Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Kataoka, Noriyuki*; Tanaka, Masashi*; Hosoda, Wataru*; Taniguchi, Takumi*; Fujimori, Shinichi; Wakita, Takanori*; Muraoka, Yuji*; Yokoya, Takashi*
Journal of Physics; Condensed Matter, 33(3), p.035501_1 - 035501_6, 2021/01
Times Cited Count:4 Percentile:33.7(Physics, Condensed Matter) Si
Si single crystal grown by the flux method
single crystal grown by the flux methodTakeuchi, Tetsuya*; Haga, Yoshinori; Taniguchi, Toshifumi*; Iha, Wataru*; Ashitomi, Yosuke*; Yara, Tomoyuki*; Kida, Takanori*; Tahara, Taimu*; Hagiwara, Masayuki*; Nakashima, Miho*; et al.
Journal of the Physical Society of Japan, 89(3), p.034705_1 - 034705_15, 2020/03
Times Cited Count:0 Percentile:0(Physics, Multidisciplinary) SR study of an layered organic superconductor
SR study of an layered organic superconductor  -(BEDT-TTF)
-(BEDT-TTF) Hg
Hg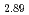 Br
Br
Sato, Kazuhiko*; Fujita, Hidemi*; Katayama, Kazuhiro*; Taniguchi, Hiromi*; Ito, Takashi; Oishi, Kazuki*; Higemoto, Wataru
Physica B; Condensed Matter, 404(5-7), p.597 - 599, 2009/04
Times Cited Count:4 Percentile:21.33(Physics, Condensed Matter)Zero-field muon spin relaxation and high-field transverse muon spin rotation have been measured for an organic superconductor  -(BEDT-TTF)
-(BEDT-TTF) Hg
Hg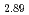 Br
Br . No anomaly is found in zero-field relaxation spectrum at the superconducting transition temperature, 4.2 K. The muon Knight shift determined by transverse muon spin rotation at 6 T exhibits Curie-Weiss like behavior down to 2 K, whereas static magnetic susceptibility shows a peak around 30 K. The muon Knight shift does not scale with the magnetic susceptibility at low temperatures.
. No anomaly is found in zero-field relaxation spectrum at the superconducting transition temperature, 4.2 K. The muon Knight shift determined by transverse muon spin rotation at 6 T exhibits Curie-Weiss like behavior down to 2 K, whereas static magnetic susceptibility shows a peak around 30 K. The muon Knight shift does not scale with the magnetic susceptibility at low temperatures.
 SR study of organic antiferromagnet
SR study of organic antiferromagnet  '-(BEDT-TTF)
'-(BEDT-TTF) ICl
ICl under high pressure
under high pressureSato, Kazuhiko*; Sato, Koichi*; Yoshida, Tetsushige*; Taniguchi, Hiromi*; Goko, Tatsuro*; Ito, Takashi; Oishi, Kazuki*; Higemoto, Wataru
Physica B; Condensed Matter, 404(5-7), p.600 - 602, 2009/04
Times Cited Count:3 Percentile:16.82(Physics, Condensed Matter)Zero-field muon spin relaxation was measured for organic antiferromagnet  '-(BEDT-TTF)
'-(BEDT-TTF) ICl
ICl under high pressure of up to 1.37 GPa. Neel temperature, which is 22 K at ambient pressure, increases with increasing pressure and becomes approximately 48 K at 1.37 GPa. Muon precession frequency at 1.37 GPa, becomes about 5 times larger than that at ambient pressure.
under high pressure of up to 1.37 GPa. Neel temperature, which is 22 K at ambient pressure, increases with increasing pressure and becomes approximately 48 K at 1.37 GPa. Muon precession frequency at 1.37 GPa, becomes about 5 times larger than that at ambient pressure.
