Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
 Ni
NiShimizu, Noritaka*; Utsuno, Yutaka; Futamura, Yasunori*; Sakurai, Tetsuya*; Mizusaki, Takahiro*; Otsuka, Takaharu*
Physics Letters B, 753, p.13 - 17, 2016/02
Times Cited Count:23 Percentile:81.2(Astronomy & Astrophysics)Nuclear level density plays an important role in applications to nuclear energy and nuclear astrophysics, dominating neutron-capture cross sections. In this paper, we propose a new, practical and accurate method of estimating nuclear level density within the framework of the nuclear shell model, and show its feasibility and usefulness. This method is based on the idea that the level density is obtained by the number of eigenstates that is represented as a contour integral in the complex plane. We first confirm the feasibility of this method using a small system in which the exact eigenstates are available, and then calculate parity-dependent level density in  Ni, which cannot be calculated with direct eigenstate counting. We succeed in reproducing the experimental result that the
Ni, which cannot be calculated with direct eigenstate counting. We succeed in reproducing the experimental result that the 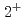 and
and 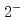 level densities are almost identical in low-energy regions, which cannot be obtained with conventional methods of estimating level densities.
level densities are almost identical in low-energy regions, which cannot be obtained with conventional methods of estimating level densities.

Shimizu, Hirotaka*; Kosugi, Shinya*; Tahara, Yuki*; Yasunaga, Kazufumi*; Kaneta, Yasunori*; Ishikawa, Norito; Hori, Fuminobu*; Matsui, Toshiyuki*; Iwase, Akihiro*
Nuclear Instruments and Methods in Physics Research B, 286, p.291 - 294, 2012/09
Times Cited Count:27 Percentile:87.49(Instruments & Instrumentation)We have studied the magnetic properties of pure CeO irradiated with swift heavy ions. Experiment a results showed that the ferromagnetism was induced even at room temperature by 200 MeV Xe ion irradiation. The value of saturation magnetization, Ms, systematically changes as a function of ion-fluence. The X-ray diffraction (XRD) spectra show that the lattice constant of CeO
irradiated with swift heavy ions. Experiment a results showed that the ferromagnetism was induced even at room temperature by 200 MeV Xe ion irradiation. The value of saturation magnetization, Ms, systematically changes as a function of ion-fluence. The X-ray diffraction (XRD) spectra show that the lattice constant of CeO increases with increasing ion-fluence. This result and our previous XPS result show that the ion-irradiation produced oxygen vacancies. The present study implies that the ferromagnetic behavior of the ion-irradiated CeO
increases with increasing ion-fluence. This result and our previous XPS result show that the ion-irradiation produced oxygen vacancies. The present study implies that the ferromagnetic behavior of the ion-irradiated CeO is attributed to the magnetic moments of localized 4f electrons on Ce
is attributed to the magnetic moments of localized 4f electrons on Ce atoms, which are related to oxygen vacancies.
atoms, which are related to oxygen vacancies.
Ueda, Yoshio*; Oya, Kaoru*; Ashikawa, Naoko*; Ito, Atsushi*; Ono, Tadayoshi*; Kato, Daiji*; Kawashima, Hisato; Kawamura, Gakushi*; Kenmotsu, Takahiro*; Saito, Seiki*; et al.
Purazuma, Kaku Yugo Gakkai-Shi, 88(9), p.484 - 502, 2012/09
no abstracts in English
Ogata, Kazuyuki*; Matsumoto, Takuma*; Hashimoto, Shintaro; Minomo, Kosho*; Egami, Tomoaki*; Iseri, Yasunori*; Kono, Michio*; Chiba, Satoshi; Bertulani, C. A.*; Shimizu, Yoshifumi*; et al.
Journal of Physics; Conference Series, 312, p.082008_1 - 082008_10, 2011/09
Times Cited Count:1 Percentile:47.57(Physics, Nuclear)Recent studies on breakup reactions with the continuum-discretized coupled channels method are reviewed. The topics covered are: four-body breakup processes for  He induced reaction, dynamical relativistic effects on coulomb breakup, microscopic description of projectile breakup processes, description of ternary processes (new triple-
He induced reaction, dynamical relativistic effects on coulomb breakup, microscopic description of projectile breakup processes, description of ternary processes (new triple- reaction rate) and new approach to inclusive breakup processes.
reaction rate) and new approach to inclusive breakup processes.
Oya, Kaoru*; Inai, Kensuke*; Shimizu, Katsuhiro; Takizuka, Tomonori; Kawashima, Hisato; Hoshino, Kazuo; Hatayama, Akiyoshi*; Toma, Mitsunori*; Tomita, Yukihiro*; Kawamura, Gakushi*; et al.
