Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Takai, Shizuka; Shimada, Taro; Takeda, Seiji; Koike, Katsuaki*
Mathematical Geosciences, 56(2), p.333 - 360, 2024/02
Times Cited Count:0 Percentile:0.01(Geosciences, Multidisciplinary)To enable proper remediation of accidental groundwater contamination, the contaminant plume evolution needs to be accurately estimated. In the estimation, uncertainties in both the contaminant source and hydrogeological structure should be considered, especially the temporal release history and hydraulic transmissivity. Although the release history can be estimated using geostatistical approaches, previous studies use the deterministic hydraulic property field. Geostatistical approaches can also effectively estimate an unknown heterogeneous transmissivity field via the joint data use, such as a combination of hydraulic head and tracer data. However, tracer tests implemented over a contaminated area necessarily disturb the in situ condition of the contamination. Conversely, measurements of the transient concentration data over an area are possible and can preserve the conditions. Accordingly, this study develops a geostatistical method for the joint clarification of contaminant plume and transmissivity distributions using both head and contaminant concentration data. The applicability and effectiveness of the proposed method are demonstrated through two numerical experiments assuming a two-dimensional heterogenous confined aquifer. The use of contaminant concentration data is key to accurate estimation of the transmissivity. The accuracy of the proposed method using both head and concentration data was verified achieving a high linear correlation coefficient of 0.97 between the true and estimated concentrations for both experiments, which was 0.67 or more than the results using only the head data. Furthermore, the uncertainty of the contaminant plume evolution was successfully evaluated by considering the uncertainties of both the initial plume and the transmissivity distributions, based on their conditional realizations.
Shimada, Taro; Sasagawa, Tsuyoshi; Miwa, Kazuji; Takai, Shizuka; Takeda, Seiji
Proceedings of International Conference on Environmental Remediation and Radioactive Waste Management (ICEM2023) (Internet), 7 Pages, 2023/10
Nuclear regulatory inspection should be performed on the basis of the risk information during the decommissioning phase of the nuclear power plant. However, it is difficult because the methodology for quantitatively assessing the radiation exposure risk during decommissioning activities has not been established. Therefore, a decommissioning risk assessment code, DecAssess-R, has been developed based on the decommissioning safety assessment code, DecAssess, which creates event trees from initiating events and evaluates the radiation risk resulting from public exposure dose for each accident sequence. The assessment took into account that mobile radioactive inventories that can be easily dispersed in the work area, such as radioactive dust accumulated in HEPA filters attached to a contamination control enclosure, will fluctuate with the progress of the decommissioning work. Initiating events were selected based on the investigation of accidents and malfunctions during dismantling, disassembly, and component replacement activities around the world, and event trees were created from the initiating events to indicate the progress scenario. The frequencies of occurrence were determined with reference to general industry data in addition to the above accidents and malfunctions, and the probabilities of event progression were determined with reference to failure data during the operation phase. The exposure risks during dismantling of components in the reference BWR were evaluated. As a result, the public exposure dose was maximum in case of fire during dismantling of reactor internals and fire spread to combustibles and filters, including radioactivity temporarily stored in the work area. The exposure risk was also maximum because the probability of occurrence of this accident sequence was greater than that of other scenarios.
Sawaguchi, Takuma; Takai, Shizuka; Sasagawa, Tsuyoshi; Uchikoshi, Emiko*; Shima, Yosuke*; Takeda, Seiji
MRS Advances (Internet), 8(6), p.243 - 249, 2023/06
In the intermediate depth disposal of relatively high-level radioactive waste, a method to confirm whether the borehole for monitoring is properly sealed should be developed in advance. In this study, groundwater flow analyses were performed for the hydrogeological structures with backfilled boreholes, assuming sedimentary rock area, to understand what backfill design conditions could prevent significant water pathways in the borehole, and to identify the confirmation points of borehole sealing. The results indicated the conditions to prevent water pathways in the borehole and BDZ (Borehole Disturbed Zone), such as designing the permeability of bentonite material less than or equal to that of the host rock, and grouting BDZ.