 SR study of an antiferromagnetic insulator (BEDT-TTF)(TCNQ)
SR study of an antiferromagnetic insulator (BEDT-TTF)(TCNQ)Sato, Kazuhiko*; Fujita, Hidemi*; Sato, Ryosuke*; Taniguchi, Hiromi*; Higemoto, Wataru
Physica B; Condensed Matter, 374-375, p.102 - 105, 2006/03
Times Cited Count:3 Percentile:17.99(Physics, Condensed Matter)Zero-field  SR measurements for an antiferromagnetic Mott insulator (BEDT-TTF)(TCNQ) were performed in order to study the microscopic magnetic properties of this organics. Slight increase of the relaxation rate is observed below 20K owing to the antiferromagnetic ordering of BEDT-TTF dimers, whereas clear muon precession signal is observed below 3K owing to the antiferromagnetic ordering of TCNQ. Below 3K, there exist at least two antiferromagnetic domains whose volume fractions changes with temperature.
SR measurements for an antiferromagnetic Mott insulator (BEDT-TTF)(TCNQ) were performed in order to study the microscopic magnetic properties of this organics. Slight increase of the relaxation rate is observed below 20K owing to the antiferromagnetic ordering of BEDT-TTF dimers, whereas clear muon precession signal is observed below 3K owing to the antiferromagnetic ordering of TCNQ. Below 3K, there exist at least two antiferromagnetic domains whose volume fractions changes with temperature.
 SR study of an antiferromagnetic Mott insulator
SR study of an antiferromagnetic Mott insulator 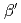 -(BEDT-TTF)
-(BEDT-TTF) ICl
ICl
Sato, Kazuhiko*; Taniguchi, Hiromi*; Kawamoto, Atsushi*; Higemoto, Wataru
Physica B; Condensed Matter, 374-375, p.99 - 101, 2006/03
Times Cited Count:5 Percentile:27.22(Physics, Condensed Matter)Zero-field  SR measurements on the antiferromagnetic Mott insulator
SR measurements on the antiferromagnetic Mott insulator 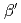 -(BEDT-TTF)
-(BEDT-TTF) ICl
ICl were performed in order to study themicroscopic magnetic properties of this organics. The volume fraction of the antiferromagnetic phase was found to be temperature independent. Muon precession frequency, which is proportional to the magnitude of the magnetic moment at the dimer of two BEDTTTF molecules, does not follow the simple model based on the mean-field approximation.
were performed in order to study themicroscopic magnetic properties of this organics. The volume fraction of the antiferromagnetic phase was found to be temperature independent. Muon precession frequency, which is proportional to the magnitude of the magnetic moment at the dimer of two BEDTTTF molecules, does not follow the simple model based on the mean-field approximation.
Utsumi, Wataru; Saito, Hiroyuki; Taniguchi, Takashi*; Aoki, Katsutoshi
Oyo Butsuri, 74(5), p.593 - 596, 2005/05
New method of the single crystal growth of GaN is introduced, which is based on the slow cooling of its melt under high pressure. Applying high pressures above 6 GPa prevented decomposition into Ga and nitrogen and allowed the congruent melt of GaN at high temperature. Using a large volume high pressure-temperature apparatus, high quality single crystals of GaN were successfully synthesized. This technique is also applied for the synthesis of other nitride crystals such as AlN-GaN alloy and InN.
 X-ray diffraction of graphite-diamond transformation using various catalysts under high pressures and high temperatures
X-ray diffraction of graphite-diamond transformation using various catalysts under high pressures and high temperaturesUtsumi, Wataru; Okada, Taku; Taniguchi, Takashi*; Funakoshi, Kenichi*; Kikegawa, Takumi*; Hamaya, Nozomu; Shimomura, Osamu
Journal of Physics; Condensed Matter, 16(14), p.S1017 - S1026, 2004/04
Times Cited Count:14 Percentile:54(Physics, Condensed Matter)The graphite-diamond transformation was investigated using in-situ time-resolved X-ray diffraction experiments with a MgO dissolved aqueous fluid as the diamond forming catalyst under conditions of 6.6-8.8 GPa and 1400-1835 C. Experiments were conducted using a 180-ton DIA-type cubic-anvil apparatus installed on the beamline BL14B1 at SPring-8, a third-generation synchrotron radiation facility in Japan. By analyzing the kinetic data using the JMAK rate equation, it was clarified that altering the pressure-temperature conditions drastically changes the nucleation and growth process of diamond.
