Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Miura, Yasufumi*; Suzuki, Kenji*; Morooka, Satoshi; Shobu, Takahisa
Quantum Beam Science (Internet), 8(1), p.1_1 - 1_14, 2024/03
Suzuki, Kenji*; Miura, Yasufumi*; Shiro, Ayumi*; Toyokawa, Hidenori*; Saji, Choji*; Shobu, Takahisa; Morooka, Satoshi
Zairyo, 72(4), p.316 - 323, 2023/04
Suzuki, Kenji*; Kura, Komoe*; Miura, Yasufumi*; Shiro, Ayumi*; Toyokawa, Hidenori*; Saji, Choji*; Kajiwara, Kentaro*; Shobu, Takahisa
Zairyo, 71(12), p.1005 - 1012, 2022/12
This paper describes a stress measurement from a welded part of an austenitic stainless steel using synchrotron X-rays. Difficulty measuring the X-ray stress of the welded part is caused by the broadening of the diffraction spot in the radial and circumferential directions. The bending strains of the rectangular bar made of the welded part were measured using synchrotron white X-rays and the double exposure method. To improve the energy resolution, monochromatic synchrotron X-ray of 70 keV was used. The diffraction pattern showed the sharp arc like a pattern from texture material. The diffraction profile was obtained from the integral of the diffraction intensity in the direction of the circumference. The diffraction angle was determined using the double exposure method. As a result, the distribution of the residual stresses of the welded part could be measured.
Suenaga, Daiki*; Araki, Yasufumi; Suzuki, Kei; Yasui, Shigehiro*
Physical Review D, 105(7), p.074028_1 - 074028_19, 2022/04
Times Cited Count:2 Percentile:36.77(Astronomy & Astrophysics)We propose a new mechanism of the heavy-quark spin polarization (HQSP) in quark matter induced by the Kondo effect under an external magnetic field. The Kondo effect is caused by a condensate between a heavy and a light quark called the Kondo condensate leading to a mixing of the heavy- and light-quark spins. Thus, the HQSP is driven through the Kondo effect from light quarks coupling with the magnetic field in quark matter. For demonstration, we employ the Nambu-Jona-Lasinio type model under a magnetic field and investigate the HQSP within the linear response theory with vertex corrections required by the 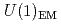 electromagnetic gauge invariance. As a result, we find that the HQSP arises significantly with the appearance of the Kondo effect. Our findings are testable in future sign-problem-free lattice simulations.
electromagnetic gauge invariance. As a result, we find that the HQSP arises significantly with the appearance of the Kondo effect. Our findings are testable in future sign-problem-free lattice simulations.
Araki, Yasufumi; Suenaga, Daiki*; Suzuki, Kei; Yasui, Shigehiro*
Physical Review Research (Internet), 3(2), p.023098_1 - 023098_17, 2021/05
Spins of relativistic fermions are related to their orbital degrees of freedom. In order to quantify the effect of hybridization between relativistic and nonrelativistic degrees of freedom on spin-orbit coupling, we focus on the spin-orbital (SO) crossed susceptibility arising from spin-orbit coupling. The SO crossed susceptibility is defined as the response function of their spin polarization to the "orbital" magnetic field, namely the effect of magnetic field on the orbital motion of particles as the vector potential. Once relativistic and nonrelativistic fermions are hybridized, their SO crossed susceptibility gets modified at the Fermi energy around the band hybridization point, leading to spin polarization of nonrelativistic fermions as well. These effects are enhanced under a dynamical magnetic field that violates thermal equilibrium, arising from the interband process permitted by the band hybridization. Its experimental realization is discussed for Dirac electrons in solids with slight breaking of crystalline symmetry or doping, and also for quark matter including dilute heavy quarks strongly hybridized with light quarks, arising in a relativistic heavy-ion collision process.
Suenaga, Daiki*; Araki, Yasufumi; Suzuki, Kei; Yasui, Shigehiro*
Physical Review D, 103(5), p.054041_1 - 054041_17, 2021/03
Times Cited Count:5 Percentile:45.23(Astronomy & Astrophysics)We investigate the influence of the Kondo effect, namely, the nonperturbative effect induced by heavy impurities, on the chiral separation effect (CSE) in quark matter. We employ a simple effective model incorporating the Kondo condensate made of a light quark and a heavy quark, and compute the response function of the axial current to the magnetic field in the static and dynamical limits. As a result, we find that the Kondo effect catalyzes the CSE in both of the limits, and in particular the CSE in the dynamical limit can be enhanced by a factor of approximately 3. Our findings clearly show that the presence of heavy impurities in quark matter can play an important role in the transport phenomena of light quarks induced by a magnetic field.
Araki, Yasufumi; Suenaga, Daiki*; Suzuki, Kei; Yasui, Shigehiro*
Physical Review Research (Internet), 3(1), p.013233_1 - 013233_12, 2021/03
We investigate two different types of relativistic Kondo effects, distinguished by heavy-impurity degrees of freedom, by focusing on the energy-momentum dispersion relations of the ground state with condensates composed of a light Dirac fermion and a nonrelativistic impurity fermion. Heavy fermion degrees of freedom are introduced in terms of two types of heavy-fermion effective theories, in other words, two heavy-fermion limits for the heavy Dirac fermion, which is known as the heavy-quark effective theories (HQETs) in high-energy physics. While the first one includes only the heavy-particle component, the second one contains both the heavy-particle and heavy-antiparticle components, which are opposite in their parity. From these theories, we obtain two types of Kondo effects, in which the dispersions near the Fermi surface are very similar, but they differ in the structure at low momentum. We also classify the possible forms of condensates in the two limits. The two Kondo effects will be examined by experiments with Dirac/Weyl semimetals or quark matter, lattice simulations, and cold-atom simulations.