Takai, Shizuka; Shimada, Taro; Takeda, Seiji; Koike, Katsuaki*
Journal of Contaminant Hydrology, 251, p.104097_1 - 104097_12, 2022/12
Times Cited Count:3 Percentile:49.4(Environmental Sciences)When assessing the risk from an underground environment that is contaminated by radioactive nuclides and hazardous chemicals and planning for remediation, the contaminant plume distribution and the associated uncertainty from measured data should be estimated accurately. While the release history of the contaminant plume may be unknown, the extent of the plume caused by a known source and the associated uncertainty can be calculated inversely from the concentration data using a geostatistical method that accounts for the temporal correlation of its release history and groundwater flow modeling. However, the preceding geostatistical approaches have three drawbacks: (1) no applications of the three-dimensional plume estimation in real situations, (2) no constraints for the estimation of the plume distribution, which can yield negative concentration and large uncertainties, and (3) few applications to actual cases with multiple contaminants. To address these problems, the non-negativity constraint using Gibbs sampling was incorporated into the geostatistical method with groundwater flow modeling for contaminant plume estimation. This method was then tested on groundwater contamination in the Gloucester landfill in Ontario, Canada. The method was applied to three water soluble organic contaminants: 1,4-dioxane, tetrahydrofuran, and diethyl ether. The effectiveness of the proposed method was verified by the general agreement of the calculated plume distributions of the three contaminants with concentration data from 66 points in 1982 (linear correlation coefficient of about 0.7). In particular, the reproduced large spill of organic contaminants of 1,4-dioxane in 1978 was more accurate than the result of preceding minimum relative entropy-based studies. The same peak also appeared in the tetrahydrofuran and diethyl ether distributions approximately within the range of the retardation factor derived from the fraction of organic carbon.
Takai, Shizuka; Namekawa, Masakazu*; Shimada, Taro; Takeda, Seiji
IEEE Transactions on Nuclear Science, 69(7), p.1789 - 1798, 2022/07
Times Cited Count:0 Percentile:0.01(Engineering, Electrical & Electronic)To reduce a large amount of contaminated concrete rubble stored in the Fukushima Daiichi Nuclear Power Station site, recycling low-radioactivity rubble within the site is a possible remedy. To promote recycling while ensuring safety, not only the average radioactivity but also the radioactivity distribution of concrete rubble should be efficiently evaluated because the details of rubble contamination caused by the accident remain unclear and likely include hotspots. However, evaluating inhomogeneous contamination of thick and/or dense materials is difficult using previous measurement systems, such as clearance monitors. This study experimentally confirmed the potential applicability of image reconstruction algorithms for radioactivity distribution evaluation in concrete rubble filled in a chamber. Radiation was measured using plastic scintillation fiber around the chamber (50  50
50  40 cm
40 cm ). Localized hotspots were simulated using standard sources of
). Localized hotspots were simulated using standard sources of  Cs, which is one of the main nuclides of contaminated rubble. The radioactivity distribution was calculated for 100 or 50 voxels (voxel size: (10 cm)
Cs, which is one of the main nuclides of contaminated rubble. The radioactivity distribution was calculated for 100 or 50 voxels (voxel size: (10 cm) or 10
or 10  10
10  20 cm
20 cm ) constituting the chamber. For 100 voxels, inner hotspots were undetected, whereas, for 50 voxels, both inner and surface hotspots were reconstructible. The distribution evaluated using the maximum likelihood expectation maximization algorithm was the most accurate; the average radioactivity was estimated within 70% accuracy in all seven cases.
) constituting the chamber. For 100 voxels, inner hotspots were undetected, whereas, for 50 voxels, both inner and surface hotspots were reconstructible. The distribution evaluated using the maximum likelihood expectation maximization algorithm was the most accurate; the average radioactivity was estimated within 70% accuracy in all seven cases.
