Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
 O in Fe
O in Fe O
O film on Fe formed in an NaOH solution containing oxidants
film on Fe formed in an NaOH solution containing oxidantsHaruna, Takumi*; Miyataki, Yuki*; Hirohata, Yohei*; Shibata, Toshio*; Taniguchi, Naoki; Tachikawa, Hirokazu*
Zairyo To Kankyo, 67(9), p.375 - 380, 2018/09
This research aimed to confirm the formation of Fe O
O film on Fe immersed in aqueous 45 mass% NaOH solution containing some oxidants at the boiling temperature, to recognize the optimum immersion time for the formation of thick and protective film, and to reveal the absorption behavior of D
film on Fe immersed in aqueous 45 mass% NaOH solution containing some oxidants at the boiling temperature, to recognize the optimum immersion time for the formation of thick and protective film, and to reveal the absorption behavior of D O in the Fe
O in the Fe O
O film at room temperature. The results were obtained as follows. It was confirmed that Fe
film at room temperature. The results were obtained as follows. It was confirmed that Fe O
O film was formed on Fe immersed in the NaOH solution for a time more than 0.6 ks, and the film thickness increased parabolically with an increase in the immersion time. D
film was formed on Fe immersed in the NaOH solution for a time more than 0.6 ks, and the film thickness increased parabolically with an increase in the immersion time. D O absorption test was carried out to the films formed in the NaOH solution for immersion times of 1.2 and 3.6 ks. An amount of D
O absorption test was carried out to the films formed in the NaOH solution for immersion times of 1.2 and 3.6 ks. An amount of D O absorbed into the film increased with an increase in an absorption time up to 1000 ks, and an absorption time more than 1000 ks made an amount of D
O absorbed into the film increased with an increase in an absorption time up to 1000 ks, and an absorption time more than 1000 ks made an amount of D O constant. The constant amount of D
O constant. The constant amount of D O was larger for the film formed on Fe immersed in the NaOH solution for 3.6 ks than that for 1.2 ks. The transient of the amount of D
O was larger for the film formed on Fe immersed in the NaOH solution for 3.6 ks than that for 1.2 ks. The transient of the amount of D O absorbed into the film was analyzed on the basis of Fick's law for diffusion, and diffusion coefficients of D
O absorbed into the film was analyzed on the basis of Fick's law for diffusion, and diffusion coefficients of D O were obtained to be 5.1
O were obtained to be 5.1 10
10 cm
cm s
s and 9.9
and 9.9 10
10 cm
cm s
s for the films formed for 1.2 and 3.6 ks, respectively. Therefore it was estimated that the diffusion coefficient of the Fe
for the films formed for 1.2 and 3.6 ks, respectively. Therefore it was estimated that the diffusion coefficient of the Fe O
O film was in the region from 5.1
film was in the region from 5.1 10
10 cm
cm s
s to 9.9
to 9.9 10
10 cm
cm s
s .
.
Sugiyama, Daisuke*; Kimura, Hideo; Tachikawa, Hirokazu*; Iimoto, Takeshi*; Kawata, Yosuke*; Ogino, Haruyuki*; Okoshi, Minoru*
Journal of Radiological Protection, 38(1), p.456 - 462, 2018/03
Times Cited Count:0 Percentile:0.01(Environmental Sciences)Experience after the accident at the Fukushima Daiichi Nuclear Power Station has shown that there is a need to establish radiation protection criteria for radioactive waste management consistent with the criteria adopted for the remediation of existing exposure situations. A stepwise approach to setting such criteria is proposed. Initially, a reference level for annual effective dose from waste management activities in the range 1-10 mSv should be set, with the reference level being less than the reference level for ambient dose. Subsequently, the reference level for annual effective dose from waste management activities should be reduced in one or more steps to achieve a final target value of 1 mSv. The dose criteria at each stage should be determined with relevant stakeholder involvement. Illustrative case studies show how this stepwise approach might be applied in practice.
 irradiation
irradiationYukawa, Takuji*; Inoue, Hiroyuki*; Kojima, Takao*; Iwase, Akihiro*; Taniguchi, Naoki; Tachikawa, Hirokazu*
Zairyo To Kankyo 2016 Koenshu (CD-ROM), p.359 - 362, 2016/05
The immersion tests of pure titanium were carried out in aqueous solution containing carbonate/bicarbonate with 50 mM-chloride ion under gamma irradiation. The effect of pH on general corrosion rate of titanium were studied. The experimental results showed that the concentration of hydrogen preoxide was increased with pH, and the corrosion rate increased with the hydrogen preoxide concentration. The corrosion rate in pH12 and 13 were 5 to10 times larger than those under unirradiated conditions.
