Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Onuki, Shun*; Shinohara, Yoshiaki*; Sutrisna, F.*; Utsumi, Michiaki*; Uchida, Hirohisa*; Matsumura, Yoshihito*; Abe, Hiroshi
no journal, ,
The ion irradiation treatment improved the hydrogen absorption rate. The irradiation of electron beam to the LaNi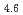 Al
Al hydrogen storage alloy surface was performed bye the dose of 1
hydrogen storage alloy surface was performed bye the dose of 1  10
10 e
e /cm
/cm , at 1 MeV and 2 MeV of acceleration energy, in vacuum at 2 Pa and atmospheric pressure in air. Electron beam irradiated sample was found to induce a higher absorption rate than that of the un-irradiated one. The maximum value of the hydrogen absorption rate was obtained in the sample irradiated by 2 MeV electron beam in the vacuum condition. X-ray Photoelectron Spectra (XPS) of the samples indicate that composition of oxide layer by electron beam irradiation. The electron beam irradiation was found as an effective way to enhance the rate of the initial activation of the hydrogen absorption of La-Ni alloy.
, at 1 MeV and 2 MeV of acceleration energy, in vacuum at 2 Pa and atmospheric pressure in air. Electron beam irradiated sample was found to induce a higher absorption rate than that of the un-irradiated one. The maximum value of the hydrogen absorption rate was obtained in the sample irradiated by 2 MeV electron beam in the vacuum condition. X-ray Photoelectron Spectra (XPS) of the samples indicate that composition of oxide layer by electron beam irradiation. The electron beam irradiation was found as an effective way to enhance the rate of the initial activation of the hydrogen absorption of La-Ni alloy.
Abe, Hiroshi; Onuki, Shun*; Shinohara, Yoshiaki*; Sutrisna, F.*; Utsumi, Michiaki*; Matsumura, Yoshihito*; Oshima, Takeshi
no journal, ,
Recently, Ni-MH batteries with hydrogen storage La-Ni based alloys as negative electrodes are installed many hybrid cars (HV: Hybrid Vehicle). In this study, we investigate the effects of ion irradiation on the electrochemical hydriding rate of the alkaline pretreatment LaNi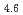 Al
Al alloy. We also analyzed the chemical compositions at the surface of the irradiated/un-irradiated samples, their crystal structures, and the phases of bulk. The samples were irradiated with K ion at an acceleration energy of 350 keV with a dose of 1
alloy. We also analyzed the chemical compositions at the surface of the irradiated/un-irradiated samples, their crystal structures, and the phases of bulk. The samples were irradiated with K ion at an acceleration energy of 350 keV with a dose of 1  10
10 cm
cm using the 400 kV ion implanter, at the TIARA, JAEA. X-ray Photoelectron spectra of the samples indicate that composition of oxide layer was varied on irradiated conditions. These results suggest that improvement of initial hydrogen absorption rate for sample surface is caused by formation of conductive oxide layer by ion irradiation.
using the 400 kV ion implanter, at the TIARA, JAEA. X-ray Photoelectron spectra of the samples indicate that composition of oxide layer was varied on irradiated conditions. These results suggest that improvement of initial hydrogen absorption rate for sample surface is caused by formation of conductive oxide layer by ion irradiation.