Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Kokubun, Yuji; Nakada, Akira; Seya, Natsumi; Koike, Yuko; Nemoto, Masashi; Tobita, Keiji; Yamada, Ryohei*; Uchiyama, Rei; Yamashita, Daichi; Nagai, Shinji; et al.
JAEA-Review 2023-046, 164 Pages, 2024/03
The Nuclear Fuel Cycle Engineering Laboratories conducts environmental radiation monitoring around the reprocessing plant in accordance with the "Safety Regulations for Reprocessing Plant of JAEA, Part IV: Environmental Monitoring". This report summarizes the results of environmental radiation monitoring conducted during the period from April 2022 to March 2023 and the results of dose calculations for the surrounding public due to the release of radioactive materials into the atmosphere and ocean. In the results of the above environmental radiation monitoring, many items were affected by radioactive materials emitted from the accident at the Fukushima Daiichi Nuclear Power Plant of Tokyo Electric Power Company, Incorporated (changed to Tokyo Electric Power Company Holdings, Inc. on April 1, 2016), which occurred in March 2011. Also included as appendices are an overview of the environmental monitoring plan, an overview of measurement methods, measurement results and their changes over time, meteorological statistics results, radioactive waste release status, and an evaluation of the data which deviated of the normal range.
Nakada, Akira; Kanai, Katsuta; Seya, Natsumi; Nishimura, Shusaku; Futagawa, Kazuo; Nemoto, Masashi; Tobita, Keiji; Yamada, Ryohei*; Uchiyama, Rei; Yamashita, Daichi; et al.
JAEA-Review 2022-078, 164 Pages, 2023/03
Environmental radiation monitoring around the Tokai Reprocessing Plant has been performed by the Nuclear Fuel Cycle Engineering Laboratories, based on "Safety Regulations for the Reprocessing Plant of Japan Atomic Energy Agency, Chapter IV - Environmental Monitoring". This annual report presents the results of the environmental monitoring and the dose estimation to the hypothetical inhabitant due to the radioactivity discharged from the plant to the atmosphere and the sea during April 2021 to March 2022. In this report, some data include the influence of the accidental release from the Fukushima Daiichi Nuclear Power Station of Tokyo Electric Power Co., Inc. (the trade name was changed to Tokyo Electric Power Company Holdings, Inc. on April 1, 2016) in March 2011. Appendices present comprehensive information, such as monitoring programs, monitoring methods, monitoring results and their trends, meteorological data and discharged radioactive wastes. In addition, the data which were influenced by the accidental release and exceeded the normal range of fluctuation in the monitoring, were evaluated.
Nakada, Akira; Nakano, Masanao; Kanai, Katsuta; Seya, Natsumi; Nishimura, Shusaku; Nemoto, Masashi; Tobita, Keiji; Futagawa, Kazuo; Yamada, Ryohei; Uchiyama, Rei; et al.
JAEA-Review 2021-062, 163 Pages, 2022/02
Environmental radiation monitoring around the Tokai Reprocessing Plant has been performed by the Nuclear Fuel Cycle Engineering Laboratories, based on "Safety Regulations for the Reprocessing Plant of Japan Atomic Energy Agency, Chapter IV - Environmental Monitoring". This annual report presents the results of the environmental monitoring and the dose estimation to the hypothetical inhabitant due to the radioactivity discharged from the plant to the atmosphere and the sea during April 2020 to March 2021. In this report, some data include the influence of the accidental release from the Fukushima Daiichi Nuclear Power Station of Tokyo Electric Power Co., Inc. (the trade name was changed to Tokyo Electric Power Company Holdings, Inc. on April 1, 2016) in March 2011. Appendices present comprehensive information, such as monitoring programs, monitoring methods, monitoring results and their trends, meteorological data and discharged radioactive wastes. In addition, the data which were influenced by the accidental release and exceeded the normal range of fluctuation in the monitoring, were evaluated.
Nakano, Masanao; Fujii, Tomoko; Nemoto, Masashi; Tobita, Keiji; Seya, Natsumi; Nishimura, Shusaku; Hosomi, Kenji; Nagaoka, Mika; Yokoyama, Hiroya; Matsubara, Natsumi; et al.
