Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Tetsu, Keiichi*; Takayama, Yusuke; Sawada, Atsushi
JAEA-Research 2022-005, 84 Pages, 2022/08
Nuclide migration analyses are conducted for the safety assessment in geological disposal system of HLW. Nuclide migration evaluation of fractured host rock mainly uses a model that approximates the fracture with parallel flat plates. However, the actual fractures in the host rock are different from the parallel flat plates, the fractures have complex characteristics such as roughness of fracture surface and the fillings in the fracture. In approximating a fracture model, the methodology development how to set parameter values such as the transmissivity coefficient and the fracture aperture is an issue. One of the issues is to investigate the geometrical features of actual fractures in the host rock. In this study, for the purpose of understanding the geometrical features of fractures including fracture intersection, the internal fracture shape was measured in detail using the method of surface grinding on 50cm scale granodiorite with natural fracture intersection. Thus, the fracture width, fracture aperture, and the shape of the fracture surfaces were obtained. From the obtain data, characteristics such as the average value of the fracture width, the roughness of the fracture surfaces, and the distribution of the fracture aperture were evaluated. As a result, it was confirmed that one of the fractures near the fracture intersection has a particularly large fracture width and fracture aperture as compared with the other part of fractures. Thus, in the granodiorite rock block used in this study, it was inferred that the most permeable path is not the fracture intersection itself, but the particularly large fracture aperture in the vicinity of the fracture intersection.
Kitazato, Kohei*; Milliken, R. E.*; Iwata, Takahiro*; Abe, Masanao*; Otake, Makiko*; Matsuura, Shuji*; Takagi, Yasuhiko*; Nakamura, Tomoki*; Hiroi, Takahiro*; Matsuoka, Moe*; et al.
Nature Astronomy (Internet), 5(3), p.246 - 250, 2021/03
Times Cited Count:43 Percentile:96.93(Astronomy & Astrophysics)Here we report observations of Ryugu's subsurface material by the Near-Infrared Spectrometer (NIRS3) on the Hayabusa2 spacecraft. Reflectance spectra of excavated material exhibit a hydroxyl (OH) absorption feature that is slightly stronger and peak-shifted compared with that observed for the surface, indicating that space weathering and/or radiative heating have caused subtle spectral changes in the uppermost surface. However, the strength and shape of the OH feature still suggests that the subsurface material experienced heating above 300  C, similar to the surface. In contrast, thermophysical modeling indicates that radiative heating does not increase the temperature above 200
C, similar to the surface. In contrast, thermophysical modeling indicates that radiative heating does not increase the temperature above 200  C at the estimated excavation depth of 1 m, even if the semimajor axis is reduced to 0.344 au. This supports the hypothesis that primary thermal alteration occurred due to radiogenic and/or impact heating on Ryugu's parent body.
C at the estimated excavation depth of 1 m, even if the semimajor axis is reduced to 0.344 au. This supports the hypothesis that primary thermal alteration occurred due to radiogenic and/or impact heating on Ryugu's parent body.
Sato, Hisashi*; Sawada, Atsushi; Takayama, Yusuke
JAEA-Research 2020-012, 37 Pages, 2020/11
In the safety assessment of the geological disposal of high-level radioactive waste, it is important to fully understand the permeability and mass transport properties of actual fractures when setting parameters for permeability and mass transport properties of fractures. Permeability and mass transport properties of a fracture are affected by the void structure of the fracture. Therefore, it is necessary not only to conduct a hydraulic test but also to evaluate hydraulic properties based on the void structure of the fracture. Therefore, the purpose of this study is to develop a technique to acquire a three-dimensional void structure of a fracture from fracture surface shape data, and to obtain a dataset of three- dimensional void structure data and hydraulic data of the fracture. Specifically, we made a transparent replica sample of fracture and measure the fracture surface shape data in the exact coordinates. The three-dimensional void structure data was constituted from fracture surface shape data in the same coordinates. In addition, we conducted a permeability test and tracer test for the same sample to obtain a permeability and mass transport properties of the fracture. To assess the validity of the acquired data, we compared it with the apertures evaluated based on different methods. As a result, the average aperture from the fracture void structure was almost same as the average aperture acquired by different methods, from the above that the test result was validated.
