Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
 layers in the triple-layer cuprate Bi
layers in the triple-layer cuprate Bi Sr
Sr Ca
Ca Cu
Cu O
O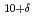 studied by angle-resolved photoemission spectroscopy
studied by angle-resolved photoemission spectroscopyIdeta, Shinichiro*; Johnston, S.*; Yoshida, Teppei*; Tanaka, Kiyohisa*; Mori, Michiyasu; Anzai, Hiroaki*; Ino, Akihiro*; Arita, Masashi*; Namatame, Hirofumi*; Taniguchi, Masaki*; et al.
Physical Review Letters, 127(21), p.217004_1 - 217004_6, 2021/11
Times Cited Count:6 Percentile:60.19(Physics, Multidisciplinary) irradiation
irradiationYukawa, Takuji*; Inoue, Hiroyuki*; Kojima, Takao*; Iwase, Akihiro*; Taniguchi, Naoki; Tachikawa, Hirokazu*
Zairyo To Kankyo 2016 Koenshu (CD-ROM), p.359 - 362, 2016/05
The immersion tests of pure titanium were carried out in aqueous solution containing carbonate/bicarbonate with 50 mM-chloride ion under gamma irradiation. The effect of pH on general corrosion rate of titanium were studied. The experimental results showed that the concentration of hydrogen preoxide was increased with pH, and the corrosion rate increased with the hydrogen preoxide concentration. The corrosion rate in pH12 and 13 were 5 to10 times larger than those under unirradiated conditions.
 ion beams for ITER NB accelerator
ion beams for ITER NB acceleratorUmeda, Naotaka; Kashiwagi, Mieko; Taniguchi, Masaki; Tobari, Hiroyuki; Watanabe, Kazuhiro; Dairaku, Masayuki; Yamanaka, Haruhiko; Inoue, Takashi; Kojima, Atsushi; Hanada, Masaya
Review of Scientific Instruments, 85(2), p.02B304_1 - 02B304_3, 2014/02
Times Cited Count:12 Percentile:48.35(Instruments & Instrumentation)In order to realize neutral beam systems in ITER whose target is to produce D ion beam of 1 MeV, 200 A/m
ion beam of 1 MeV, 200 A/m during 3600s, the electrostatic five-stages negative ion accelerator has been developed at JAEA. To extend pulse length, heat load of the acceleration grids was reduced by controlling the ion beam trajectory. Namely, the beam deflection due to the residual magnetic filter in the accelerator was suppressed with the newly developed extractor with a 0.5 mm off-set aperture displacement. The use of new extractor improved the deflection angle from 6 mrad to 1 mrad, resulting in the reduction of direct interception of negative ions from 23% to 15% of the total acceleration power, respectively. As a result, the pulse length of 130 A/m
during 3600s, the electrostatic five-stages negative ion accelerator has been developed at JAEA. To extend pulse length, heat load of the acceleration grids was reduced by controlling the ion beam trajectory. Namely, the beam deflection due to the residual magnetic filter in the accelerator was suppressed with the newly developed extractor with a 0.5 mm off-set aperture displacement. The use of new extractor improved the deflection angle from 6 mrad to 1 mrad, resulting in the reduction of direct interception of negative ions from 23% to 15% of the total acceleration power, respectively. As a result, the pulse length of 130 A/m , 881 keV H
, 881 keV H ion beam has been successfully extended from a previous value of 0.4s to 8.7s.
ion beam has been successfully extended from a previous value of 0.4s to 8.7s.
Kashiwagi, Mieko; Umeda, Naotaka; Tobari, Hiroyuki; Kojima, Atsushi; Yoshida, Masafumi; Taniguchi, Masaki; Dairaku, Masayuki; Maejima, Tetsuya; Yamanaka, Haruhiko; Watanabe, Kazuhiro; et al.
