Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
 O
O with electrochemical Li
with electrochemical Li intercalation
intercalationMurase, Satoshi*; Yoshikawa, Yumi*; Fujiwara, Kosuke*; Fukada, Yukimasa*; Teranishi, Takashi*; Kano, Jun*; Fujii, Tatsuo*; Inada, Yasuhiro*; Katayama, Misaki*; Yoshii, Kenji; et al.
Journal of Physics and Chemistry of Solids, 162, p.110468_1 - 110468_6, 2022/03
Times Cited Count:0 Percentile:0(Chemistry, Multidisciplinary)We report a trial of the valence control for mixed valence iron triangular oxide YbFe O
O in order to develop an effective technique to control the frustration of charges in strongly correlated electron systems. The electro-chemical doping of Li
in order to develop an effective technique to control the frustration of charges in strongly correlated electron systems. The electro-chemical doping of Li into YbFe
into YbFe O
O was examined on the cell type sample similar to the Li-ion secondary battery cell. Systematic change of the lattice constant, Fe-Fe and Fe-Yb distance were observed with Li doping. Maximum value of the doping was over 300 mAh/g. An EXAFS experiment indicated that Li positioned between Yb octahedron layer (U-layer) and Fe-bipyramidal layer (W-layer). However, detailed change of iron valence state of YbFe
was examined on the cell type sample similar to the Li-ion secondary battery cell. Systematic change of the lattice constant, Fe-Fe and Fe-Yb distance were observed with Li doping. Maximum value of the doping was over 300 mAh/g. An EXAFS experiment indicated that Li positioned between Yb octahedron layer (U-layer) and Fe-bipyramidal layer (W-layer). However, detailed change of iron valence state of YbFe O
O was not clearly observed because of the superimpose of the signal from iron metal nano particles in XANES observation. The results indicate that the electrochemical method might be one of the potential technique to control the frustration of charges in YbFe
was not clearly observed because of the superimpose of the signal from iron metal nano particles in XANES observation. The results indicate that the electrochemical method might be one of the potential technique to control the frustration of charges in YbFe O
O .
.
Inagawa, Jun; Kitatsuji, Yoshihiro; Otobe, Haruyoshi; Nakada, Masami; Takano, Masahide; Akie, Hiroshi; Shimizu, Osamu; Komuro, Michiyasu; Oura, Hirofumi*; Nagai, Isao*; et al.
JAEA-Technology 2021-001, 144 Pages, 2021/08
Plutonium Research Building No.1 (Pu1) was qualified as a facility to decommission, and preparatory operations for decommission were worked by the research groups users and the facility managers of Pu1. The operation of transportation of whole nuclear materials in Pu1 to Back-end Cycle Key Element Research Facility (BECKY) completed at Dec. 2020. In the operation included evaluation of criticality safety for changing permission of the license for use nuclear fuel materials in BECKY, cask of the transportation, the registration request of the cask at the institute, the test transportation, formulation of plan for whole nuclear materials transportation, and the main transportation. This report circumstantially shows all of those process to help prospective decommission.
Suzuki, Shintaro*; Takubo, Ko*; Kuga, Kentaro*; Higemoto, Wataru; Ito, Takashi; Tomita, Takahiro*; Shimura, Yasumichi*; Matsumoto, Yosuke*; Bareille, C.*; Wadachi, Hiroki*; et al.
Physical Review Research (Internet), 3(2), p.023140_1 - 023140_12, 2021/05
We report our experimental discovery of the transition temperature reaching 20 K in a Yb-based compound at ambient pressure. The Mn substitution at the Al site in an intermediate valence state of  -YbAlB
-YbAlB not only induces antiferromagnetic transition at a record high temperature of 20 K but also transforms the heavy-fermion liquid state in
not only induces antiferromagnetic transition at a record high temperature of 20 K but also transforms the heavy-fermion liquid state in  -YbAlB
-YbAlB into a highly resistive metallic state proximate to a Kondo insulator.
into a highly resistive metallic state proximate to a Kondo insulator.
Segawa, Yukari; Horita, Takuma; Kitatsuji, Yoshihiro; Kumagai, Yuta; Aoyagi, Noboru; Nakada, Masami; Otobe, Haruyoshi; Tamura, Yukito*; Okamoto, Hisato; Otomo, Takashi; et al.