Kitazato, Kohei*; Milliken, R. E.*; Iwata, Takahiro*; Abe, Masanao*; Otake, Makiko*; Matsuura, Shuji*; Arai, Takehiko*; Nakauchi, Yusuke*; Nakamura, Tomoki*; Matsuoka, Moe*; et al.
Science, 364(6437), p.272 - 275, 2019/04
Times Cited Count:259 Percentile:99.73(Multidisciplinary Sciences)The near-Earth asteroid 162173 Ryugu, the target of Hayabusa2 sample return mission, is believed to be a primitive carbonaceous object. The Near Infrared Spectrometer (NIRS3) on Hayabusa2 acquired reflectance spectra of Ryugu's surface to provide direct measurements of the surface composition and geological context for the returned samples. A weak, narrow absorption feature centered at 2.72 micron was detected across the entire observed surface, indicating that hydroxyl (OH)-bearing minerals are ubiquitous there. The intensity of the OH feature and low albedo are similar to thermally- and/or shock-metamorphosed carbonaceous chondrite meteorites. There are few variations in the OH-band position, consistent with Ryugu being a compositionally homogeneous rubble-pile object generated from impact fragments of an undifferentiated aqueously altered parent body.
Sawada, Yusuke*; Uozumi, Yusuke*; Nogamine, Sho*; Yamada, Takehiro*; Iwamoto, Yosuke; Sato, Tatsuhiko; Niita, Koji*
Nuclear Instruments and Methods in Physics Research B, 291, p.38 - 44, 2012/11
Times Cited Count:17 Percentile:76.97(Instruments & Instrumentation)The Intranuclear cascade with emission of light fragment (INC-ELF) code has been developed and implemented in the particle and heavy ion transport code system (PHITS). The INC-ELF code explicitly includes nucleon correlations within the framework of the INC model to describe light fragment emissions from nuclear spallation reactions. In addition to the degrees of freedom of nucleons, the developed code also accounts for pions, 
 and
and 

 , and it can cover the energy range up to 3 GeV. The predictive capabilities of the ELF/PHITS system have been verified through comparison with a diverse set of experimental observations. As a result, our ELF/PHITS code has demonstrated strong predictive capability for all of these data, although areas requiring future study remain due to the lack of experimental data on high-energy cluster production.
, and it can cover the energy range up to 3 GeV. The predictive capabilities of the ELF/PHITS system have been verified through comparison with a diverse set of experimental observations. As a result, our ELF/PHITS code has demonstrated strong predictive capability for all of these data, although areas requiring future study remain due to the lack of experimental data on high-energy cluster production.
Uozumi, Yusuke*; Sawada, Yusuke*; Mzhavia, A.*; Nogamine, Sho*; Iwamoto, Hiroki; Kin, Tadahiro; Hohara, Shinya*; Wakabayashi, Genichiro*; Nakano, Masahiro*
Physical Review C, 84(6), p.064617_1 - 064617_11, 2011/12
Times Cited Count:18 Percentile:72.25(Physics, Nuclear)Deuteron production from intermediate-energy proton-nucleus interactions was investigated through experiments and model calculations, mainly to develop a theoretical model by elucidating the mechanism of cluster production. Spectral double-differential cross sections were measured for inclusive ( ,
, 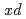 ) reactions on five targets in the periodic table, namely
) reactions on five targets in the periodic table, namely  C,
C,  Al,
Al, 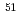 V,
V,  Nb, and
Nb, and  Au, at beam energies of 300 and 392 MeV. The cross sections were determined in almost the entire outgoing energy range from the highest down to 30 MeV and at laboratory angles from 20
Au, at beam energies of 300 and 392 MeV. The cross sections were determined in almost the entire outgoing energy range from the highest down to 30 MeV and at laboratory angles from 20 to 104
to 104 . To interpret the measured spectra, we proposed a new model that includes the nucleon correlations of the initial- and final-state interactions to describe cluster knockout and pickup within the intranuclear cascade model. The results of the model calculations showed reasonable agreements with those of the experiments. Moreover, the model indicated reasonable predictive power for the (
. To interpret the measured spectra, we proposed a new model that includes the nucleon correlations of the initial- and final-state interactions to describe cluster knockout and pickup within the intranuclear cascade model. The results of the model calculations showed reasonable agreements with those of the experiments. Moreover, the model indicated reasonable predictive power for the ( ,
,  He
He ), (
), ( ,
, 
 ), and (
), and ( ,
, 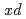 ) reactions measured elsewhere.
