Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Ishida, Takekazu*; Vu, TheDang*; Shishido, Hiroaki*; Aizawa, Kazuya; Oku, Takayuki; Oikawa, Kenichi; Harada, Masahide; Kojima, Kenji M*; Miyajima, Shigeyuki*; Koyama, Tomio*; et al.
Journal of Low Temperature Physics, 214(3-4), p.152 - 157, 2024/02
Times Cited Count:0 Percentile:0.02(Physics, Applied)Kadowaki, Masanao; Nagai, Haruyasu; Yoshida, Toshiya*; Terada, Hiroaki; Tsuzuki, Katsunori; Sawa, Hiroki*
Journal of Nuclear Science and Technology, 60(10), p.1194 - 1207, 2023/10
Times Cited Count:2 Percentile:72.91(Nuclear Science & Technology)This study develops an estimation method using machine learning for uncertainty in forecasted plume directions. Bayesian machine learning was used in the machine learning approach. A three-day forecast simulation was conducted every day from 2015-2020, considering a hypothetical release of  Cs from a nuclear facility to create training and test datasets for the machine learning. The findings reveal that the rate of good predictability was greater than 50% even in the forecast 36 h later when investigating the effectiveness of the Bayesian model on uncertainty estimation. Additionally, the frequency of miss prediction of higher uncertainty was low (0.9%-7.9%) throughout the forecast period. However, the rate of over-prediction of uncertainty increased with forecast time up to 31.2%, which is acceptable as a conservative estimation. These results show that the Bayesian model used in this study effectively estimates the uncertainty of plume directions predicted through atmospheric dispersion simulations.
Cs from a nuclear facility to create training and test datasets for the machine learning. The findings reveal that the rate of good predictability was greater than 50% even in the forecast 36 h later when investigating the effectiveness of the Bayesian model on uncertainty estimation. Additionally, the frequency of miss prediction of higher uncertainty was low (0.9%-7.9%) throughout the forecast period. However, the rate of over-prediction of uncertainty increased with forecast time up to 31.2%, which is acceptable as a conservative estimation. These results show that the Bayesian model used in this study effectively estimates the uncertainty of plume directions predicted through atmospheric dispersion simulations.
 single crystals based on Bragg-dip analysis using a delay-line superconducting sensor
single crystals based on Bragg-dip analysis using a delay-line superconducting sensorShishido, Hiroaki*; Vu, TheDang*; Aizawa, Kazuya; Kojima, Kenji M*; Koyama, Tomio*; Oikawa, Kenichi; Harada, Masahide; Oku, Takayuki; Soyama, Kazuhiko; Miyajima, Shigeyuki*; et al.
Journal of Applied Crystallography, 56(4), p.1108 - 1113, 2023/08
Times Cited Count:0 Percentile:0.02(Chemistry, Multidisciplinary)Terada, Hiroaki; Nagai, Haruyasu; Kadowaki, Masanao; Tsuzuki, Katsunori
Journal of Nuclear Science and Technology, 60(8), p.980 - 1001, 2023/08
Times Cited Count:4 Percentile:98.08(Nuclear Science & Technology)It is essential to establish a method for reconstructing the source term and spatiotemporal distribution of radionuclides released into the atmosphere due to a nuclear accident for emergency countermeasures. We examined the dependency of a source term estimation method based on Bayesian inference using atmospheric dispersion simulation and environmental monitoring data on the availability of various monitoring data. Additionally, we examined the applicability of this method to a real-time estimation conducted immediately after an accident. A sensitivity analysis of the estimated source term during the Fukushima Daiichi Nuclear Power Station (FDNPS) accident for combinations of various monitoring data indicated that using monitoring data with a high temporal and spatial resolution and the concurrent use of air concentration and surface deposition data is effective for accurate estimation. A real-time source term estimation experiment assuming the situation of monitoring data acquisition during the FDNPS accident revealed that this method could provide the necessary source term for grasping the overview of surface contamination in the early phase and evaluating the approximate accident scale. If the immediate online acquisition of monitoring data and regular operation of an atmospheric dispersion simulation are established, this method can provide the source term in near-real time.