JAEA-Review 2020-069, 163 Pages, 2021/02
Environmental radiation monitoring around the Tokai Reprocessing Plant has been performed by the Nuclear Fuel Cycle Engineering Laboratories, based on "Safety Regulations for the Reprocessing Plant of Japan Atomic Energy Agency, Chapter IV - Environmental Monitoring". This annual report presents the results of the environmental monitoring and the dose estimation to the hypothetical inhabitant due to the radioactivity discharged from the plant to the atmosphere and the sea during April 2019 to March 2020. In this report, some data include the influence of the accidental release from the Fukushima Daiichi Nuclear Power Station of Tokyo Electric Power Co., Inc. (the trade name was changed to Tokyo Electric Power Company Holdings, Inc. on April 1, 2016) in March 2011. Appendices present comprehensive information, such as monitoring programs, monitoring methods, monitoring results and their trends, meteorological data and discharged radioactive wastes. In addition, the data which were influenced by the accidental release and exceeded the normal range of fluctuation in the monitoring, were evaluated.
Nakano, Masanao; Fujii, Tomoko; Nemoto, Masashi; Tobita, Keiji; Kono, Takahiko; Hosomi, Kenji; Nishimura, Shusaku; Matsubara, Natsumi; Maehara, Yushi; Narita, Ryosuke; et al.
JAEA-Review 2019-048, 165 Pages, 2020/03
Environmental radiation monitoring around the Tokai Reprocessing Plant has been performed by the Nuclear Fuel Cycle Engineering Laboratories, based on "Safety Regulations for the Reprocessing Plant of Japan Atomic Energy Agency, Chapter IV - Environmental Monitoring". This annual report presents the results of the environmental monitoring and the dose estimation to the hypothetical inhabitant due to the radioactivity discharged from the plant to the atmosphere and the sea during April 2018 to March 2019. In this report, some data include the influence of the accidental release from the Fukushima Daiichi Nuclear Power Station of Tokyo Electric Power Co., Inc. (the trade name was changed to Tokyo Electric Power Company Holdings, Inc. on April 1, 2016) in March 2011. Appendices present comprehensive information, such as monitoring programs, monitoring methods, monitoring results and their trends, meteorological data and discharged radioactive wastes. In addition, the data which were influenced by the accidental release and exceeded the normal range of fluctuation in the monitoring, were evaluated.
Nakano, Masanao; Fujita, Hiroki; Mizutani, Tomoko; Nemoto, Masashi; Tobita, Keiji; Kono, Takahiko; Hosomi, Kenji; Hokama, Tomonori; Nishimura, Tomohiro; Matsubara, Natsumi; et al.
JAEA-Review 2018-025, 171 Pages, 2019/02
Environmental radiation monitoring around the Tokai Reprocessing Plant has been performed by the Nuclear Fuel Cycle Engineering Laboratories, based on "Safety Regulations for the Reprocessing Plant of Japan Atomic Energy Agency, Chapter IV - Environmental Monitoring". This annual report presents the results of the environmental monitoring and the dose estimation to the hypothetical inhabitant due to the radioactivity discharged from the plant to the atmosphere and the sea during April 2016 to March 2017. In this report, some data include the influence of the accidental release from the Fukushima Daiichi Nuclear Power Station of Electric Power Company Holdings, Inc. in March 2011. Appendices present comprehensive information, such as monitoring programs, monitoring methods, monitoring results and their trends, meteorological data and discharged radioactive wastes. In addition, the data which were influenced by the accidental release and were exceeded the normal range of fluctuation in the monitoring, were evaluated.
Nakano, Masanao; Fujita, Hiroki; Mizutani, Tomoko; Nemoto, Masashi; Tobita, Keiji; Hosomi, Kenji; Nagaoka, Mika; Hokama, Tomonori; Nishimura, Tomohiro; Koike, Yuko; et al.
