Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Nugraha, E. D.*; Hosoda, Masahiro*; Kusdiana*; Untara*; Mellawati, J.*; Nurokhim*; Tamakuma, Yuki*; Ikram, A.*; Syaifudin, M.*; Yamada, Ryohei; et al.
Scientific Reports (Internet), 11(1), p.14578_1 - 14578_16, 2021/07
Times Cited Count:19 Percentile:84.25(Multidisciplinary Sciences)Mamuju is one of the regions in Indonesia which retains natural conditions but has relatively high exposure to natural radiation. The goals of the present study were to characterize exposure of the entire Mamuju region as a high natural background radiation area (HNBRA) and to assess the existing exposure as a means for radiation protection of the public and the environment. A cross-sectional study method was used with cluster sampling areas by measuring all parameters that contribute to external and internal radiation exposures. It was determined that Mamuju was a unique HNBRA with the annual effective dose between 17 and 115 mSv, with an average of 32 mSv. The lifetime cumulative dose calculation suggested that Mamuju residents could receive as much as 2.2 Sv on average which is much higher than the average dose of atomic bomb survivors for which risks of cancer and non-cancer diseases are demonstrated. The study results are new scientific data allowing better understanding of health effects related to chronic low-dose-rate radiation exposure and they can be used as the main input in a future epidemiology study.
Hosoda, Masahiro*; Nugraha, E. D.*; Akata, Naofumi*; Yamada, Ryohei; Tamakuma, Yuki*; Sasaki, Michiya*; Kelleher, K.*; Yoshinaga, Shinji*; Suzuki, Takahito*; Rattanapongs, C. P.*; et al.
Science of the Total Environment, 750, p.142346_1 - 142346_11, 2021/01
Times Cited Count:23 Percentile:86.19(Environmental Sciences)The biological effects of low dose-rate radiation exposures on humans remains unknown. In fact, the Japanese nation still struggles with this issue after the Fukushima Dai-ichi Nuclear Power Plant accident. Recently, we have found a unique area in Indonesia where naturally high radiation levels are present, resulting in chronic low dose-rate radiation exposures. We aimed to estimate the comprehensive dose due to internal and external exposures at the particularly high natural radiation area, and to discuss the enhancement mechanism of radon. A car-borne survey was conducted to estimate the external doses from terrestrial radiation. Indoor radon measurements were made in 47 dwellings over three to five months, covering the two typical seasons, to estimate the internal doses. Atmospheric radon gases were simultaneously collected at several heights to evaluate the vertical distribution. The absorbed dose rates in air in the study area vary widely between 50 nGy h and 1109 nGy h
and 1109 nGy h . Indoor radon concentrations ranged from 124 Bq m
. Indoor radon concentrations ranged from 124 Bq m to 1015 Bq m
to 1015 Bq m . That is, the indoor radon concentrations measured exceed the reference levels of 100 Bq m
. That is, the indoor radon concentrations measured exceed the reference levels of 100 Bq m recommended by the World Health Organization. Furthermore, the outdoor radon concentrations measured were comparable to the high indoor radon concentrations. The annual effective dose due to external and internal exposures in the study area was estimated to be 27 mSv using the median values. It was found that many residents are receiving radiation exposure from natural radionuclides over the dose limit for occupational exposure to radiation workers. This enhanced outdoor radon concentration might be as a result of the stable atmospheric conditions generated at an exceptionally low altitude. Our findings suggest that this area provides a unique opportunity to conduct an epidemiological study related to health effects due to chronic low dose-rate radiation exposure.
recommended by the World Health Organization. Furthermore, the outdoor radon concentrations measured were comparable to the high indoor radon concentrations. The annual effective dose due to external and internal exposures in the study area was estimated to be 27 mSv using the median values. It was found that many residents are receiving radiation exposure from natural radionuclides over the dose limit for occupational exposure to radiation workers. This enhanced outdoor radon concentration might be as a result of the stable atmospheric conditions generated at an exceptionally low altitude. Our findings suggest that this area provides a unique opportunity to conduct an epidemiological study related to health effects due to chronic low dose-rate radiation exposure.
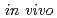 dosimetry system based on an optical fiber-coupled microsized photostimulable phosphor for stereotactic body radiation therapy
dosimetry system based on an optical fiber-coupled microsized photostimulable phosphor for stereotactic body radiation therapyYada, Ryuichi*; Maenaka, Kazusuke*; Miyamoto, Shuji*; Okada, Go*; Sasakura, Aki*; Ashida, Motoi*; Adachi, Masashi*; Sato, Tatsuhiko; Wang, T.*; Akasaka, Hiroaki*; et al.
