Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Nagatani, Taketeru; Kosuge, Yoshihiro*; Shirato, Atsuhiko*; Sato, Takashi*; Shiromo, Hideo; Asano, Takashi
Proceedings of INMM 57th Annual Meeting (Internet), 10 Pages, 2016/07
Nagatani, Taketeru; Shirato, Atsuhiko*; Kosuge, Yoshihiro*; Sato, Takashi*; Kawakubo, Yoko; Shiromo, Hideo; Asano, Takashi
Proceedings of INMM 56th Annual Meeting (Internet), 10 Pages, 2015/07
As one of the candidate material accountancy technologies for the fuel debris at Fukushima Daiichi Nuclear Power Plants (1F), we propose the application of a passive neutron technique. The applicability of the new concept to the fuel debris at 1F was evaluated by simulation and the results were presented at the last INMM annual meeting. As the next phase, we conducted experimental tests to confirm the validity of the simulation results. Because actual fuel debris or irradiated fuel cannot be handled at our facility due to a licensing limitation, un-irradiated MOX samples, neutron absorbers and Cf-252 sources were utilized as the best available material to imitate the property of the fuel debris and various configurations were measured using an Epithermal Neutron Multiplicity Counter. The fissile mass in the samples, neutron absorber mass surrounding the samples and intensity of Cf-252 source were varied to confirm the correlation between DDSI response and the leakage multiplication. Test results agreed well with the trend of the simulation results. This indicates that DDSI has sufficient capability to evaluate the leakage multiplication of a sample which includes an unknown amount of fissile material and neutron absorber such as the fuel debris at 1F. This paper provides experimental studies of passive neutron measurement based on the combination of DDSI technique and coincidence counting for fuel debris at 1F.
Tatebe, Kazuaki; Suzuki, Yurina; Shirato, Seiichi; Sato, Yoshinori
JAEA-Data/Code 2011-024, 84 Pages, 2012/02
The recent society requires business activities with environmental consideration to every enterprise. Also, Japanese laws require those activities. For example, "Environmental Consideration Law" mandates publication of a report relating to the activities of environmental consideration to each enterprise over a certain size. "Act on the Rational Use of Energy" mandates the report of the results of energy consumption and the long-term plan of the rational use of energy. Moreover, "Act on Promotion of Global Warming Countermeasures" mandates the report of the greenhouse gas emissions. In addition to those, "Water Pollution Control Law" and other environmental laws as well as environmental ordinances require business activities with environmental consideration to all companies. So, it is very important for JAEA to report business activities with environmental consideration in order to build up trustful relations with the people and communities. The Environmental Data Management System has been developed as the data base of business activities with environmental consideration at JAEA and the means to promote the activities at every site and office of JAEA. This report summarizes the structure of the environmental data management system, kinds of environmental performance data treated by the system, and gathering methods of the data.
Yamanaka, Atsushi; Hashimoto, Kowa; Uchida, Toyomi; Shirato, Yoji; Isozaki, Toshihiko; Nakamura, Yoshinobu
Proceedings of International Conference on Toward and Over the Fukushima Daiichi Accident (GLOBAL 2011) (CD-ROM), 6 Pages, 2011/12
The Tokai Reprocessing Plant (TRP) adopted the PUREX method in 1977 and has reprocessed spent nuclear fuel of 1140 tHM (tons of heavy metals) since then. The reprocessing equipment suffers from various corrosion phenomena because of high nitric acidity, solution ion concentrations, such as uranium, plutonium, and fission products, and temperature. Therefore, considering corrosion performance in such a severe environment, stainless steels, titanium steel, and so forth were employed as corrosion resistant materials. The severity of the corrosive environment depends on the nitric acid concentration and the temperature of the solution, and uranium in the solution reportedly does not significantly affect the corrosion of stainless steels and controls the corrosion rates of titanium steel. The TRP equipment that handles uranyl nitrate solution operates at a low nitric acid concentration and has not experienced corrosion problems until now. However, there is a report that corrosion rates of some stainless steels increase in proportion to rising uranium concentrations. The equipment that handles the uranyl nitrate solution in the TRP includes the evaporators, which concentrate uranyl nitrate to a maximum concentration of about 1000 gU/L (grams of uranium per liter), and the denitrator, where uranyl nitrate is converted to UO powder at about 320
powder at about 320 C. These equipments are therefore required to grasp the degree of the progress of corrosion to handle high-temperature and high-concentration uranyl nitrate. The evaluation of this equipment on the basis of thickness measurement confirmed only minor corrosion and indicated that the equipment would be fully adequate for future operation.
C. These equipments are therefore required to grasp the degree of the progress of corrosion to handle high-temperature and high-concentration uranyl nitrate. The evaluation of this equipment on the basis of thickness measurement confirmed only minor corrosion and indicated that the equipment would be fully adequate for future operation.
