in devices with a capability of using ECRH assist. For the current ramp up, good control of the plasma inductance is obtained using a full bore plasma shape with early X-point formation. This allows optimization of the flux usage from the PF set. Additional heating keeps 
 (3)
(3)  0.85 during the ramp up to
0.85 during the ramp up to 
 = 3. A rise phase with an H-mode transition is capable of achieving
= 3. A rise phase with an H-mode transition is capable of achieving 
 (3)
(3)  0.7 at the start of the FT. Operation of the H-mode reference scenario at
0.7 at the start of the FT. Operation of the H-mode reference scenario at 

 3 and the hybrid scenario at
3 and the hybrid scenario at 
 = 4-4.5 during the FT phase is documented, providing data for the
= 4-4.5 during the FT phase is documented, providing data for the 
 (3) evolution after the H-mode transition and the
(3) evolution after the H-mode transition and the 
 (3) evolution after a back-transition to L-mode. During the ITER ramp down it is important to remain diverted and to reduce the elongation. The inductance could be kept
(3) evolution after a back-transition to L-mode. During the ITER ramp down it is important to remain diverted and to reduce the elongation. The inductance could be kept  1.2 during the first half of the current decay, using a slow
1.2 during the first half of the current decay, using a slow 
 ramp down, but still consuming flux from the transformer. Alternatively, the discharges can be kept in H-mode during most of the ramp down, requiring significant amounts of additional heating.
ramp down, but still consuming flux from the transformer. Alternatively, the discharges can be kept in H-mode during most of the ramp down, requiring significant amounts of additional heating.
Jacquinot, J.*; Albajar, F.*; Beaumont, B.*; Becoulet, A.*; Bonicelli, T.*; Bora, D.*; Campbell, D.*; Chakraborty, A.*; Darbos, C.*; Decamps, H.*; et al.
Fusion Engineering and Design, 84(2-6), p.125 - 130, 2009/06
Times Cited Count:24 Percentile:82.29(Nuclear Science & Technology)The electron cyclotron (EC), ion cyclotron (IC), neutral beam (NB) and, lower hybrid (LH) systems for ITER have been reviewed in 2007/2008 in light of progress of physics and technology. Although the overall specifications are unchanged, notable changes have been approved. Firstly, the full 73MW should be commissioned and available on a routine basis before the D/T phase. Secondly, the possibility to operate the NB at full power during the hydrogen phase requiring new shine through protection; IC with 2 antennas with increased robustness; 2 MW transmission systems to provide an easier upgrading of the EC power; the addition of a building dedicated to the RF power sources and to a testing facility for acceptance of diagnostics and heating port plugs. Thirdly, the need of a plan for developing, in time for the active phase, a CD system such as LH suitable for very long pulse operation of ITER was recognized.
Kurihara, Kenichi; Lister, J. B.*; Humphreys, D. A.*; Ferron, J. R.*; Treutterer, W.*; Sartori, F.*; Felton, R.*; Br mond, S.*; Moreau, P.*; JET-EFDA Contributors*
mond, S.*; Moreau, P.*; JET-EFDA Contributors*
Fusion Engineering and Design, 83(7-9), p.959 - 970, 2008/12
Times Cited Count:25 Percentile:81.47(Nuclear Science & Technology)The existing large and medium-size tokamaks are expected to explore more advanced operation scenarios toward the ITER and a future power reactor. To specify one or more solutions to keep a steady-state plasma with high performance, and to avoid plasma instabilities almost completely, a plasma control system for ITER should have two important aspects: Technical inheritance of the currently-working functions, and flexible or adaptive structure. First, we make review on the system configuration and essential functions employed in each plasma control system from the viewpoint of hardware as well as software. Second, we survey ITER control system requirements for the current CODAC design. Third, flexible structure in the plasma control system should be discussed. Finally, on the basis of the above discussion, we would like to envisage a future plasma control system for ITER and a fusion power plant.
Sips, A. C. C.*; Casper, T. A.*; Doyle, E. J.*; Giruzzi, G.*; Gribov, Y.*; Hobirk, J.*; Hogeweij, G. M. D.*; Horton, L. D.*; Hubbard, A. E.*; Hutchinson, I.*; et al.
