Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Miyamoto, Seiji*; Isayama, Akihiko; Bandyopadhyay, I.*; Jardin, S. C.*; Khayrutdinov, R. R.*; Lukash, V.*; Kusama, Yoshinori; Sugihara, Masayoshi*
Nuclear Fusion, 54(8), p.083002_1 - 083002_19, 2014/08
Times Cited Count:32 Percentile:82.75(Physics, Fluids & Plasmas)Two well-established simulation codes, DINA and TSC, are compared with each other using benchmark scenarios in order to validate the ITER 2D disruption modelling by those codes. Although the simulation models employed in those two codes ought to be equivalent in the resistive time scale, it has long been unanswered whether the one of the two codes is really able to reproduce the other result correctly, since a large number of code-wise differences render the comparison task exceedingly complicated. In this paper, it is demonstrated that after simulations are set up accounting for the model differences, in general, a good agreement is attained on a notable level, corroborating the correctness of the code results. When the halo current generation and its poloidal path in the first wall are included, however, the situation is more complicated. Because of the surface averaged treatment of the magnetic field (current density) diffusion equation, DINA can only approximately handle the poloidal electric currents in the first wall that cross field lines. Validation is carried out for DINA simulations of halo current generation by comparing with TSC simulations, where the treatment of halo current dynamics is more justifiable. The particularity of each code is depicted and the consequence in ITER disruption prediction is discussed.
Miyamoto, Seiji; Sugihara, Masayoshi*; Shinya, Kichiro*; Nakamura, Yukiharu*; Toshimitsu, Shinichi*; Lukash, V. E.*; Khayrutdinov, R. R.*; Sugie, Tatsuo; Kusama, Yoshinori; Yoshino, Ryuji*
Fusion Engineering and Design, 87(11), p.1816 - 1827, 2012/11
Times Cited Count:15 Percentile:71.22(Nuclear Science & Technology)Shibata, Yoshihide*; Watanabe, Kiyomasa*; Ono, Noriyasu*; Okamoto, Masaaki*; Isayama, Akihiko; Kurihara, Kenichi; Oyama, Naoyuki; Nakano, Tomohide; Kawano, Yasunori; Matsunaga, Go; et al.
Plasma and Fusion Research (Internet), 6, p.1302136_1 - 1302136_4, 2011/10
no abstracts in English
Bandyopadhyay, I.*; Gerhardt, S.*; Jardin, S.*; Sayer, R. O.*; Nakamura, Yukiharu*; Miyamoto, Seiji; Pautasso, G.*; Sugihara, Masayoshi*; ASDEX Upgrade Team*; NSTX Team*
Proceedings of 23rd IAEA Fusion Energy Conference (FEC 2010) (CD-ROM), 8 Pages, 2010/10
Vertical Displacement Events (VDEs) and Major Disruptions (MDs) of the plasma current will induce large electromagnetic forces on the ITER machine. Estimation of these forces based on accurate modeling of these events is necessary for a robust ITER design. Originally the estimates for electromagnetic forces on ITER were carried out with the help of DINA simulations. However, since simulations of these events may be significantly influenced by model assumptions of a given code it is important to validate the results against other codes like TSC, as also benchmark and update the codes with experimental data. In this paper, we present TSC modeling of the VDE and MD events in NSTX and ASDEX-U devices, which help in improving and validating the models used in the code. The predictive modeling results for ITER with the updated code, including the force predictions, are also presented.
Mikake, Shinichiro; Yamamoto, Masaru; Ikeda, Koki; Sugihara, Kozo; Takeuchi, Shinji; Hayano, Akira; Sato, Toshinori; Takeda, Shinichi; Ishii, Yoji; Ishida, Hideaki; et al.
JAEA-Technology 2010-026, 146 Pages, 2010/08
The Mizunami Underground Research Laboratory (MIU), one of the main facilities in Japan for research and development of the technology for high-level radioactive waste disposal, is under construction in Mizunami City. In planning the construction, it was necessary to get reliable information on the bedrock conditions, specifically the rock mass stability and hydrogeology. Therefore, borehole investigations were conducted before excavations started. The results indicated that large water inflow could be expected during the excavation around the Ventilation Shaft at GL-200m and GL-300m Access/Research Gallery. In order to reduce water inflow, pre-excavation grouting was conducted before excavation of shafts and research tunnels. Grouting is the injection of material such as cement into a rock mass to stabilize and seal the rock. This report describes the knowledge and lessons learned during the planning and conducting of pre-excavation grouting.