JAEA-Review 2017-028, 177 Pages, 2018/01
Environmental radiation monitoring around the Tokai Reprocessing Plant has been performed by the Nuclear Fuel Cycle Engineering Laboratories, based on "Safety Regulations for the Reprocessing Plant of Japan Atomic Energy Agency, Chapter IV - Environmental Monitoring". This annual report presents the results of the environmental monitoring and the dose estimation to the hypothetical inhabitant due to the radioactivity discharged from the plant to the atmosphere and the sea during April 2016 to March 2017. In this report, some data include the influence of the accidental release from the Fukushima Daiichi Nuclear Power Station of Electric Power Company Holdings, Inc. in March 2011. Appendices present comprehensive information, such as monitoring programs, monitoring methods, monitoring results and their trends, meteorological data and discharged radioactive wastes. In addition, the data which were influenced by the accidental release and were exceeded the normal range of fluctuation in the monitoring, were evaluated.
Nakano, Masanao; Fujita, Hiroki; Mizutani, Tomoko; Hosomi, Kenji; Nagaoka, Mika; Hokama, Tomonori; Yokoyama, Hiroya; Nishimura, Tomohiro; Matsubara, Natsumi; Maehara, Yushi; et al.
JAEA-Review 2016-035, 179 Pages, 2017/03
Environmental radiation monitoring around the Tokai Reprocessing Plant has been performed by the Nuclear Fuel Cycle Engineering Laboratories, based on "Safety Regulations for the Reprocessing Plant of Japan Atomic Energy Agency, Chapter IV - Environmental Monitoring". This annual report presents the results of the environmental monitoring and the dose estimation to the hypothetical inhabitant due to the radioactivity discharged from the plant to the atmosphere and the sea during April 2015 to March 2016. In this report, some data include the influence of the accidental release from the Fukushima Daiichi Nuclear Power Station of Electric Power Company Holdings, Inc. in March 2011. Appendices present comprehensive information, such as monitoring programs, monitoring methods, monitoring results and their trends, meteorological data and discharged radioactive wastes. In addition, the data which were influenced by the accidental release and were exceeded the normal range of fluctuation in the monitoring, were evaluated.
Watanabe, Hitoshi; Nakano, Masanao; Fujita, Hiroki; Takeyasu, Masanori; Mizutani, Tomoko; Isozaki, Tokuju*; Nagaoka, Mika; Hokama, Tomonori; Yokoyama, Hiroya; Nishimura, Tomohiro; et al.
JAEA-Review 2015-034, 175 Pages, 2016/03
Environmental radiation monitoring around the Tokai Reprocessing Plant has been performed by the Nuclear Fuel Cycle Engineering Laboratories, based on "Safety Regulations for the Reprocessing Plant of Japan Atomic Energy Agency, Chapter IV - Environmental Monitoring". This annual report presents the results of the environmental monitoring and the dose estimation to the hypothetical inhabitant due to the radioactivity discharged from the plant to the atmosphere and the sea during April 2014 to March 2015. In this report, some data include the influence of the accidental release from the Fukushima Daiichi Nuclear Power Station of Tokyo Electric Power Co. in March 2011.
 -Co films
-Co filmsSakai, Seiji; Mitani, Seiji*; Sugai, Isamu; Takanashi, Koki; Matsumoto, Yoshihiro; Entani, Shiro; Naramoto, Hiroshi*; Avramov, P.; Maeda, Yoshihito
Physical Review B, 83(17), p.174422_1 - 174422_6, 2011/05
Times Cited Count:8 Percentile:36.17(Materials Science, Multidisciplinary)Saegusa, Yoshie*; Sugai, Toshihiko*; Ogami, Takashi*; Kashima, Kaoru*; Sasao, Eiji
Quaternary International, 230(1-2), p.67 - 77, 2011/01
Times Cited Count:8 Percentile:24.09(Geography, Physical)We reconstructed Holocene environmental changes by analyzing diatom assemblages of four drilling cores from the Nobi Plain, central Japan. We identified five diatom assemblage zones: (1) freshwater species dominant; (2) increase of marine and brackish-marine species, indicating transgression; (3) marine species dominant; (4) increase of freshwater species, indicating marine regression as a result of delta progradation; and (5) freshwater species dominant, in ascending order. It became clear that the shoreline migrated landward (transgression) faster than it migrated seaward (regression) by the comparison the diatom assemblages and lithological units. The transgressive diatom assemblage changes (decrease in marine-brackish water species) took up to 1000 years, whereas regressive changes required only a few hundred years. Diatom analysis is useful for reconstructing not only Holocene sea-level changes and sedimentary environments but also local geographic effects.
