Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
 Ni
Ni In
In
Sakai, Hironori; Tokunaga, Yo; Kambe, Shinsaku; Zhu, J.-X.*; Ronning, F.*; Thompson, J. D.*; Kotegawa, Hisashi*; To, Hideki*; Suzuki, Kohei*; Oshima, Yoshiki*; et al.
Physical Review B, 106(23), p.235152_1 - 235152_8, 2022/12
Times Cited Count:0 Percentile:0(Materials Science, Multidisciplinary)We investigate the electronic state of Ni-substituted CeCo Ni
Ni In
In by nuclear quadrupole and magnetic resonance (NQR/NMR) techniques. The heavy fermion superconductivity below
by nuclear quadrupole and magnetic resonance (NQR/NMR) techniques. The heavy fermion superconductivity below 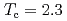 K for
K for 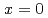 is suppressed by Ni substitutions, and
is suppressed by Ni substitutions, and  reaches zero for
reaches zero for 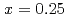 . The
. The  In NQR spectra for
In NQR spectra for 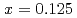 and 0.25 can be explained by simulating the electrical field gradient that is calculated for a virtual supercell with density functional theory. The spin-lattice relaxation rate
and 0.25 can be explained by simulating the electrical field gradient that is calculated for a virtual supercell with density functional theory. The spin-lattice relaxation rate  indicates that Ni substitution weakens antiferromagnetic correlations that are not localized near the substituent but instead are uniform in space. The temperature (
indicates that Ni substitution weakens antiferromagnetic correlations that are not localized near the substituent but instead are uniform in space. The temperature ( ) dependence of
) dependence of  for
for 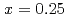 shows a maximum around
shows a maximum around 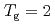 K and
K and  decreases toward almost zero when temperature is further reduced as if a gap might be opening in the magnetic excitation spectrum; however, the magnetic specific heat and the static magnetic susceptibility evolve smoothly through
decreases toward almost zero when temperature is further reduced as if a gap might be opening in the magnetic excitation spectrum; however, the magnetic specific heat and the static magnetic susceptibility evolve smoothly through 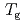 with a
with a 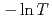 dependence. The peculiar T dependence of
dependence. The peculiar T dependence of  and non-Fermi-liquid specific heat and susceptibility can be interpreted in a unified way by assuming nested antiferromagnetic spin fluctuations in a quasi-two-dimensional electronic system.
and non-Fermi-liquid specific heat and susceptibility can be interpreted in a unified way by assuming nested antiferromagnetic spin fluctuations in a quasi-two-dimensional electronic system.
 ;
;  In NQR/NMR and
In NQR/NMR and  Co NMR study
Co NMR studySakai, Hironori; Tokunaga, Yo; Kambe, Shinsaku; Zhu, J.-X.*; Ronning, F.*; Thompson, J. D.*; Ramakrishna, S. K.*; Reyes, A. P.*; Suzuki, Kohei*; Oshima, Yoshiki*; et al.
Physical Review B, 104(8), p.085106_1 - 085106_12, 2021/08
Times Cited Count:3 Percentile:27.71(Materials Science, Multidisciplinary)Antiferromagnetism in a prototypical quantum critical metal CeCoIn is known to be induced by slight substitutions of non-magnetic Zn atoms for In. In nominally 7% Zn substituted CeCoIn
is known to be induced by slight substitutions of non-magnetic Zn atoms for In. In nominally 7% Zn substituted CeCoIn , an antiferromagnetic (AFM) state coexists with heavy fermion superconductivity. Heterogeneity of the electronic states is investigated in Zn doped CeCoIn
, an antiferromagnetic (AFM) state coexists with heavy fermion superconductivity. Heterogeneity of the electronic states is investigated in Zn doped CeCoIn by means of nuclear quadrupole and magnetic resonances (NQR and NMR). Site-dependent NQR relaxation rates
by means of nuclear quadrupole and magnetic resonances (NQR and NMR). Site-dependent NQR relaxation rates  indicate that the AFM state is locally nucleated around Zn substituents in the matrix of a heavy fermion state, and percolates through the bulk at the AFM transition temperature
indicate that the AFM state is locally nucleated around Zn substituents in the matrix of a heavy fermion state, and percolates through the bulk at the AFM transition temperature  . At lower temperatures, an anisotropic superconducting (SC) gap below the SC transition temperature
. At lower temperatures, an anisotropic superconducting (SC) gap below the SC transition temperature  , and the SC state permeates through the AFM regions via a SC proximity effect. Applying an external magnetic field induces a spin-flop transition near 5 T, reducing the volume of the AFM regions. Consequently, a short ranged inhomogeneous AFM state survives and coexists with a paramagnetic Fermi liquid state at high fields.