Review of Scientific Instruments, 85(2), p.02B320_1 - 02B320_3, 2014/02
Times Cited Count:29 Percentile:75.07(Instruments & Instrumentation)The negative ion extractor for high power and long-pulse operations is newly developed toward the neutral beam injector (NBI) for heating & current drive of future fusion machines such as ITER, JT-60 Super Advanced (SA) and DEMO reactor. The satisfactory cooling capability is designed in the thermal analysis. A negative ion production and a suppression of electrons are experimentally validated for this new extractor. As the results, the negative ion current shows increases by a factor of 1.3 with suppressing the electron current. The beam divergence angle is also maintained small enough, 4 mrad.
Kojima, Atsushi; Hanada, Masaya; Yoshida, Masafumi; Inoue, Takashi; Watanabe, Kazuhiro; Taniguchi, Masaki; Kashiwagi, Mieko; Umeda, Naotaka; Tobari, Hiroyuki; Grisham, L. R.*; et al.
Fusion Engineering and Design, 88(6-8), p.918 - 921, 2013/10
Times Cited Count:6 Percentile:43.8(Nuclear Science & Technology)In this paper, the recent activities are reported toward demonstration of the long pulse production. As for the improvement of uniform beam current profile, a symmetric magnetic field configuration for the source plasma production, a so-called tent-shaped filter, was found to be effective to improve the uniformity of the beam current profile. A similar configuration is applied to the JT-60 negative ion source whose plasma size is 1220 mm  564 mm. An estimation from trajectory calculations of primary electrons with the symmetric magnetic field configuration showed that the primary electrons were distributed uniformly in a longitudinal direction. As for the temperature control of the plasma grid, a prototype of the grid with cooling/heating by circulating a high-temperature fluorinated fluid has been developed. This grid was found to have a capability to control the temperature with a time constant of 10 s by considering the physical properties of the fluid.
564 mm. An estimation from trajectory calculations of primary electrons with the symmetric magnetic field configuration showed that the primary electrons were distributed uniformly in a longitudinal direction. As for the temperature control of the plasma grid, a prototype of the grid with cooling/heating by circulating a high-temperature fluorinated fluid has been developed. This grid was found to have a capability to control the temperature with a time constant of 10 s by considering the physical properties of the fluid.
 Se
Se
Ye, M.*; Kuroda, Kenta*; Takeda, Yukiharu; Saito, Yuji; Okamoto, Kazuaki*; Zhu, S.-Y.*; Shirai, Kaito*; Miyamoto, Koji*; Arita, Masashi*; Nakatake, Masashi*; et al.
Journal of Physics; Condensed Matter, 25(23), p.232201_1 - 232201_5, 2013/06
Times Cited Count:12 Percentile:48.62(Physics, Condensed Matter)no abstracts in English
 Se
Se induced by cobalt adatom in the absence of ferromagnetic ordering
induced by cobalt adatom in the absence of ferromagnetic orderingYe. M.*; Eremeev, S. V.*; Kuroda, Kenta*; Krasovskii, E. E.*; Chulkov, E. V.*; Takeda, Yukiharu; Saito, Yuji; Okamoto, Kazuaki*; Zhu, S. Y.*; Miyamoto, Koji*; et al.
Physical Review B, 85(20), p.205317_1 - 205317_5, 2012/05
Times Cited Count:62 Percentile:89.57(Materials Science, Multidisciplinary)no abstracts in English
Kojima, Atsushi; Hanada, Masaya; Hilmi, A.*; Inoue, Takashi; Watanabe, Kazuhiro; Taniguchi, Masaki; Kashiwagi, Mieko; Umeda, Naotaka; Tobari, Hiroyuki; Kobayashi, Shinichi*; et al.