Takai, Shizuka; Shimada, Taro; Takeda, Seiji; Koike, Katsuaki*
Joho Chishitsu, 32(3), P. 95, 2021/09
We received best presentation award GEOINROUM-2021 for the presentation on "Estimation of contaminated materials concentration by a geostatistical method with groundwater flow". We submit the comments of impression for getting the Award to Geoinformatics.
Takai, Shizuka; Kimura, Hideo*; Uchikoshi, Emiko*; Munakata, Masahiro; Takeda, Seiji
JAEA-Data/Code 2020-007, 174 Pages, 2020/09
The MIG2DF computer code is a computer program that simulates groundwater flow and radionuclide transport in porous media for the safety assessment of radioactive waste disposal. The original version of MIG2DF was released in 1992. The original code employs a two-dimensional (vertical or horizontal cross-section, or an axisymmetric configuration) finite-element method to approximate the governing equations for density-dependent saturated-unsaturated groundwater flow and radionuclide transport. Meanwhile, for geological disposal of radioactive wastes, landscape evolution such as uplift and erosion needs to be assessed as a long-term geological and climate events, considering site conditions. In coastal areas, the impact to groundwater flow by change of salinity distribution to sea level change also needs to be considered. To deal with these events in the assessment, we have revised the original version of MIG2DF and developed the external program which enables MIG2DF to consider unsteady landscape evolution. In these developments, this report describes an upgrade of MIG2DF (Version 2) and presents the configuration, equations, methods, and verification. This reports also give the explanation external programs of MIG2DF: PASS-TRAC (the particle tracking code), PASS-PRE (the code for dataset preparation), and PASS-POST (the post-processing visualization system).
Sawaguchi, Takuma; Takai, Shizuka; Takeda, Seiji
JAEA-Research 2020-005, 47 Pages, 2020/06
After the Fukushima Daiichi Nuclear Power Station accident, large quantities of radiocesium-contaminated soil were generated from decontamination activities in the Fukushima prefecture. The removed soil has been stored in the prefecture until its final disposal. To complete the final disposal outside Fukushima prefecture, reducing the disposal volume through recycling can prove effective. The Ministry of the Environment, Japan (MOE) has presented a policy to recycle low-radioactive removed soil as recycled materials under the management of public authority. The recycling is limited to civil engineering structures in public projects. In this study, to contribute to guideline development for removed soil recycling by MOE, dose estimation in recycling of removed soil as embankment materials of seaside protection forest was conducted. First, additional doses to workers and the public in construction and service scenarios were evaluated. From the result, the radioactive cesium concentration level of recycled materials, where all additional doses meet the radiation criterion of 1 mSv/y, was derived to be 5,000 Bq/kg. Then, construction conditions were reviewed to reduce additional doses to the public in a service scenario. With the derived radioactivity level of 5,000 Bq/kg, the covered soil thickness of 39 cm or more limited the doses to less than 10  Sv/y. Finally, additional doses in a disaster scenario were evaluated. The doses were confirmed to be below 1 mSv/y when the removed soil of 5,000 Bq/kg was used.
Sv/y. Finally, additional doses in a disaster scenario were evaluated. The doses were confirmed to be below 1 mSv/y when the removed soil of 5,000 Bq/kg was used.
Takai, Shizuka; Shimada, Asako; Sawaguchi, Takuma; Takeda, Seiji; Kimura, Hideo
Radiation Protection Dosimetry, 188(1), p.1 - 7, 2020/01
Times Cited Count:0 Percentile:0.01(Environmental Sciences)After the Fukushima Nuclear Power Plant accident, most of radiocesium-contaminated soil generated from decontamination activities outside Fukushima prefecture has been stored at decontamination sites such as schools, parks and residential lands (storage at sites) according to the Decontamination Guidelines. However, additional exposure due to the present storage has not been evaluated. Moreover, entering storage sites, which is not restricted for storage at sites, was not considered in safety assessment conducted in the guidelines. To continue the storage and confirm the effectiveness, understanding of present possible exposures is important. In this study, we evaluated exposure doses for residents and users of storage sites based on the present situation. As a result, annual doses due to residence were 10 to 10
to 10 mSv y
mSv y and doses due to annual entries were of the order of 10
and doses due to annual entries were of the order of 10 mSv y
mSv y . Hence, we confirmed that the exposure due to present storage outside Fukushima is significantly less than 1 mSv y
. Hence, we confirmed that the exposure due to present storage outside Fukushima is significantly less than 1 mSv y .
