Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Kitazato, Kohei*; Milliken, R. E.*; Iwata, Takahiro*; Abe, Masanao*; Otake, Makiko*; Matsuura, Shuji*; Takagi, Yasuhiko*; Nakamura, Tomoki*; Hiroi, Takahiro*; Matsuoka, Moe*; et al.
Nature Astronomy (Internet), 5(3), p.246 - 250, 2021/03
Times Cited Count:43 Percentile:96.93(Astronomy & Astrophysics)Here we report observations of Ryugu's subsurface material by the Near-Infrared Spectrometer (NIRS3) on the Hayabusa2 spacecraft. Reflectance spectra of excavated material exhibit a hydroxyl (OH) absorption feature that is slightly stronger and peak-shifted compared with that observed for the surface, indicating that space weathering and/or radiative heating have caused subtle spectral changes in the uppermost surface. However, the strength and shape of the OH feature still suggests that the subsurface material experienced heating above 300  C, similar to the surface. In contrast, thermophysical modeling indicates that radiative heating does not increase the temperature above 200
C, similar to the surface. In contrast, thermophysical modeling indicates that radiative heating does not increase the temperature above 200  C at the estimated excavation depth of 1 m, even if the semimajor axis is reduced to 0.344 au. This supports the hypothesis that primary thermal alteration occurred due to radiogenic and/or impact heating on Ryugu's parent body.
C at the estimated excavation depth of 1 m, even if the semimajor axis is reduced to 0.344 au. This supports the hypothesis that primary thermal alteration occurred due to radiogenic and/or impact heating on Ryugu's parent body.
Shirai, Hiroshi; Barabaschi, P.*; Kamada, Yutaka; JT-60SA Team
Fusion Engineering and Design, 109-111(Part B), p.1701 - 1708, 2016/11
Times Cited Count:21 Percentile:88.83(Nuclear Science & Technology)The JT-60SA Project has shown steady progress toward the first plasma in 2019. JT-60SA is a superconducting tokamak designed to operate in the break-even conditions for a long pulse duration with a maximum plasma current of 5.5 MA. Design and fabrication of JT-60SA components shared by EU and Japan started in 2007. Assembly in the torus hall started in January 2013, and welding work of the vacuum vessel sectors is currently on going on the cryostat base. Other components such as TF coils, PF coils, power supplies, cryogenic system, cryostat vessel, thermal shields and so forth were or are being delivered to Naka site for installation, assembly and commissioning. This paper gives technical progress on fabrication, installation and assembly of tokamak components and ancillary systems, as well as progress of JT-60SA Research Plan being developed jointly by EU and Japanese fusion communities.
Higashijima, Satoru; Kamada, Yutaka; Barabaschi, P.*; Shirai, Hiroshi; JT-60SA Team
Fusion Science and Technology, 68(2), p.259 - 266, 2015/09
Times Cited Count:0 Percentile:0.01(Nuclear Science & Technology)Nagao, Keisuke*; Okazaki, Ryuji*; Nakamura, Tomoki*; Miura, Yayoi*; Osawa, Takahito; Bajo, Kenichi*; Matsuda, Shintaro*; Ebihara, Mitsuru*; Ireland, T.*; Kitajima, Fumio*; et al.
Science, 333(6046), p.1128 - 1131, 2011/08
Times Cited Count:130 Percentile:95.22(Multidisciplinary Sciences)A steroid surface materials record regolith processes and a history of cosmic-ray irradiation. Noble gas isotopes in three rocky grains from Itokawa have been determined. High concentrations of solar He, Ne, and Ar, as high as those in lunar soils, are released at variable temperatures from each sample. The isotopic compositions are essentially identical to those of solar wind but distinguishable in He relative abundance. These noble gas characteristics can be explained by repeated implantation and preferential loss of solar He by removal of weathered He-rich rim on the grain surface through friction among regolith grains on Itokawa. Residence time of regolith materials on Itokawa is alculated to be shorter than 10 Myr, suggesting that regolith materials of small asteroids would escape easily to space.
 single crystal
single crystalKashiwaya, Hiromi*; Shirai, Kazumi*; Matsumoto, Tetsuro*; Shibata, Hajime*; Kambara, Hiroshi*; Ishikado, Motoyuki; Eisaki, Hiroshi*; Iyo, Akira*; Shamoto, Shinichi; Kurosawa, Itaru*; et al.