Review of Scientific Instruments, 83(2), p.02B117_1 - 02B117_5, 2012/02
Times Cited Count:17 Percentile:60.41(Instruments & Instrumentation)Production of 500 keV, 3 A beams has been successfully achieved in the JT-60 negative by overcoming the low voltage holding of the accelerator. Toward the design of next ion source, database for the voltage holding capability based on experimental results is required and obtained. As a result, the voltage holding capability was found to vary with 67 N power of -0.15 and with 31.7 S power of -0.125 where N is the aperture number and S is the anode surface area. When N = 1100 and S = 2 m are applied to the design of JT-60SA ion source, the factors C are estimated to be 23 and 29, respectively. Therefore, the influence of the local electric field around the apertures is stronger than that of the surface area.
are applied to the design of JT-60SA ion source, the factors C are estimated to be 23 and 29, respectively. Therefore, the influence of the local electric field around the apertures is stronger than that of the surface area.
Taniguchi, Masaki; Kashiwagi, Mieko; Umeda, Naotaka; Dairaku, Masayuki; Takemoto, Jumpei; Tobari, Hiroyuki; Tsuchida, Kazuki; Yamanaka, Haruhiko; Watanabe, Kazuhiro; Kojima, Atsushi; et al.
Review of Scientific Instruments, 83(2), p.02B121_1 - 02B121_3, 2012/02
Times Cited Count:11 Percentile:46.79(Instruments & Instrumentation)JAEA has developed the MeV accelerator to demonstrate 1 MeV, 200 A/m H
H ion beam acceleration required for ITER NBI. A key to realize such a high power accelerator is improvement of voltage holding capability. Based on detailed investigation of the voltage holding characteristics, MeV accelerator was modified to reduce electric field concentration by extending gaps between the grid supports and increasing curvature radiuses at the support corners. After the modifications, accelerator succeeded in sustaining -1 MV in vacuum without beam acceleration. Moreover, beam deflection due to the magnetic field for electron suppression and space charge repulsion was compensated by aperture displacement technique. As the result, beam deflection was compensated and voltage holding during the beam acceleration was improved. Beam parameter of the MeV accelerator was increased to 980 keV, 185 A/m
ion beam acceleration required for ITER NBI. A key to realize such a high power accelerator is improvement of voltage holding capability. Based on detailed investigation of the voltage holding characteristics, MeV accelerator was modified to reduce electric field concentration by extending gaps between the grid supports and increasing curvature radiuses at the support corners. After the modifications, accelerator succeeded in sustaining -1 MV in vacuum without beam acceleration. Moreover, beam deflection due to the magnetic field for electron suppression and space charge repulsion was compensated by aperture displacement technique. As the result, beam deflection was compensated and voltage holding during the beam acceleration was improved. Beam parameter of the MeV accelerator was increased to 980 keV, 185 A/m , which is close to the requirement of ITER accelerator.
, which is close to the requirement of ITER accelerator.
Hanada, Masaya; Kojima, Atsushi; Tanaka, Yutaka; Inoue, Takashi; Watanabe, Kazuhiro; Taniguchi, Masaki; Kashiwagi, Mieko; Tobari, Hiroyuki; Umeda, Naotaka; Akino, Noboru; et al.
Fusion Engineering and Design, 86(6-8), p.835 - 838, 2011/10
Times Cited Count:13 Percentile:69.55(Nuclear Science & Technology)Neutral beam (NB) injectors for JT-60 Super Advanced (JT-60SA) have been designed and developed. Twelve positive-ion-based and one negative-ion-based NB injectors are allocated to inject 30 MW D beams in total for 100 s. Each of the positive-ion-based NB injector is designed to inject 1.7 MW for 100s at 85 keV. A part of the power supplies and magnetic shield utilized on JT-60U are upgraded and reused on JT-60SA. To realize the negative-ion-based NB injector for JT-60SA where the injection of 500 keV, 10 MW D
beams in total for 100 s. Each of the positive-ion-based NB injector is designed to inject 1.7 MW for 100s at 85 keV. A part of the power supplies and magnetic shield utilized on JT-60U are upgraded and reused on JT-60SA. To realize the negative-ion-based NB injector for JT-60SA where the injection of 500 keV, 10 MW D beams for 100s is required, R&Ds of the negative ion source have been carried out. High-energy negative ion beams of 490-500 keV have been successfully produced at a beam current of 1-2.8 A through 20% of the total ion extraction area, by improving voltage holding capability of the ion source. This is the first demonstration of a high-current negative ion acceleration of
beams for 100s is required, R&Ds of the negative ion source have been carried out. High-energy negative ion beams of 490-500 keV have been successfully produced at a beam current of 1-2.8 A through 20% of the total ion extraction area, by improving voltage holding capability of the ion source. This is the first demonstration of a high-current negative ion acceleration of  1 A to 500 keV. The design of the power supplies and the beamline is also in progress. The procurement of the acceleration power supply starts in 2010.
