Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Kitazato, Kohei*; Milliken, R. E.*; Iwata, Takahiro*; Abe, Masanao*; Otake, Makiko*; Matsuura, Shuji*; Takagi, Yasuhiko*; Nakamura, Tomoki*; Hiroi, Takahiro*; Matsuoka, Moe*; et al.
Nature Astronomy (Internet), 5(3), p.246 - 250, 2021/03
Times Cited Count:43 Percentile:96.93(Astronomy & Astrophysics)Here we report observations of Ryugu's subsurface material by the Near-Infrared Spectrometer (NIRS3) on the Hayabusa2 spacecraft. Reflectance spectra of excavated material exhibit a hydroxyl (OH) absorption feature that is slightly stronger and peak-shifted compared with that observed for the surface, indicating that space weathering and/or radiative heating have caused subtle spectral changes in the uppermost surface. However, the strength and shape of the OH feature still suggests that the subsurface material experienced heating above 300  C, similar to the surface. In contrast, thermophysical modeling indicates that radiative heating does not increase the temperature above 200
C, similar to the surface. In contrast, thermophysical modeling indicates that radiative heating does not increase the temperature above 200  C at the estimated excavation depth of 1 m, even if the semimajor axis is reduced to 0.344 au. This supports the hypothesis that primary thermal alteration occurred due to radiogenic and/or impact heating on Ryugu's parent body.
C at the estimated excavation depth of 1 m, even if the semimajor axis is reduced to 0.344 au. This supports the hypothesis that primary thermal alteration occurred due to radiogenic and/or impact heating on Ryugu's parent body.
Kitazato, Kohei*; Milliken, R. E.*; Iwata, Takahiro*; Abe, Masanao*; Otake, Makiko*; Matsuura, Shuji*; Arai, Takehiko*; Nakauchi, Yusuke*; Nakamura, Tomoki*; Matsuoka, Moe*; et al.
Science, 364(6437), p.272 - 275, 2019/04
Times Cited Count:259 Percentile:99.73(Multidisciplinary Sciences)The near-Earth asteroid 162173 Ryugu, the target of Hayabusa2 sample return mission, is believed to be a primitive carbonaceous object. The Near Infrared Spectrometer (NIRS3) on Hayabusa2 acquired reflectance spectra of Ryugu's surface to provide direct measurements of the surface composition and geological context for the returned samples. A weak, narrow absorption feature centered at 2.72 micron was detected across the entire observed surface, indicating that hydroxyl (OH)-bearing minerals are ubiquitous there. The intensity of the OH feature and low albedo are similar to thermally- and/or shock-metamorphosed carbonaceous chondrite meteorites. There are few variations in the OH-band position, consistent with Ryugu being a compositionally homogeneous rubble-pile object generated from impact fragments of an undifferentiated aqueously altered parent body.
Iwata, Takahiro*; Kitazato, Kohei*; Abe, Masanao*; Otake, Makiko*; Arai, Takehiko*; Arai, Tomoko*; Hirata, Naru*; Hiroi, Takahiro*; Honda, Chikatoshi*; Imae, Naoya*; et al.
Space Science Reviews, 208(1-4), p.317 - 337, 2017/07
Times Cited Count:54 Percentile:71.62(Astronomy & Astrophysics)NIRS3: The Near Infrared Spectrometer is installed on the Hayabusa2 spacecraft to observe the target C-type asteroid 162173 Ryugu at near infrared wavelengths of 1.8 to 3.2 micrometer. It aims to obtain reflectance spectra in order to detect absorption bands of hydrated and hydroxide minerals in the 3 micrometer-band. We adopted a linear-image sensor with indium arsenide (InAs) photo diodes and a cooling system with a passive radiator to achieve an optics temperature of 188 K, which enables to retaining sufficient sensitivity and noise level in the 3 micrometer wavelength region. We conducted ground performance tests for the NIRS3 flight model (FM) to confirm its baseline specifications. The results imply that the properties such as the signal-to-noise ratio (SNR) conform to scientific requirements to determine the degree of aqueous alteration, such as CM or CI chondrite, and the stage of thermal metamorphism on the asteroid surface.
