Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Takigami, Machiko*; Maehara, Yasunobu*; Nagasawa, Naotsugu
Bio Industry, 27(9), p.50 - 55, 2010/09
no abstracts in English
Takigami, Machiko*; Nagasawa, Naotsugu; Hiroki, Akihiro; Kasai, Noboru; Yoshii, Fumio; Tamada, Masao; Takigami, Shoji*; Shibata, Takuya*; Aketagawa, Yasushi*; Ozaki, Masuo*
Transactions of the Materials Research Society of Japan, 35(3), p.647 - 650, 2010/09
There are many livestock farmers in Gunma Prefecture. Many of the farms are located under Mt. Akagi and Haruna, which attract tourists. Furthermore, rivers around the mountains are source of water supply to metropolitan area. Therefore, the waste treatments are very important. Regulations of smell and COD (chemical oxygen demand) are severe in Gunma Prefecture. Although there is no regulation for color of drain water, color in secondary treated water from livestock urine waste has been one of the major concerns for livestock farmers. The color is a metabolite of microorganisms and not easy to be removed. People have tried to remove the color by ozone treatment, absorption using activated carbon or soils. An absorbent was prepared by radiation grafting; fibers were irradiated with  Co
Co  -rays and some kinds of monomers were grafted onto the fibers. The absorbent thus prepared were used to decolorize the secondary treated water. The color and COD were removed by the absorbent, however, COD removal was more difficult than decolorization. Degree of grafting (weight increase expressed in % by grafting reaction to initial weight of the fiber), treated water/absorbent ratio, flow rate of treated water, and direction of flow affected color and COD removal. The used absorbent could be used repeatedly after washing.
-rays and some kinds of monomers were grafted onto the fibers. The absorbent thus prepared were used to decolorize the secondary treated water. The color and COD were removed by the absorbent, however, COD removal was more difficult than decolorization. Degree of grafting (weight increase expressed in % by grafting reaction to initial weight of the fiber), treated water/absorbent ratio, flow rate of treated water, and direction of flow affected color and COD removal. The used absorbent could be used repeatedly after washing.
Kasahara, Takamitsu*; Takigami, Machiko*; Nagasawa, Naotsugu; Takigami, Shoji*
Transactions of the Materials Research Society of Japan, 34(3), p.395 - 398, 2009/09
no abstracts in English
Takigami, Machiko*; Hiroki, Akihiro; Nagasawa, Naotsugu; Kasahara, Takamitsu*; Takigami, Shoji*; Tamada, Masao
Transactions of the Materials Research Society of Japan, 34(3), p.391 - 394, 2009/09
Carboxymethyl cellulose (CMC) with different molar mass was prepared by acid hydrolysis at 121 C. CMC thus prepared was mixed with citric acid aqueous solution to form CMC-acid gel. By replacing sodium existing as counter ion in carboxymethyl group with hydrogen, CMC molecules coagulate and hydrogen bonds are formed among CMC molecules. The CMC-acid gel prepared in that way was subjected to evaluation of gel fraction, water absorption and mechanical properties. Gel fraction was higher in CMC with higher molar mass than that in CMC with lower molar mass at short incubation time. However, there was no difference in gel fraction attributable to molar mass of CMC after long time incubation. CMC with higher molar mass crosslinked more easily than CMC with lower molar mass. The gel made of CMC with lower molar mass was softer and absorbed more amount of water than that with higher molar mass. All the results were elucidated by number of hydrogen bonds in CMC molecule. The gel made of higher molar mass CMC becomes stiff and brittle after long time incubation, however, the gel made of lower molar mass CMC keeps softness and strength longer.
C. CMC thus prepared was mixed with citric acid aqueous solution to form CMC-acid gel. By replacing sodium existing as counter ion in carboxymethyl group with hydrogen, CMC molecules coagulate and hydrogen bonds are formed among CMC molecules. The CMC-acid gel prepared in that way was subjected to evaluation of gel fraction, water absorption and mechanical properties. Gel fraction was higher in CMC with higher molar mass than that in CMC with lower molar mass at short incubation time. However, there was no difference in gel fraction attributable to molar mass of CMC after long time incubation. CMC with higher molar mass crosslinked more easily than CMC with lower molar mass. The gel made of CMC with lower molar mass was softer and absorbed more amount of water than that with higher molar mass. All the results were elucidated by number of hydrogen bonds in CMC molecule. The gel made of higher molar mass CMC becomes stiff and brittle after long time incubation, however, the gel made of lower molar mass CMC keeps softness and strength longer.