Sutherland, K.*; Miyajima, Satoshi*; Date, Hiroyuki*; Shirato, Hiroki*; Ishikawa, Masayori*; Murakami, Masao*; Yamagiwa, Mitsuru; Bolton, P.; Tajima, Toshiki
Radiological Physics and Technology, 3(1), p.16 - 22, 2010/01
Orukawa, Go; Kojima, Wataru; Shirato, Nobuaki*; Saito, Toshiki*
Konkurito Kogaku Nenji Rombunshu (DVD-ROM), 28(1), p.1637 - 1642, 2006/00
no abstracts in English
Shirato, Nobuaki*; Matsui, Hiroya; Morioka, Hiroshi; Hatanaka, Koichiro; Takeuchi, Ryuji; Hatakeyama, Nobuya; Ohara, Hidefumi; Nakajima, Takahiro; Kunitomo, Takahiro
JNC TN5440 2005-001, 412 Pages, 2005/06
We held Horonobe technical review meeting 4 times a year. The first meeting is for the plan of Horonobe underground research laboratory and others. The secound meeting is for geology of Horonobe area and modeling study and data acquisition for safety assessment methodology and others. The third meeting is for ventilation network analyses on URL plan. The fourth meeting is for the remote monitoring system using ACROSS. This report is records of these meetings.
Matsui, Hiroya; MORIOKA, Hiroyuki; Shirato, Nobuaki; Ouchi, Kazutoshi
JNC TN5410 2004-001, 236 Pages, 2004/08
JNC(Japan Nuclear Cycle development institute) has been conducting the project called "Horonobe URL project" in Horonobe-cho, Hokkkaido, Japan. The aim of the project is to establish the scientific and technical basis for geological disposal on sedimentary rock. In the project, a underground facility with 500m depth will be constructed. This report is summarized the results on support design of the planned underground facility based on the data obtained by the several borehole investigations from ground surface. Owing to rational support design, the detailed compartment of the input parameters for the stability analysis in surrounding rock at position of underground facility were made based on the results of borehole investigation in HDB-1, HDB-3, which were drilled near the position. Moreover, the idea of double support system was adopted in this study to minimize the support in underground facility.
Shirato, Nobuaki; Ouchi, Kazutoshi; Yamazaki, Shinichi
JNC TN5400 2004-003, 1854 Pages, 2004/08
The Horonobe underground Research Laboratory (URL) programme hosted by sedimentary rocks is aimed to obtain deep geological characteristics of sedimentary rock mass and to confirm the applicability of the investigation methods for the geological environment and the engineering technology for the geological disposal described in the H12 report. In addition, the URL is aimed to have public people experience a deep geological environment in order to understand a deep geological disposal of HLW. Based on the results of the report in H13 the followings are carried out : (i)design of the section of the drifts and shafts (ii)stability analysis of the drifts and shafts considering the anisotropy of initial stress (iii)drawing of the fundamental plan (iv)refuge planning of the URL based on the estimation of gas flow (v)research planning of the second and the third stage of the URL (vi)study on construction method of the drifts and shafts (vii)planning of the facilities during construction and operation (viii)construction schedule analysis and cost estimation of the URL (ix)planning of the facility and guidance of visitors (x)closing planning of the URL This work was re-edited from the results performed by Taisei Corporation, 0bayashi Corporation, Kajima Corporation and Shimizu Corporation under contract with JNC; "Feasibility study on construction of Horonobe URL (JNC TJ1400 2002-003)".
Shirato, Nobuaki; Ouchi, Kazutoshi; Yamazaki, Shinichi
JNC TN5400 2004-002, 485 Pages, 2004/08
The Horonobe underground Research Laboratory (URL) programme hosted by sedimentary rocks is aimed to obtain deep geological characteristics of sedimentary rock mass and to confirm the applicability of the investigation methods for the geological environment and the engineering technology for the geological disposal described in the H12 report. In addition, the URL is aimed to have public people experience a deep geological environment in order to understand a deep geological disposal of HLW. The objective of this report is to make the ground of the site selection of the Horonobe URL Based on the results obtained from two deep investigation boreholes drilled in the B1 and B2 district two kinds of geological model were constructed. For each geological model four types of preliminary layout were prepared for the feasibility study. The types of the URL were as follows: (i)two shafts (ii)three shafts (iii)spiral drift and one shaft (iv)spiral drift and two shafts. For the combination of the geological model and the layout tbe construction schedule and the construction cost were estimated through the study of the construction method with the auxiliary method, the construction procedure and the cycle time. The analysis of vibration and noise during construction was also estimated. The results of the feasibility study indicated that mechanical excavation was employed for the whole construction. The shafts were suggested to be constructed by the short step sinking method and the drifts and the spiral drifts by NATM. The mucking system should be rail haulage for the drift for the case of shafts(i) and (ii)), and road haulage for the drift for the case of spiral drifts(iii) and (iv)). The estimation of construction time was around seventy months for the case of shafts(i) and (ii)) and around ninety months for the case of spiral drifts(iii) and (iv)). This work was re-edited from the results performed by Taisei Corporation under contract with JNC; "Feasibility study on ...