, and the SC state permeates through the AFM regions via a SC proximity effect. Applying an external magnetic field induces a spin-flop transition near 5 T, reducing the volume of the AFM regions. Consequently, a short ranged inhomogeneous AFM state survives and coexists with a paramagnetic Fermi liquid state at high fields.
Kawasaki, Kohei; Shinada, Kenta; Okamoto, Naritoshi; Kageyama, Tomio; Eda, Takashi; Okazaki, Hiro; Suzuki, Hiromichi; Yamamoto, Kazuya; Otabe, Jun
JAEA-Technology 2020-025, 80 Pages, 2021/03
Plutonium Fuel Production Facility was built in 1988 for the purpose of mainly producing MOX fuel of the prototype fast breeder reactor MONJU, and large glove boxes were installed for handling unsealed nuclear fuel material remotely. The panels of these glove boxes are made of acrylic, except for those installed after December 2013. For fires inside the glove box, automatic fire extinguishing systems using halides have been introduced since the beginning of construction, but for fires outside the glove box, there have been issues with direct measures for acrylic. Therefore, we have developed a fireproof sheet that mitigates the effect of fire outside the glove box on the panels as much as possible. As a result, fire-retardant sheets have been selected and attached to the glove box panels. We conducted a flammability test of the acrylic plate attached with these fireproof sheets and a usage environment influence test of fireproof sheets, and obtained good results. In addition, we set up a working group in the Plutonium Fuel Development Center in view of reducing external exposure during the work of attaching fireproof sheets, in which we discussed and examined the work procedure, and summarized it in the basic procedure manual.
Kitazato, Kohei*; Milliken, R. E.*; Iwata, Takahiro*; Abe, Masanao*; Otake, Makiko*; Matsuura, Shuji*; Takagi, Yasuhiko*; Nakamura, Tomoki*; Hiroi, Takahiro*; Matsuoka, Moe*; et al.
Nature Astronomy (Internet), 5(3), p.246 - 250, 2021/03
Times Cited Count:43 Percentile:96.93(Astronomy & Astrophysics)Here we report observations of Ryugu's subsurface material by the Near-Infrared Spectrometer (NIRS3) on the Hayabusa2 spacecraft. Reflectance spectra of excavated material exhibit a hydroxyl (OH) absorption feature that is slightly stronger and peak-shifted compared with that observed for the surface, indicating that space weathering and/or radiative heating have caused subtle spectral changes in the uppermost surface. However, the strength and shape of the OH feature still suggests that the subsurface material experienced heating above 300  C, similar to the surface. In contrast, thermophysical modeling indicates that radiative heating does not increase the temperature above 200
C, similar to the surface. In contrast, thermophysical modeling indicates that radiative heating does not increase the temperature above 200  C at the estimated excavation depth of 1 m, even if the semimajor axis is reduced to 0.344 au. This supports the hypothesis that primary thermal alteration occurred due to radiogenic and/or impact heating on Ryugu's parent body.
C at the estimated excavation depth of 1 m, even if the semimajor axis is reduced to 0.344 au. This supports the hypothesis that primary thermal alteration occurred due to radiogenic and/or impact heating on Ryugu's parent body.