Proceedings of 22nd IAEA Fusion Energy Conference (FEC 2008) (CD-ROM), 8 Pages, 2008/10
The ITER discharge evolution has been verified in dedicated experiments. Results show that breakdown at E 0.23-0.32 V/m is possible un-assisted (ohmic) for large devices like JET and attainable in all devices with ECRH assist. For the current ramp up, good control of the plasma inductance is obtained using a full bore plasma shape with early X-point formation. Operation of the H-mode reference scenario at q
0.23-0.32 V/m is possible un-assisted (ohmic) for large devices like JET and attainable in all devices with ECRH assist. For the current ramp up, good control of the plasma inductance is obtained using a full bore plasma shape with early X-point formation. Operation of the H-mode reference scenario at q = 3 and the hybrid scenario at q95=4-4.5 during the flat top phase was documented. Specific studies during the flat top phase provide data for the li evolution after the H-mode transition and the li evolution after a back-transition to L-mode. During the ITER ramp down it is important to remain diverted and to reduce the elongation.
= 3 and the hybrid scenario at q95=4-4.5 during the flat top phase was documented. Specific studies during the flat top phase provide data for the li evolution after the H-mode transition and the li evolution after a back-transition to L-mode. During the ITER ramp down it is important to remain diverted and to reduce the elongation.
de Vries, P. C.*; Salmi, A.*; Parail, V.*; Giroud, C.*; Andrew, Y.*; Biewer, T. M.*; Cromb , K.*; Jenkins, I.*; Johnson, T.*; Kiptily, V.*; et al.
, K.*; Jenkins, I.*; Johnson, T.*; Kiptily, V.*; et al.
Nuclear Fusion, 48(3), p.035007_1 - 035007_6, 2008/03
Times Cited Count:48 Percentile:85.94(Physics, Fluids & Plasmas)Dedicated experiments on TF ripple effects on the performance of tokamak plasmas have been carried out at JET. The TF ripple was found to have a profound effect on the plasma rotation. The central Mach number, M, defined as the ratio of the rotation velocity and the thermal velocity, was found to drop as a function of TF ripple amplitude from an average value of M = 0.40-0.55 for operations at the standard JET ripple of 0.08% to M = 0.25-0.40 for 0.5% ripple and M = 0.1-0.3 for 1% ripple. With standard co-current injection of neutral beam injection (NBI), plasmas were found to rotate in the co-current direction. However, for higher TF ripple amplitudes (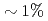 ) an area of counter rotation developed at the edge of the plasma, while the core kept its co-rotation.
) an area of counter rotation developed at the edge of the plasma, while the core kept its co-rotation.
Oyama, Naoyuki; Saibene, G.*; Kamada, Yutaka; Kamiya, Kensaku; Loarte, A.*; L nnroth, J.*; Parail, V.*; Sakamoto, Yoshiteru; Salmi, A.*; Sartori, R.*; et al.
nnroth, J.*; Parail, V.*; Sakamoto, Yoshiteru; Salmi, A.*; Sartori, R.*; et al.
Journal of Physics; Conference Series, 123, p.012015_1 - 012015_13, 2008/00
Times Cited Count:8 Percentile:90.42(Physics, Fluids & Plasmas)The effect of the toroidal field ripple and the edge toroidal rotation on H-mode and pedestal performance as well as ELM characteristics are investigated both in JET and JT-60U. In JT-60U, the amplitude of TF ripple was reduced from 1.2 % to 0.5 % after the installation of ferritic steel tiles. In JET, the ripple amplitude can actively be varied. In both devices, edge rotation in the same direction to the plasma current was reduced with increasing the ripple amplitude. Even at the same amplitude of 0.5 %, the achievable edge rotation in JT-60U was still lower than that in JET. A series of power and density scans performed at several ripple amplitude indicated that plasmas with smaller ripple amplitude and/or larger co-rotation are favorable to achieve higher pedestal pressure and plasma confinement in both devices. As for ELM characteristics, larger co-rotation seems to increase the ELM energy loss together with the reduction of the ELM frequency.