Tashiro, Koji*; Hanesaka, Makoto*; Yamamoto, Hiroko*; Wasanasuk, K.*; Jayaratri, P.*; Yoshizawa, Yoshinori*; Tanaka, Ichiro*; Niimura, Nobuo*; Kusaka, Katsuhiro*; Hosoya, Takaaki*; et al.
Kobunshi Rombunshu, 71(11), p.508 - 526, 2014/11
Times Cited Count:6 Percentile:22.37(Polymer Science)The crystal structure analysis of various polymer substances has been reviewed on the basis of wide-angle high-energy X-ray and neutron diffraction data. The progress in structural analytical techniques of polymer crystals have been reviewed at first. The structural models proposed so far were reinvestigated and new models have been proposed for various kinds of polymer crystals including polyethylene, poly(vinyl alcohol), poly(lactic acid) and its stereocomplex etc. The hydrogen atomic positions were also clarified by the quantitative analysis of wide-angle neutron diffraction data, from which the physical properties of polymer crystals have been evaluated theoretically. The bonded electron density distribution has been estimated for a polydiacetylene single crystal on the basis of the so-called X-N method or by the combination of structural information derived from X-ray and neutron diffraction data analysis. Some comments have been added about future developments in the field of structure-property relationship determination.
Chai, G.-L.*; Hou, Z.*; Shu, D.-J.*; Ikeda, Takashi; Terakura, Kiyoyuki*
Journal of the American Chemical Society, 136(39), p.13629 - 13640, 2014/10
Times Cited Count:252 Percentile:97.75(Chemistry, Multidisciplinary)Carbon alloy catalysts (CACs) are promising catalysts for oxygen reduction reaction (ORR) to substitute Pt. However, despite extensive studies on CACs the reaction sites and mechanisms for ORR are still in controversy. Herein, we present rather general consideration on possible ORR mechanisms for various structures in nitrogen doped CACs based on the first principles calculations. Our study indicates that only a particular structure of a nitrogen pair doped Stone-Wales defect provides a good active site. The ORR activity of this structure can be tuned by the curvature around the active site, which makes its limiting potential approaching the maximum limiting potential (0.80 V) in the volcano plot for the ORR activity of CACs. The calculated results can be compared with the recent experimental ones of the half wave potential for CAC systems that range from 0.60 V to 0.80 V in the reversible-hydrogen-electrode scale.
Hou, Z.*; Shu, D.-J.*; Chai, G.-L.*; Ikeda, Takashi; Terakura, Kiyoyuki*
Journal of Physical Chemistry C, 118(34), p.19795 - 19805, 2014/08
Times Cited Count:11 Percentile:35.81(Chemistry, Physical)In most of the N-doped graphene which attracts strong attention in the context of precious-metal free catalysts and nanoelectronics, the oxygen content is generally higher than or at least comparable to the nitrogen content. We perform density functional theory calculations to study the interplay of oxidized monovacancies and the nitrogen doping, motivated by the fact that MV is more frequently observed and more chemically active than divacancy and Stone-Wales defect. We determine the phase diagrams of un-doped and nitrogen-doped oxidized MVs as a function of temperature and partial pressure of O and H
and H gases. The modification of the electronic structure of MV by oxidation and N doping is studied. Our results show that the ether group is a common component in stable configurations of oxidized MVs. Most of the stable configurations of oxidized MVs do not induce any carriers.
gases. The modification of the electronic structure of MV by oxidation and N doping is studied. Our results show that the ether group is a common component in stable configurations of oxidized MVs. Most of the stable configurations of oxidized MVs do not induce any carriers.
