Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Kimura, Atsushi; Nagasawa, Naotsugu; Shimada, Akihiko; Taguchi, Mitsumasa
Radiation Physics and Chemistry, 124, p.130 - 134, 2016/07
Times Cited Count:9 Percentile:64.88(Chemistry, Physical)no abstracts in English
Seguchi, Tadao*; Tamura, Kiyotoshi*; Kudo, Hisaaki*; Shimada, Akihiko; Sugimoto, Masaki
IEEE Transactions on Dielectrics and Electrical Insulation, 22(6), p.3197 - 3206, 2015/12
Times Cited Count:28 Percentile:76.71(Engineering, Electrical & Electronic)The degradation of ethylene propylene rubber (EPR) sheets as a cable insulation material for nuclear power plants (NPP) was studied by accelerated thermal ageing, radiation ageing and thermal - radiation combined ageing. The oxidation of EPR proceeded with ageing and the decay of mechanical property was closely related to the content of oxidation products. The antioxidant as a stabilizer in EPR was effective for the thermal oxidation, but not for the radiation oxidation. For the thermal and radiation combined oxidation, the mechanical property and the content of oxidation products were different among the treatment sequences due to the decay of antioxidant. The lifetime of EPR cable is closely related to the remaining content of antioxidant, and the lifetime evaluation would be recommended by the reverse sequential combination (thermal ageing after radiation ageing).
Abe, Hiroshi; Shimomura, Takuya; Tokuhira, Shinnosuke*; Shimada, Yukihiro*; Takenaka, Yusuke*; Furuyama, Yuta*; Nishimura, Akihiko; Uchida, Hirohisa*; Daido, Hiroyuki; Oshima, Takeshi
Proceedings of 7th International Congress on Laser Advanced Materials Processing (LAMP 2015) (Internet), 4 Pages, 2015/08
A short pulse laser (the nanosecond and femtosecond) was applied to hydrogen absorbing alloys surface layer, and a surface modification experiment was put into effective to aim at improvement of hydrogen adsorption functionally. It was investigated about correlation between an initial hydrogen absorption reaction rate of hydrogen alloys and a laser irradiation in this research. The laser irradiation condition was done with pulse width 100 fsec and energy 0.2 - 3.4 mJ/pulse. It blazed down on hydrogen absorbing alloys (LaNi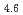 Al
Al ) and changed local order in the surface. As a result, the initial hydrogen absorption reaction rate was 1.5 - 3.0 times as fast as a irradiated sample, and the result and laser irradiated sample found out that a hydrogen absorption function improves. A laser irradiation can conclude to be effective in surface modification of the hydrogen storage materials.
) and changed local order in the surface. As a result, the initial hydrogen absorption reaction rate was 1.5 - 3.0 times as fast as a irradiated sample, and the result and laser irradiated sample found out that a hydrogen absorption function improves. A laser irradiation can conclude to be effective in surface modification of the hydrogen storage materials.
 -ray irradiated polyethylene with KOH treatment and SEM-EDS
-ray irradiated polyethylene with KOH treatment and SEM-EDSShimada, Akihiko; Sugimoto, Masaki; Yoshikawa, Masahito
JAEA-Review 2014-050, JAEA Takasaki Annual Report 2013, P. 30, 2015/03
In case of the accelerated ageing test on polymer cable insulation used for the nuclear power facility, it is very important to recognize whether oxygen penetrates in the polymer wholly or not. To confirm this, there are the method by which polymer is soaked in the KOH solution at 70 C for 5 minutes, dried and observed by a SEM-EDS, only for ethylene propylene rubber, one of the polymers. This study is to apply that method for polyethylene. Polyethylene sheet of 2 mm thickness was irradiated by
C for 5 minutes, dried and observed by a SEM-EDS, only for ethylene propylene rubber, one of the polymers. This study is to apply that method for polyethylene. Polyethylene sheet of 2 mm thickness was irradiated by  ray at a dose rate of 2 kGy/h for 400 h. A piece of irradiated polyethylene was picked up and the piece was soaked in the KOH solution for 24 h. After that, the piece was observed by a SEM-EDS. At the region within 70 micro meters from the surface, potassium is observed. It means that oxidation is occurred in this region. From now on, optimum soaking time will be examined.
ray at a dose rate of 2 kGy/h for 400 h. A piece of irradiated polyethylene was picked up and the piece was soaked in the KOH solution for 24 h. After that, the piece was observed by a SEM-EDS. At the region within 70 micro meters from the surface, potassium is observed. It means that oxidation is occurred in this region. From now on, optimum soaking time will be examined.