Yoshida, Toshiya; Nagai, Haruyasu; Terada, Hiroaki; Tsuzuki, Katsunori; Sawa, Hiroki*
Journal of Nuclear Science and Technology, 59(1), p.55 - 66, 2022/01
Times Cited Count:3 Percentile:45.99(Nuclear Science & Technology)Atmospheric transport, dispersion, and deposition models (ATDMs) can support decision-making during nuclear emergencies; however, uncertainties in the ATDM results need to be carefully evaluated. To investigate the uncertainties derived from meteorological forecast inputs, we conducted three-day forecast simulations every day for one year with hypothetical releases of radionuclides (one-hour releases every 6 h) from a nuclear facility. The forecast outputs were compared with the analysis outputs during the same period. The difference between the outputs is treated as the uncertainty in the forecasts and is represented as an angle based on the discrepancy in the plume directions between the analysis and forecast outputs. Using meteorological inputs made by Japan Meteorological Agency, the discrepancy angle (Ang) increased by approximately 10 per day on an annual average basis. Meanwhile, the Ang values were occasionally 4-5 times higher than the annual average during short time periods. Since the Ang time series show seasonal and diurnal changes, the statistical characteristics likely depend on the geographical and meteorological conditions, as well as the types of meteorological inputs. Additionally, a main factor in the uncertainty is the wind-direction difference between the analysis and forecast outputs on scales of more than or less than 100 km.
per day on an annual average basis. Meanwhile, the Ang values were occasionally 4-5 times higher than the annual average during short time periods. Since the Ang time series show seasonal and diurnal changes, the statistical characteristics likely depend on the geographical and meteorological conditions, as well as the types of meteorological inputs. Additionally, a main factor in the uncertainty is the wind-direction difference between the analysis and forecast outputs on scales of more than or less than 100 km.
Shishido, Hiroaki*; Nishimura, Kazuma*; Vu, TheDang*; Aizawa, Kazuya; Kojima, Kenji M*; Koyama, Tomio*; Oikawa, Kenichi; Harada, Masahide; Oku, Takayuki; Soyama, Kazuhiko; et al.
IEEE Transactions on Applied Superconductivity, 31(9), p.2400505_1 - 2400505_5, 2021/12
Times Cited Count:0 Percentile:0(Engineering, Electrical & Electronic)In this study, we employed a superconducting detector, current-biased kinetic-inductance detector (CB-KID) for neutron imaging using a pulsed neutron source. We employed the delay-line method, and high spatial resolution imaging with only four reading channels was achieved. We also performed wavelength-resolved neutron imaging by the time-of-flight method. We obtained the neutron transmission images of a Gd-Al alloy sample, inside which single crystals of GdAl were grown, using the delay-line CB-KID. Single crystals were well imaged, in both shapes and distributions, throughout the Al-Gd alloy. We identified Gd nuclei via neutron transmissions that exhibited characteristic suppression above the neutron wavelength of 0.03 nm. In addition, the
were grown, using the delay-line CB-KID. Single crystals were well imaged, in both shapes and distributions, throughout the Al-Gd alloy. We identified Gd nuclei via neutron transmissions that exhibited characteristic suppression above the neutron wavelength of 0.03 nm. In addition, the 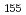 Gd resonance dip, a dip structure of the transmission caused by the nuclear reaction between an isotope and neutrons, was observed even when the number of events was summed over a limited area of 15
Gd resonance dip, a dip structure of the transmission caused by the nuclear reaction between an isotope and neutrons, was observed even when the number of events was summed over a limited area of 15  m
m  12
12  m. Gd selective imaging was performed using the resonance dip of
m. Gd selective imaging was performed using the resonance dip of 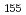 Gd, and it showed clear Gd distribution even with a limited neutron wavelength range of 1 pm.