C. Experiments were conducted using a 180-ton DIA-type cubic-anvil apparatus installed on the beamline BL14B1 at SPring-8, a third-generation synchrotron radiation facility in Japan. By analyzing the kinetic data using the JMAK rate equation, it was clarified that altering the pressure-temperature conditions drastically changes the nucleation and growth process of diamond.
Shimizu, Hiroyasu*; Utsumi, Wataru; Kume, Tetsuji*; Kondo, Tadashi*; Shimizu, Katsuya*; Sotani, Tomohiro*; Taniguchi, Takashi*; Nakamura, Kazutaka*
Koatsuryoku No Kagaku To Gijutsu, 11(4), p.334 - 338, 2001/12
no abstracts in English
Chijimatsu, Masakazu*; Taniguchi, Wataru; Suzuki, Hideaki*; Nishigaki, Makoto*
Doboku Gakkai Rombunshu, (687), p.9 - 25, 2001/09
None
Chijimatsu, Masakazu*; Fujita, Tomoo; Sugita, Yutaka; Taniguchi, Wataru
JNC TN8400 2000-008, 339 Pages, 2000/01
Geological disposal of high-level radioactive waste (HLW) in Japan is based on a multibarrier system composed of engineered and natural barriers. The engineered barriers are composed of vitrified waste confined within a canister, overpack and buffer material. Highly compacted bentonite clay is considered one of the most promising candidate buffer material mainly because of its low hydraulic conductivity and high adsorption capacity of radionuclides. In a repository for HLW, complex thermal, hydraulic and mechanical (T-H-M) phenomena will take place, involving the interactive processes between radioactive decay heat from the vitrified waste, infiltration of ground water and stress generation due to the earth pressure, the thermal loading and the swelling pressure of the buffer material. In order to evaluate the performance of the buffer material, the coupled T-H-M behaviors within the compacted bentonite have to be modelled. Before establishing a fully coupled T-H-M model, the mechanism of each single Phenomenon or partially coupled phenomena should be identified. Furthermore, in order to evaluate the coupled T-H-M phenomena, the analysis model was developed physically and numerically and the adequacy and the applicability was tested though the engineered scale laboratory test and in-situ test. In this report, the investigative results for the development of coupled T-H-M model were described. This report consists of eight chapters. In Chapter l, the necessity of coupled T-H-M model in the geological disposal project of the high-level radioactive waste was described. In Chapter 2, the laboratory test results of the rock sample and the buffer material for the coupled T-H-M analysis were shown. The rock samples were obtained from the in-situ experimental site at Kamaishi mine. As the buffer material, bentonite clay (Kunigel V1 and Kunigel OT-9607) and bentonite-sand mixture were used. In Chapter 3, in-situ tests to obtain the rock property were shown. As ...
Sugino, Hiroyuki; Fujita, Tomoo; Taniguchi, Wataru; Iwasa, Kengo; Hasegawa, Hiroshi
JNC TN8400 99-096, 23 Pages, 1999/12
The Japan Nuclear Cycle Development Institute (JNC) has prepared a second progress report (entitled H12) on research and development for geological disposal of high-level waste (HLW) in Japan. H12 report consist of a Project Overview Report and three Supporting Reports which cover the three major fields described in the AEC Guidelines: (1)evaluation of the geological environment, (2)repository design and engineering technology, (3)performance assessment. This report is prepared to explain background information of buffer design which is descried in Supporting Report 2 (Repository Design and Engineering Technology). In buffer design of H12 report, the design requirements of the buffer are assumed and the relationship between buffer thickness and density was shown corresponding design requirement as an area map. This report describes the background information such as the numerical formulations, assumptions, engineering judgement and so on.