.
Takai, Shizuka; Sawaguchi, Takuma; Takeda, Seiji
Health Physics, 115(4), p.439 - 447, 2018/10
Times Cited Count:4 Percentile:38.58(Environmental Sciences)After the Fukushima Nuclear Power Station accident, large quantities of radiocesium-contaminated soil generated from decontamination activities have been stored in the Fukushima Prefecture. To reduce the disposal volume, the Ministry of the Environment of Japan has presented a policy to recycle low-radioactive decontamination soil limited to civil engineering structures. However, there has been no practical instance or safety assessment of decontamination soil recycling. In this study, the way of ensuring the safety for decontamination soil recycling for road embankments was discussed. First, based on Japanese construction standards, additional doses to workers and the public in construction and service scenarios were evaluated. From the result, the radioactive cesium concentration level of recycled materials, where all additional doses meet the radiation criterion of 1 mSv y , was derived to be 6,000 Bq kg
, was derived to be 6,000 Bq kg . To confine additional doses to the public in a service scenario below 0.01 mSv y
. To confine additional doses to the public in a service scenario below 0.01 mSv y , soil slope protection of 40 cm or more was needed. Finally, additional doses in a disaster scenario were confirmed to be below 1 mSv y
, soil slope protection of 40 cm or more was needed. Finally, additional doses in a disaster scenario were confirmed to be below 1 mSv y .
.
Takai, Shizuka; Sawaguchi, Takuma; Takeda, Seiji
Proceedings of International Waste Management Symposia 2018 (WM2018) (Internet), 14 Pages, 2018/03
After the Fukushima Nuclear Power Station accident, large quantities of radiocesium-contaminated soil generated from decontamination activities have been stored in the Fukushima prefecture. To complete the final disposal of decontamination soil, the Ministry of the Environment of Japan presented policy to reduce the disposal volume by using low-level decontamination soil as recycled materials. The use will be limited to civil engineering structures in public projects, such as coastal levee and road embankment. However, there has been no example or safety assessment of recycling of decontamination soil. To contribute to guideline development for the recycling by the Ministry of the Environment, we conducted the safety assessment for recycling of decontamination soil as coastal levee. First, we evaluated additional doses to workers and the public in the case of construction and service of coastal levee. From the result, the radioactive cesium concentration level of recycled materials was derived to be 6,800 Bq/kg. For general designs of coastal levee in Japan, additional doses to the public in the case of service were below 0.01 mSv/y with derived radioactivity level. Finally, we confirmed additional doses in the case of disaster to be below 1 mSv/y.
Sawaguchi, Takuma; Takai, Shizuka; Umezawa, Katsuhiro; Takeda, Seiji; Okada, Takashi
Nihon Genshiryoku Gakkai-Shi ATOMO , 59(8), p.445 - 447, 2017/08
, 59(8), p.445 - 447, 2017/08
no abstracts in English
Takai, Shizuka; Takayama, Hideki*; Takeda, Seiji
JAEA-Data/Code 2016-020, 40 Pages, 2017/03
In this report, another group of scenarios for occurrence of earthquake at construction stage, operation stage and closure stage of disposal facility was presented. At first, we compiled information about damage cases of tunnel by earthquake and analyzed conditions for occurrence of damage. Base on this result and the previous report, information of influence of the accidents and human factors on safety functions and information of FEP about THMC variation, we specified events to be considered, which occur by earthquake and influence engineering barriers, natural barriers and long-term safety after closure stage of disposal facility. We compiled influence of the events on safety functions after closure stage of disposal and showed the chains of the influence on long-term safety as scenarios. These results were integrated as a database that could support development of scenarios caused by application of engineering technologies to geological disposal.
