Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Fujita, Natsuko; Miyake, Masayasu; Matsubara, Akihiro*; Ishii, Masahiro*; Watanabe, Takahiro; Jinno, Satoshi; Nishio, Tomohiro*; Ogawa, Yumi; Kimura, Kenji; Shimada, Akiomi; et al.
Dai-35-Kai Tandemu Kasokuki Oyobi Sono Shuhen Gijutsu No Kenkyukai Hokokushu, p.17 - 19, 2024/03
The JAEA-AMS-TONO facility at the Tono Geoscience Center, JAEA has three accelerator mass spectrometers. We report the present status of the JAEA-AMS-TONO.
Kokubu, Yoko; Fujita, Natsuko; Watanabe, Takahiro; Matsubara, Akihiro; Ishizaka, Chika; Miyake, Masayasu*; Nishio, Tomohiro*; Kato, Motohisa*; Ogawa, Yumi*; Ishii, Masahiro*; et al.
Nuclear Instruments and Methods in Physics Research B, 539, p.68 - 72, 2023/06
Times Cited Count:0 Percentile:0.02(Instruments & Instrumentation)The JAEA-AMS-TONO facility at the Tono Geoscience Center, JAEA has an accelerator mass spectrometer (JAEA-AMS-TONO-5MV). The spectrometer enabled us to use a multi-nuclide AMS of carbon-14 ( C), beryllium-10, aluminium-26 and iodine-129, and we have recently been proceeding test measurement of chlorine-36. In response to an increase of samples, we installed a state-of-the-art multi-nuclide AMS with a 300 kV Tandetron accelerator in 2020. Recently, we are driving the development of techniques of isobar separation in AMS and of sample preparation. Ion channeling is applied to remove isobaric interference and we are building a prototype AMS based on this technique for downsizing of AMS. The small sample graphitization for
C), beryllium-10, aluminium-26 and iodine-129, and we have recently been proceeding test measurement of chlorine-36. In response to an increase of samples, we installed a state-of-the-art multi-nuclide AMS with a 300 kV Tandetron accelerator in 2020. Recently, we are driving the development of techniques of isobar separation in AMS and of sample preparation. Ion channeling is applied to remove isobaric interference and we are building a prototype AMS based on this technique for downsizing of AMS. The small sample graphitization for  C has been attempted using an automated graphitization equipment equipped with an elemental analyzer.
C has been attempted using an automated graphitization equipment equipped with an elemental analyzer.
Matsubara, Akihiro*; Fujita, Natsuko; Miyake, Masayasu; Ishii, Masahiro*; Watanabe, Takahiro; Kokubu, Yoko; Nishio, Tomohiro*; Ogawa, Yumi; Jinno, Satoshi; Kimura, Kenji; et al.
JAEA-Conf 2022-002, p.55 - 62, 2023/03
We report the present status of the JAEA-AMS-TONO. Particularly, the destructions of varistors used in the beamline equipment will be presented. The cause of the destruction as well as implementation of the safety measures are mentioned.
Fujita, Natsuko; Miyake, Masayasu; Matsubara, Akihiro*; Ishii, Masahiro*; Watanabe, Takahiro; Jinno, Satoshi; Nishio, Tomohiro*; Ogawa, Yumi; Yamamoto, Yusuke; Kimura, Kenji; et al.
Dai-23-Kai AMS Shimpojiumu Hokokushu, p.1 - 4, 2022/12
The JAEA-AMS-TONO facility at the Tono Geoscience Center, JAEA has three accelerator mass spectrometers. We report the present status of the JAEA-AMS-TONO.