Nakamura, Yukiharu*; Pautasso, G.*; Sugihara, Masayoshi*; Miyamoto, Seiji; Toshimitsu, Shinichi; Yoshino, Ryuji; ASDEX Upgrade Team*
Proceedings of 37th European Physical Society Conference on Plasma Physics (EPS 2010) (CD-ROM), 4 Pages, 2010/06
Of particular importance for the assessment of electromagnetic loads on vacuum vessel and in-vessel components of ITER is the halo current which achieves a maximum during VDEs (VDE: vertical displacement event). However, halo current models have a limited development so far with a few exceptions such as a validation study of the JT-60U halo current modelling using the DINA code. Recently, several experimental groups have prepared systematic halo current data, and further model development and validation with these data need to be performed using an axisymmetric, two-dimensional, free boundary code, TSC. To enhance an understanding of the maximum halo current and large vertical shifts, a reference discharge was selected from those included in the ASDEX upgrade disruption database. Systematic TSC simulations were performed to mimic the observation of a slow VDE of hot plasma and an ensuing fast downward-going VDE during a subsequent plasma current quench. Careful parameter adjustment of the temperature and width of the halo region was examined to mimic measurements of the halo current. A spontaneous, downward-going VDE was reproduced accurately in a manner that closely resembled experimental observations.
Shibata, Yoshihide*; Watanabe, Kiyomasa*; Okamoto, Masaaki*; Ono, Noriyasu*; Isayama, Akihiko; Kurihara, Kenichi; Nakano, Tomohide; Oyama, Naoyuki; Kawano, Yasunori; Matsunaga, Go; et al.
Nuclear Fusion, 50(2), p.025015_1 - 025015_7, 2010/01
Times Cited Count:17 Percentile:52.35(Physics, Fluids & Plasmas)no abstracts in English
Kawano, Yasunori; Sugihara, Masayoshi*; Tobita, Kenji
Purazuma, Kaku Yugo Gakkai-Shi, 86(1), p.3 - 16, 2010/01
Physical phenomena and control techniques of disruptions in tokamak are reviewed. The article covers current quench, thermal quench, halo current, run-away electrons and the suppression techniques including predictions, avoidance and mitigation. Also described are anticipated electromagnetic forces and heat load in ITER. In the last part, reactor design related with disruptions on DEMO is described.
Takenaga, Hidenobu; Ogawa, Yuichi*; Takizuka, Tomonori; Yagi, Masatoshi*; Yamada, Hiroshi*; Sakamoto, Yoshiteru; Toi, Kazuo*; Fukuda, Takeshi*; Fukuyama, Atsushi*; Fujita, Takaaki; et al.
Purazuma, Kaku Yugo Gakkai-Shi, 84(7), p.465 - 467, 2008/07
no abstracts in English
Yamaguchi, Taiki; Kawano, Yasunori; Fujieda, Hirobumi; Kurihara, Kenichi; Sugihara, Masayoshi*; Kusama, Yoshinori
Plasma Physics and Controlled Fusion, 50(4), p.045004_1 - 045004_15, 2008/04
The poloidal polarimeter will be installed in the International Thermonuclear Experimental Reactor (ITER) to measure the safety factor profile. The number of viewing chords is restricted to about 15 channels. Therefore optimization of the viewing chord arrangement is necessary to diagnose the accurate safety factor profile. In this study, we studied the optimum viewing chord arrangement for the equilibria of ITER operation scenarios using the equilibrium reconstruction. For the burning phase of inductive scenario, the error of the safety factor on the magnetic axis was 35% if the viewing chords are not arranged in the peripheral region. It was improved to 3% by arranging the viewing chord of the upper port to peripheral region. This arrangement was used for the reconstruction of the burning phase in the noninductive scenario and of the phase of the plasma current 3.5 MA in the inductive operation scenario. As the result, the accuracy does not decrease drastically.
Yamaguchi, Taiki; Kawano, Yasunori; Fujieda, Hirobumi; Kurihara, Kenichi; Sugihara, Masayoshi*; Kusama, Yoshinori
Plasma Physics and Controlled Fusion, 50(4), p.045004_1 - 045004_15, 2008/04
Times Cited Count:10 Percentile:38.22(Physics, Fluids & Plasmas)We have studied the viewing chord arrangement of the poloidal polarimeter in the International Thermonuclear Experimental Reactor (ITER). We have optimized the viewing chord arrangement based on the evaluation using a magnetohydrodynamic equilibrium reconstruction code. This reconstruction code has been developed in this study. We have successfully optimized viewing chord arrangements for three equilibria of the ITER operation scenario. The accuracy of the central safety factor within 3% has been achieved in each case. Furthermore, the viewing chord arrangement, which is optimized for the inductive operation scenario II at the start of the burn phase (S2-SOB), has been applied for other equilibria. As the result, the accuracy has not deteriorated drastically compared with the accuracy which is evaluated using the optimized arrangement for each equilibrium. The viewing chord arrangement for S2-SOB is proposed as the most promising candidate of the ITER poloidal polarimeter.