1 A to 500 keV. The design of the power supplies and the beamline is also in progress. The procurement of the acceleration power supply starts in 2010.
Kojima, Atsushi; Hanada, Masaya; Tanaka, Yutaka*; Taniguchi, Masaki; Kashiwagi, Mieko; Inoue, Takashi; Umeda, Naotaka; Watanabe, Kazuhiro; Tobari, Hiroyuki; Kobayashi, Shinichi*; et al.
AIP Conference Proceedings 1390, p.466 - 475, 2011/09
Times Cited Count:2 Percentile:53.22(Physics, Atomic, Molecular & Chemical)Voltage holding tests by using JT-60 negative ion source and small electrodes was carried out because JT-60 negative ion source had a critical problem about low voltage holding capability for long time. As a result, the voltage holding capability is decreased with the increase of area where local electric field is generated, as well as the surface area according to existing scaling low about surface area. Therefore, in order to improve the voltage holding without changing the existing accelerator, the voltage holding test was carried out by extending gap lengths of the negative ion source. In order to improve the voltage holding, beam radiation shield needs to be optimized additionally. As a result, the voltage holding has been improved to 500 kV and stabilized. By using this modified ion source, negative ion beams of 500 keV up to 3A has been successfully produced.
Hanada, Masaya; Kojima, Atsushi; Inoue, Takashi; Watanabe, Kazuhiro; Taniguchi, Masaki; Kashiwagi, Mieko; Tobari, Hiroyuki; Umeda, Naotaka; Akino, Noboru; Kazawa, Minoru; et al.
AIP Conference Proceedings 1390, p.536 - 544, 2011/09
Times Cited Count:7 Percentile:84.66(Physics, Atomic, Molecular & Chemical)no abstracts in English
Taniguchi, Masaki; Kashiwagi, Mieko; Inoue, Takashi; Umeda, Naotaka; Watanabe, Kazuhiro; Tobari, Hiroyuki; Dairaku, Masayuki; Yamanaka, Haruhiko; Tsuchida, Kazuki; Kojima, Atsushi; et al.
AIP Conference Proceedings 1390, p.449 - 456, 2011/09
Times Cited Count:2 Percentile:53.22(Physics, Atomic, Molecular & Chemical)At JAEA, MeV accelerator has been developed as a proof-of-principle accelerator for ITER NBI. To achieve the acceleration of 1 MeV, 200 A/m beam required for ITER, improvement of the voltage holding capability is essential. Review of voltage holding results ever obtained with various geometries of the accelerators showed that voltage holding capability was about a half of that for ideal small electrode. This is due to local electric field concentration in the accelerators, such as edge and corner between grids and its support structures. Based on these results, accelerator was modified to reduce the electric field concentration by reshaping the support structures and expanding the gap length. After the modifications, voltage holding capability in vacuum was increased from 835 kV to 1 MV. Voltage holding progressed the energy and current to 879 keV, 0.36 A (157 A/m
beam required for ITER, improvement of the voltage holding capability is essential. Review of voltage holding results ever obtained with various geometries of the accelerators showed that voltage holding capability was about a half of that for ideal small electrode. This is due to local electric field concentration in the accelerators, such as edge and corner between grids and its support structures. Based on these results, accelerator was modified to reduce the electric field concentration by reshaping the support structures and expanding the gap length. After the modifications, voltage holding capability in vacuum was increased from 835 kV to 1 MV. Voltage holding progressed the energy and current to 879 keV, 0.36 A (157 A/m ).