Kasahara, Takamitsu*; Takigami, Machiko*; Nagasawa, Naotsugu; Prawitwong, P.*; Takigami, Shoji*
Transactions of the Materials Research Society of Japan, 33(4), p.927 - 930, 2008/12
Carboxymethyl cellulose (CMC) forms a gel when mixed with acid as a result of replacement of sodium in carboxymethyl group with hydrogen; hydrogen bonds are formed among CMC molecules. CMC gel gets new property by mixing with other materials. Konjac mannan (KM) is a water soluble glucomannan with high molar mass and has high viscosity in low concentration aqueous solution. CMC gel is expected to have more elasticity by mixing with KM. Novel CMC-KM mixture gel is made by two processes; (1) mixing CMC with KM solution, (2) immersion of CMC-KM mixture in hydrochloric acid aqueous solution. Interaction of CMC and KM was studied by using KM with different molar mass. Molar mass of KM easily decreases by  -irradiation. The effect of KM molar mass on characteristics of CMC-KM mixture is examined using tensile test fixture.
-irradiation. The effect of KM molar mass on characteristics of CMC-KM mixture is examined using tensile test fixture.
Takigami, Machiko*; Amada, Haruyo*; Nagasawa, Naotsugu; Hiroki, Akihiro; Kasai, Noboru; Yoshii, Fumio; Tamada, Masao
Transactions of the Materials Research Society of Japan, 33(4), p.849 - 852, 2008/12
Shortage of phosphorus becomes a serious problem in the world. The removal of phosphorus in swine urine is a big concern for the environmental conservation. To solve both problems, absorbent to absorb phosphorus in swine urine was developed using carboxymethyl cellulose (CMC) and Iron. The gel formation proceeded instantaneously when CMC and Iron (III) chloride were mixed, while gel was not formed immediately when Iron (II) chloride was used. Oxidation of Iron (II) to Iron (III) occurs gradually in Iron (II) aqueous solution. However, addition of CMC to the Iron (II) solution promoted the oxidation to form gel. The rate of gel formation could be controlled by addition of acid to CMC-Iron (II) mixture. The resultant gel absorbed phosphorus in swine urine. The absorption was about 97% in swine urine containing 78 mg/L of phosphorus.
Takigami, Machiko*; Amada, Haruyo*; Nagasawa, Naotsugu; Hiroki, Akihiro; Kasai, Noboru; Yoshii, Fumio; Tamada, Masao
JAEA-Review 2008-055, JAEA Takasaki Annual Report 2007, P. 44, 2008/11
no abstracts in English
Kasahara, Takamitsu*; Takigami, Machiko*; Nagasawa, Naotsugu; Prawitwong, P.*; Tamada, Masao; Takigami, Shoji*
JAEA-Review 2008-055, JAEA Takasaki Annual Report 2007, P. 45, 2008/11
Carboxymethyl cellulose (CMC) forms a gel when mixed with acid as a result of replacement of sodium in carboxymethyl group with hydrogen; hydrogen bonds are formed among CMC molecules. CMC gel gets new property by mixing with other materials. Konjac mannan (KM) is a water soluble glucomannan with high molar mass and has high viscosity in low concentration aqueous solution. CMC gel is expected to have more elasticity by mixing with KM. Novel CMC-KM mixture gel is made by two processes; (1) mixing CMC with KM solution, (2) immersion of CMC-KM mixture in hydrochloric acid aqueous solution. Interaction of CMC and KM was studied by using KM with different molar mass. Molar mass of KM easily decreases by  -irradiation. The effect of KM molar mass on characteristics of CMC-KM mixture is examined using tensile test fixture.
-irradiation. The effect of KM molar mass on characteristics of CMC-KM mixture is examined using tensile test fixture.
