Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Hattori, Koichi*; Suenaga, Daiki*; Suzuki, Kei; Yasui, Shigehiro*
Physical Review B, 108(24), p.245110_1 - 245110_11, 2023/12
Times Cited Count:0 Percentile:0(Materials Science, Multidisciplinary)We develop a mean-field theory of a novel Kondo effect emerging in systems without a Fermi surface, which instead emerges under strong magnetic fields. We determine the magnitude of the Kondo condensate, which is a particle pairing composed of conducting Dirac fermions and localized impurities. We focus on the competition between the Kondo effect and the energy gap formation that stems from the pairing among the Dirac fermions leading to the dynamical chiral symmetry breaking. We find that this competition induces a quantum critical point. We also investigate finite-temperature effects. This system at vanishing fermion density can be studied with Monte Carlo lattice simulations, which do not suffer from the sign problem.
Kim, Y.*; Oka, Makoto; Suenaga, Daiki*; Suzuki, Kei
Physical Review D, 107(7), p.074015_1 - 074015_15, 2023/04
Times Cited Count:1 Percentile:54.75(Astronomy & Astrophysics)A chiral effective theory of scalar and vector diquarks is formulated, which is based on 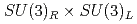 chiral symmetry and includes interactions between scalar and vector diquarks with one or two mesons. We find that the diquark interaction term with two mesons breaks the
chiral symmetry and includes interactions between scalar and vector diquarks with one or two mesons. We find that the diquark interaction term with two mesons breaks the 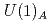 and flavor
and flavor 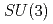 symmetries. To determine the coupling constants of the interaction Lagrangians, we investigate one-pion emission decays of singly heavy baryons
symmetries. To determine the coupling constants of the interaction Lagrangians, we investigate one-pion emission decays of singly heavy baryons  (
(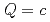 ,
,  and
and 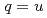 ,
,  ,
,  ), where baryons are regarded as diquark-heavy-quark two-body systems. Using this model, we present predictions of the unobserved decay widths of singly heavy baryons. We also study the change of masses and strong decay widths of singly heavy baryons under partial restoration of chiral symmetry.
), where baryons are regarded as diquark-heavy-quark two-body systems. Using this model, we present predictions of the unobserved decay widths of singly heavy baryons. We also study the change of masses and strong decay widths of singly heavy baryons under partial restoration of chiral symmetry.
Hattori, Koichi*; Suenaga, Daiki*; Suzuki, Kei; Yasui, Shigehiro*
EPJ Web of Conferences, 276, p.01015_1 - 01015_5, 2023/03
Times Cited Count:0 Percentile:0.91(Physics, Atomic, Molecular & Chemical)We investigate the QCD phase diagram in strong magnetic fields with heavy-quark impurities and determine the ground state within the mean-field analysis. The ground state is characterized by magnitudes of the pairing not only between the light quark and antiquark, i.e., chiral condensate, but also between the light quark and heavy-quark impurity, dubbed the Kondo condensate. We propose signatures of the interplay and/or competition between those two pairing phenomena reflected in the magnitude of the chiral condensate that is saturated with respect to the magnetic-field strength and anomalously increases with increasing temperature.
Arifi, A. J.*; Suenaga, Daiki*; Hosaka, Atsushi; Oh, Y. S.*
Physical Review D, 105(9), p.094006_1 - 094006_17, 2022/05
Times Cited Count:7 Percentile:77.92(Astronomy & Astrophysics)Suenaga, Daiki*; Araki, Yasufumi; Suzuki, Kei; Yasui, Shigehiro*
Physical Review D, 105(7), p.074028_1 - 074028_19, 2022/04
Times Cited Count:2 Percentile:36.77(Astronomy & Astrophysics)We propose a new mechanism of the heavy-quark spin polarization (HQSP) in quark matter induced by the Kondo effect under an external magnetic field. The Kondo effect is caused by a condensate between a heavy and a light quark called the Kondo condensate leading to a mixing of the heavy- and light-quark spins. Thus, the HQSP is driven through the Kondo effect from light quarks coupling with the magnetic field in quark matter. For demonstration, we employ the Nambu-Jona-Lasinio type model under a magnetic field and investigate the HQSP within the linear response theory with vertex corrections required by the 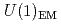 electromagnetic gauge invariance. As a result, we find that the HQSP arises significantly with the appearance of the Kondo effect. Our findings are testable in future sign-problem-free lattice simulations.
electromagnetic gauge invariance. As a result, we find that the HQSP arises significantly with the appearance of the Kondo effect. Our findings are testable in future sign-problem-free lattice simulations.
