Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
 and Ag
and Ag clusters
clustersKoizumi, Akihito*; Tachikawa, Masanori*; Shiga, Motoyuki
Chemical Physics, 419, p.44 - 49, 2013/06
Times Cited Count:1 Percentile:2.56(Chemistry, Physical)The structures and infrared spectra of Ag (H
(H O)
O)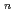 (
( = 1-4) and Cu
= 1-4) and Cu (H
(H O) are studied by
O) are studied by 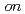 -
-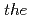 -
-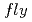
 MD,
MD, 
 PIMD, and
PIMD, and 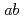
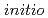 RPMD simulations. It is found that the anharmonicity due to nuclear quantum and thermal effects acts differently depending on the system as well as the type of vibrational mode. In the low-frequency region, the spectra become a broad band as the cluster size increases due to the complex mode couplings, which is qualitatively different from the harmonic spectra. In contrast, the HOH bending modes are systematically red-shifted by a small amount due to the anharmonicity. The OH stretching modes are found to be also red-shifted, but the amount of shift is more dependent on the system. Consequently, these effects cannot be described by unique scaling of harmonic frequencies.
RPMD simulations. It is found that the anharmonicity due to nuclear quantum and thermal effects acts differently depending on the system as well as the type of vibrational mode. In the low-frequency region, the spectra become a broad band as the cluster size increases due to the complex mode couplings, which is qualitatively different from the harmonic spectra. In contrast, the HOH bending modes are systematically red-shifted by a small amount due to the anharmonicity. The OH stretching modes are found to be also red-shifted, but the amount of shift is more dependent on the system. Consequently, these effects cannot be described by unique scaling of harmonic frequencies.
Suzuki, Kimichi*; Tachikawa, Masanori*; Shiga, Motoyuki
Journal of Chemical Physics, 138(18), p.184307_1 - 184307_7, 2013/05
Times Cited Count:10 Percentile:35.72(Chemistry, Physical)Temperature dependence on the structural fluctuations of Zundel cation, H O
O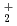 , and its isotopomers, D
, and its isotopomers, D O
O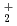 and T
and T O
O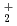 , have been studied using path integral molecular dynamics simulations in which nuclear quantum effect is fully taken into account. It has been found that the fluctuations of hydrogen-oxygen and oxygen-oxygen distances, which are relevant to the hydrogen bonded structure, grow drastically as the temperature increases within the range of investigation between 100 K and 900 K. The fluctuation with respect to the position of non-bonded hydrogen also increases substantially as the temperature increases. The temperature dependence on the fluctuation is greater for D
, have been studied using path integral molecular dynamics simulations in which nuclear quantum effect is fully taken into account. It has been found that the fluctuations of hydrogen-oxygen and oxygen-oxygen distances, which are relevant to the hydrogen bonded structure, grow drastically as the temperature increases within the range of investigation between 100 K and 900 K. The fluctuation with respect to the position of non-bonded hydrogen also increases substantially as the temperature increases. The temperature dependence on the fluctuation is greater for D O
O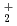 or T
or T O
O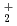 than that of H
than that of H O
O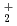 , since the zero-point effect of the former is less than the latter.
, since the zero-point effect of the former is less than the latter.