Gd, and it showed clear Gd distribution even with a limited neutron wavelength range of 1 pm.
 Cs
CsKadowaki, Masanao; Furuno, Akiko; Nagai, Haruyasu; Kawamura, Hideyuki; Terada, Hiroaki; Tsuzuki, Katsunori; El-Asaad, H.
Journal of Environmental Radioactivity, 237, p.106704_1 - 106704_18, 2021/10
Times Cited Count:2 Percentile:13.39(Environmental Sciences)The source term of  Cs for the Fukushima Daiichi Nuclear Power Station (FDNPS) accident was estimated from the results of local-scale atmospheric dispersion simulations and measurements. To confirm the source term's validity for reproducing the large-scale atmospheric dispersion of
Cs for the Fukushima Daiichi Nuclear Power Station (FDNPS) accident was estimated from the results of local-scale atmospheric dispersion simulations and measurements. To confirm the source term's validity for reproducing the large-scale atmospheric dispersion of  Cs, this study conducted hemispheric-scale atmospheric and oceanic dispersion simulations. In the dispersion simulations, the atmospheric-dispersion database system Worldwide version of System for Prediction of Environmental Emergency Dose Information (WSPEEDI)-DB and oceanic dispersion model SEA-GEARN-FDM were used. Compared with the air concentrations of
Cs, this study conducted hemispheric-scale atmospheric and oceanic dispersion simulations. In the dispersion simulations, the atmospheric-dispersion database system Worldwide version of System for Prediction of Environmental Emergency Dose Information (WSPEEDI)-DB and oceanic dispersion model SEA-GEARN-FDM were used. Compared with the air concentrations of  Cs measured by the Comprehensive Nuclear-Test-Ban Treaty Organization, overall, the WSPEEDI-DB simulation reproduced the measurements with some overestimation. Furthermore, the deposition amounts of
Cs measured by the Comprehensive Nuclear-Test-Ban Treaty Organization, overall, the WSPEEDI-DB simulation reproduced the measurements with some overestimation. Furthermore, the deposition amounts of  Cs was investigated using concentrations of
Cs was investigated using concentrations of  Cs in seawater. The simulated seawater concentrations of
Cs in seawater. The simulated seawater concentrations of  Cs were underestimated regionally in the North Pacific. The overestimation and underestimation could be improved without contradiction between the air and seawater concentrations of
Cs were underestimated regionally in the North Pacific. The overestimation and underestimation could be improved without contradiction between the air and seawater concentrations of  Cs using more realistic precipitation in atmospheric dispersion simulations. This shows that the source term validated in this study could reproduce the spatiotemporal distribution of
Cs using more realistic precipitation in atmospheric dispersion simulations. This shows that the source term validated in this study could reproduce the spatiotemporal distribution of  Cs because of the FDNPS accident in both local and large-scale atmospheric dispersion simulations.
Cs because of the FDNPS accident in both local and large-scale atmospheric dispersion simulations.
Nemoto, Miho*; Ebine, Noriya; Okamoto, Akiko; Hosaka, Yasuhisa*; Tsuzuki, Katsunori; Terada, Hiroaki; Hayakawa, Tsuyoshi; Togawa, Orihiko
JAEA-Technology 2021-013, 41 Pages, 2021/08
When North Korea has carried out nuclear tests, Nuclear Emergency Assistance and Training Center (NEAT) predicts atmospheric dispersion of radionuclides by using the WSPEEDI-II upon requests from Nuclear Regulation Authority (NRA) and submits the predicted results to NRA in cooperation with Nuclear Science and Engineering Center (NSEC). This is a part of the activity of NEAT supporting the Japanese Government in emergency responses. The WSPEEDI-II automatic calculation system specialized for responses to nuclear tests by North Korea was developed by NSEC and was used for responses to three nuclear tests from February 2013 to September 2017. This report describes the transfer and installation of the calculation system to NEAT, and the subsequent maintenance and operation. Future issues for responses to nuclear tests are also described in this report.