Niwa, Masakazu; Amano, Kenji; Takeuchi, Ryuji; Shimada, Koji
Groundwater Monitoring & Remediation, 41(3), p.41 - 50, 2021/00
Times Cited Count:1 Percentile:8.31(Water Resources)Identification of water-conducting fractures is important for the safety assessment of underground projects in crystalline rocks at geological disposal sites. We applied a portable methane gas analyzer by wavelength-scanned cavity ring-down spectroscopy to detect the water-conducting fractures in an underground tunnel excavated in granite with CH -rich groundwater. Two approaches were taken to obtain the profile of CH
-rich groundwater. Two approaches were taken to obtain the profile of CH concentration along the gallery walls: (1) Scan by walking at the speed of 0.5 m/s and (2) monitoring for 30 s at 0.5 or 1-m intervals. In the Scan by walking approach, the peaks of the CH
concentration along the gallery walls: (1) Scan by walking at the speed of 0.5 m/s and (2) monitoring for 30 s at 0.5 or 1-m intervals. In the Scan by walking approach, the peaks of the CH concentration corresponded well with the occurrence of high water flow rate fractures. Thus, this method is useful for rapid identification of major water-conducting fractures. Monitoring at constant intervals takes more time than the Scan by walking approach; however, this method can largely detect occurrences of fractures with low fluid fluxes.
concentration corresponded well with the occurrence of high water flow rate fractures. Thus, this method is useful for rapid identification of major water-conducting fractures. Monitoring at constant intervals takes more time than the Scan by walking approach; however, this method can largely detect occurrences of fractures with low fluid fluxes.
Sanada, Yukihisa; Munakata, Masahiro; Mori, Airi; Ishizaki, Azusa; Shimada, Kazumasa; Hirouchi, Jun; Nishizawa, Yukiyasu; Urabe, Yoshimi; Nakanishi, Chika*; Yamada, Tsutomu*; et al.
JAEA-Research 2016-016, 131 Pages, 2016/10
By the nuclear disaster of Fukushima Daiichi Nuclear Power Station (FDNPS), Tokyo Electric Power Company (TEPCO), caused by the East Japan earthquake and the following tsunami occurred on March 11, 2011, a large amount of radioactive materials was released from the NPS. After the nuclear disaster, airborne radiation monitoring using manned helicopter was conducted around FDNPS. In addition, background dose rate monitoring was conducted around Sendai Nuclear Power Station. These results of the aerial radiation monitoring using the manned helicopter in the fiscal 2015 were summarized in the report.
Niwa, Masakazu; Shimada, Koji; Tamura, Hajimu*; Shibata, Kenji*; Sueoka, Shigeru; Yasue, Kenichi; Ishimaru, Tsuneari; Umeda, Koji*
Clays and Clay Minerals, 64(2), p.86 - 107, 2016/04
Times Cited Count:10 Percentile:34.63(Chemistry, Physical)no abstracts in English
Shimada, Asako; Ozawa, Mayumi; Yabuki, Koshi*; Kimiyama, Kazuhiro; Sato, Kenji; Kameo, Yutaka
Journal of Chromatography A, 1371, p.163 - 167, 2014/12
Times Cited Count:14 Percentile:48.77(Biochemical Research Methods)Yasue, Kenichi; Asamori, Koichi; Niwa, Masakazu; Kokubu, Yoko; Kobori, Kazuo; Makuuchi, Ayumu; Matsubara, Akihiro; Shibata, Kenji; Tamura, Hajimu; Tanabe, Hiroaki; et al.
JAEA-Review 2014-033, 43 Pages, 2014/09
The concept of geological disposal of HLW in Japan is based on a multi-barrier system which combines a stable geological environment with a robust barrier system. Potential geological host formations and their surroundings are chosen, in particular, for their long-term stability, taking into account the fact that Japan is located in a tectonically active zone. This report is a plan of research and development (R&D) on geosphere stability for long-term isolation of HLW in JAEA, in fiscal year 2014. The objectives and contents in fiscal year 2014 are described in detail based on the outline of 5 years plan (fiscal years 2010-2014). In addition, the planned framework is structured into the following categories: (1) Development and systematization of investigation techniques, (2) Development of models for long-term estimation and effective assessment, (3) Development of dating techniques.
