Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Saga, Ryo*; Matsuya, Yusuke; Takahashi, Rei*; Hasegawa, Kazuki*; Date, Hiroyuki*; Hosokawa, Yoichiro*
Scientific Reports (Internet), 11(1), p.8258_1 - 8258_10, 2021/04
Times Cited Count:4 Percentile:47.6(Multidisciplinary Sciences)Hyaluronan synthesis inhibitor 4-methylumbelliferone (4-MU) is a candidate of radiosensitizers in X-ray therapy. The curative effects under such 4-MU administration have been investigated in vitro; however, the radiosensitizing mechanisms remain unclear. Here, we investigated the radiosensitizing effects under 4-MU treatment from cell experiments and model estimations. We generated experimental surviving fractions of human fibrosarcoma cells (HT1080) after 4-MU treatment combined with X-ray irradiation. Meanwhilst, we also modelled the pharmacological effects of 4-MU treatment and theoretically analyzed the synergetic effects between 4-MU treatment and X-ray irradiation. The results show that the enhancement of cell killing by 4-MU treatment is the greatest in the intermediate dose range of around 4 Gy, which indicates the involvement of intercellular communication. In addition, the oxidative stress level, which leads to DNA damage induction, significantly increased under 4-MU treatment, and the radiosensitization by 4-MU can be suppressed by the inhibitors for intercellular communication. These findings suggest that the synergetic effects between 4-MU treatment and irradiation are predominantly attributed to intercellular communication and provide more efficient tumour control than conventional X-ray therapy.
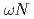 scattering length from
scattering length from  photoproduction on the proton near the reaction threshold
photoproduction on the proton near the reaction thresholdIshikawa, Takatsugu*; Fujimura, Hisako*; Fukasawa, Hiroshi*; Hashimoto, Ryo*; He, Q.*; Honda, Yuki*; Hosaka, Atsushi; Iwata, Takahiro*; Kaida, Shun*; Kasagi, Jirota*; et al.
Physical Review C, 101(5), p.052201_1 - 052201_6, 2020/05
Times Cited Count:4 Percentile:45.12(Physics, Nuclear)Saga, Ryo*; Matsuya, Yusuke; Takahashi, Rei*; Hasegawa, Kazuki*; Date, Hiroyuki*; Hosokawa, Yoichiro*
Journal of Radiation Research, 60(3), p.298 - 307, 2019/05
Times Cited Count:23 Percentile:81.57(Biology)In radiotherapy, it is recognized that cancer stem cells (CSCs) in tumor tissue shows radio-resistance. However, the relationship between content percentage of the CSCs and dose-response curve on cell survival remain unclear. In this study, we developed a stochastic model considering progeny cells and stem cells, and investigated the impact of stem cells on radio-sensitivity. From the flow-cytometric analysis (cell experiments), the content percentage of stem cells was 3.2% or less which agreed well with the model estimation from the cell survival curve. Based on the verification, it is suggested that cell survival in high-dose range is largely affected by the CSCs. In addition, regarding the sub-population of stem cells, the present model well reproduces the dose response on lethal lesions to DNA comparing with the conventional LQ model. This outcome indicates that the stem cells must be considered for describing the dose-response curve in wide dose range.
Taguchi, Yasujiro*; Sakai, Hideaki*; Okuyama, Daisuke*; Ishiwata, Shintaro*; Fujioka, Jun*; Fukuda, Tatsuo; Hashizume, Daisuke*; Kagawa, Fumitaka*; Takahashi, Yoichiro*; Shimano, Ryo*; et al.
Physica B; Condensed Matter, 407(11), p.1685 - 1688, 2012/06
Times Cited Count:5 Percentile:23.98(Physics, Condensed Matter)Kuroki, Ryoichiro; Ito, Fuminori*; Nakata, Hisakazu; Yamamoto, Shuji; Takahashi, Kuniaki
JAEA-Technology 2009-016, 124 Pages, 2009/06
The concept of "Waste Management System" which manages all the waste data from generation to disposal in Japan Atomic Energy Agency (JAEA) was studied. At first, development policy was defined on investigation results of the present state and problem of waste management in JAEA, and target information supplied by "Waste Management System" were extracted. Then over 400 data items to be managed in this system, system configuration and specific functions were shown as system concept. The waste data managed on this system are classified into two categories; for quality assurance of waste packages and for optimization study of waste conditioning and disposal and information service. This system consists of analytical part (i.e. program) and management part (i.e. database) for each data, then all these parts are constructed on network.