Taniguchi, Wataru; Suzuki, Hideaki*; Sugino, Hiroyuki*; Matsumoto, Kazuhiro*; Chijimatsu, Masakazu*; Shibata, Masahiro
JNC TN8400 99-052, 73 Pages, 1999/12
For the buffer of geological disposal of High-level radioactive waste (HLW) in Japan, it is expected to maintain its low water permeability, self-sealing properties, radionuclides adsorption retardation properties, thermal conductivity, etc. It is considered that compacted bentonite or a compacted sand-mixtured bentonite that satisfy many of the expected properties mentioned above are superior. JNC (Japan Nuclear Fuel Development Corporation) has studied the measurement method for the properties of buffer and measured to use the measurement results for the design and performance assessment analysis. Also, we have conducted the design of engineered barrier and underground facility based on assuming geological condition. For the design of engineered barrier and underground facility, high thermal conductivity of buffer is design requirement to avoid mineralogical alternation. Also, the design is not conducted using the density of buffer less than the bulk density (powder-mass density). Therefore, the bulk density (powder-mass density) is one of the design requirements. In this report, the thermal properties and the bulk density (powder-mass density) of the buffer material is measured. Then thermal analysis in the near field is conducted using the measurement results, and we studied the relationships between the dry density, sand-mixtured ratio, water content and thickness of the buffer to satisfy the design requirement from the view point of thermal condition, based on the temperature constraint of the buffer.
Sato, Toshinori; Taniguchi, Wataru; Fujita, Tomoo; Hasegawa, Hiroshi
JNC TN7400 99-011, 36 Pages, 1999/12
In order to understand the general thermal and mechanical properties of rock masses and initial stress of rock at depth, data were compiled from the published literature in Japan and collected from investigations carried out at Kamaishi mine and Tono mine. Statistical examinations derived the ranges, means and medians of the mechanical properties for the different rock types. It was confirmed that the correlations between the mechanical properties were in agreement with correlations determined previously in other similar surveys. The unconfined compressive strength of Neogene sedimentary rocks showed a tendency to increase with increasing depth ( 500 m). An examination of the measured initial stress data collected through literature surveys showed that the vertical stress can be approximated by the extent of gravitational loading at a particular point. There is an approximately linear relationship between the average stress in a horizontal plane and the depth. The lateral pressure coefficient tends to have a high value and large range at shallow depths, but tends towards
500 m). An examination of the measured initial stress data collected through literature surveys showed that the vertical stress can be approximated by the extent of gravitational loading at a particular point. There is an approximately linear relationship between the average stress in a horizontal plane and the depth. The lateral pressure coefficient tends to have a high value and large range at shallow depths, but tends towards  1 with increasing depth.
1 with increasing depth.
Taniguchi, Wataru; Hasegawa, Hiroshi; Iwasa, Kengo; Sato, Toshinori
JNC TN8400 99-053, 66 Pages, 1999/11
To develop appropriate designs, as well as the manufacture, installation and construction technologies for the engineered barrier system and disposal facilities, it is necessary to evaluate physical properties of the rock mass that relate to mechanical stability analysis, thermal analysis, and seismic analysis (hereinafter referred to as "mechanical properties", "thermal properties", and "dynamic properties"). Since H3 Report, these physical properties have been broadly collected from the open literature, including field measurement data, as well as in-situ data obtained in the Tono area and at the Kamaishi Mine, in order to obtain more reliable data and to promote understanding of the deep geological environment for the purpose of design. These collected data have been added to databases on rock properties developed in H3. Thus, this report contains the upgraded databases on rocks, which include the features from a wide range of geological environments in Japan. In this report, rock types are classified into groups that have equivalent properties from the viewpoint of engineering, based on these databases of rocks. Then, design values of physical properties for the classified rock groups are determined by considering the correlation between each physical property. To date, the mechanical properties and thermal properties have been generally treated separately from each other. Here, the mechanical properties and thermal properties are determined by applying relationships between effective porosity and both mechanical and thermal properties. For the mechanical properties and dynamic properties, depth dependence are also taken into consideration.