Suenaga, Daiki*; Suzuki, Kei; Araki, Yasufumi; Yasui, Shigehiro*
Physical Review Research (Internet), 2(2), p.023312_1 - 023312_13, 2020/06
The Kondo effect is induced by the interaction between light fermions near the Fermi surface and heavy impurities, and it affects electric/thermal/transport properties of matter. The chirality (right-handed or left-handed) is one of the unique properties of relativistic (Dirac or Weyl) fermions. In normal matter, the numbers of right- and left-handed particles are equivalent to each other, but environments with a chirality imbalance can also be realized. In this paper, we theoretically propose the Kondo effect driven by a chirality imbalance (or chiral chemical potential) of relativistic light fermions. This effect is caused by the mixing between a right-handed (or left-handed) fermion and a heavy impurity in the chirality imbalanced matter. This is different from the usual Kondo effect induced by finite density (or chemical potential) for light fermions. We construct an effective model with an interaction between a relativistic fermion and a heavy impurity, and we derive the realization of the Kondo effect from both a perturbative calculation and a nonperturbative mean-field approach. We also discuss the temperature dependence, the coupling constant dependence, the susceptibilities, and the order of the phase transition for the Kondo effect. Such a Kondo effect will be tested by future lattice simulations.
Suzuki, Yasufumi
Genshiryoku eye, 50(6), p.10 - 11, 2004/06
no abstracts in English
Suzuki, Yasufumi; Dojiri, Shigeru; Ono, Akio; Maeda, Atsushi; Sugikawa, Susumu
Proceedings of International Conference on Back-End of the Fuel Cycle: From Research to Solutions (GLOBAL 2001) (CD-ROM), 7 Pages, 2001/09
no abstracts in English
 in comparison with undoped UO
in comparison with undoped UO , Mg-Nb doped UO
, Mg-Nb doped UO and Ti doped UO
and Ti doped UO
Fujino, Takeo*; Shiratori, Tetsuo; Sato, Nobuaki*; Fukuda, Kosaku; Yamada, Kota*; Suzuki, Yasufumi; Serizawa, Hiroyuki
Journal of Nuclear Materials, 297(2), p.176 - 205, 2001/08
Times Cited Count:20 Percentile:79.16(Materials Science, Multidisciplinary)no abstracts in English
Sakamura, Yoshiharu*; Shirai, Osamu; Iwai, Takashi; Suzuki, Yasufumi
Journal of Alloys and Compounds, 321(1), p.76 - 83, 2001/05
Times Cited Count:57 Percentile:89.52(Chemistry, Physical)no abstracts in English
Suzuki, Yasufumi; Maeda, Atsushi; Sugikawa, Susumu; Takeshita, Isao
Proceedings of International Conference on Scientific Research on the Back-end of the Fuel Cycle for the 21st Century (ATALANTE 2000) (Internet), 8 Pages, 2000/10
no abstracts in English
Shirai, Osamu; Iizuka, Masatoshi*; Iwai, Takashi; Suzuki, Yasufumi; Arai, Yasuo
Journal of Nuclear Science and Technology, 37(8), p.676 - 681, 2000/08
no abstracts in English
 and ThO
and ThO
Serizawa, Hiroyuki; Arai, Yasuo; Suzuki, Yasufumi
Journal of Nuclear Materials, 280(1), p.99 - 105, 2000/06
Times Cited Count:22 Percentile:78.53(Materials Science, Multidisciplinary)no abstracts in English
Shirai, Osamu; Iwai, Takashi; Shiozawa, Kenichi; Suzuki, Yasufumi; Sakamura, Y.*; Inoue, Tadashi*
Journal of Nuclear Materials, 277(2-3), p.226 - 230, 2000/02
Times Cited Count:24 Percentile:80.82(Materials Science, Multidisciplinary)no abstracts in English
Sakamura, Y.*; Shirai, Osamu; Iwai, Takashi; Suzuki, Yasufumi
Journal of the Electrochemical Society, 147(2), p.642 - 649, 2000/02
Times Cited Count:20 Percentile:61.09(Electrochemistry)no abstracts in English
Suzuki, Yasufumi
Nihon Genshiryoku Gakkai-Shi, 41(4), p.376 - 377, 1999/04
no abstracts in English

Serizawa, Hiroyuki; Arai, Yasuo; Takano, Masahide; Suzuki, Yasufumi
Journal of Alloys and Compounds, 282, p.17 - 22, 1999/00
Times Cited Count:20 Percentile:74.44(Chemistry, Physical)no abstracts in English
Nakajima, Kunihisa; Arai, Yasuo; Suzuki, Yasufumi
Journal of Nuclear Materials, 275(3), p.332 - 335, 1999/00
Times Cited Count:3 Percentile:52.33(Materials Science, Multidisciplinary)no abstracts in English