Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Martin, P. G.*; Jones, C. P.*; Bartlett, S.*; Ignatyev, K.*; Megson-Smith, D.*; Satou, Yukihiko; Cipiccia, S.*; Batey, D. J.*; Rau, C.*; Sueki, Keisuke*; et al.
Scientific Reports (Internet), 10, p.22056_1 - 22056_17, 2020/12
Times Cited Count:1 Percentile:6.63(Multidisciplinary Sciences)Martin, P. G.*; Jones, C. P.*; Cipiccia, S.*; Batey, D. J.*; Hallam, K. R.*; Satou, Yukihiko; Griffiths, I.*; Rau, C.*; Richards, D. A.*; Sueki, Keisuke*; et al.
Scientific Reports (Internet), 10(1), p.1636_1 - 1636_11, 2020/01
Times Cited Count:8 Percentile:37.55(Multidisciplinary Sciences)Martin, P. G.*; Louvel, M.*; Cipiccia, S.*; Jones, C. P.*; Batey, D. J.*; Hallam, K. R.*; Yang, I. A. X.*; Satou, Yukihiko; Rau, C.*; Mosselmans, J. F. W.*; et al.
Nature Communications (Internet), 10, p.2801_1 - 2801_7, 2019/06
Times Cited Count:26 Percentile:78.93(Multidisciplinary Sciences)Synchrotron radiation (SR) analysis techniques alongside secondary ion mass spectrometry (SIMS) measurements have been made on sub-mm particulate material derived from reactor Unit 1 of the Fukushima Daiichi Nuclear Power Plant (FDNPP). Using these methods, it has been possible to investigate the distribution, state and isotopic composition of micron-scale U particulate contained within the larger Si-based ejecta material. Through combined SR micro-focused X-ray fluorescence (SR-micro-XRF) and absorption contrast SR micro-focused X-ray tomography (SR-micro-XRT), the U particulate was found to be located around the exterior circumference of the highly-porous particle. Synchrotron radiation micro-focused X-ray absorption near edge structure (SR-micro-XANES) analysis of a number of these entrapped particles revealed them to exist within the U(IV) oxidation state, as UO , and identical in structure to reactor fuel. Confirmation that this U was of nuclear origin (
, and identical in structure to reactor fuel. Confirmation that this U was of nuclear origin ( U-enriched) was provided through secondary ion mass spectrometry (SIMS) analysis with an isotopic enrichment ratio characteristic of a provenance from reactor Unit 1 at the FDNPP. These results provide clear evidence of the event scenario (that a degree of core fragmentation and release occurred from reactor Unit 1), with such spent fuel ejecta existing; (i) within the stable U(IV) oxidation state; and (ii) contained within a bulk Si-based particle. While this U is unlikely to represent an environmental or health hazard, such assertions would likely change, however, should break-up of the Si-containing bulk particle occur. However, more important to the long-term decommissioning of the reactors (and clean-up) on the FDNPP, is the knowledge that core integrity of reactor Unit 1 was compromised with nuclear material existing outside of the reactors primary containment.
U-enriched) was provided through secondary ion mass spectrometry (SIMS) analysis with an isotopic enrichment ratio characteristic of a provenance from reactor Unit 1 at the FDNPP. These results provide clear evidence of the event scenario (that a degree of core fragmentation and release occurred from reactor Unit 1), with such spent fuel ejecta existing; (i) within the stable U(IV) oxidation state; and (ii) contained within a bulk Si-based particle. While this U is unlikely to represent an environmental or health hazard, such assertions would likely change, however, should break-up of the Si-containing bulk particle occur. However, more important to the long-term decommissioning of the reactors (and clean-up) on the FDNPP, is the knowledge that core integrity of reactor Unit 1 was compromised with nuclear material existing outside of the reactors primary containment.
Miyato, Naoaki; Yagi, Masatoshi; Scott, B. D.*
Physics of Plasmas, 22(1), p.012103_1 - 012103_9, 2015/01
Times Cited Count:7 Percentile:32.46(Physics, Fluids & Plasmas)Two representations of fluid moments, which are called push-forward representations, are compared in the standard electrostatic gyrokinetic model. In the conventional representation the gyro-center part appears as the pull-back transformation of the gyro-center distribution function which contains scalar functions generating the gyro-center transformation. Usually only the lowest order solution of the generating function at first order is considered. This is true in explicitly deriving representations of scalar fluid moments with polarization terms. However, higher-order solutions are needed to derive finite Larmor radius terms of particle flux including the polarization flux from the conventional representation. On the other hand, the lowest order solution is sufficient for the other representation in which the gyro-center part is combined with the guiding-center one and the pull-back transformation of the distribution function does not appear.