Takai, Shizuka; Takeda, Seiji; Sakai, Ryutaro*; Shimada, Taro; Munakata, Masahiro; Tanaka, Tadao
Nihon Genshiryoku Gakkai Wabun Rombunshi, 16(1), p.34 - 48, 2017/03
In geological disposal, direct effect on geological repositories by active faults is avoided at a stage of site characterization; however, uncertainty remains for avoidance of faults derived from the active faults, which are concealed deep under the ground and difficult to detect in advance. In this research, the influence of growth of undetected splay faults on natural barrier in a geological disposal system, which will caused by attack of the faults in the future, was evaluated. We investigated examples of splay faults in Japan and set conditions for growth of splay faults. Furthermore, we assumed a disposal site composed of sedimentary rocks and made a hydrogeological model of growth of splay faults. We carried out groundwater flow analyses, changing parameters such as location and depth of repository and growth velocity of splay faults. The results indicate that main flow path from the repository is changed into upward flow along the splay fault due to its growth and the average velocity to the ground surface becomes one or two orders of magnitude higher than that before its growth. The results also suggest that the splay fault growth leads into the possibility of downward flow of oxidizing groundwater from ground surface area.
Takai, Shizuka; Takayama, Hideki*; Takeda, Seiji
JAEA-Data/Code 2015-018, 96 Pages, 2015/11
In the safety assessment for the high-level radioactive waste geological disposal, scenarios need to be developed in consideration of influence on barrier features by accidents and human factors caused by application of engineering technologies at each stage of site characterization, construction, operation and closure of disposal facility. To develop scenarios on application of engineering technologies from the point of view of safety regulation, deviation events which are deviated states of engineered and natural barriers from intended states were specified and possible evolution of features of barriers or loss/reduction of safety functions of barriers was shown as a scenario in JAEA-Data/Code 2014-026. In this study, we compiled information of existence of engineering measures against the accidents and human factors and deviation events, application performance and development status of the measures. From this information, we identified deviation events which need developing of engineering measures as remarkable deviation events. These results were integrated as a database that could support development of scenarios caused by application of engineering technologies to geological disposal.
Takai, Shizuka; Seki, Masaya; Kimura, Hideo; Takeda, Seiji
Hoken Butsuri, 50(1), p.50 - 66, 2015/03
Wood (thinned wood from forest etc.) and wooden wastes (demolished wood etc.) potentially contaminated by radioactive cesium released by Fukushima Daiichi Nuclear Power Plant have been used for various purposes as wooden chips. However, there has been no dose estimation for use of such contaminated wood so far. Up to now, use of wood has been conducted according to a standard value of 100 Bq/kg for radioactive cesium based on clearance level of concrete and metal generated at nuclear power plant. The purpose of this study is to evaluate the safety of present use of wood by dose estimation for reuse of contaminated wooden chips, which are reused for main five use purposes (particle board, paper, compost, biomass power fuel, mulching). We also calculated activity concentrations of radioactive cesium in wooden chips corresponding to standard dose for safety reuse of radioactive wastes and regarded the minimum calculated activity concentration as a standard value of activity concentration for each reuse purposes. From the result, the minimum standard value of activity concentration of radioactive cesium in wooden chips for all reuse purposes is estimated to be 120 Bq/kg for reuse of wooden chips for particle board. Since this standard value is more than 100 Bq/kg, the safety of present use of wood is confirmed.