Hayakawa, Sho*; Doihara, Kohei*; Okita, Taira*; Itakura, Mitsuhiro; Aichi, Masaatsu*; Suzuki, Katsuyuki*
Journal of Materials Science, 54(17), p.11509 - 11525, 2019/09
Times Cited Count:15 Percentile:56.33(Materials Science, Multidisciplinary)Kitazato, Kohei*; Milliken, R. E.*; Iwata, Takahiro*; Abe, Masanao*; Otake, Makiko*; Matsuura, Shuji*; Arai, Takehiko*; Nakauchi, Yusuke*; Nakamura, Tomoki*; Matsuoka, Moe*; et al.
Science, 364(6437), p.272 - 275, 2019/04
Times Cited Count:259 Percentile:99.73(Multidisciplinary Sciences)The near-Earth asteroid 162173 Ryugu, the target of Hayabusa2 sample return mission, is believed to be a primitive carbonaceous object. The Near Infrared Spectrometer (NIRS3) on Hayabusa2 acquired reflectance spectra of Ryugu's surface to provide direct measurements of the surface composition and geological context for the returned samples. A weak, narrow absorption feature centered at 2.72 micron was detected across the entire observed surface, indicating that hydroxyl (OH)-bearing minerals are ubiquitous there. The intensity of the OH feature and low albedo are similar to thermally- and/or shock-metamorphosed carbonaceous chondrite meteorites. There are few variations in the OH-band position, consistent with Ryugu being a compositionally homogeneous rubble-pile object generated from impact fragments of an undifferentiated aqueously altered parent body.
Nakanishi, Daiki*; Kawabata, Tomoya*; Doihara, Kohei*; Okita, Taira*; Itakura, Mitsuhiro; Suzuki, Katsuyuki*
Philosophical Magazine, 98(33), p.3034 - 3047, 2018/09
Times Cited Count:10 Percentile:47.84(Materials Science, Multidisciplinary)By using the six sets of interatomic potentials for face-centredcubic metals that differ in the stacking fault energy (SFE) while most of the other material parameters are kept almost identical, we conducted molecular dynamics simulations to evaluate the effects of SFE on the defect formation process through collision cascades. The ratio of glissile SIA clusters tends to decrease with increasing SFE. This is because perfect loops, the edges of which split into two partial dislocations with stacking fault structures between them in most cases, prefer to form at lower SFEs. The enhanced formation of glissile SIA clusters at lower SFEs can also be observed even at increased temperature.
Doihara, Kohei*; Okita, Taira*; Itakura, Mitsuhiro; Aichi, Masaatsu*; Suzuki, Katsuyuki*
Philosophical Magazine, 98(22), p.2061 - 2076, 2018/05
Times Cited Count:20 Percentile:71.42(Materials Science, Multidisciplinary)In this study, molecular dynamics simulations were performed to elucidate the effects of stacking fault energy (SFE) on the physical interactions between an edge dislocation and a spherical void in the crystal structure of face-centred cubic metals at various temperatures and for different void sizes. Four different types of interaction morphologies were observed, in which (1) two partial dislocations detached from the void separately, and the maximum stress corresponded to the detachment of the trailing partial; (2) two partial dislocations detached from the void separately, and the maximum stress corresponded to the detachment of the leading partial; (3) the partial dislocations detached from the void almost simultaneously without jog formation; and (4) the partial dislocations detached from the void almost simultaneously with jog formation. With an increase in void size or SFE, the interaction morphology changed in the above-mentioned order. It was observed that the magnitude of the critical resolved shear stress (CRSS) and its dependence on the SFE were determined by these interaction morphologies. The value of the CRSS in the case of interaction morphology (1) is almost equal to an analytical one based on the linear elasticity by employing the Burgers vector of a single partial dislocation. The maximum value of the CRSS is also obtained by the analytical model with the Burgers vector of the two partial dislocations.
Ino, Kohei*; Hernsdorf, A. W.*; Konno, Yuta*; Kozuka, Mariko*; Yanagawa, Katsunori*; Kato, Shingo*; Sunamura, Michinari*; Hirota, Akinari*; Togo, Yoko*; Ito, Kazumasa*; et al.