Kuji, Masayoshi; Sato, Toshinori; Mikake, Shinichiro; Hara, Masato; Minamide, Masashi; Sugihara, Kozo
Journal of Power and Energy Systems (Internet), 2(1), p.153 - 163, 2008/00
The Mizunami Underground Research Laboratory (MIU) is being constructed. The MIU consists of two 1,000 m-deep shafts with several research galleries. The goals of MIU project are to establish techniques for investigation, analysis and assessment of deep geological environment, and to develop a range of engineering expertise for application to deep underground crystalline rocks, such as Granite. The diameter of the Main and the Ventilation shafts are 6.5 m and 4.5 m respectively. The Middle stage at about 500 m depth, and the Main stage at about 1,000 m depth will be the main locations for scientific investigations. Current depths of both shafts are 200 m, in August 2007.During the construction, the water inflow into the shafts is increasing and disturbing the project progress. For reducing the water inflow, post-excavation grouting was planned. A test of post-excavation grouting was undertaken and the applicability of several techniques was evaluated.
Sasao, Mamiko*; Kusama, Yoshinori; Kawano, Yasunori; Kawahata, Kazuo*; Mase, Atsushi*; Sugie, Tatsuo; Fujita, Takaaki; Fukuda, Takeshi*; Fukuyama, Atsushi*; Sakamoto, Yoshiteru; et al.
Purazuma, Kaku Yugo Gakkai-Shi, 83(9), p.779 - 782, 2007/09
This is a report of highlights from 2007 spring meetings of seven Topical Groups (TG) of International Tokamak Physics Activity (ITPA). In each meeting, high priority issues in physics of International Thermonuclear Experimental Reactor (ITER) and other burning plasma experiments have been discussed and investigated. Twenty-seven scientists from Japan have participated in those meetings. Dates and places of the meetings are shown below. (1) Diagnostics TG: 26-30 March, Princeton (USA), (2) Transport Physics TG: 7-10 May, Lausanne (Switzerland), (3) Confinement Database and Modeling TG: 7-10 May, Lausanne (Switzerland), (4) Edge Pedestal Physics TG: 7-10 May, Garching (Germany) (5) Steady State Operation TG: 9-11 May, Daejeon (South Korea), (6)MHD TG: 21-24 May, San Diego (USA), (7) Scrape-off-layer and Divertor Physics TG: 7-10 May, Garching (Germany).
Fujieda, Hirobumi; Sugihara, Masayoshi*; Shimada, Michiya; Gribov, Y.*; Ioki, Kimihiro*; Kawano, Yasunori; Khayrutdinov, R.*; Lukash, V.*; Omori, Junji; Neyatani, Yuzuru
JAEA-Research 2007-052, 115 Pages, 2007/07
Impacts of plasma disruptions on ITER have been investigated to confirm the robustness of the design of the machine to the potential consequential loads. The loads include both electro-magnetic (EM) and heat on the in-vessel components and the vacuum vessel. Several representative disruption scenarios are specified. Disruption simulations with the DINA code and EM load analyses with a 3D finite element method code are performed for these scenarios. Some margins are confirmed in the EM load. Heat load on the first wall due to the vertical movement and the thermal quench (TQ) is calculated with a 2D heat conduction code. For vertical displacement event, beryllium (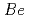 ) wall will not melt during the vertical movement, prior to the TQ. Significant melting is anticipated for the upper
) wall will not melt during the vertical movement, prior to the TQ. Significant melting is anticipated for the upper 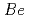 wall and tungsten baffle due to the TQ after the vertical movement. However, its impact could be mitigated by implementing a reliable detection system of the vertical movement and a mitigation system.
wall and tungsten baffle due to the TQ after the vertical movement. However, its impact could be mitigated by implementing a reliable detection system of the vertical movement and a mitigation system.
Hender, T. C.*; Wesley, J. C.*; Bialek, J.*; Bondeson, A.*; Boozer, A. H.*; Buttery, R. J.*; Garofalo, A.*; Goodman, T. P.*; Granetz, R. S.*; Gribov, Y.*; et al.