Suenaga, Daiki*; Hosaka, Atsushi
Physical Review D, 105(7), p.074036_1 - 074036_13, 2022/04
Times Cited Count:5 Percentile:67.33(Astronomy & Astrophysics)Suenaga, Daiki*; Hosaka, Atsushi
Physical Review D, 104(3), p.034009_1 - 034009_7, 2021/08
Times Cited Count:7 Percentile:51.62(Astronomy & Astrophysics)Arifi, A. J.*; Suenaga, Daiki*; Hosaka, Atsushi
Physical Review D, 103(9), p.094003_1 - 094003_6, 2021/05
Times Cited Count:17 Percentile:84.37(Astronomy & Astrophysics)Araki, Yasufumi; Suenaga, Daiki*; Suzuki, Kei; Yasui, Shigehiro*
Physical Review Research (Internet), 3(2), p.023098_1 - 023098_17, 2021/05
Spins of relativistic fermions are related to their orbital degrees of freedom. In order to quantify the effect of hybridization between relativistic and nonrelativistic degrees of freedom on spin-orbit coupling, we focus on the spin-orbital (SO) crossed susceptibility arising from spin-orbit coupling. The SO crossed susceptibility is defined as the response function of their spin polarization to the "orbital" magnetic field, namely the effect of magnetic field on the orbital motion of particles as the vector potential. Once relativistic and nonrelativistic fermions are hybridized, their SO crossed susceptibility gets modified at the Fermi energy around the band hybridization point, leading to spin polarization of nonrelativistic fermions as well. These effects are enhanced under a dynamical magnetic field that violates thermal equilibrium, arising from the interband process permitted by the band hybridization. Its experimental realization is discussed for Dirac electrons in solids with slight breaking of crystalline symmetry or doping, and also for quark matter including dilute heavy quarks strongly hybridized with light quarks, arising in a relativistic heavy-ion collision process.
Suenaga, Daiki*; Araki, Yasufumi; Suzuki, Kei; Yasui, Shigehiro*
Physical Review D, 103(5), p.054041_1 - 054041_17, 2021/03
Times Cited Count:5 Percentile:45.23(Astronomy & Astrophysics)We investigate the influence of the Kondo effect, namely, the nonperturbative effect induced by heavy impurities, on the chiral separation effect (CSE) in quark matter. We employ a simple effective model incorporating the Kondo condensate made of a light quark and a heavy quark, and compute the response function of the axial current to the magnetic field in the static and dynamical limits. As a result, we find that the Kondo effect catalyzes the CSE in both of the limits, and in particular the CSE in the dynamical limit can be enhanced by a factor of approximately 3. Our findings clearly show that the presence of heavy impurities in quark matter can play an important role in the transport phenomena of light quarks induced by a magnetic field.
Araki, Yasufumi; Suenaga, Daiki*; Suzuki, Kei; Yasui, Shigehiro*
Physical Review Research (Internet), 3(1), p.013233_1 - 013233_12, 2021/03
We investigate two different types of relativistic Kondo effects, distinguished by heavy-impurity degrees of freedom, by focusing on the energy-momentum dispersion relations of the ground state with condensates composed of a light Dirac fermion and a nonrelativistic impurity fermion. Heavy fermion degrees of freedom are introduced in terms of two types of heavy-fermion effective theories, in other words, two heavy-fermion limits for the heavy Dirac fermion, which is known as the heavy-quark effective theories (HQETs) in high-energy physics. While the first one includes only the heavy-particle component, the second one contains both the heavy-particle and heavy-antiparticle components, which are opposite in their parity. From these theories, we obtain two types of Kondo effects, in which the dispersions near the Fermi surface are very similar, but they differ in the structure at low momentum. We also classify the possible forms of condensates in the two limits. The two Kondo effects will be examined by experiments with Dirac/Weyl semimetals or quark matter, lattice simulations, and cold-atom simulations.