Kawamura, Yoshinori; Shu, Wataru*; Matsuyama, Masao*; Yamanishi, Toshihiko
Fusion Science and Technology, 60(3), p.986 - 989, 2011/10
Times Cited Count:4 Percentile:32.59(Nuclear Science & Technology)Assuming the blanket sweep gas at the outlet of the blanket, tritium gas monitor by  -ray induced X-ray spectroscopy has been modified, and has measured tritium at 120
-ray induced X-ray spectroscopy has been modified, and has measured tritium at 120  C. The counting rate at 120
C. The counting rate at 120  C was about 1/2 of that at the room temperature. In this work, the measurement system was a closed system. When two systems have same volume and same pressure, the number of molecules in higher temperature system is smaller. This is one of the causes of small counting rate. The deterioration of the scintillator after heating was not observed.
C was about 1/2 of that at the room temperature. In this work, the measurement system was a closed system. When two systems have same volume and same pressure, the number of molecules in higher temperature system is smaller. This is one of the causes of small counting rate. The deterioration of the scintillator after heating was not observed.
Alimov, V.; Shu, Wataru*; Roth, J.*; Lindig, S.*; Balden, M.*; Isobe, Kanetsugu; Yamanishi, Toshihiko
Journal of Nuclear Materials, 417(1-3), p.572 - 575, 2011/10
Times Cited Count:79 Percentile:98.58(Materials Science, Multidisciplinary)Blistering and deuterium retention in re-crystallized tungsten exposed to a low energy (38 eV/D) and high deuterium ion flux (10 D/m
D/m s) D plasma at ion fluences of 10
s) D plasma at ion fluences of 10 and 10
and 10 D/m
D/m at temperatures in the range from 320 to 800 K have been examined with scanning electron microscopy, thermal desorption spectroscopy (TDS), and the nuclear reaction. During exposure to the D plasma blisters with various shapes and sizes depending on the exposure temperature are formed on the W surface. At the temperatures above 700 K the blisters disappear. The deuterium retention increases with the exposure temperature, reaching its maximum value of about 7
at temperatures in the range from 320 to 800 K have been examined with scanning electron microscopy, thermal desorption spectroscopy (TDS), and the nuclear reaction. During exposure to the D plasma blisters with various shapes and sizes depending on the exposure temperature are formed on the W surface. At the temperatures above 700 K the blisters disappear. The deuterium retention increases with the exposure temperature, reaching its maximum value of about 7 10
10 D/m
D/m at 530 K and about 1
at 530 K and about 1 10
10 D m
D m at 480 K for ion fluences of 10
at 480 K for ion fluences of 10 and 10
and 10 D/m
D/m , respectively. As the temperature grows further, the D retention decreases to about 10
, respectively. As the temperature grows further, the D retention decreases to about 10 D/m
D/m at 800 K.
at 800 K.
 Ru
Ru )
) Sb
Sb and Pr
and Pr La
La Os
Os Sb
Sb
Shu, L.*; Higemoto, Wataru; Aoki, Yuji*; Hillier, A. D.*; Oishi, Kazuki*; Ishida, Kenji*; Kadono, Ryosuke*; Koda, Akihiro*; Bernal, O. O.*; MacLaughlin, D. E.*; et al.
Physical Review B, 83(10), p.100504_1 - 100504_4, 2011/03
Times Cited Count:34 Percentile:77.76(Materials Science, Multidisciplinary)Zero-field muon spin relaxation experiments have been carried out in the Pr(Os Ru
Ru )
) Sb
Sb and Pr
and Pr La
La Os
Os Sb
Sb alloy systems to investigate broken time-reversal symmetry (TRS) in the superconducting state, signaled by the onset of a spontaneous static local magnetic field B
alloy systems to investigate broken time-reversal symmetry (TRS) in the superconducting state, signaled by the onset of a spontaneous static local magnetic field B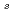 . In both alloy series B
. In both alloy series B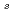 initially decreases linearly with solute concentration. Ru doping is considerably more efficient than La doping, with a 50% faster initial decrease. The data suggest that broken TRS is suppressed for Ru concentration
initially decreases linearly with solute concentration. Ru doping is considerably more efficient than La doping, with a 50% faster initial decrease. The data suggest that broken TRS is suppressed for Ru concentration 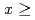 0.6 but persists for essentially all La concentrations. Our data support a crystal-field excitonic cooper pairing mechanism for TRS-breaking superconductivity.