 O in the film on Fe oxidized at high temperature in air
O in the film on Fe oxidized at high temperature in airHaruna, Takumi*; Yamamoto, Tatsuya*; Miyairi, Yoji*; Shibata, Toshio*; Taniguchi, Naoki; Sakamaki, Keiko; Tachikawa, Hirokazu*
Zairyo To Kankyo, 64(5), p.201 - 206, 2015/05
Diffusion coefficients of D O in the films was determined in order to estimate corrosion rate of carbon steel for the overpack in ground water. Fe plates were heated to form oxide films. The films were characterized with XRD and SEM. After that, the specimen was contacted with D
O in the films was determined in order to estimate corrosion rate of carbon steel for the overpack in ground water. Fe plates were heated to form oxide films. The films were characterized with XRD and SEM. After that, the specimen was contacted with D O for 5184 ks, followed by subjected to TDS to obtain an amount of D
O for 5184 ks, followed by subjected to TDS to obtain an amount of D O absorbing into the film. As a result, single-layered film of Fe
O absorbing into the film. As a result, single-layered film of Fe O
O was formed at 573 and 723 K, and double-layered film of Fe
was formed at 573 and 723 K, and double-layered film of Fe O
O and Fe
and Fe O
O was formed at 873 K. It was found that an amount of D
was formed at 873 K. It was found that an amount of D O in the film correlated linearly with a square root of the absorption period, and that the amount was steady for a long period. From the results and Fick's second law, diffusion coefficients of D
O in the film correlated linearly with a square root of the absorption period, and that the amount was steady for a long period. From the results and Fick's second law, diffusion coefficients of D O was determined as 9.7
O was determined as 9.7 10
10 cm
cm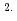 s
s for the Fe
for the Fe O
O film, and 5.5
film, and 5.5 10
10 cm
cm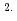 s
s to 2.2
to 2.2 10
10 cm
cm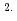 s
s for Fe
for Fe O
O film.
film.
Doi, Reisuke; Tachikawa, Hirokazu*; Yui, Mikazu
Journal of Nuclear Science and Technology, 47(3), p.278 - 285, 2010/03
Times Cited Count:6 Percentile:40.28(Nuclear Science & Technology)Se solubility and its solubility-limiting solid phase were investigated in a simulated geological repository environment. Experiments in bentonite equilibrated waters and the simple condition experiment without bentonite were performed. With bentonite approximately 10 mol/dm
mol/dm Se concentration was obtained. The experiment without bentonite was conducted to confirm the solubility-limiting solid phase. This experiment was carried out at a higher temperature (80
Se concentration was obtained. The experiment without bentonite was conducted to confirm the solubility-limiting solid phase. This experiment was carried out at a higher temperature (80 C) to accelerate the solid transformation of Se. The Se concentration decreased with increasing time. Several Se solid phases were identified. Though Se(cr) was dominant at first, this solid phase gradually transformed with time and Fe-Se solids began to form. It is suggested that FeSe
C) to accelerate the solid transformation of Se. The Se concentration decreased with increasing time. Several Se solid phases were identified. Though Se(cr) was dominant at first, this solid phase gradually transformed with time and Fe-Se solids began to form. It is suggested that FeSe , which is the most thermodynamically stable phase, is likely to be the Se solubility-limiting solid phase under a geological repository environment in the long-term.
, which is the most thermodynamically stable phase, is likely to be the Se solubility-limiting solid phase under a geological repository environment in the long-term.
Tachikawa, Hirokazu*; Kawakubo, Fumie*; Shimizu, Akihiko*; Shibata, Toshio*; Azumi, Kazuhisa*; Inoue, Hiroyuki*; Sugimoto, Katsuhisa*; Tsuru, Toru*; Fujimoto, Shinji*
JAEA-Research 2007-086, 74 Pages, 2008/02
The corrosion life time of the overpack has been investigated on the basis of experimental data and past research, assuming the ranging geological environment of Japan. However, some subject for the realization of the overpack design, such as the behavior of the overpack under high pH conditions, the behavior of the overpack with change of near-field environmental condition and the corrosion behavior of the welds have still been left. To take into account these conditions, expert committee composed of metal corrosion science experts were established in the Nuclear Safety Research Association and past research outcomes and the theory of safety assessment for long term corrosion resistance were investigated from the view points of metal corrosion science.
Tachikawa, Hirokazu*; Kawakubo, Fumie*; Shimizu, Akihiko*; Shibata, Toshio*; Sugimoto, Katsuhisa*; Seo, Masahiro*; Tsuru, Toru*; Fujimoto, Shinji*; Inoue, Hiroyuki*
JAEA-Research 2006-058, 80 Pages, 2006/10
The Japan Nuclear Cycle Development Institute submitted "Second Progress Report on Research and Development for the Geological Disposal of HLW in Japan" to the Japanese government. This report contains investigations of the corrosion life time of the overpack on the basis of experimental data and past research, assuming the ranging geological environment of Japan. However some subjects, such as the behavior of the overpack under high pH conditions and the behavior of the engineering barrier with change of near-field environmental condition with time for promoting reliability have still been left. To take into account these conditions, expert committee composed of metal corrosion science experts were established in the Nuclear Safety Research Association and past research outcomes and the theory of safety assessment were investigated from the view points of long term stability and corrosion resistance of engineering barrier.