Niwa, Yuichi*; Sugai, Toshihiko*; Saegusa, Yoshie*; Ogami, Takashi*; Sasao, Eiji
Quaternary International, 230(1-2), p.78 - 86, 2011/01
Times Cited Count:10 Percentile:28.95(Geography, Physical)We assessed the usefulness of electrical conductivity (EC) of stirred Holocene deltaic sediments from three cores from the Nobi Plain, Japan, as a proxy for marine transgression and regression. Marine deposits showed high EC, terrestrial deposits low EC, and brackish deposits intermediate. Because it was positively correlated with the percentage of marine diatom species, EC in inner bay deposits primarily reflected salinity. In the YM core (the youngest of the three cores), EC of the inner bay deposits was weakly positively correlated with clay content. EC of inner bay clayey deposits was generally higher in YM than in KZN, suggesting that the lower EC in older clayey sediments results from compaction. These findings suggest that the EC values of fine sediments initially record salinity but may decrease gradually over time under the influence of compaction. Thus, to reconstruct the original salinity, the effects of compaction and of grain size distribution should be evaluated.
 -Co granular thin films
-Co granular thin filmsSugai, Isamu*; Sakai, Seiji; Matsumoto, Yoshihiro; Naramoto, Hiroshi*; Mitani, Seiji*; Takanashi, Koki; Maeda, Yoshihito
Journal of Applied Physics, 108(6), p.063920_1 - 063920_7, 2010/09
Times Cited Count:8 Percentile:34.38(Physics, Applied)Samoto, Hirotaka; Kimura, Norimichi; Otani, Takehisa; Sugai, Eiji; Hayashi, Shinichiro
Proceedings of International Conference on Advanced Nuclear Fuel Cycle; Sustainable Options & Industrial Perspectives (Global 2009) (CD-ROM), p.458 - 463, 2009/09
JAEA has been developing technology to immobilize radioactive krypton gas to metal alloy by ion-implantation method as a stable storage technique of krypton gas recovered from a reprocessing plant. The characteristics of implantation of krypton gas and of krypton implanted alloy were investigated by the cold test performed so far. In this paper, we report the results of the hot immobilization test performed at the Krypton Recovery development Facility (hereafter called KRF) which is attached to the Tokai Reprocessing Plant (hereafter called TRP). In this test, we immobilized the radioactive krypton gas recovered from TRP by cryogenic distillation process of KRF and investigated the gas retention characteristics of the implanted alloy.
 C datings
C datingsOgami, Takashi*; Sugai, Toshihiko*; Fujiwara, Osamu*; Yamaguchi, Masaaki*; Sasao, Eiji
Chigaku Zasshi, 118(4), p.665 - 685, 2009/00
The depositional process of the latest Pleistocene to Holocene shallow marine and fluvial sequences is investigated by using five drill cores from the Kiso river delta, central Japan. Based on facies analysis, the sediments were classified into 5 units; A: basal gravel, B: fluvial to intertidal sand and silt, C: transgressive lag deposit, prodelta mud or sandy silt, D: delta-front-slope sandy silt or sand, delta-front-platform sand, E: delta-plain to fluvial sand and silt. Detailed age-depth curves of each cores are reconstructed based on 107 AMS  C ages. The curves are divided into four sections; I: mainly consists of unit B with rapid accumulation (7.3-21.4 mm/yr), II: mainly consists of unit C with moderate accumulation (2.4-2.8 mm/yr), III: mainly consists of unit D with rapid accumulation (6.7-17.8 mm/yr), IV: consists of unit D and E with moderate accumulation (1.3-3.9 mm/yr). The section boundaries of I/II and II/III reflect inundation into the bay and achievement of progradational delta-front slope, respectively. The expanding rate of the bay is 10 m/yr during 10,200-7,900 cal yrs BP. The progradation rates of the delta are 3-4 m/yr (6.500-4,100 cal yrs BP), 5 m/yr (4,100-1,300 cal yrs BP), 10 m/yr (1,300 cal yrs BP to the present). These indicate the transition from transgression to regression occurred between 7,800 to 7,300 cal yrs BP. The geological cross section along the Kiso river coupled with isochrones indicates following history. (1) 10,000-7,280 cal yrs BP (K-Ah horizon): During the expansion of the bay, onlap of unit C on unit B is visible, and unit C overlapped all the core sites. (2) 7,280 cal yrs BP to present: Isochrones younger than 6,500 cal yrs BP are similar each other and cross unit boundaries of C/D and D/E. This demonstrates units C, D and E are contemporaneous heterotopic facies formed by progradational delta.