Shimoyama, Iwao; Hakoda, Teruyuki; Shimada, Akihiko; Baba, Yuji
Carbon, 81, p.260 - 271, 2015/01
Times Cited Count:23 Percentile:58.72(Chemistry, Physical)The relationship between catalytic activity and local structure at dopant sites of phosphorus-doped graphite prepared by ion implantation was studied by electrochemical measurements and near-edge X-ray absorption fine structure (NEXAFS) spectroscopy. The P K-edge NEXAFS spectra of samples doped at room temperature and high temperature showed different polarization dependences, with graphite-like clear polarization dependence observed for the sample prepared by high-temperature doping. NEXAFS spectra were analyzed by density functional theory calculations to reveal the chemical-bonding states of P sites. In electrochemical measurements with an acid solution, samples with relatively small polarization dependence of NEXAFS exhibited marked catalytic activity in oxygen reduction reactions while those with larger polarization dependence showed lower catalytic activity. This indicates the influence of the configuration at dopant sites on catalytic activity and suggests that the introduction of curved structures is one way to design carbon catalysts with high catalytic activity.
Shimada, Akihiko
Hoshasen To Sangyo, (136), p.33 - 35, 2014/06
Recovery from the accident at Tokyo Electric Power Company Fukushima Dai-ichi Nuclear Power Plant (NPP) is a matter of great urgency. In order to realize safe and secure operation for decontamination and decommissioning of NPP, it is indispensable to use equipments with sufficient radiation resistance (RR). In JAEA as well as other agency, various studies on RR of various materials and equipments have been conducted and a number of reports and papers have been published. Then, we started construction of a database named as "Database of Radiation Resistance on Polymer Materials and Equipments" and announced this database in a press release on June 1, 2012. At present, the database includes 878 data of materials, which are consisted of 423 data of polymer materials, 223 data of equipments and parts, 103 data of oils, fats and paintcoatings and 129 data of organic composite materials. The database will be extended and expected to be utilized for safe and secure operation.
Shimada, Akihiko; Sugimoto, Masaki; Miyashita, Atsumi; Yoshikawa, Masahito
JAEA-Review 2013-059, JAEA Takasaki Annual Report 2012, P. 29, 2014/03
Recovery from the accident at Tokyo Electric Power Company Fukushima Dai-ichi Nuclear Power Plant (NPP) is a matter of great urgency. In order to realize safe and secure operation for decontamination and decommissioning of NPP, it is indispensable to use equipments with sufficient radiation resistance (RR). In JAEA as well as other agency, various studies on RR of various materials and equipments have been conducted and a number of reports and papers have been published. Then, we started construction of a database named as "Database of Radiation Resistance on Polymer Materials and Equipments" and announced this database in a press release on June 1, 2012. At present, the database includes 878 data of materials, which are consisted of 423 data of polymer materials, 223 data of equipments and parts, 103 data of oils, fats and paintcoatings and 129 data of organic composite materials. The database will be extended and expected to be utilized for safe and secure operation.
Hiyama, Kazuhisa; Hanawa, Nobuhiro; Kurosawa, Akihiko; Eguchi, Shohei; Hori, Naohiko; Kusunoki, Tsuyoshi; Ueda, Hisao; Shimada, Hiroshi; Kanda, Hiroaki*; Saito, Isamu*
JAEA-Technology 2013-045, 32 Pages, 2014/02
This report summarizes regarding to develop of real-time multifunctional access control system which is able to manage worker's access control and exposure dose at real-time in the reactor building, besides worker's location and worker might be fall down by accident.