Sato, Toshinori; Shirato, Nobuaki
Gamban Rikigaku Iinkai Nyusu Reta, (2), , 2004/00
Focusing on the cover layer materials (as the Radon Barrier Materials), which could have the effect to restrain the radon from scattering into the air and the effect of the radiation shielding, we produced the radon barrier materials with crude bentonite on an experimental basis, using the rotary type comprehensive unit for grinding and mixing, through which we carried out the evaluation of the characteristics thereof.
Sato, Toshinori; Shirato, Nobuaki
Tunneling Activities in Japan 2014, P. 24, 2004/00
no abstracts in English
Matsumoto, Shiro*; Uchiyama, Gunzo; Ozawa, Masaki*; Kobayashi, Y.*; Shirato, K.*
Radiochemistry, 45(3), p.219 - 224, 2003/05
no abstracts in English
; Nakatsuka, Noboru; Eki, Nobuhiro; ; Takeuchi, Ryuji; ; Shirato, Nobuaki
JNC TN1400 2002-017, 31 Pages, 2002/06
no abstracts in English
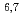 Li(n,d)
Li(n,d)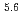 He and
He and 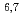 Li(n,t)
Li(n,t)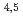 He at 14.1 MeV
He at 14.1 MeVShirato, Shoji*; Shibuya, Shinji*; Hata, Kazuhiro*; Ando, Yoshiaki*; Shibata, Keiichi
JAERI-M 89-107, 27 Pages, 1989/08
no abstracts in English
*; *; Shirato, Seiichi*; *; Nakanishi, Seiji; *
PNC TN9410 88-177, 340 Pages, 1988/09
This report summarized the results of the study on the capital cost assessment methods in FY1987 which is one of the economic estimation system for FBR that had been developing from FY1986. In this study, the assessment methods developed in FY1986 were investigated in more detail concentrating on equipments and components peculiar to FBR. Moreover, the Land, Structure and Building which compose the capital cost were modeled to be able to calculate the total capital cost. The results of this study are as follows. (1)Investigation of the assessment model for equipments and components peculiar to FBR The assessment methods for equipments and components peculiar to FBR which extracted in FY1986 were evaluated in more detail. Thus, the cost is assessed as the accumulation of the materials and manufacturing cost of the equipments and components in principle. (2)Land, Structure and Building cost model. The cost assessment model for the FBR buildings was determined based on the cost of the total area of the buildings which estimated in reference to the investigation of the materials of LWR (PWR). On the other hand, the model for the Land and Structures was used as the same model as that of LWR. (3)Trial cost estimation of 1000MW FBR plant. The capital cost of 1000MW FBR plant except some facilities which the materials and specifications are unknown was estimated for trial using both the assessment methods developed in FY1986 and 1987. (4)Preparation of the data base of the economic estimation system for the advanced LWR. With regard to the Advanced PWR and BWR which chose as the subject of the economic estimation for FBR considering the phase of commercial FBR deployment, important improvements and differences from the present LWR design were summarized from the view point of the cost estimation and were prepared for the data base of the Advanced LWR. In the future, the capital cost assessment methods developed in this study will be coded to be easily use and ...
Kaneko, Yoshihisa*; Nishikimi, Masakazu*; Shirato, Seiichi*; Morimoto, Makoto*; *
PNC TN941 85-25, 347 Pages, 1985/02
Nickel membrane type hydrogen meter is used to detect earlier water leakage from heat transfer tubes in the steam generator for Fast Breeder Reactor. The nickel membrane is one of the most important pieces for the hydrogen meter and is used under the severe condition such as high temperature of 500 C so that it may happen that corrosion, conversion in microstructure and shortage of mechanical strength etc. Various material tests for 11 kinds of nickel membranes used in the test facility for a longterm were done and following results were obtained. (1)A little corrosion was observed for the nickel membrane used over a long term. (2)The microstructure of the nickel membrane have been converted to recrystal microstructure. The microstructure for the weld is dendritic structure and it has atendency of the growth of crystal grain by the welding heat. (3)The tensile strength of the nickel membrane is decreased slightly, but, it keeps sufficiently the permissible tensile strength. The hardness of the nickel membrane have been decreased to the hardness of annealing material. (4)Iron, chromium and manganese etc. were attached to the surface of the nickel membrane and especiallyy the manganese soaked into several micron in the nickel membrane. But, these deposits haven't any effect for the hydrogen meter. (5)The leak position on the nickel membrane was found in the welding side between the nickel membrane and the vacuum pipe (made of stainless steel). Then, one of important factors having an influence on the membrane's life may be the welding.