Vu, TheDang; Shishido, Hiroaki*; Aizawa, Kazuya; Kojima, Kenji M*; Koyama, Tomio*; Oikawa, Kenichi; Harada, Masahide; Oku, Takayuki; Soyama, Kazuhiko; Miyajima, Shigeyuki*; et al.
Nuclear Instruments and Methods in Physics Research A, 1006, p.165411_1 - 165411_8, 2021/08
Times Cited Count:1 Percentile:18.91(Instruments & Instrumentation)Vu, TheDang; Shishido, Hiroaki*; Kojima, Kenji M*; Koyama, Tomio*; Oikawa, Kenichi; Harada, Masahide; Miyajima, Shigeyuki*; Oku, Takayuki; Soyama, Kazuhiko; Aizawa, Kazuya; et al.
Superconductor Science and Technology, 34(1), p.015010_1 - 015010_10, 2021/01
Times Cited Count:3 Percentile:27.71(Physics, Applied)Shishido, Hiroaki*; Nishimura, Kazuma*; Vu, TheDang*; Kojima, Kenji M*; Koyama, Tomio*; Oikawa, Kenichi; Harada, Masahide; Miyajima, Shigeyuki*; Hidaka, Mutsuo*; Oku, Takayuki; et al.
Journal of Physics; Conference Series, 1590, p.012033_1 - 012033_8, 2020/10
Times Cited Count:0 Percentile:0.01(Engineering, Electrical & Electronic) Si
Si O
O
Suzuki, Eriko; Nakajima, Kunihisa; Osaka, Masahiko; Oishi, Yuji*; Muta, Hiroaki*; Kurosaki, Ken*
Journal of Nuclear Science and Technology, 57(7), p.852 - 857, 2020/07
Times Cited Count:4 Percentile:45.45(Nuclear Science & Technology)The low temperature heat capacity of Cs Si
Si O
O , which is one of the cesium chemisorbed compounds onto stainless steel during severe accident of the light water nuclear reactor, was experimentally determined for the first time in the temperature range of 1.9 - 302 K. The experimentally determined heat capacity,
, which is one of the cesium chemisorbed compounds onto stainless steel during severe accident of the light water nuclear reactor, was experimentally determined for the first time in the temperature range of 1.9 - 302 K. The experimentally determined heat capacity, 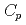
 (298.15K), and the standard entropy,
(298.15K), and the standard entropy, 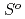 (298.15K), were 249.4
(298.15K), were 249.4  1.1 J K
1.1 J K mol
mol and 322.1
and 322.1  1.3 J K
1.3 J K mol
mol , respectively. The standard Gibbs energy of formation of Cs
, respectively. The standard Gibbs energy of formation of Cs Si
Si O
O at high temperatures,
at high temperatures, 

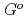 (
( ), were reevaluated by using the presently obtained
), were reevaluated by using the presently obtained 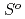 (298.15K) and the previously reported experimental results of the standard enthalpy of formation,
(298.15K) and the previously reported experimental results of the standard enthalpy of formation, 

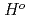 (298.15K), and the standard enthalpy increments at high temperatures,
(298.15K), and the standard enthalpy increments at high temperatures, 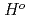 (
( )-
)-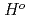 (298.15K).
(298.15K).