Suenaga, Daiki*; Suzuki, Kei; Araki, Yasufumi; Yasui, Shigehiro*
Physical Review Research (Internet), 2(2), p.023312_1 - 023312_13, 2020/06
The Kondo effect is induced by the interaction between light fermions near the Fermi surface and heavy impurities, and it affects electric/thermal/transport properties of matter. The chirality (right-handed or left-handed) is one of the unique properties of relativistic (Dirac or Weyl) fermions. In normal matter, the numbers of right- and left-handed particles are equivalent to each other, but environments with a chirality imbalance can also be realized. In this paper, we theoretically propose the Kondo effect driven by a chirality imbalance (or chiral chemical potential) of relativistic light fermions. This effect is caused by the mixing between a right-handed (or left-handed) fermion and a heavy impurity in the chirality imbalanced matter. This is different from the usual Kondo effect induced by finite density (or chemical potential) for light fermions. We construct an effective model with an interaction between a relativistic fermion and a heavy impurity, and we derive the realization of the Kondo effect from both a perturbative calculation and a nonperturbative mean-field approach. We also discuss the temperature dependence, the coupling constant dependence, the susceptibilities, and the order of the phase transition for the Kondo effect. Such a Kondo effect will be tested by future lattice simulations.
Suenaga, Daiki*; Suzuki, Kei; Yasui, Shigehiro*
Physical Review Research (Internet), 2(2), p.023066_1 - 023066_11, 2020/04
The QCD Kondo effect is a quantum phenomenon in which heavy (charm or bottom) quarks exist as impurity particles in quark matter composed of light quarks at extremely high density. In this paper, we theoretically predict the existence of the exciton modes above the ground state of the quark matter governed by the QCD Kondo effect. We construct an effective model based on the mean field approximation and investigate possible quantum numbers (such as spin and parity) of excitons and their dispersion relations. These excitons can be electrically (color) neutral, so that they are observed as the neutral currents in transport phenomena. As a result, they contribute to violation of the Wiedemann-Franz law for the electric (color) and heat conductivities. Such Kondo excitons are an universal phenomenon for relativistic (Dirac or Weyl) fermions, and the same concept will also be applied to Dirac or Weyl electron systems.
 mesons as a probe of Casimir effect for chiral symmetry breaking
mesons as a probe of Casimir effect for chiral symmetry breakingIshikawa, Tsutomu*; Nakayama, Katsumasa*; Suenaga, Daiki*; Suzuki, Kei
Physical Review D, 100(3), p.034016_1 - 034016_14, 2019/08
Times Cited Count:5 Percentile:31.16(Astronomy & Astrophysics)We propose  mesons as probes to investigate finite-volume effects for chiral symmetry breaking at zero and finite temperatures. By using the 2+1-flavor linear sigma model with constituent light quarks, we analyze the Casimir effects for the
mesons as probes to investigate finite-volume effects for chiral symmetry breaking at zero and finite temperatures. By using the 2+1-flavor linear sigma model with constituent light quarks, we analyze the Casimir effects for the  mean fields; the chiral symmetry is rapidly restored by the antiperiodic boundary for light quarks, and the chiral symmetry breaking is catalyzed by the periodic boundary. We also show the phase diagram of the
mean fields; the chiral symmetry is rapidly restored by the antiperiodic boundary for light quarks, and the chiral symmetry breaking is catalyzed by the periodic boundary. We also show the phase diagram of the  mean fields on the volume and temperature plane. For
mean fields on the volume and temperature plane. For  mesons, we employ an effective model based on the chiral-partner structure, in which the volume dependence of
mesons, we employ an effective model based on the chiral-partner structure, in which the volume dependence of  mesons is induced by the
mesons is induced by the  mean fields. We find that
mean fields. We find that 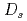 mesons are less sensitive to finite volume than
mesons are less sensitive to finite volume than  mesons, which is caused by the insensitivity of
mesons, which is caused by the insensitivity of 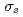 mean fields. An anomalous mass shift of
mean fields. An anomalous mass shift of  mesons at high temperature with the periodic boundary will be useful in examinations with lattice QCD simulations. The dependence on the number of compactified spatial dimensions is also studied.
mesons at high temperature with the periodic boundary will be useful in examinations with lattice QCD simulations. The dependence on the number of compactified spatial dimensions is also studied.
Suzuki, Kei; Ishikawa, Tsutomu*; Nakayama, Katsumasa*; Suenaga, Daiki*
no journal, ,
D mesons are expected to be clear probes of the chiral condensate. For the Casimir effect in the QCD vacuum, non-perturbative properties of the QCD vacuum are modified by the volume size and boundary conditions. In this talk, we focus on the modification of the chiral symmetry breaking by the Casimir effect and the response of D mesons. By using an effective Lagrangian based on chiral partner structures for D mesons, we discuss the dependences on volume, boundary, and temperature, and the applications to lattice QCD simulations.