JAEA-Technology 2016-039, 64 Pages, 2017/03
The laboratory building No.1 for the plutonium research program (Bldg. Pu1) was chosen as one of the facilities to decommission by Japan Atomic Energy Agency Reform in September, 2013. The research groups, users of Bldg. Pu1, were driven by necessity to remove used equipment and transport nuclear fuel to other facilities from Bldg. Pu1. Research Group for Radiochemistry proactively established the Used Equipment Removal Team for the smooth operation of the removal in April, 2015. The team classified six types of work into the nature of the operation, removal of used equipment, disposal of chemicals, stabilization of mercury, stabilization of nuclear fuel, transportation of nuclear fuel and radioisotope, and survey of contamination status inside the glove boxes. These works were completed in December, 2015. This report circumstantially shows six works process, with the exception of the approval of the changes on the usage of nuclear fuel in Bldg. Pu1 to help prospective decommission.
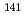 Pr nuclear spin dynamics associated with antiferroquadrupolar order in PrV
Pr nuclear spin dynamics associated with antiferroquadrupolar order in PrV Al
Al
Ito, Takashi; Higemoto, Wataru; Sakai, Akito*; Nakatsuji, Satoru*; Tsujimoto, Masaki*
Physical Review B, 92(12), p.125151_1 - 125151_5, 2015/09
Times Cited Count:5 Percentile:23.78(Materials Science, Multidisciplinary)
 ground quartet systems Sm
ground quartet systems Sm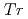
 Al
Al (
(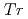 : Ti, V, Cr)
: Ti, V, Cr)Ito, Takashi; Higemoto, Wataru; Ninomiya, Kazuhiko; Sakai, Akito*; Nakatsuji, Satoru*
Journal of the Physical Society of Japan, 81(Suppl.B), p.SB050_1 - SB050_4, 2012/12
Recently, 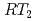 Al
Al compounds (
compounds ( : rare earth,
: rare earth,  : transition metal) have attracted much attention due to interesting physical properties closely related to their caged-structure. Each
: transition metal) have attracted much attention due to interesting physical properties closely related to their caged-structure. Each  ion is confined in a Frank-Kasper cage consisting of 16 Al atoms and the large coordination number leads to strong
ion is confined in a Frank-Kasper cage consisting of 16 Al atoms and the large coordination number leads to strong  -
- hybridization. In addition, the Frank-Kasper cage allows various multipole degrees of freedom for the
hybridization. In addition, the Frank-Kasper cage allows various multipole degrees of freedom for the  -electrons at low
-electrons at low  because of a highly symmetric crystalline-electric-field (CEF). Among the
because of a highly symmetric crystalline-electric-field (CEF). Among the 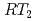 Al
Al series, Pr
series, Pr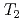 Al
Al (
( : Ti, V) and Sm
: Ti, V) and Sm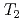 Al
Al (
( : Ti, V, Cr) exhibit both these features. The
: Ti, V, Cr) exhibit both these features. The 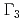 ground doublet systems Pr
ground doublet systems Pr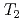 Al
Al (
( : Ti, V) show a phase transition at
: Ti, V) show a phase transition at 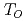 = 2.0K (Ti) and 0.6K (V). The order parameter is believed to be an electric quadrupole active in the
= 2.0K (Ti) and 0.6K (V). The order parameter is believed to be an electric quadrupole active in the 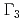 subspace. A possibility of the quadrupole Kondo effect has been discussed based on characteristic
subspace. A possibility of the quadrupole Kondo effect has been discussed based on characteristic  -dependence in specific heat, resistivity, and magnetic susceptibility. The
-dependence in specific heat, resistivity, and magnetic susceptibility. The 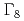 ground quartet systems Sm
ground quartet systems Sm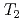 Al
Al (
( : Ti, V, Cr) also exhibit a phase transition at
: Ti, V, Cr) also exhibit a phase transition at 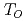 = 6.4K (Ti), 2.3K (V), and 1.8K (Cr). A nuclear specific heat study in SmTi
= 6.4K (Ti), 2.3K (V), and 1.8K (Cr). A nuclear specific heat study in SmTi Al
Al suggests that the primary order parameter is a magnetic dipole in spite of field-insensitive nature of the phase boundary. A possible importance of a secondarily ordered octupole moment was discussed. We here present a microscopic study of PrTi
suggests that the primary order parameter is a magnetic dipole in spite of field-insensitive nature of the phase boundary. A possible importance of a secondarily ordered octupole moment was discussed. We here present a microscopic study of PrTi Al
Al and Sm
and Sm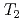 Al
Al (
( : Ti, V, Cr) using muon spin relaxation. In PrTi
: Ti, V, Cr) using muon spin relaxation. In PrTi Al
Al , no additional local field was observed in the ordered phase. This strongly supports the quadrupole ordering scenario. On the other hand, an appearance of a coherent local field was observed below
, no additional local field was observed in the ordered phase. This strongly supports the quadrupole ordering scenario. On the other hand, an appearance of a coherent local field was observed below 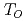 in Sm
in Sm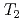 Al
Al . This is consistent with the primary magnetic dipole ordering. The frequency distribution suggests that the magnetic structure is possibly different between the Sm
. This is consistent with the primary magnetic dipole ordering. The frequency distribution suggests that the magnetic structure is possibly different between the Sm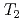 Al
Al compounds.
compounds.