).
 studied by photoemission and soft X-ray absorption spectroscopies
studied by photoemission and soft X-ray absorption spectroscopiesUtsumi, Yuki*; Sato, Hitoshi*; Kurihara, Hidenao*; Maso, Hiroyuki*; Hiraoka, Koichi*; Kojima, Kenichi*; Tobimatsu, Komei*; Okochi, Takuo*; Fujimori, Shinichi; Takeda, Yukiharu; et al.
Physical Review B, 84(11), p.115143_1 - 115143_7, 2011/09
Times Cited Count:11 Percentile:44.51(Materials Science, Multidisciplinary)We have studied conduction-band (CB) electronic states of a typical valence-transition compound YbInCu by means of temperature-dependent hard X-ray photoemission spectroscopy (HX-PES), soft X-ray absorption spectroscopy (XAS), and soft X-ray photoemission spectroscopy (SX-PES) of the valence band. We have described the valence transition in YbInCu
by means of temperature-dependent hard X-ray photoemission spectroscopy (HX-PES), soft X-ray absorption spectroscopy (XAS), and soft X-ray photoemission spectroscopy (SX-PES) of the valence band. We have described the valence transition in YbInCu in terms of the charge transfer from the CB to Yb 4
in terms of the charge transfer from the CB to Yb 4 states.
states.
Kojima, Atsushi; Hanada, Masaya; Tanaka, Yutaka*; Kawai, Mikito*; Akino, Noboru; Kazawa, Minoru; Komata, Masao; Mogaki, Kazuhiko; Usui, Katsutomi; Sasaki, Shunichi; et al.
Nuclear Fusion, 51(8), p.083049_1 - 083049_8, 2011/08
Times Cited Count:51 Percentile:88.28(Physics, Fluids & Plasmas)Hydrogen negative ion beams of 490 keV, 3 A and 510 keV, 1 A have been successfully produced in the JT-60 negative ion source with three acceleration stages. These successful productions of the high-energy beams at high current have been achieved by overcoming the most critical issue, i.e., a poor voltage holding of the large negative ion sources with the grids of 2 m for JT-60SA and ITER. To improve voltage holding capability, the breakdown voltages for the large grids was examined for the first time. It was found that a vacuum insulation distance for the large grids was 6-7 times longer than that for the small-area grid (0.02 m
for JT-60SA and ITER. To improve voltage holding capability, the breakdown voltages for the large grids was examined for the first time. It was found that a vacuum insulation distance for the large grids was 6-7 times longer than that for the small-area grid (0.02 m ). From this result, the gap lengths between the grids were tuned in the JT-60 negative ion source. The modification of the ion source also realized a significant stabilization of voltage holding and a short conditioning time. These results suggest a practical use of the large negative ion sources in JT-60SA and ITER.
). From this result, the gap lengths between the grids were tuned in the JT-60 negative ion source. The modification of the ion source also realized a significant stabilization of voltage holding and a short conditioning time. These results suggest a practical use of the large negative ion sources in JT-60SA and ITER.
Kojima, Atsushi; Hanada, Masaya; Tanaka, Yutaka*; Kawai, Mikito*; Akino, Noboru; Kazawa, Minoru; Komata, Masao; Mogaki, Kazuhiko; Usui, Katsutomi; Sasaki, Shunichi; et al.
Proceedings of 23rd IAEA Fusion Energy Conference (FEC 2010) (CD-ROM), 8 Pages, 2011/03
Hydrogen negative ion beams of 490keV, 3A and 510 keV, 1A have been successfully produced in the JT-60 negative ion source with three acceleration stages. These successful productions of the high-energy beams at high current have been achieved by overcoming the most critical issue, i.e., a poor voltage holding of the large negative ion sources with the grids of  2 m
2 m for JT-60SA and ITER. To improve voltage holding capability, the breakdown voltages for the large grids was examined for the first time. It was found that a vacuum insulation distance for the large grids was 6-7 times longer than that for the small-area grid (0.02 m
for JT-60SA and ITER. To improve voltage holding capability, the breakdown voltages for the large grids was examined for the first time. It was found that a vacuum insulation distance for the large grids was 6-7 times longer than that for the small-area grid (0.02 m ). From this result, the gap lengths between the grids were tuned in the JT-60 negative ion source. The modification of the ion source also realized a significant stabilization of voltage holding and a short conditioning time. These results suggest a practical use of the large negative ion sources in JT-60 SA and ITER.
