Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Shiga, Motoyuki; Thomsen, B.; Kimizuka, Hajime*
Physical Review B, 109(5), p.054303_1 - 054303_12, 2024/02
Inelastic neutron scattering spectra of hydrogen in palladium were calculated considering nuclear quantum effects at finite temperatures. A computational method combining semiclassical molecular dynamics based on path integrals and machine learning potentials was used. The calculated spectra agree well with the experimental spectra with respect to the positions and intensities of the peaks corresponding to the fundamental and first harmonic of the vibrational excitation of hydrogen atoms. Comparison with classical molecular dynamics shows that nuclear quantum effects play an essential role in the inelastic neutron scattering spectra.
Shiga, Motoyuki; Thomsen, B.; Nagai, Yuki
Ansanburu, 25(4), p.303 - 310, 2023/10
The parallel molecular simulation software "PIMD" will be presented. The use of PIMD will be explained through specific examples such as water structure by ab initio path integral molecular dynamics, quantum diffusion of hydrogen in metal by ring polymer molecular dynamics, machine learning potential generation and phonon properties of superconductors, and polyalcohol dehydration reaction by metadynamics.
Kimizuka, Hajime*; Thomsen, B.; Shiga, Motoyuki
Journal of Physics; Energy (Internet), 4(3), p.034004_1 - 034004_13, 2022/07
Times Cited Count:9 Percentile:73.15(Energy & Fuels)Artificial neural network-based interatomic potential for a system of palladium and hydrogen was developed, and path integral molecular dynamics simulations were performed to study the quantum diffusion of hydrogen isotopes in palladium crystals. Diffusion coefficients of light and heavy hydrogen were calculated over a wide temperature range of 50-1500 K to clarify the difference in diffusion mechanisms at low and high temperatures.
 path integral simulations
path integral simulationsThomsen, B.; Shiga, Motoyuki
Physical Chemistry Chemical Physics, 24(18), p.10851 - 10859, 2022/05
Times Cited Count:2 Percentile:32.24(Chemistry, Physical) study of nuclear quantum effects on sub- and supercritical water
study of nuclear quantum effects on sub- and supercritical waterThomsen, B.; Shiga, Motoyuki
Journal of Chemical Physics, 155(19), p.194107_1 - 194107_11, 2021/11
Times Cited Count:6 Percentile:50.99(Chemistry, Physical) path integral molecular dynamics
path integral molecular dynamicsThomsen, B.; Shiga, Motoyuki
Journal of Chemical Physics, 154(8), p.084117_1 - 084117_10, 2021/02
Times Cited Count:8 Percentile:62.77(Chemistry, Physical)In this study we investigate the nuclear quantum effects on the acidity constant of liquid water isotopologues at the ambient condition by  path integral molecular dynamics simulations. This technique not only reproduces the acidity constants of liquid D
path integral molecular dynamics simulations. This technique not only reproduces the acidity constants of liquid D O experimentally measured but also allows for a theoretical prediction of the acidity constants of liquid T
O experimentally measured but also allows for a theoretical prediction of the acidity constants of liquid T O, aqueous HDO and HTO, which are unknown due to its scarcity. The results indicate that the nuclear quantum effects play an indispensable role in the absolute determination of acidity constants.
O, aqueous HDO and HTO, which are unknown due to its scarcity. The results indicate that the nuclear quantum effects play an indispensable role in the absolute determination of acidity constants.
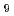 O
O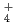 Infra-Red spectrum through clustering of path integral molecular dynamics trajectories
Infra-Red spectrum through clustering of path integral molecular dynamics trajectoriesThomsen, B.; Shiga, Motoyuki
no journal, ,
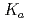 (H
(H O) and p
O) and p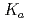 (D
(D O) using path integral molecular dynamics
O) using path integral molecular dynamicsThomsen, B.; Shiga, Motoyuki
no journal, ,
Thomsen, B.; Shiga, Motoyuki
no journal, ,
Thomsen, B.; Shiga, Motoyuki
no journal, ,
Thomsen, B.; Shiga, Motoyuki
no journal, ,
Thomsen, B.; Shiga, Motoyuki
no journal, ,
Thomsen, B.; Shiga, Motoyuki
no journal, ,
Thomsen, B.; Shiga, Motoyuki
no journal, ,
Path integral molecular dynamics (PIMD) and related methods, based on the Feynman path formulation of quantum mechanics, offer a direct way of modelling nuclear quantum effects in bulk phase materials. Each timestep of these methods does however require the evaluation of several electronic structure energies, gradients and stress vectors at the ab initio level. They are thus very computationally expensive to pursue at the ab initio level. Recently machine learned potentials (MLPs) have been suggested as a way to bring down the cost and allow long time dynamics to be studied with ab initio accuracy for PIMD methods. In this presentation we present the results of studying hydrogen diffusion in Palladium metal across several temperatures. We will also discuss our ongoing efforts to apply MLPs to PIMD studies of water and its isotopologues.
Thomsen, B.; Shiga, Motoyuki
no journal, ,
We report our ongoing efforts to investigate how nuclear quantum effects (NQEs) influence the structure and dynamics properties of water. To model the NQEs we employ path integral molecular dynamics (PIMD), this does however require several ab initio calculations to be performed in each timestep to model the NQEs. In order to make the simulations more computationally affordable, we are currently working to describe the system using a machine learned potential (MLP). This MLP should be transferable across the isotopologues of water, and work across the phase diagram of water. We will here give an update on our ongoing work to improve the MLP description of water, and the results of PIMD simulations using this MLP.
Thomsen, B.; Shiga, Motoyuki
no journal, ,
Water is a liquid which structure and properties are highly influenced by nuclear quantum effects (NQEs), as evidenced by the observed differences between light (H O) and heavy (D
O) and heavy (D O) water. These differences are in theory revealed by conducting so called path integral molecular dynamics (PIMD) simulations. In the past we have used ab initio DFT based potentials to conduct such studies, which come with a large computational cost. We will here use machine learned potentials (MLPs) in place of DFT in order to reduce the computational cost and allow longer and more converged simulations of light and heavy water.
O) water. These differences are in theory revealed by conducting so called path integral molecular dynamics (PIMD) simulations. In the past we have used ab initio DFT based potentials to conduct such studies, which come with a large computational cost. We will here use machine learned potentials (MLPs) in place of DFT in order to reduce the computational cost and allow longer and more converged simulations of light and heavy water.