Taniguchi, Wataru; Iwasa, Kengo
JNC TN8400 99-051, 129 Pages, 1999/11
For the underground facility of the geological disposal of high-level radioactive waste (HLW), the space is needed to set the engineered barrier, and the set engineered barrier and rock-mass of near field are needed to satisfy some conditions or constraints for their performance. One of the conditions above mentioned is thermal condition arising from heat outputs of vitrified waste and initial temperature at the disposal depth. Hence, it is needed that the temperature of the engineered barrier and rock mass is less degree than the constraint temperature of each other. Therefore, the design of engineered barrier and underground facility is conducted so that the temperature of the engineered barrier and rock mass is less degree than the constraint temperature of each other. One of these design is establishment of the disposal tunnel spacing and waste package pitch. In this report, thermal analysis is conducted to establish the disposal tunnel spacing and waste package pitch to satisfy the constraint temperature in the near field. Also, other conditions or constraints for establishment of the disposal tunnel spacing and waste package pitch are investigated. Then, design of the disposal tunnel spacing and waste package pitch, considering these conditions or constraints, is conducted. For the near field configuration using the results of the design above mentioned, the temperature with time dependency is studied by analysis, and then the temperature variation due to the gaps, that will occur within the engineered barrier and between the engineered barrier and rock mass in setting engineered barrier in the disposal tunnel or pit, is studied. At last, the disposal depth variation is studied to satisfy the temperature constraint in the near field.
Takachi, Kazuhiko; Taniguchi, Wataru
JNC TN8400 99-042, 68 Pages, 1999/11
The buffer material is expected to maintain its low water permeability, self-sealing properties, radionuclides adsorption and retardation properties, thermal conductivity, chemical buffering properties, overpack supporting properties, stress buffering properties, etc. over a long period of time. Natural clay is mentioned as a material that can relatively satisfy above. Among the kinds of natural clay, bentonite when compacted is superior because (1)it has exceptionally low water permeability and properties to control the movement of water in buffer, (2)it fills void spaces in the buffer and fractures in the host rock as it swells upon water uptake, (3)it has the ability to exchange cations and to adsorb cationic radioelements. In order to confirm these functions for the purpose of safety assessment, it is necessary to evaluate buffer properties through laboratory tests and engineering-scale tests, and to make assessments based on the ranges in the data obtained. This report describes the procedures, test conditions, results and examinations on the buffer material of dynamic triaxial tests, measurement of elastic wave velocity and liquefaction tests that aim at getting hold of dynamic mechanical properties. MWe can get hold of dependency on the shearing strain of the shearing modulus and hysteresis damping constant, the application for the mechanical model etc. by dynamic triaxial tests, the acceptability of maximum shearing modulus obtained from dynamic triaxial tests etc. by measurement of elastic wave velocity and dynamic strength caused by cyclic stress etc. by liquefaction tests.
; Taniguchi, Wataru; Koo, Shigeru*; Hasegawa, Hiroshi; Sugino, Hiroyuki; Kubota, Shigeru*; Dewa, Katsuyuki*
JNC TN8400 99-037, 281 Pages, 1999/11
It is planned to construct the tunnels and emplace waste packages at several hundred meters to 1,000 meters under the ground for the repository of high-level radioactive waste based on a policy to assure the safe life environment. It is required to be mechanically stable for the tunnels to assure the work safety throughout the construction, operation and closure phase. In this report, the mechanical stability of tunnels, that is a factor of design requisites, was evaluated by the analyses to present an outline of the technical reliability of geological disposal. To put it concretely, the tunnel sections were determined to have the required areas and shapes, and the analyses on the mechanical stability at tunnel excavations and earthquake, at tunnel intersections were conducted by the theoretical analysis and finite element method. The results obtained by these investigations are shown below: (1)It will be able to construct the tunnels with present techniques. The mechanical stability of tunnels will be assured if proper supports are given, and adequate tunnel spacing and disposal-pit pitches are set. (2)The mechanical stability will be assured at the tunnels intersections if proper reinforcement measures are taken. The reinforcement will be required for the intersection areas over the distance of 1D (D: diameter of tunnels) on the obtuse angle side, and 4D on the acute angle side, when intersection angle is set at 30 degrees. (3)The investigations were conducted on the assumption that the experienced big earthquake occurred. The results show that the effect of earthquake on the mechanical stability of tunnels is small, and tunnels are stable at the earthquake when the mechanical stability at tunnel excavations is assured.