Shimada, Akihiko; Sugimoto, Masaki; Kudo, Hisaaki*; Tamura, Kiyotoshi*; Seguchi, Tadao*
IEEE Transactions on Dielectrics and Electrical Insulation, 21(1), p.16 - 23, 2014/02
The thermal and radiation ageing behaviors and degradation mechanisms of SiR for the cable insulation of nuclear power plants were studied. The thermal ageing and radiation ageing in air were conducted up to 235 C and 195
C and 195 C, respectively. The dose rate of radiation ageing is 1 kGy/h. Thermal ageing in vacuum as well as in air was also conducted. The degraded SiR is evaluated by tensile test, gel fraction measurement, swelling ratio measurement and weight measurement, and then the results are analyzed. It is appeared that the radiation degradation of SiR at high temperature is much more severe than that of SiR at low temperature at the same dose. Focusing on the molecular structure, it is supposed that crosslinking reagents which are included in SiR are removed, oxygen atom is attached instead of the reagents and new crosslinking is foamed. Their behaviors are different from the polymer of hydrocarbon.
C, respectively. The dose rate of radiation ageing is 1 kGy/h. Thermal ageing in vacuum as well as in air was also conducted. The degraded SiR is evaluated by tensile test, gel fraction measurement, swelling ratio measurement and weight measurement, and then the results are analyzed. It is appeared that the radiation degradation of SiR at high temperature is much more severe than that of SiR at low temperature at the same dose. Focusing on the molecular structure, it is supposed that crosslinking reagents which are included in SiR are removed, oxygen atom is attached instead of the reagents and new crosslinking is foamed. Their behaviors are different from the polymer of hydrocarbon.
Shimada, Akihiko; Sugimoto, Masaki; Kudo, Hisaaki*; Tamura, Kiyotoshi*; Seguchi, Tadao*
IEEE Transactions on Dielectrics and Electrical Insulation, 20(6), p.2107 - 2116, 2013/12
Times Cited Count:39 Percentile:82.85(Engineering, Electrical & Electronic)The degradation of cables by the accelerated thermal and radiation ageing for nuclear power plant was studied. The thermal oxidation of crosslinked polyethylene (XLPE) as a cable insulation showed the heterogeneous features along the depth of sheet specimens. The degree of oxidation was closely related to the distribution of antioxidant content due to the decay of antioxidant content by the evaporation and radiation decomposition during accelerated ageing. The specific relations were observed between the tensile properties and the yield of oxidation products and also between the oxidation products and antioxidant content in XLPE specimens. The yields and the content and their distribution were detected by FTIR. The oxidation of XLPE containing antioxidant of enough content proceeded proportionally with ageing time or radiation dose at any ageing conditions. When the antioxidant content decreased less than a limited content by thermal and/or radiation ageing, the oxidation rate by thermal ageing increased sharply with ageing time. Therefore, the oxidation at surface of XLPE was much accelerated when the antioxidant decreased to result the heterogeneous oxidation. The mechanical properties depend closely on the degree of oxidation at the surface. The behavior of oxidation was also affected by the types of antioxidant.
Shimada, Yukihiro; Nishimura, Akihiko
Journal of Laser Micro/Nanoengineering, 8(1), p.110 - 114, 2013/01
Times Cited Count:7 Percentile:37.82(Nanoscience & Nanotechnology)A fiber Bragg grating (FBG) sensor with heat resistance was produced via a point microfabrication technique using a femtosecond pulse laser. The FBG sensor was reinforced by weaving with a carbon fiber tape. As a result, both high strength and a structure for mounting the sensor were readily incorporated. In a high-temperature tolerance evaluation of the FBG sensor, the temperature and strain were measured by the sensor at 600  C. Therefore, the sensor is effective, and in addition, the problems associated with mounting the sensor on high-temperature piping have been eliminated.
C. Therefore, the sensor is effective, and in addition, the problems associated with mounting the sensor on high-temperature piping have been eliminated.
Sugimoto, Masaki; Shimada, Akihiko; Kudo, Hisaaki*; Tamura, Kiyotoshi; Seguchi, Tadao*
Radiation Physics and Chemistry, 82, p.69 - 73, 2013/01
Times Cited Count:61 Percentile:97.76(Chemistry, Physical)The oxidation products formed by thermal and radiation ageing of crosslinked polyethylene for cable insulation were analyzed by FTIR-ATR spectrometry. The most of products were composed of carboxylic acid, carboxylic ester, and carboxylic anhydride. The carboxylic acid was the primal product, and the others were the secondary products by the thermal reaction of carboxylic acids. The carboxylic acid as the primal oxidation product supports the proposed new oxidation mechanisms that the main chain scission should occur directly by oxidation of polyethylene radicals.
