Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Shibano, Junichi*; Kajiwara, Kentaro*; Tsukamoto, Takuya*; Kawai, Hirokazu*; Miura, Setsuo*; Zhang, S.*; Shobu, Takahisa
Zairyo, 63(7), p.533 - 538, 2014/07
A ductile damage progress of an aluminum single crystal with the prior activity of the single slip system under tensile loading was verified by a profile analysis using white X-ray obtained in BL28B2 beam line of SPring-8. In profile analysis, an instrumental function was defined in consideration both of a divergence by slits and a response function peculiar to the energy dispersive method. As a result, dislocation density increased as ductile damage progressed, but it was relatively low near the notch. The influence of a release of the strain energy by a ductile damage progress was expected. The characteristics of ductile damage progress near the notch of the aluminum single crystal with a prior activity of a single slip system under the tensile loading were clarified from the distribution of dislocation density.
Shibano, Junichi*; Kajiwara, Kentaro*; Tsukamoto, Takuya*; Kawai, Hirokazu*; Miura, Setsuo*; Zhang, S.*; Shobu, Takahisa; Kobayashi, Michiaki*
Materials Science Forum, 777, p.176 - 181, 2014/02
Times Cited Count:1 Percentile:53.38(Materials Science, Multidisciplinary)Shibano, Junichi*; Kiso, Minoru*; Kajiwara, Kentaro*; Shobu, Takahisa; Miura, Setsuo*; Kobayashi, Michiaki*
Zairyo, 62(7), p.443 - 450, 2013/07
The ductile damage progress of the FCC single crystal was verified by the profile analysis using the white X-ray obtained in BL28B2 beam-line of SPring-8. In this study, an aluminum single crystal of the purity 6N was used as a specimen prepared in the I-type geometry for tensile test. The notch was introduced into one side of the center of a parallel part of the specimen by wire electric discharge machining. White X-ray, which has 200 microns in height and 100 microns in width, was incident into the specimen on the Bragg angle of 3 in the horizontal plane using energy dispersive X-ray diffraction technique. As a result, in 1.1% of applied strain, increase of the lattice strain was observed in the direction of about 45
in the horizontal plane using energy dispersive X-ray diffraction technique. As a result, in 1.1% of applied strain, increase of the lattice strain was observed in the direction of about 45 of slant from the notch bottom. In 2.2% of applied strain, the lattice strain reduced in the direction of about 45
of slant from the notch bottom. In 2.2% of applied strain, the lattice strain reduced in the direction of about 45 of slant from the notch bottom. Non-uniform strain and dislocation density decreased similarly.
of slant from the notch bottom. Non-uniform strain and dislocation density decreased similarly.
Shibano, Junichi*; Kajiwara, Kentaro*; Kiriyama, Koji*; Shobu, Takahisa; Suzuki, Kenji*; Nishimura, Suguru*; Miura, Setsuo*; Kobayashi, Michiaki*
Materials Science Forum, 638-642, p.2476 - 2481, 2010/01
Shobu, Takahisa; Shibano, Junichi*
Zairyo, 58(11), p.948 - 954, 2009/11
no abstracts in English
Shibano, Junichi*; Kiriyama, Koji; Kajiwara, Kentaro*; Shobu, Takahisa; Suzuki, Kenji*; Arai, Takayuki*; Miura, Setsuo*; Kobayashi, Michiaki*
Zairyo, 58(7), p.596 - 602, 2009/07
Shibano, Junichi*; Kajiwara, Kentaro*; Kiriyama, Koji; Shobu, Takahisa; Suzuki, Kenji*; Nishimura, Suguru*; Miura, Setsuo*; Kobayashi, Michiaki*
Zairyo, 57(7), p.667 - 673, 2008/07
Shibano, Junichi*; Shobu, Takahisa; Suzuki, Kenji*; Kiriyama, Koji; Kajiwara, Kentaro*; Kaneko, Hiroshi; Kobayashi, Michiaki*
Materials Science Forum, 571-572, p.267 - 270, 2008/00
Shibano, Junichi*; Shobu, Takahisa; Suzuki, Kenji*; Hirata, Tomoyuki*; Kaneko, Hiroshi; Kobayashi, Michiaki*
Zairyo, 56(10), p.985 - 992, 2007/10
This paper presents a basic research on a measurement of strain in the bulk of materials by using high energy white X-rays from a synchrotron radiation source of SPring-8. WEL-TEN780E (JIS G3128 SHY685) whose grain size was 0.013 mm was used as a specimen. The specimen was loaded with four point bending. The white X-ray beam, which has a height of 0.05 mm and width of 0.03 mm, was incident in it. Bending strain at the surface of specimen was measured by a strain gauge. The internal strain of SHY685 of 5 mm thickness could be evaluated using white X-rays which range of energy from 60 keV to 150 keV. Furthermore, the measurement error of strain could be decreased by using the diffracted X-rays with high energy, high peak count and the profile which is close to Gaussian curve. The results showed that the high energy white X-ray is effective for internal strain measurements.