 =20 shell in
=20 shell in 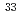 Al investigated through the ground-state electric quadrupole moment
Al investigated through the ground-state electric quadrupole momentShimada, Kenji*; Ueno, Hideki*; Neyens, G.*; Asahi, Koichiro*; Balabanski, D. L.*; Daugas, J. M.*; Depuydt, M.*; De Rydt, M.*; Gaudefroy, L.*; Gr vy, S.*; et al.
vy, S.*; et al.
Physics Letters B, 714(2-5), p.246 - 250, 2012/08
Times Cited Count:7 Percentile:41.35(Astronomy & Astrophysics)no abstracts in English
Kojima, Keiji*; Onishi, Yuzo*; Watanabe, Kunio*; Nishigaki, Makoto*; Tosaka, Hiroyuki*; Shimada, Jun*; Aoki, Kenji*; Tochiyama, Osamu*; Yoshida, Hidekazu*; Ogata, Nobuhisa; et al.
JAEA-Research 2011-033, 126 Pages, 2012/02
The next advancements for the research of radioactive waste repository was started to improve and systematize the investigation and evaluation techniques on geological environment in consideration of intra-field of science and technology. Intra-field means the various fields among each study area of (a) geological environment, (b) design and engineering, (c) safety evaluation for radioactive waste repository, here. The following items were studied and discussed this year. (1) To Reconstruct Near Field (NF) Concept in consideration of coupled phenomena on geological environment. (2) To develop systematic investigation techniques on the geological environment in consideration of intra-field among each study area above mentioned (a), (b) and (c). Regarding (1), examination of NF concept focused on the realistic crystalline rock was carried out. Also through the overall discussion in the committee, comments from the all commissioners in relation to the intra-field of their study area were made to reflect on reconstruction of NF concept. Regarding (2), the research and development in consideration of NF and intra-field among each study area were conducted.
Kojima, Keiji*; Onishi, Yuzo*; Watanabe, Kunio*; Nishigaki, Makoto*; Tosaka, Hiroyuki*; Shimada, Jun*; Aoki, Kenji*; Tochiyama, Osamu*; Yoshida, Hidekazu*; Ogata, Nobuhisa; et al.
JAEA-Research 2010-049, 282 Pages, 2011/02
This report summarizes studies that have been carried out with the aim of assessing and systemizing the technology used for the investigation and analysis of the deep underground geological environment in relation to the disposal of radioactive waste. The main studies were: (1) a study on the research and development (R&D) topics proven to have practical application for the investigation, and analysis and understanding of the deep underground geological environment, and, (2) a study on leading edge technology that can provide the advanced technical basis for the investigation, analysis and understanding of the deep underground geological environment. Regarding the R&D topics (1, above), specific investigations, measurements, numerical analyses and chemical analyses were performed and reviewed with respect to the topics, (a) Repository design, engineering technology (b) Geological environment and (c) Safety evaluation. Based on the result of the review, topics requiring collaboration research in overlapping research fields, including safety assessment, were identified. Also, the near field concept (NFC) was reconsidered in terms of its realistic construction model. Regarding advanced technology (2, above), based on the objectives of the JAEA (Japan Atomic Energy Agency) research project, the study was implemented considering previous R&D results and detailed research result at the research site and thus an assessment of the need for advanced technical basis for investigation and analysis. This study contributed to the R&D development and its practical application.
Sakanaka, Shogo*; Akemoto, Mitsuo*; Aoto, Tomohiro*; Arakawa, Dai*; Asaoka, Seiji*; Enomoto, Atsushi*; Fukuda, Shigeki*; Furukawa, Kazuro*; Furuya, Takaaki*; Haga, Kaiichi*; et al.
Proceedings of 1st International Particle Accelerator Conference (IPAC '10) (Internet), p.2338 - 2340, 2010/05
Future synchrotron light source using a 5-GeV energy recovery linac (ERL) is under proposal by our Japanese collaboration team, and we are conducting R&D efforts for that. We are developing high-brightness DC photocathode guns, two types of cryomodules for both injector and main superconducting (SC) linacs, and 1.3 GHz high CW-power RF sources. We are also constructing the Compact ERL (cERL) for demonstrating the recirculation of low-emittance, high-current beams using above-mentioned critical technologies.
