Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Suzuki, Hiroshi; Kusunoki, Koichi*; Satake, Kosuke*; Kanematsu, Manabu*; Koyama, Taku*; Niwa, Akinobu*; Kabayama, Kenji*; Mukai, Tomohisa*; Kawasaki, Takuro; Harjo, S.
Hihakai Kensa, 67(4), p.180 - 186, 2018/04
The bond behavior between rebar and concrete under bending moment was investigated by measuring the stress distribution in the two-dimensionally distributed rebars embedded in the reinforced concrete (RC) beam using neutron diffraction. The stress distributions in both of the main rebar and the transverse stirrups embedded in concrete were successfully measured at the fixed measurement configuration without any sample rotations, by suggesting a simple measurement technique on the premise that the transverse restriction from the surrounding concrete to the main rebar is negligible. The bending and shear fracture behavior of the RC beam specimen was predicted by comparing changes in the stress distribution in the rebars measured by neutron diffraction with respect to the applied stress, with the macroscopic deformation measured by strain gauges fixed on the concrete surface. In this study, it was found that the neutron diffraction technique can be a useful technique to evaluate not only the anchorage performance but also the bending behavior of the RC beam.
Ishizawa, Akihiro*; Idomura, Yasuhiro; Imadera, Kenji*; Kasuya, Naohiro*; Kanno, Ryutaro*; Satake, Shinsuke*; Tatsuno, Tomoya*; Nakata, Motoki*; Nunami, Masanori*; Maeyama, Shinya*; et al.
Purazuma, Kaku Yugo Gakkai-Shi, 92(3), p.157 - 210, 2016/03
The high-performance computer system Helios which is located at The Computational Simulation Centre (CSC) in The International Fusion Energy Research Centre (IFERC) started its operation in January 2012 under the Broader Approach (BA) agreement between Japan and the EU. The Helios system has been used for magnetised fusion related simulation studies in the EU and Japan and has kept high average usage rate. As a result, the Helios system has contributed to many research products in a wide range of research areas from core plasma physics to reactor material and reactor engineering. This project review gives a short catalogue of domestic simulation research projects. First, we outline the IFERC-CSC project. After that, shown are objectives of the research projects, numerical schemes used in simulation codes, obtained results and necessary computations in future.
Nakatsuji, Satoru*; Kuga, Kentaro*; Kimura, Kenta*; Satake, Ryuta*; Katayama, Naoyuki*; Nishibori, Eiji*; Sawa, Hiroshi*; Ishii, Rieko*; Hagiwara, Masayuki*; Bridges, F.*; et al.
Science, 336(6081), p.559 - 563, 2012/05
Times Cited Count:114 Percentile:95.29(Multidisciplinary Sciences)Frustrated magnetic materials can remain disordered to the lowest temperatures. Such is the case for Ba CuSb
CuSb O
O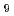 , which is magnetically anisotropic at the atomic scale but curiously isotropic on mesoscopic length and time scales. We find that the frustration on the triangular lattice is imprinted in a nanostructured honeycomb lattice of Cu
, which is magnetically anisotropic at the atomic scale but curiously isotropic on mesoscopic length and time scales. We find that the frustration on the triangular lattice is imprinted in a nanostructured honeycomb lattice of Cu ions that resists a coherent static Jahn-Teller distortion. The resulting two-dimensional random-bond spin-1/2 system on the honeycomb lattice has a broad spectrum of spin-dimer like excitations and low-energy spin degrees of freedom that retain.
ions that resists a coherent static Jahn-Teller distortion. The resulting two-dimensional random-bond spin-1/2 system on the honeycomb lattice has a broad spectrum of spin-dimer like excitations and low-energy spin degrees of freedom that retain.
Satake, Hiroshi*; Kita, Yuichiro*; Hayashi, Haruna*; Murata, Masanobu*
Geodynamics of Atotsugawa Fault System, p.123 - 148, 2007/00
no abstracts in English
 C
CHayashi, Maki*; Satake, Kenji*; Sasamoto, Hiroshi
JAEA-Data/Code 2006-012, 25 Pages, 2006/03
An international interlaboratory study (ILS) was coordinated by Argonne National Laboratory (ANL) to evaluate the precision and bias of a single-pass flow-through (SPFT) test method that can be used to measure the forward dissolution rate of borosilicate glass. In this report we present the results of tests conducted at 70 C using the LRM glass prepared by ANL. Based on measurements of the concentrations of glass components (i.e., Si, B and Na) in effuluent solutions and the solution flow rate, glass dissolution rates were calculated under the steady-state concentrations of glass components. The rates in the absence of glass components were estimated by extrapolation of the experimental results to zero concentration of glass components. Results show that the average pH of effuluent solutions was 11.68
C using the LRM glass prepared by ANL. Based on measurements of the concentrations of glass components (i.e., Si, B and Na) in effuluent solutions and the solution flow rate, glass dissolution rates were calculated under the steady-state concentrations of glass components. The rates in the absence of glass components were estimated by extrapolation of the experimental results to zero concentration of glass components. Results show that the average pH of effuluent solutions was 11.68 0.23 (0.23 refers to standard deviation) at room temperature (21.78
0.23 (0.23 refers to standard deviation) at room temperature (21.78 4.03
4.03 C, 4.03 means standard deviation). The estimated dissolution rate of LRM glass, based on variations in Si, B and Na concentrations in the absence of solution-feedback effects, is 2.11, 1.99 and 1.93 (g/m
C, 4.03 means standard deviation). The estimated dissolution rate of LRM glass, based on variations in Si, B and Na concentrations in the absence of solution-feedback effects, is 2.11, 1.99 and 1.93 (g/m d), respectively. The reliability of these estimates is questionable, however, due to considerable scatter in the aqueous concentration data. Based on these results, it is suggested that carefully controlled and constant flow rates are required to obtain reliable data using the SPFT test method.
d), respectively. The reliability of these estimates is questionable, however, due to considerable scatter in the aqueous concentration data. Based on these results, it is suggested that carefully controlled and constant flow rates are required to obtain reliable data using the SPFT test method.
Hayashi, Maki*; Satake, Kenji*; Sasamoto, Hiroshi; Yoshikawa, Hideki; Yui, Mikazu
no journal, ,
In the analysis of radionuclides migration in the performance assessment of geological disposal system, the release of radionuclides from vitrified glass is considered as the source-term for radionuclides migration, and model development and quantitative assessment of glass dissolution are necessary for the analysis. For a realistic assessment of radionuclides release from the vitrified waste glass, further research to improve understanding based on the scientific basis and development of robust glass dissolution model are important. As one of the tool to reflect these researches, we have been developing the Glass Dissolution Rate Database. This database has information on the dissolution behavior of glass. We researched the documents about the leaching tests of HLW glass, and registered the data of normalized elemental mass loss from HLW glass with experimental conditions. At present the prototype database has been developed using Microsoft Access.
Satake, Kosuke*; Kusunoki, Koichi*; Mukai, Tomohisa*; Kanematsu, Manabu*; Koyama, Taku*; Suzuki, Hiroshi
no journal, ,
no abstracts in English
Suzuki, Hiroshi; Satake, Kosuke*; Kusunoki, Koichi*; Kanematsu, Manabu*; Mukai, Tomohisa*
no journal, ,
no abstracts in English