0.6 but persists for essentially all La concentrations. Our data support a crystal-field excitonic cooper pairing mechanism for TRS-breaking superconductivity.
Alimov, V.; Roth, J.*; Shu, Wataru*; Komarov, D. A.*; Isobe, Kanetsugu; Yamanishi, Toshihiko
Journal of Nuclear Materials, 399(2-3), p.225 - 230, 2010/04
Times Cited Count:32 Percentile:89.14(Materials Science, Multidisciplinary)A study of the influence of the deposition conditions on the surface morphology and deuterium concentration in tungsten deposition layers formed by magnetron sputtering and in the linear plasma generator has been carried out. Adhesion of the W layer to substrate is shown to depend on the coefficients of thermal expansion for tungsten and substrate material, thickness of the W layer, and the substrate temperature during layer deposition. A decreased D concentration for increased substrate temperatures and deposition rate are observed.
Alimov, V.; Shu, Wataru*; Roth, J.*; Sugiyama, Kazuyoshi*; Lindig, S.*; Balden, M.*; Isobe, Kanetsugu; Yamanishi, Toshihiko
Physica Scripta, T138, p.014048_1 - 014048_5, 2009/12
Times Cited Count:123 Percentile:95.28(Physics, Multidisciplinary)Blistering and deuterium retention in re-crystallized tungsten exposed to low-energy, high flux (10 D/m
D/m s) pure and helium-seeded D plasmas to a fluence of 10
s) pure and helium-seeded D plasmas to a fluence of 10 D/m
D/m have been examined with scanning electron microscopy, thermal desorption spectroscopy (TDS), and the D(
have been examined with scanning electron microscopy, thermal desorption spectroscopy (TDS), and the D( He,p)
He,p) He nuclear reaction at a
He nuclear reaction at a  He energy varied from 0.69 to 4.0 MeV. In the case of exposure to pure D plasma (38 eV/D), blisters with various shapes and sizes depending on the exposure temperature are found on the W surface. No blisters appear at temperatures above 700 K. The deuterium retention increases with the exposure temperature, reaching a maximum value of about 10
He energy varied from 0.69 to 4.0 MeV. In the case of exposure to pure D plasma (38 eV/D), blisters with various shapes and sizes depending on the exposure temperature are found on the W surface. No blisters appear at temperatures above 700 K. The deuterium retention increases with the exposure temperature, reaching a maximum value of about 10 D/m
D/m at 480 K, and then decreases as the temperature rises further. Seeding of helium into the D plasma to the He ion concentration of 0.2 and 5% significantly reduces the D retention at elevated temperatures and prevents formation of the blisters.
at 480 K, and then decreases as the temperature rises further. Seeding of helium into the D plasma to the He ion concentration of 0.2 and 5% significantly reduces the D retention at elevated temperatures and prevents formation of the blisters.
Shu, Wataru; Nakamichi, Masaru; Alimov, V.; Luo, G.-N.*; Isobe, Kanetsugu; Yamanishi, Toshihiko
Journal of Nuclear Materials, 390-391, p.1017 - 1021, 2009/06
Times Cited Count:50 Percentile:95.12(Materials Science, Multidisciplinary)no abstracts in English
Shu, Wataru; Kawasuso, Atsuo; Yamanishi, Toshihiko
Journal of Nuclear Materials, 386-388, p.356 - 359, 2009/04
Times Cited Count:44 Percentile:93.19(Materials Science, Multidisciplinary)Tungsten is a most promising plasma facing material because of its high melting point. The blistering and deuterium retention in recrystallized tungsten samples were investigated by using simulated edge-plasma of fusion reactors. High-dome blisters appeared at the tungsten surface after deuterium plasma exposure, and their ratios of height against chord of the blisters were even one-order greater that reported before. In addition, there was a cavity in the inside of small blisters, whereas there was a void/crack along the grain boundary beneath the big blister and there is no lid for big blisters. Besides the strong dependence upon the exposure temperature, blistering and deuterium retention also showed significant dependence upon the features of microstructure.