Medical Physics, 47(10), p.5235 - 5249, 2020/10
Times Cited Count:7 Percentile:52.3(Radiology, Nuclear Medicine & Medical Imaging)The 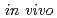 dosimeter system is capable of real-time, accurate, and precise measurement under stereotactic body radiation therapy (SBRT) conditions. The probe is smaller than a conventional dosimeter, has excellent spatial resolution, and can be valuable in SBRT with a steep dose distribution over a small field. The developed PSP dosimeter system appears to be suitable for in vivo SBRT dosimetry.
dosimeter system is capable of real-time, accurate, and precise measurement under stereotactic body radiation therapy (SBRT) conditions. The probe is smaller than a conventional dosimeter, has excellent spatial resolution, and can be valuable in SBRT with a steep dose distribution over a small field. The developed PSP dosimeter system appears to be suitable for in vivo SBRT dosimetry.
Tamakuma, Yuki*; Yamada, Ryohei; Suzuki, Takahito*; Kuroki, Tomohiro*; Saga, Rikiya*; Mizuno, Hiroyuki*; Sasaki, Hiroyuki*; Iwaoka, Kazuki*; Hosoda, Masahiro*; Tokonami, Shinji*
Radiation Protection Dosimetry, 184(3-4), p.307 - 310, 2019/10
Times Cited Count:1 Percentile:11.15(Environmental Sciences)After the Fukushima Daiichi Nuclear Power Plant accident, the radiation dose for first responders was not evaluated accurately due to lack of the monitoring data. It has been important to evaluate a radiation dose for workers in emergency response at a nuclear accident. In this study, a new device which can evaluate both of external and internal exposure doses was developed and the performance of various environmental radiation monitors including commercially available monitors were tested and compared from the viewpoint of an environmental monitoring at emergency situation. Background counts of the monitors and the ambient dose equivalent rate were measured in Fukushima Prefecture. The detection limit for beta particles was evaluated by the method of ISO11929. The sensitivity for gamma-rays of the dust monitor using a ZnS(Ag) and a plastic scintillator was high, but that of the external exposure monitor using a silicon photodiode with CsI(Tl) crystal was relatively low. The detection limit ranged 190-280 Bq m at 100
at 100  Sv h
Sv h , exceeding the detection limit of 100 Bq m
, exceeding the detection limit of 100 Bq m in the minimum requirement by the National Regulation Authority in Japan. Use of the shielding with lead is necessary to achieve the minimum requirement. These results indicate that the dust monitor using a ZnS(Ag) scintillator and a plastic scintillator is suitable for the external exposure monitor and the developed internal exposure monitor is for the internal exposure monitor at emergency situation among the evaluated monitors. In the future study, the counting efficiency, the relative uncertainty and the performance of the detection for alpha particles will be evaluated, and it will be considered which type of a monitor is suitable after taking the portability into account.
in the minimum requirement by the National Regulation Authority in Japan. Use of the shielding with lead is necessary to achieve the minimum requirement. These results indicate that the dust monitor using a ZnS(Ag) scintillator and a plastic scintillator is suitable for the external exposure monitor and the developed internal exposure monitor is for the internal exposure monitor at emergency situation among the evaluated monitors. In the future study, the counting efficiency, the relative uncertainty and the performance of the detection for alpha particles will be evaluated, and it will be considered which type of a monitor is suitable after taking the portability into account.
Sasaki, Jun; Okuda, Eiji; Suzuki, Nobuhiro; Ota, Katsu; Owada, Ryohei; Takamatsu, Misao
no journal, ,
no abstracts in English
Sasaki, Michiya*; Yamada, Ryohei; Akata, Naofumi*; Tokonami, Shinji*; Hosoda, Masahiro*; Iwaoka, Kazuki*; Chanis, P.*; Kudo, Hiromi*; Sahoo, K.*; Iskandar, D.*; et al.
no journal, ,
Recently, Mamuju city in Sulawesi Island, Indonesia and its surrounding area is known as the high background radiation area, and is regarded as a possible area for an epidemiological study. In this study we have measured the hourly dose rates of individuals and the environment with the D-shuttle dosimeter, which has been developed by the Chiyoda Technol Corporation. With the aid of local residents living at Botteng village, which is located south of Mamuju city, short term and long term measurements were conducted for three days and nine months, respectively. Two volunteers have equipped the D-shuttle for the short term measurement, and seven families supported the short and long term measurements of the environmental dose rate, for both inside and outside the house. From our results, since some variation was observed regarding with day or night, correlation with radon concentration was suggested.
Sasaki, Michiya*; Yamada, Ryohei; Nugraha, E.*; Akata, Naofumi*; Tokonami, Shinji*; Hosoda, Masahiro*; Iwaoka, Kazuki*; Pornnumpa, C.*; Kudo, Hiromi*; Sahoo, K.*; et al.
no journal, ,
The area around Mamuju city in West Sulawesi, Indonesia has high possibility of being a target of epidemiological research as a high natural radiation area. We would like to report the difference in radiation dose at different heights from the ground measured by the D-Shuttle.
Hashimoto, Hiroki*; Yamada, Ryohei; Yamaguchi, Kanna*; Sasaki, Koichi*; Tamakuma, Yuki*; Hosoda, Masahiro*; Akata, Naofumi*; Tokonami, Shinji*
no journal, ,
no abstracts in English