ISME Journal, 12(1), p.31 - 47, 2018/01
Times Cited Count:49 Percentile:91.33(Ecology)In this study, we found the dominance ofanaerobic methane-oxidizing archaea in groundwater enriched in sulfate and methane from a 300-m deep underground borehole in granitic rock.
Hirayama, Hideo*; Kondo, Kenjiro*; Suzuki, Seishiro*; Tanimura, Yoshihiko; Iwanaga, Kohei*; Nagata, Hiroshi*
EPJ Web of Conferences, 153, p.08010_1 - 08010_3, 2017/09
Times Cited Count:2 Percentile:78.04(Nuclear Science & Technology)Pulse height distributions were measured using a CdZnTe detector inside a lead collimator to investigate main source producing high dose rates above the shield plugs of Unit 3 at Fukushima Daiichi Nuclear Power Station. It was confirmed that low energy photons are dominant. Concentrations of Cs-137 under 60 cm concrete of the shield plug were estimated to be between 8.1 10
10 and 5.7
and 5.7 10
10 Bq/cm
Bq/cm from the measured peak count rate of 0.662 MeV photons. If Cs-137 was distributed on the surfaces of the gaps of the shied plugs with radius 6 m and with the averaged concentration of 5 points, 2.6
from the measured peak count rate of 0.662 MeV photons. If Cs-137 was distributed on the surfaces of the gaps of the shied plugs with radius 6 m and with the averaged concentration of 5 points, 2.6 10
10 Bq/cm
Bq/cm , total amount of Cs-137 is estimated to be 30 PBq.
, total amount of Cs-137 is estimated to be 30 PBq.
Ino, Kohei*; Konno, Yuta*; Kozuka, Mariko*; Hirota, Akinari*; Togo, Yoko*; Fukuda, Akari*; Komatsu, Daisuke*; Tsunogai, Urumu*; Tanabe, Akifumi*; Yamamoto, Satoshi*; et al.
Environmental Microbiology Reports (Internet), 8(2), p.285 - 294, 2016/04
Times Cited Count:26 Percentile:68.59(Environmental Sciences)To understand the subsurface biosphere, borehole investigation was conducted for 300-m deep granitic rocks at the Mizunami underground research laboratory, Japan. The initial biomass was the highest with the flourish of aerobic H -oxidizing Hydrogenophaga spp., whereas an uncultivated lineage of the phylum Nitrospirae became predominant after three years with decreasing biomass. The common occurrence of many species of Nitrospirae and Chlorobi phyla at the geographically distinct sites and the exclusive detection of their phylogenetically related environmental sequences from deep groundwaters and terrestrial hot springs, suggest that these bacteria are indigenous and potentially adapted to the deep terrestrial subsurface.
-oxidizing Hydrogenophaga spp., whereas an uncultivated lineage of the phylum Nitrospirae became predominant after three years with decreasing biomass. The common occurrence of many species of Nitrospirae and Chlorobi phyla at the geographically distinct sites and the exclusive detection of their phylogenetically related environmental sequences from deep groundwaters and terrestrial hot springs, suggest that these bacteria are indigenous and potentially adapted to the deep terrestrial subsurface.