Hirade, Tetsuya; Oka, Toshitaka; Morishita, Norio*; Idesaki, Akira; Shimada, Akihiko
Materials Science Forum, 733, p.151 - 154, 2013/00
Times Cited Count:7 Percentile:93.73(Materials Science, Multidisciplinary)Polyimide polymers such as Kapton show a very good performance at high radiation environment such as in space or in radiation facilities. Positron annihilation lifetime measurement is a widely used method for materials science, and the lifetime of triplet positronium (electron-positron pair) can give important information of free volume of polymers. However, there is no positronium formation in Kapton and hence this method was no applied for polymer studies. Here, we indicated that free positron annihilation lifetime can give information of change of free volume by showing the temperature dependence of the lifetime. We applied this method to study irradiation effects on Kapton and we successfully indicated that the free positron lifetime can be applied for polymer studies.
Seguchi, Tadao*; Tamura, Kiyotoshi*; Watashi, Katsumi; Suzuki, Masahide; Shimada, Akihiko; Sugimoto, Masaki; Idesaki, Akira; Yoshikawa, Masahito; Oshima, Takeshi; Kudo, Hisaaki*
JAEA-Research 2012-029, 158 Pages, 2012/12
The degradation mechanisms of ethylene-propylene rubber (EPR), crosslinked polyethylene (XLPE), polyvinylchloride (PVC), and silicone rubber (SiR) as the cable insulation materials were investigated for the cable ageing research of the nuclear power plant. The materials as same insulations for the practical cable (practical formulation) and as the model formulation containing specific additive were selected. They were exposed to the accelerated radiation and thermal environments. The mechanical properties, the crosslinking and chain scission, and the distribution of antioxidant and of oxidative products were measured and analyzed.
Seguchi, Tadao*; Tamura, Kiyotoshi; Shimada, Akihiko; Sugimoto, Masaki; Kudo, Hisaaki*
Radiation Physics and Chemistry, 81(11), p.1747 - 1751, 2012/11
Times Cited Count:44 Percentile:94.85(Chemistry, Physical)The mechanism of polymer oxidation by radiation and thermal ageing was investigated for the life evaluation of cables installed in radiation environments. The antioxidant as a stabilizer was much effective for thermal oxidation with a small content in polymers, but was not effective for radiation oxidation. The ionizing radiation induced the oxidation to result chain scission even at low temperature, because the free radicals were produced and the antioxidant could not stop the oxidation of radicals with the chain scission. A new mechanism of antioxidant effect for polymer oxidation was proposed. The effect of antioxidant was not the termination of free radicals in polymer chains such as peroxy radicals, but was the depression of initial radical formation in polymer chains by thermal activation. The antioxidant molecule was assumed to delocalize the activated energy in polymer chains by Boltzmann statics (distribution) to result decrease the probability of radical formation at a given temperature. The interaction distance (delocalization area) by one antioxidant molecule was estimated to be 5-10 nm in polymer matrix, though the value would depend on the chemical structure of antioxidant.
Shimada, Akihiko; Sugimoto, Masaki; Kudo, Hisaaki*; Tamura, Kiyotoshi; Seguchi, Tadao*
IEEE Transactions on Dielectrics and Electrical Insulation, 19(5), p.1768 - 1773, 2012/10
Times Cited Count:14 Percentile:59.03(Engineering, Electrical & Electronic)The life of cables installed in nuclear power plant was evaluated by the accelerated ageing tests of thermal and radiation degradation. For radiation degradation, the dose rate was the important points, because the oxidation distribution in the insulation was much affected by dose rate due to oxygen penetration limitation during irradiation. The oxidation distribution was observed by FTIR for crosslinked polyethylene (XLPE) and ethylene propylene rubber (EPR) of cable insulation degraded at various irradiation conditions and compared with the mechanical degradation. The oxidation profile was almost same between a low dose rate at room temperature and a high dose rate at elevated temperature (100  C), and the degradation was same for both irradiations. By increasing the irradiation temperature the oxygen penetration rate increased exponentially and the thermal degradation during irradiation was negligible at around 100
C), and the degradation was same for both irradiations. By increasing the irradiation temperature the oxygen penetration rate increased exponentially and the thermal degradation during irradiation was negligible at around 100  C. Therefore, the dose rate could be increased by 15 times by irradiation at 100
C. Therefore, the dose rate could be increased by 15 times by irradiation at 100  C instead of the irradiation at room temperature for the adequate oxidation throughout insulation. The experimental result was coincident with the theoretical analysis.