C ages. The curves are divided into four sections; I: mainly consists of unit B with rapid accumulation (7.3-21.4 mm/yr), II: mainly consists of unit C with moderate accumulation (2.4-2.8 mm/yr), III: mainly consists of unit D with rapid accumulation (6.7-17.8 mm/yr), IV: consists of unit D and E with moderate accumulation (1.3-3.9 mm/yr). The section boundaries of I/II and II/III reflect inundation into the bay and achievement of progradational delta-front slope, respectively. The expanding rate of the bay is 10 m/yr during 10,200-7,900 cal yrs BP. The progradation rates of the delta are 3-4 m/yr (6.500-4,100 cal yrs BP), 5 m/yr (4,100-1,300 cal yrs BP), 10 m/yr (1,300 cal yrs BP to the present). These indicate the transition from transgression to regression occurred between 7,800 to 7,300 cal yrs BP. The geological cross section along the Kiso river coupled with isochrones indicates following history. (1) 10,000-7,280 cal yrs BP (K-Ah horizon): During the expansion of the bay, onlap of unit C on unit B is visible, and unit C overlapped all the core sites. (2) 7,280 cal yrs BP to present: Isochrones younger than 6,500 cal yrs BP are similar each other and cross unit boundaries of C/D and D/E. This demonstrates units C, D and E are contemporaneous heterotopic facies formed by progradational delta.
Matsumoto, Yoshihiro; Sakai, Seiji; Naramoto, Hiroshi*; Hirao, Norie*; Baba, Yuji; Shimada, Toshihiro*; Sugai, Isamu; Takanashi, Koki; Maeda, Yoshihito
Materials Research Society Symposium Proceedings, Vol.1081 (Internet), 6 Pages, 2008/03
Recently, we have found the appearance of substantial MR ratio (80%) in a C /Co hybrid material. Such the MR ratio cannot be explained enough only by tunnel conduction through Co grains. Therefore, to obtain information about electronic structures of C
/Co hybrid material. Such the MR ratio cannot be explained enough only by tunnel conduction through Co grains. Therefore, to obtain information about electronic structures of C /Co hybrid material is necessary. Absorption spectra of C
/Co hybrid material is necessary. Absorption spectra of C Co are different from that of pristine C
Co are different from that of pristine C . In particular, peak intensity corresponding to
. In particular, peak intensity corresponding to 
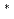 (LUMO)
(LUMO)  C 1s excitation of C
C 1s excitation of C Co is clearly attenuated. In addition, C 1s photoelectron peak of C
Co is clearly attenuated. In addition, C 1s photoelectron peak of C Co slightly shifted to lower binding energy compared to that of pristine C
Co slightly shifted to lower binding energy compared to that of pristine C . These results indicate that 3d electron of Co transfers to
. These results indicate that 3d electron of Co transfers to 
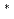 orbital of C
orbital of C and new electronic states are formed in the C
and new electronic states are formed in the C -Co compound. In fact, XPS spectra of valence excitation region also demonstrate the formation of hybrid orbital near the Fermi level due to the coupling of C
-Co compound. In fact, XPS spectra of valence excitation region also demonstrate the formation of hybrid orbital near the Fermi level due to the coupling of C and Co.
and Co.