Bolton, P.; Borghesi, M.*; Brenner, C.*; Carroll, D. C.*; De Martinis, C.*; Fiorini, F.*; Flacco, A.*; Floquet, V.*; Fuchs, J.*; Gallegos, P.*; et al.
Physica Medica; European Journal of Medical Physics, 30(3), p.255 - 270, 2014/05
Times Cited Count:79 Percentile:88.97(Radiology, Nuclear Medicine & Medical Imaging)Miyato, Naoaki; Scott, B. D.*; Yagi, Masatoshi
Plasma Physics and Controlled Fusion, 55(7), p.074011_1 - 074011_6, 2013/07
Times Cited Count:10 Percentile:40.62(Physics, Fluids & Plasmas)Miyato, Naoaki; Scott, B. D.*
Plasma and Fusion Research (Internet), 6, p.1403147_1 - 1403147_11, 2011/12
Miyato, Naoaki; Scott, B. D.*; Yagi, Masatoshi
Proceedings of Plasma Conference 2011 (PLASMA 2011) (CD-ROM), 2 Pages, 2011/11
 B flow on gyrokinetics
B flow on gyrokineticsMiyato, Naoaki; Scott, B. D.*; Tokuda, Shinji*; Yagi, Masatoshi
Proceedings of 23rd IAEA Fusion Energy Conference (FEC 2010) (CD-ROM), 8 Pages, 2011/03
Based on the phase space Lagrangian Lie-transform perturbation method and the field theory, a reduced kinetic model with large E B flow beyond the standard ordering (
B flow beyond the standard ordering (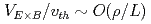 ) is constructed by modifying the guiding-centre phase space trans-formation. The model can be regarded as a natural extension of the standard model without flow since the symplectic part of the Lagrangian is the same as the standard one formally. Some aspects of the model are revealed and effects of the flow are discussed in course of comparison with the standard model. The push-forward representation of general particle fluid moment is presented in the subsonic flow case. In sonic flow case, corrections to the reduced quasi-neutrality condition due to the E
) is constructed by modifying the guiding-centre phase space trans-formation. The model can be regarded as a natural extension of the standard model without flow since the symplectic part of the Lagrangian is the same as the standard one formally. Some aspects of the model are revealed and effects of the flow are discussed in course of comparison with the standard model. The push-forward representation of general particle fluid moment is presented in the subsonic flow case. In sonic flow case, corrections to the reduced quasi-neutrality condition due to the E B flow are found by variational derivation of the push-forward representation of particle density.
B flow are found by variational derivation of the push-forward representation of particle density.
Scott, B. D.*; Da Silva, F.*; Kendl, A.*; Miyato, Naoaki; Ribeiro, T.*
Proceedings of 23rd IAEA Fusion Energy Conference (FEC 2010) (CD-ROM), 8 Pages, 2011/03
We report on developments in the theory and computation of gyrokinetic turbulence in the tokamak edge. A new formulation of the gyrokinetic Lagrangian for the strong E B-flow regime is been found, with clear correspondence to previous forms and to reduced MHD. Conservation of energy, mo-mentum, entropy, and particles is demonstrated at both theoretical and computational level. Neoclassical phenomena and MHD equilibration are shown in our electromagnetic total-f phase-space computational model FEFI. Delta-f gyrokinetic edge turbulence is computed on the full flux surface with the local fluxtube model delta-FEFI and results on the edge/core transition are given. We also present ongoing gyrofluid studies of ELM crash scenarios, including the influence of the bootstrap current in an edge pedestal model on both the initial instability and the resulting turbulence.
B-flow regime is been found, with clear correspondence to previous forms and to reduced MHD. Conservation of energy, mo-mentum, entropy, and particles is demonstrated at both theoretical and computational level. Neoclassical phenomena and MHD equilibration are shown in our electromagnetic total-f phase-space computational model FEFI. Delta-f gyrokinetic edge turbulence is computed on the full flux surface with the local fluxtube model delta-FEFI and results on the edge/core transition are given. We also present ongoing gyrofluid studies of ELM crash scenarios, including the influence of the bootstrap current in an edge pedestal model on both the initial instability and the resulting turbulence.