 H
H and F
and F H
H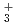
Suzuki, Kimichi*; Ishibashi, Hiroaki*; Yagi, Kiyoshi*; Shiga, Motoyuki; Tachikawa, Masanori*
Progress in Theoretical Chemistry and Physics, 26, p.207 - 216, 2012/08
The quantum nature of the strong hydrogen bonds for the F H
H and F
and F H
H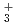 ions and their deuterated isotopomers at the room temperature has been studied using ab initio path integral molecular dynamics (PIMD) simulations. It is found that, for both of these ions, the hydrogen-bonded H/D atoms largely fluctuate around the central position of two F atoms. The average FH/FF distances of F
ions and their deuterated isotopomers at the room temperature has been studied using ab initio path integral molecular dynamics (PIMD) simulations. It is found that, for both of these ions, the hydrogen-bonded H/D atoms largely fluctuate around the central position of two F atoms. The average FH/FF distances of F H
H and F
and F H
H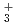 are longer than the average FD/FF distances of F
are longer than the average FD/FF distances of F D
D and F
and F H
H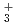 due to the primary/secondary isotope effects, which stem from the difference of the quantum nature of H and D nuclei. These results are compared with the family of Zundel-type ions, O
due to the primary/secondary isotope effects, which stem from the difference of the quantum nature of H and D nuclei. These results are compared with the family of Zundel-type ions, O H
H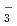 , N
, N H
H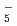 , O
, O H
H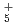 , and N
, and N H
H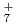 , which have been studied previously with the same ab initio PIMD approach. A comparison is also made with the previous experimental and ab initio vibrational configuration interaction results of F
, which have been studied previously with the same ab initio PIMD approach. A comparison is also made with the previous experimental and ab initio vibrational configuration interaction results of F H
H .
.
Yoshikawa, Takehiro*; Sugawara, Shuichi*; Takayanagi, Toshiyuki*; Shiga, Motoyuki; Tachikawa, Masanori*
Chemical Physics, 394(1), p.46 - 51, 2012/02
Times Cited Count:18 Percentile:55.59(Chemistry, Physical)Path-integral molecular dynamics simulations have been performed for porphycene and its isotopic variants in order to understand the effect of isotopic substitution of inner protons on the double proton transfer mechanism. Our quantum simulations show that double proton transfer of the unsubstituted porphycene at the room temperature mainly occurs via a so-called concerted mechanism through the second-order saddle point. In addition, we found that both isotopic substitution and temperature significantly affect the double proton transfer mechanism. For example, the contribution of the stepwise mechanism increases with a temperature increase. It has been found that out-of-plane vibrational motions significantly decrease the contribution of the concerted proton transfer mechanism.
 O)
O)Koizumi, Akihito*; Suzuki, Kimichi*; Shiga, Motoyuki; Tachikawa, Masanori*
International Journal of Quantum Chemistry, 112(1), p.136 - 139, 2012/01
Times Cited Count:0 Percentile:0.05(Chemistry, Physical)Ab initio path integral molecular dynamics simulation of MOH(H O) (M= Cu, Ag, and Au) clusters has been carried out to analyze how the hydrogen-bonded proton can be affected by the counter noble metal cation. The CuOH(H
O) (M= Cu, Ag, and Au) clusters has been carried out to analyze how the hydrogen-bonded proton can be affected by the counter noble metal cation. The CuOH(H O) cluster forms no hydrogen bonded structure even for the static equilibrium structures. Contrary to our previous paper of hydrated alkali metal hydroxide clusters, proton transferred distribution was not observed because of the high potential barrier heights of MOH(H
O) cluster forms no hydrogen bonded structure even for the static equilibrium structures. Contrary to our previous paper of hydrated alkali metal hydroxide clusters, proton transferred distribution was not observed because of the high potential barrier heights of MOH(H O).
O).
Sugimoto, Masataka*; Shiga, Motoyuki; Tachikawa, Masanori*
Computational and Theoretical Chemistry, 975(1-3), p.31 - 37, 2011/11
Times Cited Count:5 Percentile:11.26(Chemistry, Physical) path integral molecular dynamics based on MP2/cc-pVTZ method has been carried out for a series of small hydrogen cluster cations, H
path integral molecular dynamics based on MP2/cc-pVTZ method has been carried out for a series of small hydrogen cluster cations, H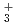 , H
, H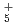 , H
, H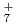 and H
and H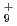 . The dissociation enthalpy for the reaction H
. The dissociation enthalpy for the reaction H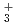 (H
(H )
)
 H
H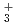 (H
(H )
)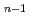 + H
+ H is found to be 5.4, 2.1 and 3.2 kcal/mol, respectively, which are slightly smaller than experimental values. It is found that energies of quantum zero-point vibration and anharmonic vibration of the respective cations are important factors that determine the value of dissociation energy.
is found to be 5.4, 2.1 and 3.2 kcal/mol, respectively, which are slightly smaller than experimental values. It is found that energies of quantum zero-point vibration and anharmonic vibration of the respective cations are important factors that determine the value of dissociation energy.