Kojima, Keiji*; Onishi, Yuzo*; Watanabe, Kunio*; Nishigaki, Makoto*; Tosaka, Hiroyuki*; Shimada, Jun*; Aoki, Kenji*; Tochiyama, Osamu*; Yoshida, Hidekazu*; Ogata, Nobuhisa; et al.
JAEA-Research 2009-055, 145 Pages, 2010/02
This report summarizes studies that were carried out with the aim of assessing and systemizing the technology used for the investigation and analysis of the deep underground geological environment in relation to the disposal of radioactive waste. The main studies were: (1) a study on the research and development (R&D) topics proven to have practical application for the investigation, analysis and understanding of the deep underground geological environment, and, (2) a study on leading edge technology that can provide the advanced technical basis for the investigation, analysis and understanding of the deep underground geological environment. The principal results obtained from the studies are as follows: Regarding the R&D topics (1, above), the specific investigations, measurements, numerical and chemical analyses were reviewed with respect to engineering technology and the geological environment in this year. Based on the results of the review, topics requiring collaboration research in overlapping research fields, including safety assessment, were identified. Also, the near field concept (NFC) was reconsidered in terms of both the generic model and for crystalline rock. Regarding advanced technology (2, above), based on the objectives of the JAEA (Japan Atomic Energy Agency) research project, the study was implemented considering previous R&D results and detailed research result at the research site and thus an assessment of the need for advanced technical basis for investigation and analysis. This study contributed to the R&D development and its practical application.
Takeuchi, Shinji; Mikake, Shinichiro; Nishio, Kazuhisa; Tsuruta, Tadahiko; Amano, Kenji; Matsuoka, Toshiyuki; Hayano, Akira; Takeuchi, Ryuji; Saegusa, Hiromitsu; Oyama, Takuya; et al.
JAEA-Review 2009-017, 29 Pages, 2009/08
Japan Atomic Energy Agency (JAEA) at Tono Geoscience Center (TGC) is developing a geoscientific research project named the Mizunami Underground Research Laboratory (MIU) project in crystalline rock environment in order to establish scientific and technological basis for geological disposal of HLW. Geoscientific research at the MIU project is planned to be carried out in three phases over a period of 20 years; Surface-based Investigation Phase (Phase 1), Construction Phase (Phase 2) and Operation Phase (Phase 3). Currently, the project is under the Construction Phase. This document presents the following 2009 fiscal year plan based on the MIU Master Plan updated in 2002, (1) Investigation Plan, (2) Construction Plan, (3) Research Collaboration Plan, etc.
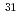 Al and determination of the effective proton charge in the sd-shell
Al and determination of the effective proton charge in the sd-shellDe Rydt, M.*; Neyens, G.*; Asahi, Koichiro*; Balabanski, D. L.*; Daugas, J. M.*; Depuydt, M.*; Gaudefroy, L.*; Gr vy, S.*; Hasama, Yuka*; Ichikawa, Yuichi*; et al.
vy, S.*; Hasama, Yuka*; Ichikawa, Yuichi*; et al.
Physics Letters B, 678(4), p.344 - 349, 2009/07
Times Cited Count:17 Percentile:69.95(Astronomy & Astrophysics)no abstracts in English
Mimata, Hideyuki*; Tani, Keiji*; Tsutsui, Hiroaki*; Tobita, Kenji; Iio, Shunji*; Shimada, Ryuichi*
Plasma and Fusion Research (Internet), 4, p.008_1 - 008_8, 2009/04
The energy dependence of the diffusion coefficients of alpha particles in rippled magnetic fields of tokamaks are numerically investigated with an orbit following Monte Carlo code. The diffusion coefficients are enhanced around the ripple resonance energy while they are reduced and has a minimum near the resonance energy, and hence they have an M-shaped dependence on the energy. The ripple resonance is caused by a radial change of the toroidal precession of banana particles, and creates islands in the phase space related with the toroidal and poloidal angles. Since the particles outside the separatrix mainly contribute to the diffusion, the M-shaped energy dependence is explained by both island structure and initial distribution of particles in the phase space. Such a ripple resonant diffusion is dominant for fusion-produced alpha particles in the slowing down process.