Araki, Yasufumi; Suenaga, Daiki*; Suzuki, Kei; Yasui, Shigehiro*
no journal, ,
no abstracts in English
Hattori, Koichi*; Suenaga, Daiki*; Suzuki, Kei; Yasui, Shigehiro*
no journal, ,
no abstracts in English
Fujii, Daisuke; Iwanaka, Akihiro*; Suenaga, Daiki*; Kitazawa, Masakiyo*
no journal, ,
The Matsubara formalism for the thermal quantum field theory introduces temperature into the theory as a boundary condition along the imaginary time direction of Euclidean spacetime. In this study, we consider the pure Yang-Mills theory on 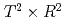 , which further imposes boundary conditions on the spatial direction, and discuss thermodynamic quantities and phase structures. Results from lattice QCD simulations show that anisotropic effects are suppressed until the spatial directional spread becomes significantly smaller near the critical temperature. By constructing the model to reproduce the lattice QCD results, it becomes clear that the system suggests the existence of a very rich phase structure.
, which further imposes boundary conditions on the spatial direction, and discuss thermodynamic quantities and phase structures. Results from lattice QCD simulations show that anisotropic effects are suppressed until the spatial directional spread becomes significantly smaller near the critical temperature. By constructing the model to reproduce the lattice QCD results, it becomes clear that the system suggests the existence of a very rich phase structure.
Fujii, Daisuke; Iwanaka, Akihiro*; Suenaga, Daiki*; Kitazawa, Masakiyo*
no journal, ,
The Matsubara formalism for the thermal quantum field theory introduces temperature into the theory as a boundary condition along the imaginary time direction of Euclidean spacetime. In this study, we further consider the pure Yang-Mills theory on 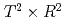 with boundary conditions in one spatial direction, and discuss thermodynamic quantities and their phase structures. The introducing of the boundary condition leads to the breaking of rotational symmetry, which results in anisotropy of the pressure. Results from lattice QCD simulations show that the anisotropic effect is suppressed until the spatial spread becomes significantly smaller near the critical temperature. This result is a very different behavior from that of free-particle systems. In order to reveal the mechanism behind this result, we employ an effective model with two Polyakov loops along the time and spatial directions. We show that introducing the competition between the two Polyakov loops as suggested in a previous study describes well the lattice data in the high temperature region. Furthermore, we show that a new first-order phase transition is suggested, which is different from the confinement phase transition.
with boundary conditions in one spatial direction, and discuss thermodynamic quantities and their phase structures. The introducing of the boundary condition leads to the breaking of rotational symmetry, which results in anisotropy of the pressure. Results from lattice QCD simulations show that the anisotropic effect is suppressed until the spatial spread becomes significantly smaller near the critical temperature. This result is a very different behavior from that of free-particle systems. In order to reveal the mechanism behind this result, we employ an effective model with two Polyakov loops along the time and spatial directions. We show that introducing the competition between the two Polyakov loops as suggested in a previous study describes well the lattice data in the high temperature region. Furthermore, we show that a new first-order phase transition is suggested, which is different from the confinement phase transition.
Fujii, Daisuke; Iwanaka, Akihiro*; Suenaga, Daiki*; Kitazawa, Masakiyo*
no journal, ,
We discuss pure Yang-Mills theory with anisotropic boundary conditions on 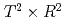 manifolds. The lattice QCD results show that anisotropy effects are suppressed until the spatial spread becomes significantly smaller near the critical temperature. We successfully reproduce the thermodynamics of lattice by extending the Polyakov loop model, which describes the usual finite temperature, on
manifolds. The lattice QCD results show that anisotropy effects are suppressed until the spatial spread becomes significantly smaller near the critical temperature. We successfully reproduce the thermodynamics of lattice by extending the Polyakov loop model, which describes the usual finite temperature, on 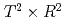 with parameters. Furthermore, by considering the physical background, we show that the competition between the two Polyakov loops introduced in the model and the existence of a new first-order phase transition are important.
with parameters. Furthermore, by considering the physical background, we show that the competition between the two Polyakov loops introduced in the model and the existence of a new first-order phase transition are important.