Daido, Masashi*; Koizumi, Akihito*; Shiga, Motoyuki; Tachikawa, Masanori*
Theoretical Chemistry Accounts, 130(2-3), p.385 - 391, 2011/10
Times Cited Count:6 Percentile:13.82(Chemistry, Physical)The structure of Watson-Crick type guanine-cytosine (G-C) base pair has been studied by classical hybrid Monte Carlo (HMC) and quantum path integral hybrid Monte Carlo (PIHMC) simulations on the semiempirical potential energy surface. For the three NH X hydrogen-bonded moieties, the intramolecular NH bonds are found systematically longer while the H
X hydrogen-bonded moieties, the intramolecular NH bonds are found systematically longer while the H X distance shorter in the PIHMC simulation than in the HMC simulation. We found that the hydrogen bonded length N
X distance shorter in the PIHMC simulation than in the HMC simulation. We found that the hydrogen bonded length N X correlates with the H
X correlates with the H X distance, but not with the NH distance. A correlation is also between the neighboring hydrogen bonds in the G-C base pair.
X distance, but not with the NH distance. A correlation is also between the neighboring hydrogen bonds in the G-C base pair.
Sugawara, Shuichi*; Yoshikawa, Takehiro*; Takayanagi, Toshiyuki*; Shiga, Motoyuki; Tachikawa, Masanori*
Journal of Physical Chemistry A, 115(42), p.11486 - 11494, 2011/09
Times Cited Count:19 Percentile:56.05(Chemistry, Physical)We have carried out path integral molecular dynamics simulations for hydrated sulfuric acid clusters to understand acid-dissociation and hydrogen-bonded structural rearrangement processes in these clusters from a quantum mechanical viewpoint. We have found that the acid dissociation processes, first and second deprotonation, effectively occur in a hydrated cluster with a specific cluster size. The mechanisms of the proton-transfer processes were analyzed in detail and it was found that the distance between O in sulfuric acid and O in the proton-accepting water is playing an important role. We also found that the water coordination number of the proton-accepting water is important in the proton-transfer processes.
Koizumi, Akihito*; Suzuki, Kimichi*; Shiga, Motoyuki; Tachikawa, Masanori*
Journal of Chemical Physics, 134(3), p.031101_1 - 031101_3, 2011/01
Times Cited Count:14 Percentile:42.14(Chemistry, Physical) path integral molecular dynamics simulation of M
path integral molecular dynamics simulation of M H
H O
O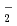 (M = Li, Na, and K) has been carried out to study how the structure and dynamics of low-barrier hydrogen-bonded Zundel anion, H
(M = Li, Na, and K) has been carried out to study how the structure and dynamics of low-barrier hydrogen-bonded Zundel anion, H O
O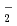 , can be affected by the counter alkali metal cation, M
, can be affected by the counter alkali metal cation, M . Our simulation predicts that the quantum proton transfer in Zundel anion can be strongly coupled to the motion of counter cation located nearby. A smaller cation can induce larger structural distortion of the Zundel anion fragment making the proton transfer barrier higher, and hence lowers the vibration excitation energy. It is also argued that a large H/D isotope effect is present.
. Our simulation predicts that the quantum proton transfer in Zundel anion can be strongly coupled to the motion of counter cation located nearby. A smaller cation can induce larger structural distortion of the Zundel anion fragment making the proton transfer barrier higher, and hence lowers the vibration excitation energy. It is also argued that a large H/D isotope effect is present.