). From this result, the gap lengths between the grids were tuned in the JT-60 negative ion source. The modification of the ion source also realized a significant stabilization of voltage holding and a short conditioning time. These results suggest a practical use of the large negative ion sources in JT-60 SA and ITER.
Kashiwagi, Mieko; Taniguchi, Masaki; Kojima, Atsushi; Dairaku, Masayuki; Hanada, Masaya; Hemsworth, R. S.*; Mizuno, Takatoshi*; Takemoto, Jumpei; Tanaka, Masanobu*; Tanaka, Yutaka*; et al.
Proceedings of 23rd IAEA Fusion Energy Conference (FEC 2010) (CD-ROM), 8 Pages, 2011/03
At JAEA, a multi-aperture multi-grid accelerator has been developed for the ITER neutral beam system. A target is H ion beam acceleration of 0.5 A (200 A/m
ion beam acceleration of 0.5 A (200 A/m ) at 1 MeV. In real accelerators, it was found that the voltage holding was about a half of that obtained in an ideal small electrode. After applying necessary gap length and radii of edges of grid supports to lower local electric field concentrations, the accelerator succeeded in sustaining 1 MV for 4000 s. As a result, beam parameters were increased to 879 keV, 0.36 A (157 A/m
) at 1 MeV. In real accelerators, it was found that the voltage holding was about a half of that obtained in an ideal small electrode. After applying necessary gap length and radii of edges of grid supports to lower local electric field concentrations, the accelerator succeeded in sustaining 1 MV for 4000 s. As a result, beam parameters were increased to 879 keV, 0.36 A (157 A/m ) at perveance matched condition from 796 kV, 0.32 A (140 A/m
) at perveance matched condition from 796 kV, 0.32 A (140 A/m ) reported in FEC2008. In the beam acceleration, the beamlet deflections due to magnetic field and space charge repulsion caused direct interceptions, that resulted in limitations in the beam energy and current. Compensation of these beamlet deflections has been tested applying aperture offset and field shaping plate, which were examined in a three-dimensional beam analysis.
) reported in FEC2008. In the beam acceleration, the beamlet deflections due to magnetic field and space charge repulsion caused direct interceptions, that resulted in limitations in the beam energy and current. Compensation of these beamlet deflections has been tested applying aperture offset and field shaping plate, which were examined in a three-dimensional beam analysis.
Iwamoto, Yosuke; Taniguchi, Shingo*; Nakao, Noriaki*; Itoga, Toshio*; Nakamura, Takashi*; Nakane, Yoshihiro; Nakashima, Hiroshi; Satoh, Daiki; Yashima, Hiroshi*; Yamakawa, Hiroshi*; et al.
Proceedings of 8th Specialists' Meeting on Shielding Aspects of Accelerators, Targets and Irradiation Facilities (SATIF-8), p.195 - 203, 2010/03
Neutron energy spectra at 0 degree produced from stopping-length thick graphite, aluminum, iron and lead targets bombarded by 250 MeV and 350 MeV protons were measured at the neutron TOF course at RCNP of Osaka University. The neutron energy spectra were obtained by using the time-of-flight technique in the energy range from 10 MeV to incident proton energy. To compare the experimental results, Monte Carlo calculations by the PHITS and MCNPX codes using the JENDL-HE and the LA150 evaluated nuclear data files were performed. It was found that these calculated results at 0-degree generally underestimated the experimental results for all targets in the energy range above 20 MeV.
 ion beam acceleration in MeV accelerator
ion beam acceleration in MeV acceleratorTaniguchi, Masaki; Mizuno, Takatoshi; Umeda, Naotaka; Kashiwagi, Mieko; Watanabe, Kazuhiro; Tobari, Hiroyuki; Kojima, Atsushi; Tanaka, Yutaka; Dairaku, Masayuki; Hanada, Masaya; et al.