Takai, Shizuka; Takeda, Seiji; Kimura, Hideo
JAEA-Research 2014-028, 13 Pages, 2015/02
A large amount of waste contaminated by radioactive cesium released by Fukushima Daiichi Nuclear Power Plant has been recycled as much as possible in order to reduce the quantity to be disposed of and to use resources effectively. At present, a standard concentration of radioactive cesium for recycled products from disaster waste is defined as 100 Bq/kg. In order to understand the actual situation of radioactivity concentration of recycled products, Ministry of the Environment conducted a survey on recycled products. The survey found that several recycled products had relatively high radioactive cesium concentration. In this study, we specified exposure pathways to calculate doses for using the recycled products detected high cesium concentration in the survey. We calculate the doses based on the survey of concentration of the recycled products and compare them with a dose criterion of 10 Sv/y for the use of recycled products. It was shown that the calculated doses were less than 10
Sv/y for the use of recycled products. It was shown that the calculated doses were less than 10 Sv/y for all recycled products but one sample of recycled asphalt with 26
Sv/y for all recycled products but one sample of recycled asphalt with 26 Sv/y. However, 26
Sv/y. However, 26 Sv/y is within the range of trivial dose indicated in ICRP Pub.104 and safety for reuse of the recycled asphalt is ensured.
Sv/y is within the range of trivial dose indicated in ICRP Pub.104 and safety for reuse of the recycled asphalt is ensured.
Takayama, Hideki*; Takai, Shizuka; Takeda, Seiji
JAEA-Data/Code 2014-026, 189 Pages, 2015/02
In the safety assessment for the high-level radioactive waste geological disposal, scenarios need to be developed in consideration of influence on barrier features by applying engineering technologies at each stage of site selection, construction, operation and closure of disposal facility. To develop scenarios on application of engineering technologies from the point of view of safety regulation, it is important to grasp information of the engineering technologies which are possibly applied to geological disposal and to organize relationships between accidents and human factors caused by application of engineering technologies and influence by the factors on safety functions of engineered and natural barriers after closure stage. In this study, the engineering technologies are listed for site selection, construction, operation and closure activities at disposal site. From this information, "deviation events" which are deviated states of engineered and natural barriers from intended design were identified. We assumed influence on geological disposal facility due to the occurrence of the deviation events and identified the accidents and human factors which can progress the deviation events. Finally, we showed the sequence of influence by the accidents and human factors on long-term safety after closure of the disposal facility as scenarios. We provided a database with these results for development of scenario on engineering technology of geological disposal.
Takai, Shizuka; Hagino, Koichi*
Nuclear Back-end and Transmutation Technology for Waste Disposal, p.3 - 11, 2015/00
One of the major problems of fuel cycle is the disposal of high-level radioactive waste which contains long-lived nuclides and high-decay heating nuclides. Transmuting such nuclides into short-lived or stable nuclides is one possible way to resolve this problem. Neutron capture reactions have been proposed for transmutations of such fission products. However, this transmutation method is not effective for nuclides with small neutron capture cross sections such as  Cs. Recently, the photo-neutron (
Cs. Recently, the photo-neutron ( ,n) reactions via giant dipole resonance with laser Compton scattering
,n) reactions via giant dipole resonance with laser Compton scattering  -rays has been suggested as an alternative method for nuclear transmutations. In this paper, we investigate in detail the effectiveness of the transmutation of
-rays has been suggested as an alternative method for nuclear transmutations. In this paper, we investigate in detail the effectiveness of the transmutation of  Cs quantitatively. For the transmutation of
Cs quantitatively. For the transmutation of  Cs of 1g with photon flux
Cs of 1g with photon flux 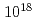 /s,
/s, 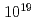 /s and
/s and 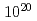 /s for 24 hours, 10%, 70% and 99% reduction of the initial amount of
/s for 24 hours, 10%, 70% and 99% reduction of the initial amount of  Cs is theoretically possible.
Cs is theoretically possible.
Takai, Shizuka; Sawaguchi, Takuma; Takeda, Seiji; Kimura, Hideo; Tanaka, Tadao
no journal, ,
no abstracts in English