Yoshikawa, Takehiro*; Sugawara, Shuichi*; Takayanagi, Toshiyuki*; Shiga, Motoyuki; Tachikawa, Masanori*
Chemical Physics Letters, 496(1-3), p.14 - 19, 2010/08
Times Cited Count:27 Percentile:67.43(Chemistry, Physical)Full-dimensional path-integral molecular dynamics simulations were performed to determine whether the double proton transfer tautomerization of porphycene is a concerted or a stepwise process. It was found that double proton transfer occurs dominantly through the concerted pathway via the second-order saddle point structure and that contribution of the stepwise mechanism increases with a temperature increase. Nuclear quantum effects play essential roles in determining the proton transfer mechanism.
 path integral hybrid Monte Carlo based on the fourth-order Trotter expansion; Application to fluoride ion-water cluster
path integral hybrid Monte Carlo based on the fourth-order Trotter expansion; Application to fluoride ion-water clusterSuzuki, Kimichi*; Tachikawa, Masanori*; Shiga, Motoyuki
Journal of Chemical Physics, 132(14), p.144108_1 - 144108_7, 2010/04
Times Cited Count:34 Percentile:75.25(Chemistry, Physical)We propose an efficient path integral hybrid Monte Carlo (PIHMC) method based on fourth-order Trotter expansion. Here, the second-order effective force is employed to generate short trial trajectories to avoid computationally expensive Hessian matrix, while the final acceptance is judged based on fourth-order effective potential. The computational performance of our PIHMC scheme is compared with that of conventional PIHMC and PIMD methods based on second- and fourth-order Trotter expansions. Our method is applied to 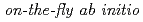 PIHMC calculation of fluoride ion-water complexes, F
PIHMC calculation of fluoride ion-water complexes, F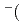 H
H O) and F
O) and F (D
(D O), at ambient temperature, particularly focusing on the geometrical isotope effect.
O), at ambient temperature, particularly focusing on the geometrical isotope effect.
 path integral simulation
path integral simulationShiga, Motoyuki; Suzuki, Kimichi*; Tachikawa, Masanori*
Journal of Chemical Physics, 132(11), p.114104_1 - 114104_7, 2010/03
Times Cited Count:17 Percentile:50.44(Chemistry, Physical)The 1H NMR chemical shift of deprotonated water dimer, H O
O
 , has been studied by ab initio path integral simulation. The simulation predicts that the isotropic shielding of hydrogen-bonded proton increases as a function of temperature. This change is about an order of magnitude larger than that of the non-hydrogen-bonded proton. It is concluded that this is caused by the significant difference in the quantum distribution of proton at high and low temperatures in the low barrier hydrogen bond.
, has been studied by ab initio path integral simulation. The simulation predicts that the isotropic shielding of hydrogen-bonded proton increases as a function of temperature. This change is about an order of magnitude larger than that of the non-hydrogen-bonded proton. It is concluded that this is caused by the significant difference in the quantum distribution of proton at high and low temperatures in the low barrier hydrogen bond.
 SO
SO
 (H
(H O)
O)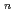 (
( =1-6) on semiempirical PM6 potential surfaces
=1-6) on semiempirical PM6 potential surfacesKakizaki, Akira*; Motegi, Haruki*; Yoshikawa, Takehiro*; Takayanagi, Toshiyuki*; Shiga, Motoyuki; Tachikawa, Masanori*
Journal of Molecular Structure; THEOCHEM, 901(1-3), p.1 - 8, 2009/05
Quantum path-integral molecular dynamics simulations for a series of sulfuric acid clusters, H SO
SO
 (H
(H O)
O)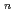 (
( =1-6), were performed using semiempirical PM6 method. It was found that the acid dissociation probability increases with an increase in the cluster size, and that so-called contact-ion-pair structures are dominant in the proton-dissociated clusters. The importance of nuclear quantum effects in the cluster structures and proton-transfer processes is demonstrated.
=1-6), were performed using semiempirical PM6 method. It was found that the acid dissociation probability increases with an increase in the cluster size, and that so-called contact-ion-pair structures are dominant in the proton-dissociated clusters. The importance of nuclear quantum effects in the cluster structures and proton-transfer processes is demonstrated.