 -glucosyltransferase from
-glucosyltransferase from 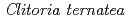
Hiromoto, Takeshi; Honjo, Eijiro*; Noda, Hisanobu*; Tamada, Taro; Kazuma, Kohei*; Suzuki, Masahiko*; Blaber, M.; Kuroki, Ryota
Protein Science, 24(3), p.395 - 407, 2015/03
Times Cited Count:62 Percentile:88.58(Biochemistry & Molecular Biology)UDP-glucose: anthocyanidin 3- -glucosyltransferase (UGT78K6) from
-glucosyltransferase (UGT78K6) from 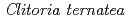 catalyzes the transfer of glucose from UDP-glucose to anthocyanidins such as delphinidin. To understand the acceptor-recognition scheme of UGT78K6, the crystal structure of UGT78K6 and its complex forms with anthocyanidin delphinidin and petunidin, and flavonol kaempferol were determined to resolutions of 1.85
catalyzes the transfer of glucose from UDP-glucose to anthocyanidins such as delphinidin. To understand the acceptor-recognition scheme of UGT78K6, the crystal structure of UGT78K6 and its complex forms with anthocyanidin delphinidin and petunidin, and flavonol kaempferol were determined to resolutions of 1.85  , 2.55
, 2.55  , 2.70
, 2.70  and 1.75
and 1.75  respectively. The anthocyanidin- and flavonol-acceptor binding details are almost identical in each complex structure, although the glucosylation activities against each acceptor were significantly different. The acceptor substrates in UGT78K6 are reversely bound to its binding site by a 180
respectively. The anthocyanidin- and flavonol-acceptor binding details are almost identical in each complex structure, although the glucosylation activities against each acceptor were significantly different. The acceptor substrates in UGT78K6 are reversely bound to its binding site by a 180 rotation about the O1-O3 axis of the flavonoid backbones observed in
rotation about the O1-O3 axis of the flavonoid backbones observed in 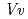 GT1 and UGT78G1. These substrate recognition schemes suggest the potential for controlled synthesis of natural pigments.
GT1 and UGT78G1. These substrate recognition schemes suggest the potential for controlled synthesis of natural pigments.
 emission reduction of active carbon recycling energy system for ironmaking by modeling with Aspen Plus
emission reduction of active carbon recycling energy system for ironmaking by modeling with Aspen PlusSuzuki, Katsuki*; Hayashi, Kentaro*; Kurihara, Kohei*; Nakagaki, Takao*; Kasahara, Seiji
ISIJ International, 55(2), p.340 - 347, 2015/02
Times Cited Count:19 Percentile:64.17(Metallurgy & Metallurgical Engineering)Use of the Active Carbon Recycling Energy System in ironmaking (iACRES) has been proposed for reducing CO emissions. To evaluate the performance of iACRES quantitatively, a process flow diagram of a blast furnace model with iACRES was developed using Aspen Plus, a chemical process simulator. CO
emissions. To evaluate the performance of iACRES quantitatively, a process flow diagram of a blast furnace model with iACRES was developed using Aspen Plus, a chemical process simulator. CO emission reduction and exergy analysis were performed by using mass and energy balance obtained from simulation results. The following CO
emission reduction and exergy analysis were performed by using mass and energy balance obtained from simulation results. The following CO reduction methods were evaluated as iACRES: solid oxide electrolysis cells (SOEC) with CO
reduction methods were evaluated as iACRES: solid oxide electrolysis cells (SOEC) with CO capture and separation (CCS), SOEC without CCS, and a reverse water-gas shift reactor powered by a high-temperature gas-cooled reactor. iACRES enabled CO
capture and separation (CCS), SOEC without CCS, and a reverse water-gas shift reactor powered by a high-temperature gas-cooled reactor. iACRES enabled CO emission reduction by 3-11% by recycling CO and H
emission reduction by 3-11% by recycling CO and H , whereas effective exergy ratio decreased by 1-7%.
, whereas effective exergy ratio decreased by 1-7%.