Applied Physics Letters, 96(20), p.202504_1 - 202504_3, 2010/05
Times Cited Count:28 Percentile:71.47(Physics, Applied)The  -axis transport properties of a high-pressure synthesized PrFeAsO
-axis transport properties of a high-pressure synthesized PrFeAsO single crystal are studied using s-shaped junctions. Resistivity anisotropy of about 120 detected at 50 K shows the presence of strong anisotropy in the electronic states. The obtained critical current density for the
single crystal are studied using s-shaped junctions. Resistivity anisotropy of about 120 detected at 50 K shows the presence of strong anisotropy in the electronic states. The obtained critical current density for the  -axis of 2.9
-axis of 2.9  10
10 A/cm
A/cm is two orders of magnitude larger than that in Bi
is two orders of magnitude larger than that in Bi Sr
Sr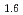 La
La CuO
CuO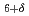 . The appearance of a hysteresis in the current-voltage curve below
. The appearance of a hysteresis in the current-voltage curve below 
 is the manifestation of the intrinsic Josephson effect similar to that in cuprate superconductors. The suppression of the critical current-normal resistance (
is the manifestation of the intrinsic Josephson effect similar to that in cuprate superconductors. The suppression of the critical current-normal resistance (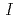


 ) product is explained by an inspecular transport in
) product is explained by an inspecular transport in 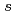
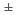 -wave pair potential.
-wave pair potential.
Neudatchin, S. V.*; Takizuka, Tomonori; Sakamoto, Yoshiteru; Hayashi, Nobuhiko; Isayama, Akihiko; Kislov, A. Ya.*; Krylov, S. V.*; Pavlov, Yu. D.*; Shirai, Hiroshi; Borshegovskii, A. A.*
Proceedings of 21st IAEA Fusion Energy Conference (FEC 2006) (CD-ROM), 8 Pages, 2007/03
Non-local transport bifurcations inside and around ITB were found in various JT-60U reverse shear (RS) and normal shear (NrS) plasmas and called ITB-events. The abrupt reduction of transport in the central part of the plasma column often interrupts a slow diffusive inward cold pulse propagation (CPP) in T-10. CPP is created by a cut-off of the off-axis ECRH. This phenomenon may referred to ITB-events as well. In many cases these events occur, when the central safety factor q decreases below unity. In JT-60U low-power heated RS plasmas, ITB-events are observed at the crossing of minimum of q equal to 3.5, 3, 2.5 values. Internal MHD n=1 activity has been reported earlier as ITB-events trigger in JT-60U. The present paper shows that an ITB-event is triggered by a series of small internal disruptions probably associated with q=2.5 surface in RS plasmas. In a high-poloidal-beta NrS shot, an ITB-event occurs in correlation with the start of ELMs series. The total heat flux reduces abruptly in the zone 0.3 r/a
r/a 0.7. This new finding of this ITB event suggests the possibility to control the ITB formation by inducing the ELM-like MHD activity.
0.7. This new finding of this ITB event suggests the possibility to control the ITB formation by inducing the ELM-like MHD activity.