Makabe, Takeshi*; Prawitwong, P.*; Takahashi, Ryo*; Takigami, Machiko*; Nagasawa, Naotsugu; Takigami, Shoji*
Transactions of the Materials Research Society of Japan, 33(2), p.471 - 474, 2008/06
Konjac mannan (KM) is a water soluble glucomannan with high molar mass. KM aqueous solution shows extremely high viscosity. The effects of  -rays irradiation and acid hydrolysis on molar mass were studied. The hydrolysis was carried out using citric acid. Characteristics of the irradiated and hydrolyzed KM were investigated using GPC-MALLS and a viscometer. The chemical structure of KM scarcely changed by both treatments. Molar mass of the irradiated KM decreased gradually with increasing dose. Molar mass of the hydrolyzed KM also decreased gradually with acid concentration. The viscosity of both treated KM aqueous solutions decreased with decreasing molar mass. High molar mass KM solution showed pseudo-plastic fluids behavior of the non-Newtonian fluid at dilute region and changed to Newtonian fluid with decrease of molar mass. Low molar mass KM solution showed behavior of Newtonian fluid at semi-dilute region. The critical concentration at the overlap limit of KM solution increased with decreasing of molar mass.
-rays irradiation and acid hydrolysis on molar mass were studied. The hydrolysis was carried out using citric acid. Characteristics of the irradiated and hydrolyzed KM were investigated using GPC-MALLS and a viscometer. The chemical structure of KM scarcely changed by both treatments. Molar mass of the irradiated KM decreased gradually with increasing dose. Molar mass of the hydrolyzed KM also decreased gradually with acid concentration. The viscosity of both treated KM aqueous solutions decreased with decreasing molar mass. High molar mass KM solution showed pseudo-plastic fluids behavior of the non-Newtonian fluid at dilute region and changed to Newtonian fluid with decrease of molar mass. Low molar mass KM solution showed behavior of Newtonian fluid at semi-dilute region. The critical concentration at the overlap limit of KM solution increased with decreasing of molar mass.
Takigami, Machiko*; Nagasawa, Naotsugu; Tamada, Masao
Kogyo Zairyo, 56(2), p.62 - 65, 2008/02
no abstracts in English
Takigami, Machiko*; Amada, Haruyo*; Nagasawa, Naotsugu; Yagi, Toshiaki; Kasahara, Takamitsu*; Takigami, Shoji*; Tamada, Masao
Transactions of the Materials Research Society of Japan, 32(3), p.713 - 716, 2007/09
Carboxymethylcellulose (CMC) gel was formed by addition of acid to CMC (CMC-acid gel). Gel fraction (weight of insoluble part/initial CMC weight) was calculated after removing uncrosslinked CMC by immersing the CMC-acid gel in water. It increased with acid concentration. Mechanism of CMC-acid gel formation was elucidated by aggregation of CMC molecules as the result of replacement of sodium in carboxyl group with hydrogen. Gels could be prepared by three different procedures; (1) mixing CMC and acid, (2) immersion of CMC or  -irradiated CMC pastes in acid, and (3)
-irradiated CMC pastes in acid, and (3)  -irradiation of CMC-acid gel. Gels with different elasticity and hardness were prepared changing degree of substitution of CMC, molar mass of CMC, species of acid, concentrations of acid and CMC, and application of
-irradiation of CMC-acid gel. Gels with different elasticity and hardness were prepared changing degree of substitution of CMC, molar mass of CMC, species of acid, concentrations of acid and CMC, and application of  -irradiation.
-irradiation.
 -dioxin and octachlorodibenzofuran in organic solvents and treatment of dioxin-containing liquid wastes
-dioxin and octachlorodibenzofuran in organic solvents and treatment of dioxin-containing liquid wastesZhao, C.; Hirota, Koichi; Taguchi, Mitsumasa; Takigami, Machiko*; Kojima, Takuji
Radiation Physics and Chemistry, 76(1), p.37 - 45, 2007/01
Times Cited Count:13 Percentile:66.15(Chemistry, Physical)no abstracts in English
Taguchi, Mitsumasa; Zennyoji, Yoshihiro*; Takigami, Machiko*; Baldacchino, G.*; Kimura, Atsushi; Hiratsuka, Hiroshi*; Namba, Hideki; Kojima, Takuji
Radiation Physics and Chemistry, 75(5), p.564 - 571, 2006/03
Times Cited Count:6 Percentile:41.45(Chemistry, Physical)The suspended fine particles formed in aqueous phenol solution under high dose irradiation were studied using the MeV electron beam and  Co
Co  -ray irradiations. The fine particle's size was 100-800 nm in diameter and became bigger at higher dose and lower dose rate. The distributions of the particle size became narrower for irradiation at higher dose rate. The fine particles were regarded to consist of molecules of about 1.9
-ray irradiations. The fine particle's size was 100-800 nm in diameter and became bigger at higher dose and lower dose rate. The distributions of the particle size became narrower for irradiation at higher dose rate. The fine particles were regarded to consist of molecules of about 1.9 10
10 molecular weight.
molecular weight.