Hayashi, Kentaro*; Suzuki, Katsuki*; Kurihara, Kohei*; Nakagaki, Takao*; Kasahara, Seiji
Tanso Junkan Seitetsu Kenkyukai Saika Hokokusho; Tanso Junkan Seitetsu No Tenkai, p.27 - 41, 2015/02
Applying Active Carbon Recycling Energy System to ironmaking (iACRES) process is a promising technology to reduce coal usage and CO emissions. To evaluate performance of iACRES quantitatively, a process flow diagram of the blast furnace model with iACRES was developed using Aspen Plus. CO
emissions. To evaluate performance of iACRES quantitatively, a process flow diagram of the blast furnace model with iACRES was developed using Aspen Plus. CO emission reduction and exergy analysis was predicted by using mass and energy balance obtained from the simulation results. The followings were investigated as iACRES: solid oxide electrolysis cells (SOEC) with CO
emission reduction and exergy analysis was predicted by using mass and energy balance obtained from the simulation results. The followings were investigated as iACRES: solid oxide electrolysis cells (SOEC) with CO capture and separation (CCS), SOEC without CCS, and a reverse water-gas shift reactor as the a CO
capture and separation (CCS), SOEC without CCS, and a reverse water-gas shift reactor as the a CO reduction reactor powered by a high-temperature gas-cooled reactor. iACRES could provide CO
reduction reactor powered by a high-temperature gas-cooled reactor. iACRES could provide CO emission reductions of 3-11% by recycling CO and H
emission reductions of 3-11% by recycling CO and H , whereas the effective exergy ratio decreased by 1-7%.
, whereas the effective exergy ratio decreased by 1-7%.
 -glucosyltransferase from
-glucosyltransferase from 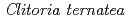
Hiromoto, Takeshi; Honjo, Eijiro*; Tamada, Taro; Noda, Hisanobu*; Kazuma, Kohei*; Suzuki, Masahiko*; Kuroki, Ryota
Journal of Synchrotron Radiation, 20(6), p.894 - 898, 2013/11
Times Cited Count:38 Percentile:86.54(Instruments & Instrumentation)Flowers of the butterfly pea ( ) accumulate a group of polyacylated anthocyanins, named ternatins, in their petals. The first step in ternatin biosynthesis is the transfer of glucose from UDP-glucose to anthocyanidins such as delphinidin, a reaction catalyzed in
) accumulate a group of polyacylated anthocyanins, named ternatins, in their petals. The first step in ternatin biosynthesis is the transfer of glucose from UDP-glucose to anthocyanidins such as delphinidin, a reaction catalyzed in  by UDP-glucose:anthocyanidin 3-
by UDP-glucose:anthocyanidin 3- -glucosyltransferase (
-glucosyltransferase ( 3GT-A; AB185904). To elucidate the structure-function relationship of
3GT-A; AB185904). To elucidate the structure-function relationship of  3GT-A, recombinant
3GT-A, recombinant  3GT-A was expressed in
3GT-A was expressed in  and its tertiary structure was determined to 1.85
and its tertiary structure was determined to 1.85  , resolution by using X-ray crystallography. The structure of
, resolution by using X-ray crystallography. The structure of  3GT-A shows a common folding topology, the GT-B fold, comprised of two Rossmann-like
3GT-A shows a common folding topology, the GT-B fold, comprised of two Rossmann-like  /
/ /
/ domains and a cleft located between the N- and C-domains containing two cavities that are used as binding sites for the donor (UDP-Glc) and acceptor substrates. By comparing the structure of
domains and a cleft located between the N- and C-domains containing two cavities that are used as binding sites for the donor (UDP-Glc) and acceptor substrates. By comparing the structure of  3GT-A with that of the flavonoid glycosyltransferase
3GT-A with that of the flavonoid glycosyltransferase 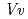 GT1 from red grape (
GT1 from red grape ( ) in complex with UDP-2-deoxy-2-fluoro glucose and kaempferol, locations of the catalytic His-Asp dyad and the residues involved in recognizing UDP-2-deoxy-2-fluoro glucose were essentially identical in
) in complex with UDP-2-deoxy-2-fluoro glucose and kaempferol, locations of the catalytic His-Asp dyad and the residues involved in recognizing UDP-2-deoxy-2-fluoro glucose were essentially identical in  3GT-A, but certain residues of
3GT-A, but certain residues of 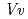 GT1 involved in binding kaempferol were found to be substituted in
GT1 involved in binding kaempferol were found to be substituted in  3GT-A. These findings are important for understanding the differentiation of acceptor-substrate recognition in these two enzymes.
3GT-A. These findings are important for understanding the differentiation of acceptor-substrate recognition in these two enzymes.