Nuclear Fusion, 47(6), p.S128 - S202, 2007/06
Times Cited Count:916 Percentile:100(Physics, Fluids & Plasmas)no abstracts in English
Doyle, E. J.*; Houlberg, W. A.*; Kamada, Yutaka; Mukhovatov, V.*; Osborne, T. H.*; Polevoi, A.*; Bateman, G.*; Connor, J. W.*; Cordey, J. G.*; Fujita, Takaaki; et al.
Nuclear Fusion, 47(6), p.S18 - S127, 2007/06
no abstracts in English
Kuji, Masayoshi; Sato, Toshinori; Mikake, Shinichiro; Hara, Masato; Minamide, Masashi; Sugihara, Kozo
Proceedings of 15th International Conference on Nuclear Engineering (ICONE-15) (CD-ROM), 7 Pages, 2007/04
The Mizunami Underground Research Laboratory (MIU) is being constructed. The MIU consists of two 1,000 m-deep shafts with several research galleries. The diameter of the shafts are 6.5 m and 4.5 m, respectively. Horizontal tunnels to connect the shafts are excavated at 100 m depth intervals. The Middle stage, at about 500 m depth, and the Main stage at about 1,000 m depth will be the main locations for scientific investigations. Current depths of shafts are 180 m and 191 m respectively, in November, 2006. During the construction, the quantity of water inflow into the shafts is increasing and disturbing the project progress. In order to reduce the quantity of water inflow, post-excavation grouting and pre-excavation grouting are planned. A test of post-excavation grouting was undertaken in the Ventilation shaft and the applicability of several techniques were evaluated.
Saegusa, Hiromitsu; Seno, Yasuhiro; Nakama, Shigeo; Tsuruta, Tadahiko; Iwatsuki, Teruki; Amano, Kenji; Takeuchi, Ryuji; Matsuoka, Toshiyuki; Onoe, Hironori; Mizuno, Takashi; et al.
JAEA-Research 2007-043, 337 Pages, 2007/03
The Mizunami Underground Laboratory (MIU) Project is a comprehensive research project investigating the deep underground environment within crystalline rock being conducted by Japan Atomic Energy Agency at Mizunami City in Gifu Prefecture, central Japan. This report summarizes the results of the Surface-based Investigation Phase, identifies future issues and provides direction for research to be conducted during Construction Phase and Operation Phase. The results compiled in this report will be utilized for the technical knowledge base on geological disposal of HLW, and can be used to enhance the technical basis for waste disposal in general and for development of government regulations.
Ioki, Kimihiro; Chuyanov, V.*; Elio, F.*; Garkusha, D.*; Gribov, Y.*; Lamzin, E.*; Morimoto, Masaaki; Shimada, Michiya; Sugihara, Masayoshi; Terasawa, Atsumi; et al.
Proceedings of 21st IAEA Fusion Energy Conference (FEC 2006) (CD-ROM), 8 Pages, 2007/03
Two important design updates have been made in the ITER VV and in-vessel components recently. One is the introduction of limiters moveable during a plasma discharge, and the other is optimization of the ferromagnetic insert configuration to minimize the toroidal field ripple. In the new limiter concept, the limiters are retracted by 8 cm during the plasma flat top phase in the divertor configuration. This concept gives important advantages: (1) the particle and heat loads due to disruptions, ELMs and blobs on the limiters will be mitigated approximately by a factor 1.5 or more; (2) the gap between the plasma and the ICRH antenna can be reduced to improve the coupling of the ICRH power. The ferromagnetic inserts have previously not been planned to be installed in the outboard midplane region between equatorial ports due to irregularity of tangential ports for NB injection. The result is a relatively large ripple (1 %) in a limited region of the plasma, which nevertheless seems acceptable from the plasma performance viewpoint. However, toroidal field flux lines fluctuate 10 mm due to the large ripple in the FW region. To avoid problems due to the large TF flux line fluctuation, additional ferromagnetic inserts are now planned to be installed in the equatorial port region.
Kamada, Yutaka; Leonard, A. W.*; Bateman, G.*; Becoulet, M.*; Chang, C. S.*; Eich, T.*; Evans, T. E.*; Groebner, R. J.*; Guzdar, P. N.*; Horton, L. D.*; et al.
Proceedings of 21st IAEA Fusion Energy Conference (FEC 2006) (CD-ROM), 8 Pages, 2007/03
no abstracts in English