Saibene, G.*; Oyama, Naoyuki; L nnroth, J.*; Andrew, Y.*; la Luna, E. de.*; Giroud, C.*; Huysmans, G. T. A.*; Kamada, Yutaka; Kempenaars, M. A. H.*; Loarte, A.*; et al.
nnroth, J.*; Andrew, Y.*; la Luna, E. de.*; Giroud, C.*; Huysmans, G. T. A.*; Kamada, Yutaka; Kempenaars, M. A. H.*; Loarte, A.*; et al.
Nuclear Fusion, 47(8), p.969 - 983, 2007/08
Times Cited Count:36 Percentile:74.52(Physics, Fluids & Plasmas)This paper summarizes results of dimensionless identity experiments in JT-60U and JET, aimed at the comparison of the H-mode pedestal and ELM behaviour in the two devices. In general, pedestal pressure in JT-60U is lower than in JET. These results motivated a closer investigation of experimental conditions in the two devices, to identify possible "hidden" physics that prevents obtaining a good match of pedestal values over a large range of plasmas parameters. Ripple-induced ion losses of the medium bore plasma used in JT-60U for the similarity experiments are identified as the main difference with JET. The magnitude of the JT-60U ripple losses is sufficient to induce counter-toroidal rotation in co-injected plasma. The influence of ripple losses was demonstrated at high q plasma: reducing ripple losses by  2 by replacing positive with negative neutral beam injection resulted in an increased pedestal pressure in JT-60U, providing a good match to full power JET H-modes.
2 by replacing positive with negative neutral beam injection resulted in an increased pedestal pressure in JT-60U, providing a good match to full power JET H-modes.
Maggi, C. F.*; Groebner, R. J.*; Oyama, Naoyuki; Sartori, R.*; Horton, L. D.*; Sips, A. C. C.*; Suttrop, W.*; ASDEX Upgrade Team; Leonard, A.*; Luce, T. C.*; et al.
Nuclear Fusion, 47(7), p.535 - 551, 2007/07
Times Cited Count:63 Percentile:88.45(Physics, Fluids & Plasmas)Pedestal and global plasma parameters are compared in ELMy H-modes and improved confinement discharges from ASDEX Upgrade (AUG), DIII-D, JET and JT-60U with varying net input power. The pedestal top pressure increases moderately with power, in broad agreement with the power dependence of the H98(y,2) scaling. For all machines and all scenarios a robust correlation between the total and the pedestal thermal stored energy is observed. In AUG the improved confinement is due to improved pedestal confinement in improved H-modes with early heating and to both improved pedestal and core confinement in improved H-modes with late heating. In DIII-D the increase in confinement is due to improved confinement in the plasma core. JT-60U reversed shear H-modes have strong internal transport barriers and thus improved core performance. In all four tokamaks improved edge stability is correlated with increasing total 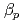 and H98(y,2) increases with pedestal
and H98(y,2) increases with pedestal 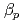 .
.
Kamiya, Kensaku; Asakura, Nobuyuki; Boedo, J. A.*; Eich, T.*; Federici, G.*; Fenstermacher, M.*; Finken, K.*; Herrmann, A.*; Terry, J.*; Kirk, A.*; et al.
Plasma Physics and Controlled Fusion, 49(7), p.s43 - s62, 2007/07
Times Cited Count:75 Percentile:91.75(Physics, Fluids & Plasmas)Edge Localized Mode (ELM) measurements in the tokamaks, including JT-60U, DIII-D, ASDEX-U and JET, are reviewed. The followings are outlines of this presentation. (1) ELM Types and basic scaling, (2) Small ELM regimes and ELM mitigation, (3) ELM filament formation and transverse motion, (4) Power deposition on divertor targets and main chamber wall.
Doyle, E. J.*; Houlberg, W. A.*; Kamada, Yutaka; Mukhovatov, V.*; Osborne, T. H.*; Polevoi, A.*; Bateman, G.*; Connor, J. W.*; Cordey, J. G.*; Fujita, Takaaki; et al.