Kim, G.; Nakajima, Kohei*; Teshima, Naoya*; Tatekawa, Takayuki; Suzuki, Yoshio; Takemiya, Hiroshi
Progress in Nuclear Science and Technology (Internet), 2, p.634 - 638, 2011/10
We developed grid-enabled application of full-scale 3D vibration simulator for an entire nuclear power plant on simple orchestration application framework (SOAF). The simulator is an analysis system to study seismic response of a whole digitalized nuclear power plant. In the simulator, components of a power plant are treated in hierarchical manner so that large components are grouped at primary level and small components such as pipes at secondary level. Boundary condition data are transferred from the primary level to the secondary level. SOAF provides functionality to enable users to simply define the data transfer in pipelined scenario which is technically difficult to realize using the existing grid technology. In this paper, we discuss technical issues of the realization of pipelined scenario on grid and demonstrate effectiveness of SOAF by analysis of High Temperature Engineering Test Reactor of JAEA using grid-enabled application implementing SOAF.
Kim, G.; Nakajima, Kohei*; Teshima, Naoya; Tatekawa, Takayuki; Suzuki, Yoshio; Takemiya, Hiroshi
Proceedings of Joint International Conference of 7th Supercomputing in Nuclear Application and 3rd Monte Carlo (SNA + MC 2010) (USB Flash Drive), 5 Pages, 2010/10
Full-Scale 3D vibration simulator for an entire nuclear power plant is a seismic response analysis system for a whole digitalized nuclear power plant. In the system, boundary data from large components are used as input data of small components. To make a whole simulation efficient, we introduced pipeline method in which the data were transferred each time step running all components simulations in parallel. In the realization of the method on grid, since there were no existing grid technologies to sufficiently support the method for a long time, we developed simple orchestration application framework (SOAF) and using the SOAF, we performed seismic response analysis of a test reactor of JAEA and succeeded simulation for a week.
Tatekawa, Takayuki; Nakajima, Kohei*; Kim, G.; Teshima, Naoya; Suzuki, Yoshio; Takemiya, Hiroshi
High Performance Computing on Vector Systems 2010, p.107 - 120, 2010/09
In the atomic field, by integrating various simulation codes which were installed on distributed computers, large-scale and detailed simulations which aim explication of complicated phenomena. However integration of each simulation codes and cooperative operation of the integrated codes make heavy burden for researchers. We have developed the Simple Orchestration Application Framework (SOAF) to cooperatively control simulation codes on remote computers from a client PC. SOAF enables researchers to cooperatively execute various codes on grid infrastructure by only describing a configuration file including the information of execution codes and file flows among them. SOAF does not need substantial modification of the simulation codes. By using SOAF, we successfully execute four plasma simulation codes included in the "Burning Plasma Integrated Code" according to the scenario described in the configuration file.
Tatekawa, Takayuki; Nakajima, Kohei*; Teshima, Naoya; Kim, G.; Suzuki, Yoshio; Takemiya, Hiroshi; Hayashi, Nobuhiko; Iba, Katsuyuki*
Proceedings of 3rd International Joint Conference on Computational Sciences and Optimization (CSO 2010), p.322 - 326, 2010/05
Tatekawa, Takayuki; Nakajima, Kohei*; Kim, G.; Kino, Chiaki; Teshima, Naoya; Suzuki, Yoshio; Takemiya, Hiroshi
FUJITSU Famirikai Rombunshu (Internet), 19 Pages, 2010/03
We have introduced about the framework to make the integration of large and complicated simulation such as a proof strength simulation of nuclear power plants and a control simulation of nuclear fusion plasma which codes are installed to distributed computers. We able to carry out detailed simulations by integrating various simulation methods with development of simulation technique. However it becomes a burden to control the integration of each simulation code for researchers. We have noticed that the execution scenarios of each code in cooperated simulation are roughly categorized to workflow type, pipeline type, and conditional branch type. Then we have developed the framework in which just write those patterns in a configuration file and achieve the cooperative execution of element codes without substantial modification of simulation codes.