 O)
O) on a semiempirical potential energy surface
on a semiempirical potential energy surfaceTakayanagi, Toshiyuki*; Takahashi, Kenta*; Kakizaki, Akira*; Shiga, Motoyuki; Tachikawa, Masanori*
Chemical Physics, 358(3), p.196 - 202, 2009/04
Times Cited Count:16 Percentile:48.94(Chemistry, Physical)Path-integral molecular dynamics simulations for the HCl(H O)
O) cluster have been performed on the ground-state potential energy surface directly obtained on-the-fly from semiempirical PM3-MAIS molecular orbital calculations. It is found that the HCl(H
cluster have been performed on the ground-state potential energy surface directly obtained on-the-fly from semiempirical PM3-MAIS molecular orbital calculations. It is found that the HCl(H O)
O) cluster has structural rearrangement above the temperature of 300 K showing a liquid-like behavior. Quantum mechanical fluctuation of hydrogen nuclei plays a significant role in structural arrangement processes in this cluster.
cluster has structural rearrangement above the temperature of 300 K showing a liquid-like behavior. Quantum mechanical fluctuation of hydrogen nuclei plays a significant role in structural arrangement processes in this cluster.
 O)
O)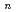 (
( =2-7) clusters on semiempirical PM6 potential energy surfaces
=2-7) clusters on semiempirical PM6 potential energy surfacesTakayanagi, Toshiyuki*; Yoshikawa, Takehiro*; Kakizaki, Akira*; Shiga, Motoyuki; Tachikawa, Masanori*
Journal of Molecular Structure; THEOCHEM, 869(1-3), p.29 - 36, 2008/11
Molecular dynamics simulations based on semiempirical PM6 method was carried out to study statistical structures of glycine-water clusters. We found that zwitterionic form is more stable than neutral form as the cluster size increases. The difference in water solvation structures around the neutral or zwitterionic glycine form is also discussed.
Suzuki, Kimichi*; Shiga, Motoyuki; Tachikawa, Masanori*
Journal of Chemical Physics, 129(144), p.144310_1 - 144310_8, 2008/10
Times Cited Count:47 Percentile:84.15(Chemistry, Physical)Path integral molecular dynamics simulation based on 4th order Trotter expansion has been performed to elucidate the geometrical isotope effect of water dimer anion, H O
O
 , D
, D O
O
 , and T
, and T O
O
 , at different temperatures from 50 K to 600 K. At low temperatures below 200 K the hydrogen-bonded hydrogen nucleus is near the center of two oxygen atoms with mostly O...
, at different temperatures from 50 K to 600 K. At low temperatures below 200 K the hydrogen-bonded hydrogen nucleus is near the center of two oxygen atoms with mostly O...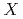 ...O geometry (where
...O geometry (where 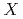 = H, D, or T), while at high temperatures above 400 K hydrogen becomes more delocalized showing the coexistence between O...
= H, D, or T), while at high temperatures above 400 K hydrogen becomes more delocalized showing the coexistence between O...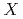 -O and O-
-O and O-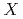 ...O. The OO distance tends to be shorter as the isotopomer is heavier at low temperatures, while this ordering becomes opposite at high temperatures. It is concluded that the coupling between the OO stretching mode and proton transfer modes is a key to understand such a temperature dependence of hydrogen-bonded structure.
...O. The OO distance tends to be shorter as the isotopomer is heavier at low temperatures, while this ordering becomes opposite at high temperatures. It is concluded that the coupling between the OO stretching mode and proton transfer modes is a key to understand such a temperature dependence of hydrogen-bonded structure.