Kobayashi, Shinji*; Nobuto, Jun*; Sugiyama, Hirokazu*; Kusano, Takashi*; Tsuji, Masakuni*; Mikake, Shinichiro; Matsui, Hiroya
Proceedings of European Rock Mechanics Symposium (EUROCK 2012) (CD-ROM), 13 Pages, 2012/05
JAEA (Japan Atomic Energy Agency) has been conducting geoscientific research and development at underground research laboratory under construction, in crystalline rock at Mizunami, Gifu. Considering water treatment expense, the water inflow should be minimized. Although cement grout has been applied to reduce the inflow at 460 m depth at the MIU (Mizunami Underground Research Laboratory), water inflow through narrow fractures which cement grout cannot penetrate might be a problem at deeper underground. Colloidal silica grout, which is liquid-type grout, has high durability as well as good penetrability and is therefore tested at a depth of 300 m. The results indicated that liquid-type grout could sufficiently reduce the hydraulic conductivity of rock mass with less than 1 Lu. In the water pressure resistance test, the ultra-high-pressure packer was set in the pilot hole. The results indicated that liquid-type grout could keep sealing effect even under high water pressures over 9 MPa.
Nakatsuji, Satoru*; Kuga, Kentaro*; Kimura, Kenta*; Satake, Ryuta*; Katayama, Naoyuki*; Nishibori, Eiji*; Sawa, Hiroshi*; Ishii, Rieko*; Hagiwara, Masayuki*; Bridges, F.*; et al.
Science, 336(6081), p.559 - 563, 2012/05
Times Cited Count:114 Percentile:95.24(Multidisciplinary Sciences)Frustrated magnetic materials can remain disordered to the lowest temperatures. Such is the case for Ba CuSb
CuSb O
O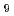 , which is magnetically anisotropic at the atomic scale but curiously isotropic on mesoscopic length and time scales. We find that the frustration on the triangular lattice is imprinted in a nanostructured honeycomb lattice of Cu
, which is magnetically anisotropic at the atomic scale but curiously isotropic on mesoscopic length and time scales. We find that the frustration on the triangular lattice is imprinted in a nanostructured honeycomb lattice of Cu ions that resists a coherent static Jahn-Teller distortion. The resulting two-dimensional random-bond spin-1/2 system on the honeycomb lattice has a broad spectrum of spin-dimer like excitations and low-energy spin degrees of freedom that retain.
ions that resists a coherent static Jahn-Teller distortion. The resulting two-dimensional random-bond spin-1/2 system on the honeycomb lattice has a broad spectrum of spin-dimer like excitations and low-energy spin degrees of freedom that retain.
 SR evidence of nonmagnetic order and
SR evidence of nonmagnetic order and 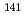 Pr hyperfine-enhanced nuclear magnetism in the cubic
Pr hyperfine-enhanced nuclear magnetism in the cubic 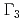 ground doublet system PrTi
ground doublet system PrTi Al
Al
Ito, Takashi; Higemoto, Wataru; Ninomiya, Kazuhiko; Luetkens, H.*; Baines, C.*; Sakai, Akito*; Nakatsuji, Satoru*
Journal of the Physical Society of Japan, 80(11), p.113703_1 - 113703_4, 2011/11
Times Cited Count:30 Percentile:78.75(Physics, Multidisciplinary)Nobuto, Jun*; Tsuji, Masakuni*; Kusano, Takashi*; Mikake, Shinichiro; Kamiya, Akira; Ishii, Yoji
Dai-40-Kai Gamban Rikigaku Ni Kansuru Shimpojiumu Koen Rombunshu (CD-ROM), p.179 - 184, 2011/01
At Mizunami Underground Research Laboratory, the water inflow should be minimized, considering water treatment expense. Although cement grout has been applied to reduce water inflow up to 460 m depth, water inflow through small fractures which cement grout cannot penetrate can not be neglected at deeper underground. Liquid-type grout which has high durability as well as good penetrability was therefore tested at the depth of 300 m. Test results indicated that liquid-type grout could sufficiently reduce hydraulic conductivity of rock mass with less than 1Lu, and could keep improvement effect even after applied water pressure of more than 9 MPa was applied.