Kuroki, Ryoichiro; Takahashi, Kuniaki
JAEA-Research 2007-082, 215 Pages, 2008/01
The environmental impact of hazardous materials and possibility of criticality were investigated to construct technical specification of radioactive waste packages. The contents and results are as following. (1) Concerning hazardous materials included in TRU waste, regulations on disposal of industrial wastes and on environmental preservation were investigated. (2) The assessment methods for environmental impact of hazardous materials included in radioactive waste in U.K, U.S.A. and France were investigated. (3) The upper limits of amounts of hazardous materials in waste packages to satisfy the environmental standard were calculated with mass transport assessment for some disposal concepts. (4) It was suggested from criticality analysis for waste packages in disposal facility that the occurrence of criticality was almost impossible under the realistic conditions.
Kuroki, Ryoichiro; Nakata, Hisakazu; Yamamoto, Shuji; Takahashi, Kuniaki
no journal, ,
Various waste data are needed for quality assurance of low level waste packages which are generated and conditioned in JAEA, and as basic data for consideration of the disposal regulation, design of the disposal facility, and so on. Therefore, the system to manage the waste data from generation to disposal will be developed. Then the concept of this system was considered. At first, development policy was defined depend on the situation and problem of waste management in JAEA, and the target needs of this system were selected. Then concept of this system was constructed, and data items to be managed in this system were selected. This system consists of four function units, each analytical and management function for quality assurance and another needs. Both management units and both analytical units are developed as the application program and as the database, these units are constructed on the network of JAEA. And over 400 data items to be managed in this system were shown.
 Mg
Mg Fe
Fe O
O by means of polarized inelastic neutron scattering
by means of polarized inelastic neutron scatteringNakajima, Taro*; Kakurai, Kazuhisa; Arima, Takahisa*; Matsuda, Masaaki*; Takahashi, Yoichiro*; Ishiwata, Shintaro*; Taguchi, Yasujiro*; Tokura, Yoshinori*
no journal, ,
no abstracts in English
Takahashi, Rei*; Saga, Ryo*; Matsuya, Yusuke; Hasegawa, Kazuki*; Fukui, Roman*; Hosokawa, Yoichiro*
no journal, ,
Inflammatory responses after irradiation induce antioxidant activity, leading to radioresistance in cancer cells. In our previous study, it was found that a hyaluronan synthesis inhibitor (4-MU) can suppress inflammatory responses, however the underlying mechanisms are still unknown. In this study, we aimed to clarify the radiosensitization mechanism induced by 4-MU in the application of cell-killing models. In terms of in vitro experiments, cultured human fibrosarcoma cells were exposed to X-rays in presence of 100  M 4-MU and scavenger of intercellular signalling (1% DMSO, 40
M 4-MU and scavenger of intercellular signalling (1% DMSO, 40  M c-PTIO), and we measured the relation between dose and cell viability by means of colony assay. The experimental results were also interpreted by using integrated cell-killing model which has been developed so as to consider non-targeted effects. From the experiments, it was found that a combination of 4-MU treatment and irradiation significantly reduced the cell survival. This reduced viability was suppressed in the presence of DMSO or c-TPIO. Meanwhile, the model analysis showed such an increase of cell-killing is predominantly attributed by non-targeted effects. These results suggest that the radiosensetization promoted by 4-MU treatment is predominantly attributed to the accumulation in non-targeted effects.
M c-PTIO), and we measured the relation between dose and cell viability by means of colony assay. The experimental results were also interpreted by using integrated cell-killing model which has been developed so as to consider non-targeted effects. From the experiments, it was found that a combination of 4-MU treatment and irradiation significantly reduced the cell survival. This reduced viability was suppressed in the presence of DMSO or c-TPIO. Meanwhile, the model analysis showed such an increase of cell-killing is predominantly attributed by non-targeted effects. These results suggest that the radiosensetization promoted by 4-MU treatment is predominantly attributed to the accumulation in non-targeted effects.
Takahashi, Yuta; Kakuda, Ayaka; Enomoto, Mayu*; Imaizumi, Ken*; Osugi, Takeshi; Sone, Tomoyuki; Kuroki, Ryoichiro
no journal, ,
no abstracts in English
Takahashi, Yuta; Enomoto, Mayu*; Kakuda, Ayaka; Sone, Tomoyuki; Osugi, Takeshi; Kuroki, Ryoichiro
no journal, ,
no abstracts in English
Takahashi, Yuta; Taniguchi, Takumi; Kuroki, Ryoichiro; Osugi, Takeshi
no journal, ,
no abstracts in English