Terada, Hiroaki; Nagai, Haruyasu; Tanaka, Atsunori*; Tsuzuki, Katsunori; Kadowaki, Masanao
Journal of Nuclear Science and Technology, 57(6), p.745 - 754, 2020/06
Times Cited Count:9 Percentile:75.92(Nuclear Science & Technology)We have estimated source term and analyzed processes of atmospheric dispersion of radioactive materials released during the Fukushima Daiichi Nuclear Power Station (FDNPS) accident by the Worldwide version of System for Environmental Emergency Dose Information. On the basis of this experience, we developed an dispersion calculation method that can respond to various needs in a nuclear emergency and provide useful information for emergency-response planning. By this method, if a release point is known, it is possible to immediately obtain the prediction results by applying provided source term to the database of dispersion-calculation results prepared in advance. With this function, it is easy to compare results by applying various source term with monitoring data, and to find out the optimum source term, which was applied for the source term estimation of the FDNPS accident. By performing this calculation with past meteorological-analysis data, it is possible to immediately get dispersion-calculation results for various source term and meteorological conditions. This database can be used for pre-accident planning, such as optimization of a monitoring plan and understanding of events to be supposed in considering emergency countermeasures.
Suzuki, Hiroaki*; Morita, Yoshihiro*; Naito, Masanori*; Nemoto, Yoshiyuki; Kaji, Yoshiyuki
Mechanical Engineering Journal (Internet), 7(3), p.19-00450_1 - 19-00450_17, 2020/06
In this study, the SAMPSON code was modified to evaluate severe accidents in a spent fuel pool (SFP). Air oxidation models based on oxidation data obtained on the Zircaroy-4 cladding (ANL model) and the Zircaroy-2 cladding (JAEA model) were included in the modified SAMPSON code. Experiments done by Sandia National Laboratory using simulated fuel assemblies equivalent to those of an actual BWR plant were analyzed by the modified SAMPSON code to confirm the functions for analysis of the severe SFP accidents. The rapid fuel rod temperature rise due to the Zr air oxidation reaction could be reasonably evaluated by the SAMPSON analysis. The SFP accident analyses were conducted with different initial water levels which were no water, water level at bottom of active fuel, and water level at half of active fuel. The present analysis showed that the earliest temperature rise of the fuel rod surface occurred when there was no water in the SFP and natural circulation of air became possible.
 F from
F from  O
O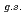 ?
?Tang, T. L.*; Uesaka, Tomohiro*; Kawase, Shoichiro; Beaumel, D.*; Dozono, Masanori*; Fujii, Toshihiko*; Fukuda, Naoki*; Fukunaga, Taku*; Galindo-Uribarri, A.*; Hwang, S. H.*; et al.
Physical Review Letters, 124(21), p.212502_1 - 212502_6, 2020/05
Times Cited Count:14 Percentile:74.18(Physics, Multidisciplinary)The structure of a neutron-rich  F nucleus is investigated by a quasifree (
F nucleus is investigated by a quasifree ( ) knockout reaction. The sum of spectroscopic factors of
) knockout reaction. The sum of spectroscopic factors of 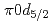 orbital is found to be 1.0
orbital is found to be 1.0  0.3. The result shows that the
0.3. The result shows that the  O core of
O core of  F nucleus significantly differs from a free
F nucleus significantly differs from a free  O nucleus, and the core consists of
O nucleus, and the core consists of  35%
35%  O
O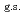 , and
, and  65% excited
65% excited  O. The result shows that the
O. The result shows that the  O core of
O core of  F nucleus significantly differs from a free
F nucleus significantly differs from a free  O nucleus. The result may infer that the addition of the
O nucleus. The result may infer that the addition of the  proton considerably changes the neutron structure in
proton considerably changes the neutron structure in  F from that in
F from that in  O, which could be a possible mechanism responsible for the oxygen dripline anomaly.
O, which could be a possible mechanism responsible for the oxygen dripline anomaly.