Shobu, Takahisa; Kaneko, Hiroshi; Mizuki, Junichiro; Konishi, Hiroyuki; Shibano, Junichi*; Hirata, Tomoyuki*; Suzuki, Kenji*
AIP Conference Proceedings 879, p.1581 - 1585, 2007/01
The third generation synchrotron X-ray source such as SPring-8 provides us intense beams of high energy X-rays. The techniques of non-destructive internal residual stress measurement for industrial applications are well established by angle dispersive diffractometry with high energy synchrotron radiation and provide valuable information. The energy dispersive diffraction techniques using white radiation is the advantage of a stress measurement compared with the angular dispersive one. For example, the multitudes of reflections recorded in one spectrum offers additional information that can be used for stress gradient evaluation. The purpose of present study is to apply high energy white X-rays to the measurement of the residual strain in the bulk specimen. The experiment was carried out on the beamline BL14B1 at SPring-8. A diffraction pattern was collected by a Ge Solid State Detector (SSD) mounted on the arm of a 2-axes diffractometer behind two sets of secondary collimating slits. The beam size of white X-rays was 0.05  0.3 mm
0.3 mm . The specimens were JIS-S45C carbon steel and JIS-SUS304 austenitic stainless steel with a thickness of 5mm. The bending stress was applied with the four-point bending and the strain at the surface of the specimen was measured by a strain gauge as shown in the figure. X-rays diffraction measurement was carried out simultaneously. The figure shows each diffraction profile of SUS304 taken with white X-rays. The strain was calculated by the ratio of the energy shift to the peak energy. Though many peaks appeared in every measured positions Y, each diffraction pattern depended on the number and the orientation of crystal grains in irradiated volume by X-rays. The calculated strain by using a single peak is depending on peak quality. The accurate internal stress can be obtained with white X-rays by selecting the peak at high energy, high peak counts and close to Gaussian peak profile.
. The specimens were JIS-S45C carbon steel and JIS-SUS304 austenitic stainless steel with a thickness of 5mm. The bending stress was applied with the four-point bending and the strain at the surface of the specimen was measured by a strain gauge as shown in the figure. X-rays diffraction measurement was carried out simultaneously. The figure shows each diffraction profile of SUS304 taken with white X-rays. The strain was calculated by the ratio of the energy shift to the peak energy. Though many peaks appeared in every measured positions Y, each diffraction pattern depended on the number and the orientation of crystal grains in irradiated volume by X-rays. The calculated strain by using a single peak is depending on peak quality. The accurate internal stress can be obtained with white X-rays by selecting the peak at high energy, high peak counts and close to Gaussian peak profile.
Shibano, Junichi*; Kiriyama, Koji; Kajiwara, Kentaro*; Shobu, Takahisa; Suzuki, Kenji*; Arai, Takayuki*; Miura, Setsuo*; Kobayashi, Michiaki*
no journal, ,
no abstracts in English
Kiriyama, Koji; Shobu, Takahisa; Shibano, Junichi*; Kaneko, Hiroshi
no journal, ,
Inner strain measurement of duplex stainless steel, many reflection data will be need to analyze strain because of considering with each strain of phase. Therefore, strain measurement method using SR white X-ray are effective to get many reflection by using energy-dispersive X-ray spectroscopy. The results show that the method is suitable to be applied to strain measure of duplex stainless steel, and that correlation between measured strain and elastic constants of reflection face.