Bottino, A.*; Scott, B. D.*; Brunner, S.*; McMillan, B. F.*; Tran, T. M.*; Vernay, T.*; Villard, L.*; Jolliet, S.; Hatzky, R.*; Peeters, A. G.*
IEEE Transactions on Plasma Science, 38(9), p.2129 - 2135, 2010/09
Times Cited Count:26 Percentile:69.17(Physics, Fluids & Plasmas)Miyato, Naoaki; Scott, B. D.*; Tokuda, Shinji*
Journal of Plasma and Fusion Research SERIES, Vol.9, p.546 - 551, 2010/08
Generally guiding-centre (GC) or gyro-centre fluid moments are different from corresponding particle fluid moments due to finite Larmor radius effects. Recently we derived a modified GC fundamental 1-form with strong E B flow from which a GC Vlasov-Poisson system was also constructed through the field theory. In contrast to conventional formulations with strong E
B flow from which a GC Vlasov-Poisson system was also constructed through the field theory. In contrast to conventional formulations with strong E B flow, the symplectic part of our GC 1-form is the same as that in the standard gyrokinetic model formally. The GC Hamiltonian also agrees with the standard gyrokinetic Hamiltonian in the long wavelength limit. Therefore it is expected that the relation between the fluid moments in the modified GC coordinates and the particle-fluid moments is similar to the one obtained from the standard gyrokinetic model in the long wavelength limit. We represent the particle fluid moment in terms of the modified GC fluid moments. The representation is compared with the standard gyrokinetic result.
B flow, the symplectic part of our GC 1-form is the same as that in the standard gyrokinetic model formally. The GC Hamiltonian also agrees with the standard gyrokinetic Hamiltonian in the long wavelength limit. Therefore it is expected that the relation between the fluid moments in the modified GC coordinates and the particle-fluid moments is similar to the one obtained from the standard gyrokinetic model in the long wavelength limit. We represent the particle fluid moment in terms of the modified GC fluid moments. The representation is compared with the standard gyrokinetic result.
Miyato, Naoaki; Scott, B. D.*
Proceedings of 37th European Physical Society Conference on Plasma Physics (EPS 2010) (CD-ROM), 4 Pages, 2010/06
Reduced kinetic models such as gyrokinetic models are constructed by phase space transformation from particle phase space to guiding-centre phase space. In the reduced quasi-neutrality condition or the Poisson equation for electrostatic potential, particle density should be represented in terms of guiding-centre things. It is called push-forward representation of particle density. Recently a reduced kinetic model with large flow was derived by modifying the standard guiding-centre transformation. The model can be regarded as a natural extension of the standard model to the large flow regime because the symplectic part in the guiding-centre phase space Lagrangian is the same as the standard one formally. The push-forward representation of particle density or the reduced quasi-neutrality condition in the transonic case is derived by the variational method. It is found that corrections due to the flow appear in the polarisation density.
 B flow
B flowMiyato, Naoaki; Scott, B. D.*; Strintzi, D.*; Tokuda, Shinji
Journal of the Physical Society of Japan, 78(10), p.104501_1 - 104501_13, 2009/10
Times Cited Count:28 Percentile:76.99(Physics, Multidisciplinary)A modified guiding-centre fundamental 1-form with strong 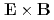 flow is derived by the phase space Lagrangian Lie perturabtion method. Since the symplectic part of the derived 1-form is the same as the standard one without the strong
flow is derived by the phase space Lagrangian Lie perturabtion method. Since the symplectic part of the derived 1-form is the same as the standard one without the strong 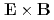 flow, it yields the standard Lagrange and Poisson brackets. Therefore the guiding-centre Hamilton equations keep their general form even when temporal evolution of the
flow, it yields the standard Lagrange and Poisson brackets. Therefore the guiding-centre Hamilton equations keep their general form even when temporal evolution of the 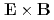 flow is allowed. Compensation of keeping the standard symplectic structure is paid by complication of the guiding-centre Hamiltonian. However it is possible to simplify the Hamiltonian in well localised transport barrier regions like a tokamak H-mode edge and an internal transport barrier in a reversed shear tokamak. The guiding-centre Vlasov and Poisson equations are derived from the variational principle. The conserved energy of the system is obtained from the Noether's theorem.
flow is allowed. Compensation of keeping the standard symplectic structure is paid by complication of the guiding-centre Hamiltonian. However it is possible to simplify the Hamiltonian in well localised transport barrier regions like a tokamak H-mode edge and an internal transport barrier in a reversed shear tokamak. The guiding-centre Vlasov and Poisson equations are derived from the variational principle. The conserved energy of the system is obtained from the Noether's theorem.
 Rf
RfQian, J.*; Heinz, A.*; Khoo, T. L.*; Janssens, R. V. F.*; Peterson, D.*; Seweryniak, D.*; Ahmad, I.*; Asai, Masato; Back, B. B.*; Carpenter, M. P.*; et al.