Nuclear Fusion, 47(6), p.S18 - S127, 2007/06
no abstracts in English
Kamada, Yutaka; Leonard, A. W.*; Bateman, G.*; Becoulet, M.*; Chang, C. S.*; Eich, T.*; Evans, T. E.*; Groebner, R. J.*; Guzdar, P. N.*; Horton, L. D.*; et al.
Proceedings of 21st IAEA Fusion Energy Conference (FEC 2006) (CD-ROM), 8 Pages, 2007/03
no abstracts in English
Parail, V. V.*; Evans, T. E.*; Johnson, T.*; L nnroth, J.*; Oyama, Naoyuki; Saibene, G.*; Sartori, R.*; Salmi, A.*; de Vries, P.*; Becoulet, M.*; et al.
nnroth, J.*; Oyama, Naoyuki; Saibene, G.*; Sartori, R.*; Salmi, A.*; de Vries, P.*; Becoulet, M.*; et al.
Proceedings of 21st IAEA Fusion Energy Conference (FEC 2006) (CD-ROM), 8 Pages, 2007/03
Ripple-induced transport and externally driven resonance magnetic perturbations (RMP) near the separatrix are considered as prospective methods of ELM mitigation in present day tokamaks and ITER. Although these methods rely on different physics to generate extra transport, the influence of this transport on plasma dynamics and ELM mitigation is either similar or supplementary. The results of extensive theoretical analysis of the underlying physics processes behind transport induced by ripple and RMP is presented together with predictive transport modelling. Comparison with experiments on present-day tokamaks is given.
Maggi, C. F.*; Groebner, R. J.*; Oyama, Naoyuki; Sartori, R.*; Horton, L. D.*; Sips, A. C. C.*; Suttrop, W.*; ASDEX Upgrade Team; Leonard, T.*; Luce, T. C.*; et al.
Proceedings of 21st IAEA Fusion Energy Conference (FEC 2006) (CD-ROM), 8 Pages, 2007/03
Pedestal and global plasma parameters are compared in ELMy H-mode discharges from ASDEX Upgrade (AUG), DIII-D, JET and JT-60U. The increase in pedestal pressure (p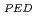 ) with power is continuous, reflecting the continuous transition from "standard H-mode" to "improved confinement scenario". In AUG improved H-modes p
) with power is continuous, reflecting the continuous transition from "standard H-mode" to "improved confinement scenario". In AUG improved H-modes p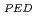 increases with power due to an increase of both pedestal top density and temperature. In DIII-D p
increases with power due to an increase of both pedestal top density and temperature. In DIII-D p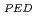 increases primarily due to an increase of the pedestal temperature. In JT-60U high
increases primarily due to an increase of the pedestal temperature. In JT-60U high 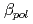 H-modes at
H-modes at 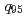 = 6.5 and high
= 6.5 and high  the improved confinement is due to an increase of
the improved confinement is due to an increase of 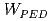 , while in reversed shear H-modes to an increase of
, while in reversed shear H-modes to an increase of 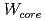 . In JET hybrid discharges at 1.4 MA
. In JET hybrid discharges at 1.4 MA 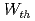 increases with power and
increases with power and  due to an increase of
due to an increase of 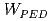 . In all four tokamaks improved edge stability is correlated to increasing total
. In all four tokamaks improved edge stability is correlated to increasing total 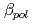 and H98(y,2) increases with pedestal
and H98(y,2) increases with pedestal 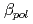 .
.
Roque, B.*; Gregg, R.*; Kilger, R.*; Laugier, F.*; Marimbeau, P.*; Ranta-Aho, A.*; Riffard, C.*; Suyama, Kenya; Thro, J. F.*; Yudkevich, M.*; et al.
Proceedings of American Nuclear Society Topical Meeting on Physics of Reactors (PHYSOR 2006) (CD-ROM), 10 Pages, 2006/09
This paper presents the results from the first phase of an international depletion calculations comparison devoted to UOx fuel cycle issues. This "benchmark" has been defined within the NEA/OECD Working Party on Scientific Issues in Reactors Systems (WPRS). The aim is to investigate a large range of isotopes, physics quantities applied to fuel and back-end cycle configurations. The results analyses have shown that there is a good agreement between participants for the mass calculation of many isotopes. In this benchmark, the poorest agreement is obtained in calculating activation products originating from fuel impurities. Some discrepancies on neutron emission rates were also observed, mainly due to the discrepancies on masses calculations. Good agreement was obtained for the total decay heat calculation.