 C
C ) irradiated hematopoietic organs in the silkworm,
) irradiated hematopoietic organs in the silkworm, 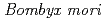 , through the way of phagocytosis of injured cells after invasion
, through the way of phagocytosis of injured cells after invasionLing, E.*; Shirai, Koji*; Kanekatsu, Rensuke*; Kiguchi, Kenji*; Kobayashi, Yasuhiko; Funayama, Tomoo; Watanabe, Hiroshi*
Developmental and Comparative Immunology, 30(6), p.531 - 543, 2006/00
Times Cited Count:13 Percentile:54.39(Fisheries)no abstracts in English
 -values in the ITB events in JT-60U reverse shear plasmas
-values in the ITB events in JT-60U reverse shear plasmasNeudatchin, S. V.*; Takizuka, Tomonori; Hayashi, Nobuhiko; Isayama, Akihiko; Shirai, Hiroshi; Fujita, Takaaki; Kamada, Yutaka; Koide, Yoshihiko; Suzuki, Takahiro
Nuclear Fusion, 44(9), p.945 - 953, 2004/09
The formation of internal transport barriers (ITBs) near q=3 surfaces in normal shear (NrS) discharges of JT-60U is known. In reverse shear (RS) JT-60U plasmas, the role of q minimum (qmin) equal to 3.5,3,2.5,2 was not obvious for ITB formation. ITB-events (non-local confinement bifurcations inside and around ITB) are found in various NrS and RS plasmas. Under sufficient heating power, ITB-events are seen at rational and not rational values of qmin. The space-time evolution of Te and Ti is similar, suggesting the same mechanism of Te and Ti transport. The temporal formation of strong ITB under passing of qmin=3 (after periodical improvements and degradations via ITB-events) in RS mode is presented. Under smaller power, ITB-events are observed only at rational values of qmin. In a weak RS shot, abrupt rise of Te is seen at qmin=3.5, while more cases of Ti rise are observed. The difference of Te and Ti evolutions seen regularly under the low power, suggests decoupling of Te and Ti transport.
 -values in the ITB events in JT-60U reverse shear plasmas
-values in the ITB events in JT-60U reverse shear plasmasNeudatchin, S. V.*; Takizuka, Tomonori; Hayashi, Nobuhiko; Isayama, Akihiko; Shirai, Hiroshi; Fujita, Takaaki; Kamada, Yutaka; Koide, Yoshihiko; Suzuki, Takahiro
Nuclear Fusion, 44(9), p.945 - 953, 2004/09
Times Cited Count:18 Percentile:51.27(Physics, Fluids & Plasmas)The formation of internal transport barriers (ITBs) near  =2,3 surfaces in normal shear (NrS) discharges of JT-60U and JET is known. In reverse shear (RS) JT-60U plasmas, the role of
=2,3 surfaces in normal shear (NrS) discharges of JT-60U and JET is known. In reverse shear (RS) JT-60U plasmas, the role of  minimum (
minimum (
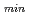 ) equal to 3.5,3,2.5,2 is not obvious for ITB formation. In this paper, the effect of low rational
) equal to 3.5,3,2.5,2 is not obvious for ITB formation. In this paper, the effect of low rational  values on ITB-events in JT-60U NrS and RS plasmas is investigated. Under sufficient neutral beam power (
values on ITB-events in JT-60U NrS and RS plasmas is investigated. Under sufficient neutral beam power (
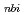
 8MW for 1.2-1.5MA/3.8T pulses), ITB-events are seen at rational and non-rational values of
8MW for 1.2-1.5MA/3.8T pulses), ITB-events are seen at rational and non-rational values of 
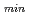 . The space-time evolutions of
. The space-time evolutions of 
 and
and 
 are similar, suggesting the same mechanism for
are similar, suggesting the same mechanism for 
 and
and 
 transports. The temporal formation of stronger ITB under passing
transports. The temporal formation of stronger ITB under passing 
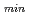 =3 (after periodical improvements and degradations via ITB-events) in RS H-mode with
=3 (after periodical improvements and degradations via ITB-events) in RS H-mode with 
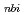 =8MW is presented. Under smaller power, ITB-events are observed only at rational
=8MW is presented. Under smaller power, ITB-events are observed only at rational 
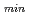 values. In a weak RS shot with
values. In a weak RS shot with 
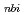 =4MW, the abrupt rise of
=4MW, the abrupt rise of 
 is seen at
is seen at 
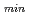 =3.5, while more cases of
=3.5, while more cases of 
 rise are observed. The difference between the
rise are observed. The difference between the 
 and
and 
 evolutions for the low power suggests the decoupling of
evolutions for the low power suggests the decoupling of 
 and
and 
 transports.
transports.
Sakamoto, Yoshiteru; Suzuki, Takahiro; Ide, Shunsuke; Koide, Yoshihiko; Takenaga, Hidenobu; Kamada, Yutaka; Fujita, Takaaki; Fukuda, Takeshi; Takizuka, Tomonori; Shirai, Hiroshi; et al.