Review of Scientific Instruments, 81(2), p.02B101_1 - 02B101_3, 2010/02
Times Cited Count:7 Percentile:34.64(Instruments & Instrumentation)A Multi-Aperture Multi-Grid (MAMuG) accelerator called "MeV accelerator" has been developed for neutral beam injection (NBI) system of ITER. The MeV accelerator succeeded in accelerating 796 keV, 320 mA H ion beam until 2007. However, pulse length was limited to 0.2 s due to un-cooled grids. In the present work, long pulse H
ion beam until 2007. However, pulse length was limited to 0.2 s due to un-cooled grids. In the present work, long pulse H ion beam acceleration was performed by the MeV accelerator equipped with water-cooled new grids. The H
ion beam acceleration was performed by the MeV accelerator equipped with water-cooled new grids. The H ion current was increased step by step at certain energy with seeding Cs up to the optimum perveance. At present, pulse length was extended to 5 s for 750 keV, 221 mA (perveance match) and maximum power of 1.01 MJ was achieved (650 keV, 163 mA, 10s). At higher energy and current, pulse length was limited by breakdowns between the grids. This was due to high heat load on A3G and GRG grid by deflection of H
ion current was increased step by step at certain energy with seeding Cs up to the optimum perveance. At present, pulse length was extended to 5 s for 750 keV, 221 mA (perveance match) and maximum power of 1.01 MJ was achieved (650 keV, 163 mA, 10s). At higher energy and current, pulse length was limited by breakdowns between the grids. This was due to high heat load on A3G and GRG grid by deflection of H ion beam.
ion beam.
Tanaka, Yutaka; Hanada, Masaya; Kojima, Atsushi; Akino, Noboru; Shimizu, Tatsuo; Oshima, Katsumi; Inoue, Takashi; Watanabe, Kazuhiro; Taniguchi, Masaki; Kashiwagi, Mieko; et al.
Review of Scientific Instruments, 81(2), p.02A719_1 - 02A719_3, 2010/02
Times Cited Count:4 Percentile:22.78(Instruments & Instrumentation)The JT-60U negative ion source is required to produce 44 A of 500 keV D ion beams for the JT-60SA. So far, acceleration voltage of 450 kV was achieved without beam acceleration and 416 kV with beam acceleration. These are lower than the rated voltage for JT-60SA due to vacuum breakdowns. To examine the cause of vacuum breakdown, the complicated structure of the accelerator was modeled for the calculation of electric field inside the accelerator. At the corners of the grid support flanges, the electric fields are locally concentrated to be 5.2-5.5 kV/mm. This is higher than other parts of the accelerator where the averaged field is around 3 kV/mm. To reduce the concentrated electric field, the support structures were modified to extend the gap lengths between grids. By repeating the high-voltage application of 3 s pulses, the applied voltage was increased. After 15 hours of conditioning, the accelerator sustained its rated value of 500 kV without beam acceleration.
ion beams for the JT-60SA. So far, acceleration voltage of 450 kV was achieved without beam acceleration and 416 kV with beam acceleration. These are lower than the rated voltage for JT-60SA due to vacuum breakdowns. To examine the cause of vacuum breakdown, the complicated structure of the accelerator was modeled for the calculation of electric field inside the accelerator. At the corners of the grid support flanges, the electric fields are locally concentrated to be 5.2-5.5 kV/mm. This is higher than other parts of the accelerator where the averaged field is around 3 kV/mm. To reduce the concentrated electric field, the support structures were modified to extend the gap lengths between grids. By repeating the high-voltage application of 3 s pulses, the applied voltage was increased. After 15 hours of conditioning, the accelerator sustained its rated value of 500 kV without beam acceleration.