Kiriyama, Koji; Shobu, Takahisa; Shibano, Junichi*; Kaneko, Hiroshi
no journal, ,
Duplex stainless steels are estimated to show complicated strain behavior when tensile loading because of a micro texture mixed  -Fe and
-Fe and  -Fe. In this study, to understand micro strain behavior of duplex stainless steels, inner strain of SUS329J1 have been measured under tensile loading using synchrotron white X-ray at SPring-8. Results showed that many lattice strains decreased at an applied strain, 0.0016e, and oscillated as applied strains increased. These suggested that local plastic deformation caused by slipping at some planes, for example
-Fe. In this study, to understand micro strain behavior of duplex stainless steels, inner strain of SUS329J1 have been measured under tensile loading using synchrotron white X-ray at SPring-8. Results showed that many lattice strains decreased at an applied strain, 0.0016e, and oscillated as applied strains increased. These suggested that local plastic deformation caused by slipping at some planes, for example 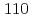 of
of  -Fe
-Fe 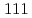 of
of  -Fe, occurred in the specimen although the range of loaded stress is under elastic deformation.
-Fe, occurred in the specimen although the range of loaded stress is under elastic deformation.
Kiriyama, Koji; Shobu, Takahisa; Shibano, Junichi*; Fujishiro, Tomoyuki; Kaneko, Hiroshi; Miura, Setsuo*
no journal, ,
Shobu, Takahisa; Yasuda, Ryo*; Shiro, Ayumi*; Yoshida, Yutaka*; Tokuda, Susumu*; Shibano, Junichi*; Kumagai, Masayoshi*
no journal, ,
A dislocation density increases and fatigue failure of the structure occur, when a metal is deformed. In this study, dislocation density of a broken 0.3 mm thick SUS316L specimen was calculated by line profile analysis obtained by high energy synchrotron X-ray diffraction method, and a relationship between fatigue fracture and dislocation density was evaluated. As a result of the analysis, it was revealed that the dislocation density abruptly increases as approaching the fracture part. In addition, it was revealed that the bcc structure appeared in the fcc structure which is the basic structure in the fracture part. In steel, the increase in dislocation density is closely related to the increase in material strength, and the material strength of steel with bcc structure is known to be higher than that with fcc structure. So, it seems that the structure has changed due to a sharp increase in dislocation density at the fracture part.
Shobu, Takahisa; Konishi, Hiroyuki; Suzuki, Kenji*; Shibano, Junichi*; Akiniwa, Yoshiaki*; Tanaka, Keisuke*
no journal, ,
no abstracts in English
Kiriyama, Koji; Shibano, Junichi*; Hirata, Tomoyuki*; Kajiwara, Kentaro*; Shobu, Takahisa; Suzuki, Kenji*
no journal, ,
no abstracts in English
Kiriyama, Koji; Shibano, Junichi*; Nishimura, Suguru*; Shobu, Takahisa; Kaneko, Hiroshi; Kajiwara, Kentaro*; Suzuki, Kenji*
no journal, ,
no abstracts in English
Kiriyama, Koji; Shibano, Junichi*; Kajiwara, Kentaro*; Shobu, Takahisa; Suzuki, Kenji*; Kaneko, Hiroshi; Nishimura, Suguru*; Arai, Takayuki*; Miura, Setsuo*; Kobayashi, Michiaki*
no journal, ,
Residual stress measurement is important to understand Stress Corrosion Cracking process. In this study, measurements of imaging and inner stress mapping around a crack-tip in steel material (alpha-Fe) have performed at beam-line BL14B1 and BL28B2 at SPring-8. The results showed that artificial cracking in the sample was clearly measured by imaging and that stress maps quite correspond to the result of imaging. Therefore, these methods are very effective tool for measurement of inner state of steel material.
Kiriyama, Koji; Shibano, Junichi*; Kajiwara, Kentaro*; Shobu, Takahisa; Suzuki, Kenji*; Kaneko, Hiroshi; Nishimura, Suguru*; Arai, Takayuki*
no journal, ,
Residual stress measurement is important to understand SCC (Stress Corrosion Cracking) process. In this study, CT (Computed Tomography) imaging and inner strain mapping of steel material (alpha-Fe) have performed at BL28B2 at SPring-8. The result showed that artificial cracking in the sample was clearly measured by CT and that strain maps quite correspond to CT image. Therefore, these methods are very effective tool to measure an inner state of steel material.