C so that it may happen that corrosion, conversion in microstructure and shortage of mechanical strength etc. Various material tests for 11 kinds of nickel membranes used in the test facility for a longterm were done and following results were obtained. (1)A little corrosion was observed for the nickel membrane used over a long term. (2)The microstructure of the nickel membrane have been converted to recrystal microstructure. The microstructure for the weld is dendritic structure and it has atendency of the growth of crystal grain by the welding heat. (3)The tensile strength of the nickel membrane is decreased slightly, but, it keeps sufficiently the permissible tensile strength. The hardness of the nickel membrane have been decreased to the hardness of annealing material. (4)Iron, chromium and manganese etc. were attached to the surface of the nickel membrane and especiallyy the manganese soaked into several micron in the nickel membrane. But, these deposits haven't any effect for the hydrogen meter. (5)The leak position on the nickel membrane was found in the welding side between the nickel membrane and the vacuum pipe (made of stainless steel). Then, one of important factors having an influence on the membrane's life may be the welding.
Kaneko, Yoshihisa*; Nishikimi, Masakazu*; Shirato, Seiichi*; Morimoto, Makoto*; *
PNC TN941 85-24, 194 Pages, 1985/02
Series of tests on the water leak detection system have been conducted in the 50MW Steam Generator Test Facility since December 1974. This report is data of water leak simulation tests (water or hydrogen injection tests) which were carried out until November 1983 since May 1978. These data (response of water leak detector) are recorded in magnetic tape and it is easy to change scale and soon.
 Water leak alarm system
Water leak alarm systemShirato, Seiichi*; Kaneko, Yoshihisa*; Nishikimi, Masakazu*; Morimoto, Makoto*; Matsumoto, Shigeharu*; Motonaga, Tsutsuji*; Imai, Hiroshi*; Fukuda, Toru
PNC TN941 85-23, 193 Pages, 1985/02
To develop the small leak sodium-water reaction detection system in the steam generator for Fast Breeder Reactor, the series studies on system evaluation tests have been carried out at the 50MW Steam Generator Test Facility. This report deals with hydrogen and injection tests into the sodium outlet pipe from the superheater, test plans and test equipments for hydrogen injection tests into the evaporator, the response performances for the hydrogen meter and oxygen meter, detection ratio for hydrogen and oxygen and the water leak alarm system etc. The test results are summarized as follows: (1)Hydrogen injection tests & water injection tests into the sodium outlet pipe from the superheater were done and the hydrogen & oxygen behaviors were understood. (2)Hydrogen injection tests at the annulus, down-comer and cover-gas region in the evaporator were done and hydrogen behaviors were understood. (3)Hydrogen detection rates depending on hydrogen injection tests & water injection tests were arranged and factors giving the effect on the rate were evaluated. Also, hydrogen transfer times were evaluated. (4)Hydrogen detection rates at the water leakage in the evaporator were evaluated by the comparison of hydrogen injection test results & water injection test results into the sodium out1et pipe from the superheater and hydrogen injection test results into the evaporator. (5)The water leak alarm system by the computor was completed and the validity was confirmed.
Kaneko, Yoshihisa*; Nishikimi, Masakazu*; Shirato, Seiichi*; *
PNC TN941 85-22, 142 Pages, 1985/02
Series of tests on water leak detection system for Monju steam generators have been excuted in the 50MW Steam Generator Test Facility (50MW SGTF). This paper describes the test results about the removal efficiency of hydrogen by the secondary cold trap, the hydrogen background concentration and hydrogen flux through heat transfer tubes to secondary sodium in steam generator (SG) in order to make clear the hydrogen behavior during ordinary plant operation from October in 1976 to July in 1983. Main results from these tests are: (1)The removal efficieney of hydrogen by the cold trap is 70 80 percents, but it shows tendency to decrease when difference between hydrogen concentration at cold trap and that in secondary main loop is small. (2)Hydrogen flux through tubes is smaller than the value which is reported in the first report of these series reports. (3)It is found that the hydrogen background concentration in the secondary main loop of 50MW SGTF is thoroughly low. (4)It is estimated that the hydrogen background concentration in the secondary main loop in Monju plant is lower than 169 ppb.
80 percents, but it shows tendency to decrease when difference between hydrogen concentration at cold trap and that in secondary main loop is small. (2)Hydrogen flux through tubes is smaller than the value which is reported in the first report of these series reports. (3)It is found that the hydrogen background concentration in the secondary main loop of 50MW SGTF is thoroughly low. (4)It is estimated that the hydrogen background concentration in the secondary main loop in Monju plant is lower than 169 ppb.