Nuclear Fusion, 44(8), p.876 - 882, 2004/08
Times Cited Count:33 Percentile:71.1(Physics, Fluids & Plasmas)Response of the ion thermal diffusivity to the radial electric field Er shear has been investigated in JT-60U and the following results were found. (1) In the case of positive magnetic shear (PS) plasma, the ion thermal diffusivity in the core region shows L mode state, weak internal transport barrier (ITB), and strong ITB depending upon the heating power. In the case of reversed magnetic shear (RS) plasma, however, no power degradation of the ion thermal diffusivity is observed. (2) In the case of weak ITB, the ion thermal diffusivity decreases gradually with increasing the Er shear for both PS and RS plasmas. There exists a threshold of an effective Er shear to change its state from weak to strong ITBs. (3) The threshold of the effective Er shear in the case of RS plasma is small compared with that in the case of PS plasma.
Tamai, Hiroshi; Ishida, Shinichi; Kurita, Genichi; Shirai, Hiroshi; Tsuchiya, Katsuhiko; Sakurai, Shinji; Matsukawa, Makoto; Sakasai, Akira
Fusion Science and Technology, 45(4), p.521 - 528, 2004/06
Times Cited Count:0 Percentile:0.01(Nuclear Science & Technology)The 1.5D time-dependent transport analysis has been carried out to investigate steady state operation scenarios with a central current hole by off-axis current drive schemes consistent with a high bootstrap current fraction for a large superconducting tokamak JT-60SC. A steady state operation scenario with HH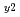 =1.4 and
=1.4 and 
 =3.7 has been obtained at I
=3.7 has been obtained at I =1.5 MA, B
=1.5 MA, B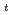 =2 T and q
=2 T and q =5 where non-inductive currents are developed during the discharge to form a current hole with beam driven currents by tangential off-axis beams in combination with bootstrap currents by additional on-axis perpendicular beams. The bootstrap fraction increases up to nearly 75% of the plasma current and the current hole region is enlarged up to about 30% of the minor radius at 35 s from the discharge initiation. The current hole is confirmed to be sustained afterward for a long duration of 60 s. The stability analysis shows that the beta limit with the conducting wall can be about
=5 where non-inductive currents are developed during the discharge to form a current hole with beam driven currents by tangential off-axis beams in combination with bootstrap currents by additional on-axis perpendicular beams. The bootstrap fraction increases up to nearly 75% of the plasma current and the current hole region is enlarged up to about 30% of the minor radius at 35 s from the discharge initiation. The current hole is confirmed to be sustained afterward for a long duration of 60 s. The stability analysis shows that the beta limit with the conducting wall can be about 
 =4.5, which is substantially above the no wall ideal MHD limit.
=4.5, which is substantially above the no wall ideal MHD limit.
Sakamoto, Yoshiteru; Shirai, Hiroshi; Fujita, Takaaki; Ide, Shunsuke; Takizuka, Tomonori; Oyama, Naoyuki; Kamada, Yutaka
Plasma Physics and Controlled Fusion, 46(5A), p.A299 - A304, 2004/05
Times Cited Count:68 Percentile:88.54(Physics, Fluids & Plasmas)no abstracts in English
Nakamura, Yukiharu; Tsutsui, Hiroaki*; Takei, Nahoko*; Shirai, Hiroshi; Sugihara, Masayoshi; Gribov, Y.*; Ozeki, Takahisa; Tobita, Kenji; Iio, Shunji*; Jardin, S. C.*
Journal of Plasma and Fusion Research SERIES, Vol.6, p.196 - 198, 2004/00
no abstracts in English

 plasmas
plasmasNeudatchin, S.*; Takizuka, Tomonori; Hayashi, Nobuhiko; Isayama, Akihiko; Shirai, Hiroshi; Fujita, Takaaki; Kamada, Yutaka; Koide, Yoshihiko; Ito, Kimitaka*; Miura, Yukitoshi
Purazuma, Kaku Yugo Gakkai-Shi, 79(12), p.1218 - 1220, 2003/12
New type of edge-core instantaneous interplay in JT-60U high-
 plasmas is found. Abrupt in time and wide in space reduction of electron heat flux in the core (called ITB-event) is correlated in ms timescale with the start of an ELM. This result gives a hint of the control to form the ITB immedeately and non-locally by inducing the ELM-like MHD activity.
plasmas is found. Abrupt in time and wide in space reduction of electron heat flux in the core (called ITB-event) is correlated in ms timescale with the start of an ELM. This result gives a hint of the control to form the ITB immedeately and non-locally by inducing the ELM-like MHD activity.