Aoyama, Eri*; Tachikawa, Hirokazu*; Shimizu, Akihiko*
JNC TJ8400 2004-034, 442 Pages, 2005/03
The Japan Nuclear Cycle Development Institute submitted 'Second Progress Report on Research and Development for the Geological Disposal of HLW in Japan' to the Japanese government. This report contains investigations of the long term behavior of alteration of bentonite, and of the corrosion life time of overpack on the basis of experimental data and past research, assuming the ranging geological environment of Japan. However some subjects, such as the behavior of the bentonite and overpack under high pH conditions and the behavior of the engineering barrier with change of near-field environmental condition with time for promoting reliability have still been left.To take into account these conditions, expert committees composed of clay science and metal corrosion science experts were established in the Nuclear Safety Research Association and past research outcomes and the theory of safety assessment were investigated from the view points of long term stability and corrosion resistance of engineering buffer materials.
Sano, Eri*; Tachikawa, Hirokazu*; Shimizu, Akihiko*
JNC TJ8420 2004-004, 342 Pages, 2005/02
The research plan of the radionuclides migration drawn up by Japan Nuclear Fuel Cycle Development Institute and its' research outcome were reviewed comprehensively by an expert committee established in Nuclear Safety Research Association. Also, experimental investigations for the migration behavior of actinide elements and fission products in engineering barrier and natural barrier media, and for solution chemistry of them were carried out and discussed by the committee, in order to enhance the reliability of prediction for migration behavior of radionuclides. The subjects investigated by the expert committee are as follows; (1)Diffusion and electromigration behavior of Plutonium in bentnite under reducing condition (2)Numerical analysis of distribution coefficients of nuclides in compacted bentonite using surface complexization model (3)Radioactive disequilibrium of decay series nuclides in natural water and various materials (4)Research on complexation reactions of f - elements
Tachikawa, Hirokazu*
JNC TJ8400 2003-082, 240 Pages, 2004/03
The Japan Nuclear Fuel Cycle Development Institute submitted 'Second Progress Report on Research and Development for the Geological Disposal of HLW in Japan' to the Japanese government. This report contains investigations of the long term behavior of alteration of bentonite, and of the corrosion life time of overpack on the basis of experimental data and past research, assuming the ranging geological environment of Japan. However some subjects, such as the behavior of the bentonite and overpack under high pH conditions and the behavior of the engineering barrier with change of near-field environmental condition with time for promoting reliability have still been left. To take into account these conditions, expert committees composed of clay science and metal corrosion science experts were established in the Nuclear Safety Research Association and past research outcomes and the theory of safety assessment were investigated and technically reviewed from the view points of long term stability and corrosion resistance of engineering buffer materials.
Tachikawa, Hirokazu*
JNC TJ8420 2003-002, 280 Pages, 2004/02
The research plan of the validation on effects of colloids and organic materials drawn up by the Japan Nuclear Fuel Cycle Development Institute and its' research outcome were reviewed comprehensively by an expert committee established in the Nuclear Safety Research Association.