Nishio, Kazuhisa; Matsuoka, Toshiyuki; Mikake, Shinichiro; Tsuruta, Tadahiko; Amano, Kenji; Oyama, Takuya; Takeuchi, Ryuji; Saegusa, Hiromitsu; Hama, Katsuhiro; Mizuno, Takashi; et al.
JAEA-Review 2009-002, 88 Pages, 2009/03
Japan Atomic Energy Agency (JAEA) at Tono Geoscience Center (TGC) is developing a geoscientific research project named Mizunami Underground Research Laboratory (MIU) Project in crystalline rock environment in order to establish scientific and technological basis for geological disposal of HLW. Geoscientific research at MIU is planned to be carried out in three phases over a period of 20 years; Surface-based Investigation Phase (Phase I), Construction Phase (Phase II) and Operation Phase (Phase III). Currently, the project is under the Construction Phase. This document presents the following results of the research and development performed in 2007 fiscal year, as a part of the Construction Phase based on the MIU Master Plan updated in 2002, (1) Investigation at the MIU Construction Site and the Shobasama Site, (2) Construction at the MIU Construction Site, (3) Research Collaboration.
Nishio, Kazuhisa; Matsuoka, Toshiyuki; Mikake, Shinichiro; Tsuruta, Tadahiko; Amano, Kenji; Oyama, Takuya; Takeuchi, Ryuji; Saegusa, Hiromitsu; Hama, Katsuhiro; Yoshida, Haruo*; et al.
JAEA-Review 2009-001, 110 Pages, 2009/03
Japan Atomic Energy Agency (JAEA) at Tono Geoscience Center (TGC) is developing a geoscientific research project named Mizunami Underground Research Laboratory (MIU) project in crystalline rock environment in order to establish scientific and technological basis for geological disposal of HLW. Geoscientific research at MIU is planned to be carried out in three phases over a period of 20 years; Surface-based Investigation Phase (Phase 1), Construction Phase (Phase 2) and Operation Phase (Phase 3). Currently, the project is under the Construction Phase. This document presents the following results of the research and development performed in 2006 fiscal year, as a part of the Construction Phase based on the MIU Master Plan updated in 2002, (1) Investigation at the MIU Construction Site, (2) Construction at the MIU Construction Site, (3) Research Collaboration.
Nishio, Kazuhisa; Matsuoka, Toshiyuki; Mikake, Shinichiro; Tsuruta, Tadahiko; Amano, Kenji; Oyama, Takuya; Takeuchi, Ryuji; Saegusa, Hiromitsu; Hama, Katsuhiro; Yoshida, Haruo*; et al.
JAEA-Review 2008-073, 99 Pages, 2009/03
Japan Atomic Energy Agency (JAEA) at Tono Geoscience Center (TGC) is developing a geoscientific research project named Mizunami Underground Research Laboratory (MIU) project in crystalline rock environment in order to establish scientific and technological basis for geological disposal of HLW. Geoscientific research at MIU is planned to be carried out in three phases over a period of 20 years; Surface-based Investigation Phase (Phase 1), Construction Phase (Phase 2) and Operation Phase (Phase 3). Currently, the project is under the Construction Phase. This document presents the following results of the research and development performed in 2005 fiscal year, as a part of the Construction Phase based on the MIU Master Plan updated in 2002, (1) Investigation at the MIU Construction Site, (2) Construction at the MIU Construction Site, (3) Research Collaboration.