Takenaga, Hidenobu; Higashijima, Satoru; Oyama, Naoyuki; Bruskin, L. G.; Koide, Yoshihiko; Ide, Shunsuke; Shirai, Hiroshi; Sakamoto, Yoshiteru; Suzuki, Takahiro; Hill, K. W.*; et al.
Nuclear Fusion, 43(10), p.1235 - 1245, 2003/10
Times Cited Count:71 Percentile:88.64(Physics, Fluids & Plasmas)no abstracts in English
 , after locally targeted irradiation with heavy ion beams
, after locally targeted irradiation with heavy ion beamsLing, E.*; Fukamoto, Kana*; Xu, S.*; Shirai, Koji*; Kanekatsu, Rensuke*; Kobayashi, Yasuhiko; Tu, Z.; Funayama, Tomoo; Watanabe, Hiroshi; Kiguchi, Kenji*
Journal of Insect Biotechnology and Sericology, 72(2), p.95 - 100, 2003/09
no abstracts in English
 ?
?Ling, E.*; Shirai, Koji*; Kanekatsu, Rensuke*; Kobayashi, Yasuhiko; Tu, Z.; Funayama, Tomoo; Watanabe, Hiroshi; Kiguchi, Kenji*
Journal of Insect Biotechnology and Sericology, 72(2), p.101 - 109, 2003/09
no abstracts in English
Shirai, Hiroshi
Purazuma, Kaku Yugo Gakkai-Shi, 79(7), p.691 - 705, 2003/07
Methods for heat transport analysis and heat transport simulation in toroidal plasmas are summarized on the basis of energy balance equation. Joule heating, NBI heating, RF heating and  heating are briefly explained. Among the energy loss mechanism, the conduction loss and the radiation loss dominate in the core plasma region and the peripheral region, respectively. In tokamaks, the anomalous transport caused by microturbulence is much larger than the neoclassical transport. The other mechanisms of enhanced transport, the sawtooth oscillation and the magnetic island formation, are also shown.
heating are briefly explained. Among the energy loss mechanism, the conduction loss and the radiation loss dominate in the core plasma region and the peripheral region, respectively. In tokamaks, the anomalous transport caused by microturbulence is much larger than the neoclassical transport. The other mechanisms of enhanced transport, the sawtooth oscillation and the magnetic island formation, are also shown.
Mikkelsen, D. R.*; Shirai, Hiroshi; Urano, Hajime*; Takizuka, Tomonori; Kamada, Yutaka; Hatae, Takaki; Koide, Yoshihiko; Asakura, Nobuyuki; Fujita, Takaaki; Fukuda, Takeshi*; et al.
Nuclear Fusion, 43(1), p.30 - 39, 2003/01
Times Cited Count:28 Percentile:64.08(Physics, Fluids & Plasmas)The stiffness of thermal transport in ELMy H-modes is explained in a series of carefully chosen JT-60U plasmas, and measured temperature are compared with the predictions of several transport models. A heating power scan with constant Tped, a scan of pedestal temperature Tped with constant heating power, and an on/off-axis heating comparison are presented. Predictions of the RLWB and IFS/PPPL models generally agree with the measured temperature outside 
 0.3
0.3 , but the Multimode model uniformly predicts temperatures that are too high except in the central region.
, but the Multimode model uniformly predicts temperatures that are too high except in the central region.
Kishimoto, Hiroshi; Shirai, Hiroshi
Proceedings of 3rd International Sakharov Conference on Physics, p.185 - 200, 2003/00
no abstracts in English