Sato, Hideyuki*; Aoki, Yuji*; Kikuchi, Daisuke*; Sugawara, Hitoshi*; Higemoto, Wataru; Oishi, Kazuki; Ito, Takashi; Heffner, R. H.; Saha, S. R.*; Koda, Akihiro*; et al.
Physica B; Condensed Matter, 404(5-7), p.749 - 753, 2009/04
Times Cited Count:5 Percentile:25.59(Physics, Condensed Matter)Wide varieties of strongly correlated electron phenomena are performed on the stage of a filled skutterudite structure. Especially when one of the players contains a plural number of 4f electrons, the orbital degrees of freedom play a major role as a new type of nonmagnetic and/or weak-magnetic phenomena. Several examples found in Pr- and Sm-based filled skutterudites are introduced in relation to muon spin relaxation experiments.
Alimov, V.; Shu, Wataru; Roth, J.*; Komarov, D. A.*; Lindig, S.*; Isobe, Kanetsugu; Nakamura, Hirofumi; Yamanishi, Toshihiko
Advanced Materials Research, 59, p.42 - 45, 2009/00
Times Cited Count:0 Percentile:0.12(Materials Science, Multidisciplinary)Shu, Wataru; Isobe, Kanetsugu; Yamanishi, Toshihiko
Fusion Engineering and Design, 83(7-9), p.1044 - 1048, 2008/12
Times Cited Count:42 Percentile:91.98(Nuclear Science & Technology)At 315 K, only sparse low-dome blisters appeared even the fluence was increased to 10 D/m
D/m . At around 400 K, the blisters became much denser and the dome of blisters became a little higher. Peculiar change occurred around 500 K, where two kinds of blisters appeared. One is the large blisters with sizes of a few tens of microns and varying ratios of height against chord (up to 0.6), and the other is the small blisters with chords of less than a few microns and large ratio of height against chord (about 0.7). In high temperature region (higher than 600 K), the blisters became much sparser with the increasing temperature and disappeared at 1000 K. Deuterium retention showed the maximum around 500 K, corresponding to the appearance of two kinds of high-dome blisters.
. At around 400 K, the blisters became much denser and the dome of blisters became a little higher. Peculiar change occurred around 500 K, where two kinds of blisters appeared. One is the large blisters with sizes of a few tens of microns and varying ratios of height against chord (up to 0.6), and the other is the small blisters with chords of less than a few microns and large ratio of height against chord (about 0.7). In high temperature region (higher than 600 K), the blisters became much sparser with the increasing temperature and disappeared at 1000 K. Deuterium retention showed the maximum around 500 K, corresponding to the appearance of two kinds of high-dome blisters.
Hayashi, Takumi; Suzuki, Takumi; Yamada, Masayuki; Shu, Wataru; Yamanishi, Toshihiko
Fusion Engineering and Design, 83(10-12), p.1429 - 1432, 2008/12
Times Cited Count:30 Percentile:86.27(Nuclear Science & Technology)In ITER facility, about 3 kg of tritium will be stored in more than 30 ZrCo hydride beds, as a reference design. The safe design and operation of tritium storage beds will be one of the most important points to enhance total safety of the facility. In the Tritium Process Lab. in Japan Atomic Energy Agency, many tritium storage beds with ZrCo have been used with/without self-accountancy measure, and the safe handling experiences have been accumulated for almost 20 years. From these experiences, the key issues to be considered for the safety design are the effect of tritium decay, such as decay heat transfer and  He behavior with the normal protection of over temperature, over pressure and leak for a metal-hydride bed. Concerning the safety operation, the key issues are the procedure of hydrogenation-dehydrogenation cycle under the requirements of the storage system and the emergency performances, such as a rapid hydrogen recovery and loss of normal cooling function.
He behavior with the normal protection of over temperature, over pressure and leak for a metal-hydride bed. Concerning the safety operation, the key issues are the procedure of hydrogenation-dehydrogenation cycle under the requirements of the storage system and the emergency performances, such as a rapid hydrogen recovery and loss of normal cooling function.