Tachikawa, Hirokazu*; Kitao, Hideo*; Katsurai, Kiyomichi*; Yanagisawa, Ichiro*; Shibata, Masahiro; Suyama, Tadahiro*; Yui, Mikazu
JNC TN8400 99-068, 108 Pages, 1999/11
In an evaluation of high level waste (HLW) repository performance, Se-79 is one of important elements to be analyzed. Selenium solubility and solubility limiting solid phase is not clear. Then, we performed solubility measurement tests from over saturation direction under reducing conditions considering the repository conditions in deep underground. In some cases, bentonite (Kunigel V1) or pyrite coexisted in the experimental system to simulate the repository conditions. Se bearing solids were determined by XRD analysis, and solubility limiting solid phase was discussed. FeSe (Ferroselite) and Se (hexagonal) were identified in the simple condition test, in which Fe(II) solution and Se solution were mixed. SeS was also identified when S(-II) solution was added. The Se concentrations in aqueous phase were approximately 10
(Ferroselite) and Se (hexagonal) were identified in the simple condition test, in which Fe(II) solution and Se solution were mixed. SeS was also identified when S(-II) solution was added. The Se concentrations in aqueous phase were approximately 10 mol/l at neutral pH and approximately 10
mol/l at neutral pH and approximately 10 mol/l at pH9 in the bentonite coexisting tests and pyrite coexisting tests. The solid phases identified in the pyrite coexisting tests were mainly Se(hexagonal) and FeSe
mol/l at pH9 in the bentonite coexisting tests and pyrite coexisting tests. The solid phases identified in the pyrite coexisting tests were mainly Se(hexagonal) and FeSe (Ferroselite) in one of the samples. Further, the possibility of Fe(S,Se) solid solution formation was presumed on the pyrite surface dipping in the test solutions. In addition, we performed another selenium solubility measurement to accelerate the transformation of Se bearing solid phase at elevated temperature (80
(Ferroselite) in one of the samples. Further, the possibility of Fe(S,Se) solid solution formation was presumed on the pyrite surface dipping in the test solutions. In addition, we performed another selenium solubility measurement to accelerate the transformation of Se bearing solid phase at elevated temperature (80 C). The concentration of Se decreases with time and reached to the detection limit of ICP-MS (4
C). The concentration of Se decreases with time and reached to the detection limit of ICP-MS (4 10
10 mol/1) in 3 months. At first, Se(hexagonal) is dominant in the precipitation, however this solid phase was gradually transformed to Fe-Se solids (FeSe, FeSe
mol/1) in 3 months. At first, Se(hexagonal) is dominant in the precipitation, however this solid phase was gradually transformed to Fe-Se solids (FeSe, FeSe ) with time. Therefore it is strongly suggested that FeSe
) with time. Therefore it is strongly suggested that FeSe which is the thermodynamically most stable phase will be a solubility limiting solid phase under repository conditions in long term. As the experimental system was confirmed as sulfate reducing bacteria free, it should be noted that whole observed reactions ...
which is the thermodynamically most stable phase will be a solubility limiting solid phase under repository conditions in long term. As the experimental system was confirmed as sulfate reducing bacteria free, it should be noted that whole observed reactions ...
Kataoka, Shinichi*; Kitao, Hideo*; Tachikawa, Hirokazu*; Shimada, Takashi*; Maeda, Kazuto*; Nemoto, Kazuaki*; Yanagisawa, Ichiro*
PNC TJ1216 98-002, 676 Pages, 1998/02
None
Mukai, Satoru*; Kitao, Hideo*; Tachikawa, Hirokazu*; Fusaeda, Shigeki*; Yanagisawa, Ichiro*; Doi, Motoo*; *
PNC TJ1216 96-003, 106 Pages, 1996/03
None
Shibata, Toshio*; Taniguchi, Naoki; Sakamaki, Keiko; Tachikawa, Hirokazu*
no journal, ,
Carbon steel has been selected as a candidate material for the overpack and its corrosion behavior has been studied. The corrosion model of carbon steel in the oxygen depleted environment has been developed in case of a magnetite (Fe O
O ) corrosion film formed on the steel surface by assuming that diffusion of H
) corrosion film formed on the steel surface by assuming that diffusion of H O through the corrosion film controls the corrosion process. The improved model which includes the dissolution of the magnetite film has been proved successfully to predict the corrosion rate after a long exposure term. This study aims to simulate the corrosion behavior of carbon steel forming the siderite (FeCO
O through the corrosion film controls the corrosion process. The improved model which includes the dissolution of the magnetite film has been proved successfully to predict the corrosion rate after a long exposure term. This study aims to simulate the corrosion behavior of carbon steel forming the siderite (FeCO ) corrosion film and compare with the behavior of the magnetite film case. Based on the experimental results reported, the corrosion rate was estimated for two cases of 0.1 M and 0.25 mM of the total carbonate and compared with the experimental results. It was concluded that the siderite film formed more likely in the 0.1 M than 0.25 mM solution.
) corrosion film and compare with the behavior of the magnetite film case. Based on the experimental results reported, the corrosion rate was estimated for two cases of 0.1 M and 0.25 mM of the total carbonate and compared with the experimental results. It was concluded that the siderite film formed more likely in the 0.1 M than 0.25 mM solution.
Shimizu, Kosuke*; Inoue, Hiroyuki*; Taniguchi, Naoki; Sakamaki, Keiko; Tachikawa, Hirokazu*
no journal, ,
The effect of solution pH to the SCC susceptibility of carbon-steel (CS) in an anaerobic ground water must be investigated to guarantees the soundness of the CS HLW overpack for ultra-long term. For the present study, the SCC susceptibility of CS at and near the reversible hydrogen evolution potentials at each solution pH was evaluated by the slow strain rate test (SSRT); as for the test solution, NaHCO /Na
/Na CO
CO solutions whose pH were adjusted 8 to 13 and purged with Ar gas were used. The SCC susceptibility became minimum at pH near 9 and 13 as well as reached maximum at pH near 11.
solutions whose pH were adjusted 8 to 13 and purged with Ar gas were used. The SCC susceptibility became minimum at pH near 9 and 13 as well as reached maximum at pH near 11.