 -nonylphenols in water and elimination of their estrogen activities by
-nonylphenols in water and elimination of their estrogen activities by  Co
Co  -ray irradiation
-ray irradiationKimura, Atsushi; Taguchi, Mitsumasa; Otani, Yoshimi*; Takigami, Machiko; Shimada, Yoshitaka*; Kojima, Takuji; Hiratsuka, Hiroshi*; Namba, Hideki
Radiation Physics and Chemistry, 75(1), p.61 - 69, 2006/01
Times Cited Count:13 Percentile:65.83(Chemistry, Physical)Decomposition of  -Nonylphenols (NPs) in water at 1
-Nonylphenols (NPs) in water at 1  mol dm
mol dm was decreased exponentially with absorbed dose when NPs were irradiated by
was decreased exponentially with absorbed dose when NPs were irradiated by  Co
Co -rays. Two products having molecular weight of 236, presumably OH adducts of NPs, were detected by LC-MS analyses. The elimination of estrogen activity of aqueous NPs solution including such irradiation products at 5000 Gy (J kg
-rays. Two products having molecular weight of 236, presumably OH adducts of NPs, were detected by LC-MS analyses. The elimination of estrogen activity of aqueous NPs solution including such irradiation products at 5000 Gy (J kg ) was confirmed by the yeast two hybrid assay. These results should expand the application of ionizing radiation to the treatment of NPs.
) was confirmed by the yeast two hybrid assay. These results should expand the application of ionizing radiation to the treatment of NPs.
Takigami, Machiko; Arai, Hidehiko*; Hirota, Koichi; Taguchi, Mitsumasa; Hakoda, Teruyuki; Kojima, Takuji
Kankyo Kagaku, 14(1), p.13 - 23, 2004/03
The Japan Atomic Energy Research Institute undertook a pilot scale electron beam decompostion of dioxins in the flue gases from the municipal solid waste incinerator at the Takahama Clean Center. The conventional method, following the Japan Industrial Standards (JIS) method, takes 2 weeks at least to extract and purify dioxins from the flue gases for analysis by GC/MS. However, using a carbon adsorbent, the time required for the extraction of dioxins was shortened from 16 to 2.5 hours. Further improvements in the clean up process enabled the overall time to be reduced to less than a half of that rquired by the JIS method. Using this simplified method allows analysts, who are not practiced in the pretreatment of flue gases, to prepare samples for dioxin analysis by GC/MS. The sampling and pretreatment of the flue gases can, with this process, be completed within 4 days with accuracy comparable to JIS method.
 -ray irradiation
-ray irradiationAbe, Yasuhiro*; Takigami, Machiko; Sugino, Koji*; Taguchi, Mitsumasa; Kojima, Takuji; Umemura, Tomonari*; Tsunoda, Kinichi*
Bulletin of the Chemical Society of Japan, 76(8), p.1681 - 1685, 2003/08
Times Cited Count:5 Percentile:26.49(Chemistry, Multidisciplinary)The decomposition of phenolic endocrine disrupting chemicals (P-EDCs), such as phenol, 4-butylphenol (BuP), and bisphenol A (BPA), in aqueous solutions by potassium permanganate (KMnO ) was studied and its efficiency was compared with that of hydroxyl radicals (OH
) was studied and its efficiency was compared with that of hydroxyl radicals (OH ) generated by
) generated by  Co
Co  -ray irradiation. Various organic acids and inorganic carbon were formed in the decomposition of P-EDCs due to either KMnO
-ray irradiation. Various organic acids and inorganic carbon were formed in the decomposition of P-EDCs due to either KMnO or OH
or OH . They were formed via direct aromatic ring cleavage in the case of KMnO
. They were formed via direct aromatic ring cleavage in the case of KMnO and OH
and OH addition-substitution reactions followed by aromatic ring cleavage in the case of OH
addition-substitution reactions followed by aromatic ring cleavage in the case of OH . Comparing the decrease in the P-EDCs based on the number of electrons, the amount of KMnO
. Comparing the decrease in the P-EDCs based on the number of electrons, the amount of KMnO spent to completely eliminate BuP and BPA was comparable to the amount of OH
spent to completely eliminate BuP and BPA was comparable to the amount of OH . Although three times more KMnO
. Although three times more KMnO was needed for phenol than OH
was needed for phenol than OH , the complete conversion of phenol into organic acids and inorganic carbon was achieved with 720
, the complete conversion of phenol into organic acids and inorganic carbon was achieved with 720 M of electrons in both cases.