Yamanishi, Toshihiko; Hayashi, Takumi; Shu, Wataru; Kawamura, Yoshinori; Nakamura, Hirofumi; Iwai, Yasunori; Kobayashi, Kazuhiro; Isobe, Kanetsugu; Arita, Tadaaki; Hoshi, Shuichi; et al.
Fusion Engineering and Design, 83(10-12), p.1359 - 1363, 2008/12
Times Cited Count:4 Percentile:29.49(Nuclear Science & Technology)At TPL (Tritium Process Laboratory) of JAEA, ITER relevant tritium technologies have been studied. The design studies of Air Detritiation System have been carried out in JAEA as a contribution of Japan to ITER. For the tritium processing technologies, our efforts have been focused on the research of the tritium recovery system of ITER test blanket system. A ceramic proton conductor has been studied as an advanced blanket system. A series of fundamental studies on tritium safety technologies not only for ITER but also for fusion DEMO plants has also been carried out at TPL of JAEA. The main research activities in this field are the tritium behavior in a confinement and its barrier materials; monitoring; accountancy; detritiation and decontamination etc. In this paper, the results of above recent activities at TPL of JAEA are summarized from viewpoint of ITER relevant and future fusion DEMO reactors.
Yamanishi, Toshihiko; Hayashi, Takumi; Shu, Wataru; Kawamura, Yoshinori; Nakamura, Hirofumi; Iwai, Yasunori; Kobayashi, Kazuhiro; Isobe, Kanetsugu
Fusion Science and Technology, 54(1), p.45 - 50, 2008/07
Times Cited Count:4 Percentile:29.49(Nuclear Science & Technology)The R&D for tritium technologies towards to the DEMO plants are carried out in Broader Approach (BA) program in Japan: (1) tritium accountancy technology; (2) basic tritium safety research; and (3) tritium durability test. A multi-purpose facility is constructed at Rokkasho in Japan to carry out the above R&Ds. Beta  radioisotopes as well as tritium (370 TBq/year) can be handled in the facility. At TPL (Tritium Process Laboratory) of JAEA, a series of R&Ds for the tritium technologies relevant to the above BA program have been started. A series of basic studies for the tritium-materials has also been carried out. The main R&D activities in this field are the tritium behavior in a confinement; monitoring; detritiation; and decontamination. In this paper, the results of above recent activities at TPL of JAEA are also summarized from viewpoint of future fusion DEMO reactors.
radioisotopes as well as tritium (370 TBq/year) can be handled in the facility. At TPL (Tritium Process Laboratory) of JAEA, a series of R&Ds for the tritium technologies relevant to the above BA program have been started. A series of basic studies for the tritium-materials has also been carried out. The main R&D activities in this field are the tritium behavior in a confinement; monitoring; detritiation; and decontamination. In this paper, the results of above recent activities at TPL of JAEA are also summarized from viewpoint of future fusion DEMO reactors.
Yamanishi, Toshihiko; Yamada, Masayuki; Suzuki, Takumi; Shu, Wataru; Kawamura, Yoshinori; Nakamura, Hirofumi; Iwai, Yasunori; Kobayashi, Kazuhiro; Isobe, Kanetsugu; Hoshi, Shuichi; et al.
Fusion Science and Technology, 54(1), p.315 - 318, 2008/07
Times Cited Count:11 Percentile:59.16(Nuclear Science & Technology)The construction of the building and safety systems of the TPL was completed until 1985. The operations of the safety systems with tritium have been started from March 1988. The amount of tritium held at the TPL was 13 PBq at March 2007. The average tritium concentration in a stream from a stack of the TPL to environment was 6.0 10
10 Bq/cm
Bq/cm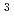 ; and is 1/100 smaller than that of the regulation value for the concentration of HTO in the air in Japan. The safety operation results with tritium have thus been obtained. A set of failure data of several main components of the TPL was also obtained as the valuable data for fusion tritium facilities.
; and is 1/100 smaller than that of the regulation value for the concentration of HTO in the air in Japan. The safety operation results with tritium have thus been obtained. A set of failure data of several main components of the TPL was also obtained as the valuable data for fusion tritium facilities.