Terada, Hiroaki; Nagai, Haruyasu; Tsuzuki, Katsunori; Furuno, Akiko; Kadowaki, Masanao; Kakefuda, Toyokazu*
Journal of Environmental Radioactivity, 213, p.106104_1 - 106104_13, 2020/03
Times Cited Count:50 Percentile:93.07(Environmental Sciences)In order to assess the radiological dose to the public resulting from the Fukushima Daiichi Nuclear Power Station accident in Japan, the spatial and temporal distribution of radioactive materials in the environment is necessary to be reconstructed by computer simulations with the atmospheric transport, dispersion and deposition model (ATDM) and source term of radioactive materials discharged into the atmosphere is essential. In this study, we carried out refinement of the source term and improvement of ATDM simulation by using an optimization method based on Bayesian inference with various measurements (air concentration, surface deposition, and fallout). We also constructed the spatiotemporal distribution of some major radionuclides in the air and on the surface (optimized dispersion database) by using the optimized release rates and ATDM simulations which is used for the comprehensive dose assessment by coupling with the behavioral pattern of evacuees from the accident.
Iizawa, Yuki*; Shishido, Hiroaki*; Nishimura, Kazuma*; Vu, TheDang*; Kojima, Kenji M*; Koyama, Tomio*; Oikawa, Kenichi; Harada, Masahide; Miyajima, Shigeyuki*; Hidaka, Mutsuo*; et al.
Superconductor Science and Technology, 32(12), p.125009_1 - 125009_8, 2019/12
Times Cited Count:13 Percentile:59.07(Physics, Applied)Iwasaki, Toshiki*; Sekiyama, Tsuyoshi*; Nakajima, Teruyuki*; Watanabe, Akira*; Suzuki, Yasushi*; Kondo, Hiroaki*; Morino, Yu*; Terada, Hiroaki; Nagai, Haruyasu; Takigawa, Masayuki*; et al.
Atmospheric Environment, 214, p.116830_1 - 116830_11, 2019/10
Times Cited Count:6 Percentile:26.43(Environmental Sciences)The utilization of numerical atmospheric dispersion prediction (NDP) models for accidental discharge of radioactive substances was recommended by a working group of the Meteorological Society of Japan. This paper is to validate the recommendation through NDP model intercomparison in the accidental release from the Fukushima Dai-ichi Nuclear Power Plant in 2011. Emission intensity is assumed to be constant during the whole forecast period for the worst-case scenario unless time sequence of emission is available. We expect to utilize forecasts of surface air contaminations for preventions of inhalations of radioactive substances, and column-integrated amounts for mitigation of radiation exposure associated with wet deposition. Although NDP forecasts have ensemble spread, they commonly figure out relative risk in space and time. They are of great benefit to disseminating effective warnings to public without failure. The multi-model ensemble technique may be effective to improve the reliability.
 O(
O( He,
He, )
) F reaction; Identification of the low-energy "super" -Gamow-Teller state
F reaction; Identification of the low-energy "super" -Gamow-Teller stateFujita, Hirohiko*; Fujita, Yoshitaka*; Utsuno, Yutaka; Yoshida, Kenichi*; Adachi, Tatsuya*; Algora, A.*; Csatl s, M.*; Deaven, J. M.*; Estevez-Aguado, E.*; Guess, C. J.*; et al.
s, M.*; Deaven, J. M.*; Estevez-Aguado, E.*; Guess, C. J.*; et al.
Physical Review C, 100(3), p.034618_1 - 034618_13, 2019/09
Times Cited Count:12 Percentile:77.09(Physics, Nuclear)no abstracts in English
Imamura, Hiroaki; Suzuki, Masashi*; Shimoyama, Kazuhito; Miyakoshi, Hiroyuki
JAEA-Technology 2019-005, 163 Pages, 2019/06
For the R&D of safety enhance in future fast reactor development, the constructed the large sodium test loop (mother loop) in advanced technology experiment sodium facility (AtheNa) was completed. The sodium test loop possesses the largest capacity of about 240 tons of the world's largest sodium and can supply impurity-controlled high temperature sodium to large structural and technology demonstration test sections. It is greatly expected as R&D such as future international cooperation. For the purpose of future R&D tests, this report compiled the design specifications, fabrication and performance confirmation results of sodium test loop.