M of electrons in both cases.
Hirota, Koichi; Hakoda, Teruyuki; Taguchi, Mitsumasa; Takigami, Machiko; Kim, H.; Kojima, Takuji
Environmental Science & Technology, 37(14), p.3164 - 3170, 2003/07
Times Cited Count:43 Percentile:65.45(Engineering, Environmental)The electron-beam technology was applied to reduce polychlorinated dibenzo-p-dioxins (PCDD) and polychlorinated dibenzofurans (PCDF) in flue gases from the municipal solid waste incinerator (MSWI) at a temperature of 200 C. More than 90% of PCDD/Fs in a flue gas of 1000 m
C. More than 90% of PCDD/Fs in a flue gas of 1000 m N/h was decomposed at a dose of 14 kGy. The decomposition of PCDD/Fs was probably initiated through reactions with OH radicals, followed by the dissociation of ether bond (-C-O-C-), the cleavage of aromatic rings, and dichlorination. The dechlorination of the higher dechlorinated PCDF homologues produced the lower chlorinated ones, which led to lower decomposition efficiency of PCDF than that of PCDD.
N/h was decomposed at a dose of 14 kGy. The decomposition of PCDD/Fs was probably initiated through reactions with OH radicals, followed by the dissociation of ether bond (-C-O-C-), the cleavage of aromatic rings, and dichlorination. The dechlorination of the higher dechlorinated PCDF homologues produced the lower chlorinated ones, which led to lower decomposition efficiency of PCDF than that of PCDD.
Kojima, Takuji; Hirota, Koichi; Taguchi, Mitsumasa; Hakoda, Teruyuki; Takigami, Machiko
Proceedings of 25th JAIF-KAIF Seminar on Nuclear Industry, p.193 - 201, 2003/00
The electron beam technology for decomposition/elimination of dioxin contained in flue gas has been developed using real waste gas of 1,000 m N/h released from the municipal solid waste incineration facility at 200
N/h released from the municipal solid waste incineration facility at 200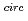 C. The decomposition efficiency, the ratio of toxic equivalent dioxin concentration before and after EB irradiation to doses above 15kGy is higher than 90%, which clears the regulation limit in the Japanese special measures of dioxin release. The chemical process of dioxin decomposition was studied and low-toxicity of irradiated gas was confirmed in terms of endocrine disrupter influence.
C. The decomposition efficiency, the ratio of toxic equivalent dioxin concentration before and after EB irradiation to doses above 15kGy is higher than 90%, which clears the regulation limit in the Japanese special measures of dioxin release. The chemical process of dioxin decomposition was studied and low-toxicity of irradiated gas was confirmed in terms of endocrine disrupter influence.
Hirota, Koichi; Hakoda, Teruyuki; Taguchi, Mitsumasa; Takigami, Machiko*; Kojima, Takuji
Proceedings of 9th International Conference on Radiation Curing (RadTech Asia '03) (CD-ROM), 4 Pages, 2003/00
The flue gas from a municipal solid waste incinerator (MSWI) was irradiated with electron beams to destroy polychlorinated dibenzo-p-dioxins (PCDDs) and polychlorinated dibenzofurans (PCDFs). A flue gas of 1,000 m /h N for the irradiation was obtained at 200
/h N for the irradiation was obtained at 200 C from a main gas stream of the MSWI. The decomposition efficiencies of PCDD/Fs were increased with absorbed dose and reached 90% at a dose of 14 kGy. The reaction mechanisim for PCDD/Fs was also considered.
C from a main gas stream of the MSWI. The decomposition efficiencies of PCDD/Fs were increased with absorbed dose and reached 90% at a dose of 14 kGy. The reaction mechanisim for PCDD/Fs was also considered.
S.Ngamnit*; Takigami, Machiko*; P.Suchada*; S.Orawan*; C.Saovapong*; Ito, Hitoshi
Biocontrol Science, 4(2), p.109 - 113, 1999/00
no abstracts in English