Purazuma, Kaku Yugo Gakkai-Shi, 85(10), p.695 - 703, 2009/10
no abstracts in English
 Al
Al
Honda, Fuminori*; M asson, M.-A.*; Nakano, Yasunori*; Yoshitani, Naohisa*; Yamamoto, Etsuji; Haga, Yoshinori; Takeuchi, Tetsuya*; Yamagami, Hiroshi*; Shimizu, Katsuya*; Settai, Rikio*; et al.
asson, M.-A.*; Nakano, Yasunori*; Yoshitani, Naohisa*; Yamamoto, Etsuji; Haga, Yoshinori; Takeuchi, Tetsuya*; Yamagami, Hiroshi*; Shimizu, Katsuya*; Settai, Rikio*; et al.
Journal of the Physical Society of Japan, 77(4), p.043701_1 - 043701_4, 2008/04
Times Cited Count:38 Percentile:81.7(Physics, Multidisciplinary)Kameyama, Yasuhiko; Watanabe, Shuji; Inoi, Hiroyuki; Shimizu, Yasunori; Aragaki, Etsushi; Shinozaki, Masayuki; Ota, Yukimaru
JAEA-Testing 2008-001, 63 Pages, 2008/03
The High Temperature Engineering Test Reactor (HTTR) has the Auxiliary Component Cooling Water System (ACCWS) and the General Cooling Water System (GCWS). ACCWS supplies the cooling water to the many facilities those are necessary to operate and cool the reactor. GCWS supplies the cooling water to the many facilities those are necessary to operate and cool the reactor in normal circumstances. Two kinds of the cooling water are cooled with the Cooling Tower. Each facility has the circulation pump, the cooling tower, the piping, the valve, the strainer and the injection system of the chemical solution. And these two facilities are operating all the year. This report describes maintenance items, improvements and management of the ACCWS and the GCWS.
Tochio, Daisuke; Kameyama, Yasuhiko; Shimizu, Atsushi; Inoi, Hiroyuki; Yamazaki, Kazunori; Shimizu, Yasunori; Aragaki, Etsushi; Ota, Yukimaru; Fujimoto, Nozomu
JAEA-Technology 2006-045, 43 Pages, 2006/09
The auxiliary component cooling water system (ACCWS) is one of the cooling system in High Temperature Engineering Test Reactor (HTTR) The ACCWS has the features not only many facilities cooling but also heat sink of the vessel cooling system which is one of the engineering safety features. Therefore, the ACCWS is required to satisfy the design criteria of heat removal performance. In this report, heat exchange performance data of the rise-to-power-up test and the in-service operation for the ACCWS cooling tower was evaluated. Moreover, the evaluated values were compared with the design values, and it is confirmed that ACCWS cooling tower has the required heat exchange performance in the design.
Kamada, Yutaka; Fujita, Takaaki; Ishida, Shinichi; Kikuchi, Mitsuru; Ide, Shunsuke; Takizuka, Tomonori; Shirai, Hiroshi; Koide, Yoshihiko; Fukuda, Takeshi; Hosogane, Nobuyuki; et al.
Fusion Science and Technology (JT-60 Special Issue), 42(2-3), p.185 - 254, 2002/09
Times Cited Count:34 Percentile:48.48(Nuclear Science & Technology)With the main aim of providing physics basis for ITER and the steady-state tokamak reactors, JT-60/JT-60U has been developing and optimizing the operational concepts, and extending the discharge regimes toward sustainment of high integrated performance in the reactor relevant parameter regime. In addition to achievement of the equivalent break-even condition (QDTeq up to 1.25) and a high fusion triple product = 1.5E21 m-3skeV, JT-60U has demonstrated the integrated performance of high confinement, high beta-N, full non-inductive current drive with a large fraction of bootstrap current in the reversed magnetic shear and in the high-beta-p ELMy H mode plasmas characterized by both internal and edge transport barriers. The key factors in optimizing these plasmas are profile and shape controls. As represented by discovery of various Internal Transport Barriers, JT-60/JT-60U has been emphasizing freedom and restriction of profiles in various confinement modes. JT-60U has demonstrated applicability of these high confinement modes to ITER and also clarified remaining issues.
Higashijima, Satoru*; Sugie, Tatsuo; Kubo, Hirotaka; Tsuji, Shunji; Shimada, Michiya; Asakura, Nobuyuki; Hosogane, Nobuyuki; Kawano, Yasunori; Nakamura, Hiroo; Itami, Kiyoshi; et al.
Journal of Nuclear Materials, 220-222, p.375 - 379, 1995/00
Times Cited Count:32 Percentile:92.83(Materials Science, Multidisciplinary)no abstracts in English
 by using swift ion beam
by using swift ion beamIwase, Akihiro*; Shimizu, Hirotaka*; Hori, Fuminobu*; Matsui, Toshiyuki*; Ishikawa, Norito; Kaneta, Yasunori*
no journal, ,
CeO is irradiated with 200 MeV Xe, and we found that it becomes ferromagnetic after the irradiation. This may be due to 4f electrons lacalized in Ce
is irradiated with 200 MeV Xe, and we found that it becomes ferromagnetic after the irradiation. This may be due to 4f electrons lacalized in Ce atoms created by the irradiation.
atoms created by the irradiation.