C instead of the irradiation at room temperature for the adequate oxidation throughout insulation. The experimental result was coincident with the theoretical analysis.
Seguchi, Tadao*; Tamura, Kiyotoshi; Kudo, Hisaaki*; Shimada, Akihiko; Sugimoto, Masaki; Idesaki, Akira; Oshima, Takeshi; Yoshikawa, Masahito
JAEA-Review 2012-027, 46 Pages, 2012/08
The research on cable degradation mechanisms was conducted for 5 years in 2006 - 2010 as the project research of plant life management for nuclear power plant by NISA (Nuclear and Industrial Safety Agency) of METI (Ministry of Economy, Trade, and Industry). At the finish of above research, the degradation mechanisms were reviewed on the analysis of many reports on cable degradation. The reports published after 1970 were mainly surveyed and the facts or data containing the experimental accuracy were selected. The verified facts, the reasonable interpretation of the facts, unresolved aspects were checked on the view points of recent techniques or analysis, and proposed the new model of degradation mechanisms was proposed.
Nishimura, Akihiko; Terada, Takaya; Shimada, Yukihiro; Yonemoto, Yukihiro*; Yamada, Tomonori
Proceedings of 20th International Conference on Nuclear Engineering and the ASME 2012 Power Conference (ICONE-20 & POWER 2012) (DVD-ROM), 5 Pages, 2012/07
Instrumentation devices using laser technologies were developed for maintenance of coolant piping system. For instrumentation devices, seismic monitoring by optical fiber sensors was able to detect vibration of piping system. X-ray absorption contrast by synchrotron radiation clarified convection motion inside a molten pool produced by laser welding. For surface control technologies, a new probing system was under development for heat exchanger tubes by laser cladding. And laser ablation could be used for surface cleaning. These technologies are expected for maintenance of the piping system of nuclear power plants.
Nishimura, Akihiko; Shimada, Yukihiro
Proceedings of 19th International Conference on Nuclear Engineering (ICONE-19) (CD-ROM), 7 Pages, 2011/10
Laser processing technologies were developed for the purpose of maintenance of FBR's heat exchanger units. Ultrashort laser processing fabricated fiber Bragg grating sensor for seismic monitoring. Fiber laser welding with a newly developed robot system repair cracks on inner wall of heat exchanger tubes. Safety operation of the heat exchanger units will be improved by the advanced laser processing technologies. These technologies are expected to be applied to the maintenance for the next generation FBR's.
Hirota, Koichi; Hakoda, Teruyuki; Shimada, Akihiko; Taguchi, Mitsumasa; Kimura, Atsushi; Kojima, Takuji
Proceedings of 12th International Conference on Radiation Curing in Asia (RadTech Asia 2011) (Internet), p.108 - 109, 2011/06
We have focused on using MnO for the oxidation of intermediates produced from electron beam irradiation of VOC. Manganese dioxide can decompose ozone, produced by the irradiation of air containing VOCs, into activated oxygen, which can ultimately oxide the intermediates. Hybrid system equipped with electron accelerator and MnO
for the oxidation of intermediates produced from electron beam irradiation of VOC. Manganese dioxide can decompose ozone, produced by the irradiation of air containing VOCs, into activated oxygen, which can ultimately oxide the intermediates. Hybrid system equipped with electron accelerator and MnO has demonstrated the complete oxidation of the intermediates produced during the irradiation of xylene and toluene. The electron-beam treatment of dioxin from municipal solid waste incinerator was carried out at Takahama Clean Center in Japan. An incinerator gas of 1000 m
has demonstrated the complete oxidation of the intermediates produced during the irradiation of xylene and toluene. The electron-beam treatment of dioxin from municipal solid waste incinerator was carried out at Takahama Clean Center in Japan. An incinerator gas of 1000 m N/h was diverted downstream of a dry electric precipitator and was irradiated with electron beams using an electron accelerator that supplied 300 kV with a maximum energy of 12 kW. The results showed electron-beam is a promising technology for destroying dioxin in exhaust gases.
N/h was diverted downstream of a dry electric precipitator and was irradiated with electron beams using an electron accelerator that supplied 300 kV with a maximum energy of 12 kW. The results showed electron-beam is a promising technology for destroying dioxin in exhaust gases.