Taniguchi, Wataru; Takachi, Kazuhiko; *; Mori, Koji*
JNC TN8400 99-055, 168 Pages, 1999/09
In Japan, where many earthquakes have been occurring, it's very important to evaluate aseismatic mechanical stability of the engineered barrier system (EBS) of high-level radioactive waste (HLW) repository. In this study as a cooperative project of JNC with National Research Institute for Earth Science and Disaster Prevention Science and Technology Agency, that started from 1992, aseismatic mechanical stability of the EBS of HLW repository have been evaluated based on the engineering scale vibration test of the engineered barrier and the analytical methods. In this report, the results of the engineering scale vibration test of the engineered barrier and the development of the analytical computer code for seismic response of the engineered barriers are described, following Study of Vibration Behavior Deep Underground Cavity and Internal Structure (1). From this study, the following conclusions are obtained (1)Engineering scale vibration test of engineered barrier. From the results of sweep wave vibration tests conducted to examine the effect of natural frequency of the EBS, the natural frequency of the EBS tends to decrease as the acceleration increases. From the results of vibration tests with the actual seismic waves characteristics, both of the simulated overpack and the buffer have no significant response against seismic and then simulated engineered barriers behave dynamically as a rigid body. (2)Development of the analytical computer code for seismic response of the engineered barrier. The analytical computer code has been developed considering the non-linear dynamic properties of the buffer material between stress and strain. verification analysis results for the engineering scale vibration test of the engineered barrier mentioned above, using the analytical computer code, agree with vibration test of the engineered barrier.
Taniguchi, Wataru; Takachi, Kazuhiko; Sugino, Hiroyuki; Mori, Koji*
JNC TN8400 99-054, 140 Pages, 1999/09
For the buffer material of geological disposal of high-level radioactive waste (HLW) in Japan, it is considered to use a compacted bentonite or a compacted sand-mixture bentonite that is one kind of clay. The buffer material is expected to maintain long-term mechanical stability, to hold the waste in designated place, and to avoid the effects on the radionuclides migration. It is considered that the cyclic load due to seismic activities affects long-term mechanical stability in Japan, where many earthquakes have been occurring. In this report, aseismic mechanical stability of engineered barrier of HLW is studied by dynamic analysis based on equation of vibration, mainly in the view point of mechanical stability of the buffer. The analytical computer code that has been developed by JNC in cooperative project with National Research Institute for Earth Science and Disaster Prevention Science and Technology Agency is used in this study. Seismic wave at the disposal depth in the assumed geological environment is established by multiple reflection theory analysis, and then seismic wave at the disposal depth is used for the aseismic mechanical stability analysis. For the aseismic mechanical stability, total stress analyses (single-phase system) with the target field of near field are conducted to evaluate the shear failure of the buffer, the displacement of overpack, and vibrational behavior of the engineered barrier, and then effective stress analyses (two-phase system) with the target field of the engineered barrier are conducted to evaluate excursion in the pore water pressure within the buffer (i. e. liquefaction), concerning the non-linear dynamic properties of the buffer material. From the results, the following conclusions are obtained. (1)From the results of the total stress analyses, it is confirmed that the buffer must not reach a shear failure condition from the stresses caused by an earthquake and the overpack must not move significantly due to the ...