Sakai, Seiji; Sugai, Isamu; Mitani, Seiji*; Takanashi, Koki; Matsumoto, Yoshihiro; Naramoto, Hiroshi*; Avramov, P.; Okayasu, Satoru; Maeda, Yoshihito
Applied Physics Letters, 91(24), p.242104_1 - 242104_3, 2007/12
Times Cited Count:30 Percentile:71.82(Physics, Applied) -Co film with high magnetoresistance
-Co film with high magnetoresistanceSakai, Seiji; Yakushiji, Kei*; Mitani, Seiji*; Sugai, Isamu; Takanashi, Koki*; Naramoto, Hiroshi*; Avramov, P.; Lavrentiev, V.*; Narumi, Kazumasa; Maeda, Yoshihito
Materials Transactions, 48(4), p.754 - 758, 2007/04
Times Cited Count:9 Percentile:51.33(Materials Science, Multidisciplinary)Magnetic properties were investigated for the alternately deposited film of C and Co which has found to exhibit tunnel magnetoresistance (MR) of 10-80 %. Magnetic field and temperature dependences of magnetization showed typical superparamagnetic behaviors with the blocking temperature of 40 K. The magnetization curve at 300 K was well fitted by the Langevin function with the size distribution of Co particles, and the mean diameter and size distribution were evaluated to be 3.1 nm and 1 nm, respectively. Based on the magnetic properties, the detailed structure and magnetotransport properties are discussed.
and Co which has found to exhibit tunnel magnetoresistance (MR) of 10-80 %. Magnetic field and temperature dependences of magnetization showed typical superparamagnetic behaviors with the blocking temperature of 40 K. The magnetization curve at 300 K was well fitted by the Langevin function with the size distribution of Co particles, and the mean diameter and size distribution were evaluated to be 3.1 nm and 1 nm, respectively. Based on the magnetic properties, the detailed structure and magnetotransport properties are discussed.
Takahashi, Koji; Imai, Tsuyoshi; Kobayashi, Noriyuki*; Sakamoto, Keishi; Kasugai, Atsushi; Hayakawa, Atsuro*; Mori, Seiji*; Mori, Kensuke*
Fusion Science and Technology, 47(1), p.1 - 15, 2005/01
An applicability of a front steering type EC launcher to a fusion reactor is described with the design and thermal, electromagnetic and nuclear analysis using the ITER design conditions. Maximum stress of the support keys of the front shield module, the welds of the keys and the mirror shaft induced by electromagnetic force are 85.5MPa and 34.1MPa and 22MPa, respectively, which are less than 1.5Sm of stainless steel(205MPa). Maximum thermal stress in the front shield module and the mirror, which are 249MPa and 350MPa, respectively, are obtained at the inner surface of a stainless steel cooling tube. The stresses are less 3Sm of stainless steel at 200 C(410MPa). The annual neutron fluence and the dose rate at the vacuum window(closure plate) are estimated to be 10
C(410MPa). The annual neutron fluence and the dose rate at the vacuum window(closure plate) are estimated to be 10
 10
10 n/cm
n/cm /yr and 45
/yr and 45 Sv/h, respectively that satisfy the shield criteria of the ITER. It appears that the design of the front steering type EC launcher is applicable to an ITER grade reactor.
Sv/h, respectively that satisfy the shield criteria of the ITER. It appears that the design of the front steering type EC launcher is applicable to an ITER grade reactor.
Sudo, Tomoko*; Ohashi, Kazutoshi*; Sato, Toshimaro*; Ota, Eiji*; Okayasu, Satoru; Sugai, Hiroyuki
Physical Review B, 71(4), p.045211_1 - 045211_7, 2005/01
Times Cited Count:1 Percentile:7.2(Materials Science, Multidisciplinary)We have measured low frequency generation-recombination noise (g-r moise) spectra of a heavily boro-doped diamond crystal over the temperature range 20-300 K. The experimental results show that there are two peaks in the g-r noise spectrum at 120 K and 67 K, respectively. The 120 K peak corresponds to experimental evidence for the existence of hard gap having width of 10.4 meV. We interpret the 67 K peak as evidence for Wigner lattice formation whose gap width is 5.8 meV.