Oyama, Naoyuki; Gohil, P.*; Horton, L. D.*; Hubbard, A. E.*; Hughes, J. W.*; Kamada, Yutaka; Kamiya, Kensaku; Leonard, A. W.*; Loarte, A.*; Maingi, R.*; et al.
Plasma Physics and Controlled Fusion, 48(5A), p.A171 - A181, 2006/05
Times Cited Count:81 Percentile:92.09(Physics, Fluids & Plasmas)no abstracts in English
Stober, J.*; Lomas, P. J.*; Saibene, G.*; Andrew, Y.*; Belo, P.*; Conway, G. D.*; Herrmann, A.*; Horton, L. D.*; Kempenaars, M.*; Koslowski, H.-R.*; et al.
Nuclear Fusion, 45(11), p.1213 - 1223, 2005/11
Times Cited Count:40 Percentile:76.37(Physics, Fluids & Plasmas)no abstracts in English
Saibene, G.*; Hatae, Takaki; Campbell, D. J.*; Cordey, J. G.*; la Luna, E. de.*; Giroud, C.*; Guenther, K.*; Kamada, Yutaka; Kempenaars, M. A. H.*; Loarte, A.*; et al.
Plasma Physics and Controlled Fusion, 46(5A), p.A195 - A205, 2004/05
Times Cited Count:10 Percentile:32.04(Physics, Fluids & Plasmas)Towards establishment of the control scheme and evaluation of the H-mode pedestal structure and behavior of the Edge Localized Mode (ELM) in ITER, we carried out an comparison experiment among the two large tokamaks (JT-60 and JET) for the first time. This paper report the initial results. In both devices, the same plasma shape was adopted and the three non-dimensional parameters (beta, normalized gyro radius and the normalized collisionality) were set identical. The pedestal width was almost similar in the two devices, however the pressure gradient was higher in JET by a factor of 1.5. The possible reason is a small aspect ration in JET.
B coulet, M.*; Huysmans, G.*; Sarazin, Y.*; Garbet, X.*; Ghendrih, P.*; Rimini, F.*; Joffrin, E.*; Litaudon, X.*; Monier-Garbet, P.*; An
coulet, M.*; Huysmans, G.*; Sarazin, Y.*; Garbet, X.*; Ghendrih, P.*; Rimini, F.*; Joffrin, E.*; Litaudon, X.*; Monier-Garbet, P.*; An , J.-M.*; et al.
, J.-M.*; et al.
Plasma Physics and Controlled Fusion, 45(12A), p.A93 - A113, 2003/12
Times Cited Count:84 Percentile:91.17(Physics, Fluids & Plasmas)no abstracts in English
Loarte, A.*; Saibene, G.*; Sartori, R.*; Campbell, D.*; Becoulet, M.*; Horton, L.*; Eich, T.*; Herrmann, A.*; Matthews, G.*; Asakura, Nobuyuki; et al.
Plasma Physics and Controlled Fusion, 45(9), p.1549 - 1569, 2003/10
Times Cited Count:449 Percentile:99.72(Physics, Fluids & Plasmas)Analysis of Type I ELMs from ongoing experiments shows that ELM energy losses are correlated with the density and temperature of the pedestal plasma before the ELM crash. The Type I ELM plasma energy loss normalized to the pedestal energy is found to correlate across experiments with the collisionality of the pedestal plasma. Other parameters affect the ELM size such as the edge magnetic shear, etc, which influence the plasma volume affected by the ELMs. ELM particle losses are influenced by this ELM affected volume and are weakly dependent on other pedestal plasma parameters. In JET and DIII-D, minimum Type I ELMs with energy losses acceptable for ITER were found, that do not affect the plasma temperature. The duration of the divertor ELM power pulse is correlated with the typical ion transport time from the pedestal to the divertor target and not with the duration of the ELM associated MHD activity. Extrapolation of the present experimental results to ITER is summarized.