) reactions measured elsewhere.
 collisions at
collisions at  = 200 and 62.4 GeV
= 200 and 62.4 GeVAdare, A.*; Afanasiev, S.*; Aidala, C.*; Ajitanand, N. N.*; Akiba, Yasuyuki*; Al-Bataineh, H.*; Alexander, J.*; Aoki, Kazuya*; Aphecetche, L.*; Armendariz, R.*; et al.
Physical Review C, 83(6), p.064903_1 - 064903_29, 2011/06
Times Cited Count:184 Percentile:99.44(Physics, Nuclear)Transverse momentum distributions and yields for  , and
, and  in
in  collisions at
collisions at  = 200 and 62.4 GeV at midrapidity are measured by the PHENIX experiment at the RHIC. We present the inverse slope parameter, mean transverse momentum, and yield per unit rapidity at each energy, and compare them to other measurements at different
= 200 and 62.4 GeV at midrapidity are measured by the PHENIX experiment at the RHIC. We present the inverse slope parameter, mean transverse momentum, and yield per unit rapidity at each energy, and compare them to other measurements at different  collisions. We also present the scaling properties such as
collisions. We also present the scaling properties such as  and
and  scaling and discuss the mechanism of the particle production in
scaling and discuss the mechanism of the particle production in  collisions. The measured spectra are compared to next-to-leading order perturbative QCD calculations.
collisions. The measured spectra are compared to next-to-leading order perturbative QCD calculations.
 and Au+Au collisions at
and Au+Au collisions at  = 200 GeV
= 200 GeVAdare, A.*; Afanasiev, S.*; Aidala, C.*; Ajitanand, N. N.*; Akiba, Yasuyuki*; Al-Bataineh, H.*; Alexander, J.*; Aoki, Kazuya*; Aphecetche, L.*; Aramaki, Y.*; et al.
Physical Review C, 83(4), p.044912_1 - 044912_16, 2011/04
Times Cited Count:8 Percentile:49.7(Physics, Nuclear)Measurements of electrons from the decay of open-heavy-flavor mesons have shown that the yields are suppressed in Au+Au collisions compared to expectations from binary-scaled  collisions. Here we extend these studies to two particle correlations where one particle is an electron from the decay of a heavy flavor meson and the other is a charged hadron from either the decay of the heavy meson or from jet fragmentation. These measurements provide more detailed information about the interaction between heavy quarks and the quark-gluon matter. We find the away-side-jet shape and yield to be modified in Au+Au collisions compared to
collisions. Here we extend these studies to two particle correlations where one particle is an electron from the decay of a heavy flavor meson and the other is a charged hadron from either the decay of the heavy meson or from jet fragmentation. These measurements provide more detailed information about the interaction between heavy quarks and the quark-gluon matter. We find the away-side-jet shape and yield to be modified in Au+Au collisions compared to  collisions.
collisions.
Takir, D.*; Kitazato, Kohei*; Milliken, R. E.*; Iwata, Takahiro*; Abe, Masanao*; Otake, Makiko*; Matsuura, Shuji*; Arai, Takehiko*; Nakauchi, Yusuke*; Nakamura, Tomoki*; et al.
no journal, ,
JAXA spacecraft and sample return mission Hayabusa2 has arrived at the near-Earth asteroid 162173 Ryugu, which is classified a primitive carbonaceous object. Here we report recent results of near-infrared spectrometer (NIRS3) on the Hayabusa2 spacecraft. The observations provide direct measurements of the surface composition of Ryugu and context for the returned samples. NIRS3 has detected a weak and narrow absorption feature centered at 2.72 micrometer across entire observed surface. This absorption feature is attributed to the presence of OH-bearing minerals. The NIRS3 observations also revealed that Ryugu is the darkest object to be observed up-close by a visiting spacecraft. The intensity of the OH feature and low albedo are consistent with thermally-and/or shock-metamorphosed, and/or carbon-rich space-weathered primitive and hydrated carbonaceous chondrites.