Physical Review C, 79(6), p.064319_1 - 064319_13, 2009/06
Times Cited Count:31 Percentile:83.80(Physics, Nuclear) -,
-,  -, and conversion electron spectroscopy experiments for
-, and conversion electron spectroscopy experiments for  Rf have been performed using Fragment Mass Analyzer at Argonne National Laboratory. A new isomer with a half-life of 160
Rf have been performed using Fragment Mass Analyzer at Argonne National Laboratory. A new isomer with a half-life of 160  s has been discovered in
s has been discovered in  Rf, and it is interpreted as a three-quasiparticle high-
Rf, and it is interpreted as a three-quasiparticle high- isomer. Neutron configurations of one-quasiparticle states in
isomer. Neutron configurations of one-quasiparticle states in 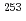 No, the
No, the  -decay daughter of
-decay daughter of  Rf, have been assigned on the basis of
Rf, have been assigned on the basis of  -decay hindrance factors. Excitation energies of the 1/2
-decay hindrance factors. Excitation energies of the 1/2 [620] states in
[620] states in  =151 isotones indicate that the deformed shell gap at
=151 isotones indicate that the deformed shell gap at  =152 increases with the atomic number.
=152 increases with the atomic number.
Miyato, Naoaki; Scott, B. D.*; Yagi, Masatoshi
no journal, ,
 B flow
B flowMiyato, Naoaki; Scott, B. D.*; Yagi, Masatoshi
no journal, ,
Reduced fluid models are widely used for nonlinear simulations of magnetised fusion plasmas. Traditionally they are derived from more rigorous fluid model such as the Braginskii model by imposing assumptions like low frequency perturbations. In the traditional derivation, calculation of the gyroviscosity is needed and it is very complicated. Alternatively reduced fluid models can be derived from fluid moment equations of reduced kinetic models. We can bypass the calculation of the gyroviscosity in the alternative method. Recently we derived a reduced kinetic model for plasmas with large E B velocity. Based on the reduced kinetic model, reduced fluid equations are derived and the gyroviscous force is obtained by comparing the reduced equations and fluid equations without reduction.
B velocity. Based on the reduced kinetic model, reduced fluid equations are derived and the gyroviscous force is obtained by comparing the reduced equations and fluid equations without reduction.
Miyato, Naoaki; Scott, B. D.*; Yagi, Masatoshi
no journal, ,
Since perturbations with short wavelength and small amplitude are considered in the standard gyrokinetic formulation, there is no reason why the standard model is still valid in the long wavelength regime. So far, we clarified by reviewing the gyrokinetic formulation in the electrostatic limit that the high-order displacement vector associated with the guiding-centre transform, which is neglected in the standard formulation, should be considered in the long wavelength regime. This time we reconsider the electromagnetic gyrokinetic model with shear Alfv n perturbation (
n perturbation (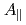 ) in which the parallel canonical momentum (
) in which the parallel canonical momentum (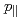 ) is one of velocity variables. The symplectic part of the model has the same form as the electrostatic one and we can apply the same guiding-centre transformation as the electrostatic case. However, the gyrokinetic Hamiltonian is modified by the magnetic perturbations.
) is one of velocity variables. The symplectic part of the model has the same form as the electrostatic one and we can apply the same guiding-centre transformation as the electrostatic case. However, the gyrokinetic Hamiltonian is modified by the magnetic perturbations.
 B flow
B flowMiyato, Naoaki; Scott, B. D.*; Strintzi, D.*; Tokuda, Shinji
no journal, ,
A guiding-centre fundamental 1-form with strong E B flow for a single charged particle is derived by the Lie transform perturbation analysis. The symplectic part of the 1-form does not include the E
B flow for a single charged particle is derived by the Lie transform perturbation analysis. The symplectic part of the 1-form does not include the E B term which is included in the symplectic part in the previous formulations. As a result, it is the same as the standard one without the strong flow formally and gives the standard Hamilton equations even when time evolution of the E
B term which is included in the symplectic part in the previous formulations. As a result, it is the same as the standard one without the strong flow formally and gives the standard Hamilton equations even when time evolution of the E B flow is allowed. Although the guiding-centre Hamiltonian is more complicated than the previous ones, it can be simplified in well localised transport barrier regions such as a tokamak H-mode edge where the strong E
B flow is allowed. Although the guiding-centre Hamiltonian is more complicated than the previous ones, it can be simplified in well localised transport barrier regions such as a tokamak H-mode edge where the strong E B flow is observed. Based on the derived 1-form, a total Lagrangian including both contributions from particles and fields is constructed. The guiding-centre Vlasov and Poisson equations are derived from the variational principle. The conserved energy of the system is obtained from the Lagrangian by the Noether method.
B flow is observed. Based on the derived 1-form, a total Lagrangian including both contributions from particles and fields is constructed. The guiding-centre Vlasov and Poisson equations are derived from the variational principle. The conserved energy of the system is obtained from the Lagrangian by the Noether method.
Miyato, Naoaki; Scott, B. D.*; Yagi, Masatoshi
no journal, ,