 H
H
 cation and N
cation and N H
H
 anion by
anion by  path integral molecular dynamics simulation
path integral molecular dynamics simulationIshibashi, Hiroaki*; Hayashi, Aiko*; Shiga, Motoyuki; Tachikawa, Masanori*
ChemPhysChem, 9(3), p.383 - 387, 2008/02
Times Cited Count:24 Percentile:64.37(Chemistry, Physical)no abstracts in English
 quantum mechanical/molecular mechanical molecular dynamics using multiple-time-scale approach and perturbation theory
quantum mechanical/molecular mechanical molecular dynamics using multiple-time-scale approach and perturbation theoryShiga, Motoyuki; Tachikawa, Masanori*
Molecular Simulation, 33(1-2), p.174 - 184, 2007/02
A new computational method is proposed for  quantum-mechanical/molecular-mechanical (QM/MM) molecular dynamics (MD) which is limited to time-independent thermodynamic analysis. The idea is to use the mass-scaling method combined with multiple-time-scale algorithm and an approximate QM/MM Hamiltonian derived from the first-order Rayleigh-Schroedinger perturbation theory in which the electronic polarization is neglected as a first approximation. If the polarization effect is not so strong, the correction can also be considered after the simulation run using the weighted sampling method. The advantage and disadvantage of the method is discussed in terms of its computational efficiency and accuracy. As a simple example, we demonstrate an MD simulation of liquid water containing 1 QM molecule and 255 MM molecules, and discuss the advantages in calculating statistical averages such as radial distribution and heat of solution.
quantum-mechanical/molecular-mechanical (QM/MM) molecular dynamics (MD) which is limited to time-independent thermodynamic analysis. The idea is to use the mass-scaling method combined with multiple-time-scale algorithm and an approximate QM/MM Hamiltonian derived from the first-order Rayleigh-Schroedinger perturbation theory in which the electronic polarization is neglected as a first approximation. If the polarization effect is not so strong, the correction can also be considered after the simulation run using the weighted sampling method. The advantage and disadvantage of the method is discussed in terms of its computational efficiency and accuracy. As a simple example, we demonstrate an MD simulation of liquid water containing 1 QM molecule and 255 MM molecules, and discuss the advantages in calculating statistical averages such as radial distribution and heat of solution.
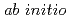 path integral molecular dynamics simulation
path integral molecular dynamics simulationHayashi, Aiko*; Shiga, Motoyuki; Tachikawa, Masanori*
Molecular Simulation, 33(1-2), p.185 - 188, 2007/02
Times Cited Count:3 Percentile:9.21(Chemistry, Physical)Ab initio path integral molecular dynamics simulation has been performed to investigate the lithium-hydrogen bond and dihydrogen bond of C H
H
 LiH complex. It has been found from the simulation that these unusual types of hydrogen bonds have large geometrical isotope effect which is similar to that of the conventional hydrogen bonding.
LiH complex. It has been found from the simulation that these unusual types of hydrogen bonds have large geometrical isotope effect which is similar to that of the conventional hydrogen bonding.
Kuchitsu, Takashi*; Tachikawa, Masanori*; Shiga, Motoyuki
Chemical Physics Letters, 433(1-3), p.193 - 198, 2006/12
Times Cited Count:1 Percentile:2.52(Chemistry, Physical)A new approach to electron dynamics in molecular system is developed, which combines  molecular orbital (MO) scheme and Gaussian wave packet dynamics. The time-dependent electronic wavefunction is described by the linear combination of atomic orbitals (LCAO) using frozen-width floating Gaussian wave packet basis functions. The equations of motion for the time-dependent variables, such as the LCAO coefficients, the Gaussian centers, and their phase factors of the respective basis function, are determined based on time-dependent variational principle. This technique is demonstrated for the attosecond propagation of electronic wavefunction of hydrogen and helium atoms in response to electrostatic field.
molecular orbital (MO) scheme and Gaussian wave packet dynamics. The time-dependent electronic wavefunction is described by the linear combination of atomic orbitals (LCAO) using frozen-width floating Gaussian wave packet basis functions. The equations of motion for the time-dependent variables, such as the LCAO coefficients, the Gaussian centers, and their phase factors of the respective basis function, are determined based on time-dependent variational principle. This technique is demonstrated for the attosecond propagation of electronic wavefunction of hydrogen and helium atoms in response to electrostatic field.