Nakanii, Nobuhiko*; Kondo, Kiminori; Yabuuchi, Toshinori*; Tsuji, Kazuki*; Tanaka, Kazuo*; Suzuki, Shinsuke*; Asaka, Takao*; Yanagida, Kenichi*; Hanaki, Hirofumi*; Kobayashi, Takashi*; et al.
Review of Scientific Instruments, 79(6), p.166102_1 - 066102_3, 2008/06
An imaging plate has been used as a useful detector of energetic electrons in laser electron acceleration and laser fusion studies. The absolute sensitivity of an imaging plate was calibrated at 1 GeV electron energy using the injector Linac of SPring-8. The sensitivity curve obtained up to 100 MeV in a previous study was extended successfully to GeV range.
Narushima, Takashi*; Hattori, Takanori; Kinoshita, Tomohiro*; Hinzmann, A*; Tsuji, Kazuhiko*
Physical Review B, 76(10), p.104204_1 - 104204_8, 2007/09
Times Cited Count:25 Percentile:68.43(Materials Science, Multidisciplinary)The structure of liquid Sn was investigated up to 19.4 GPa by synchrotron X-ray diffraction. Upon compression up to about 3-6 GPa, the structural features, which reflect the anisotropic local structure become less prominent; i.e., the hump on the high- side of the first peak in the structure factor
side of the first peak in the structure factor 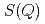 becomes smaller, the position of the second peak relative to that of the first peak in
becomes smaller, the position of the second peak relative to that of the first peak in 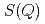 ,
, 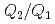 , decreases, and the coordination number, CN, increases. These features indicate that the liquid structure changes toward a simple liquid metal upon compression. However, at higher pressures, the structural parameters nearly unchanged. The parameters in this pressure range are still deviated from their respective values for simple liquid metals. These findings suggest that, contrary to previous expectations, the liquid does not monotonically approach a simple liquid metal, but takes a relatively stable intermediate form with an anisotropic local structure before approaching a simple liquid metal. The high-pressure behavior of liquid Sn is compared to those of liquid Si and liquid Ge and the systematics in liquid group 14 elements are discussed.
, decreases, and the coordination number, CN, increases. These features indicate that the liquid structure changes toward a simple liquid metal upon compression. However, at higher pressures, the structural parameters nearly unchanged. The parameters in this pressure range are still deviated from their respective values for simple liquid metals. These findings suggest that, contrary to previous expectations, the liquid does not monotonically approach a simple liquid metal, but takes a relatively stable intermediate form with an anisotropic local structure before approaching a simple liquid metal. The high-pressure behavior of liquid Sn is compared to those of liquid Si and liquid Ge and the systematics in liquid group 14 elements are discussed.
Hattori, Takanori; Taga, Naohito*; Takasugi, Yukinobu*; Kinoshita, Tomohiro*; Narushima, Takashi*; Tsuji, Kazuhiko*; Kikegawa, Takumi*
Photon Factory Activity Report 2005, Part A, p.42 - 43, 2006/11
no abstracts in English
Hattori, Takanori; Kinoshita, Tomohiro*; Narushima, Takashi*; Tsuji, Kazuhiko*; Katayama, Yoshinori
Physical Review B, 73(5), p.054203_1 - 054203_9, 2006/02
Times Cited Count:23 Percentile:68.23(Materials Science, Multidisciplinary)The structure of liquid CdTe was investigated at pressures up to 23.5GPa using synchrotron X-ray diffraction. The structure factor, S(Q), and the pair distribution function, g(r), drastically change in two pressure regions, 1.8-3.0 GPa and 7.0-9.0 GPa, accompanied with marked increase in the average coordination number, CN. These findings suggest that there exists at least three stable liquid forms below 23.5GPa. The pressure interval of the structural change is much smaller compared to other liquids of tetrahedrally bonded materials. Comparing the shapes of S(Q) and g(r), and other structural parameters with the respective data for the reference materials reveals that the lowest- and intermediate-pressure forms have the same local structures as the crystalline counterpart (zinc-blende-like local structure and a NaCl-like local structure), while the highest-pressure form has a different local structure from that in the crystalline form.
Hara, Akio; Tsuji, Takashi*; Nishimura, Mizue*; Hoshi, Kazuyoshi*; Yagi, Masahiko*; Kawada, Koji*; Hou, J.-Y.*
JAERI-Conf 2005-007, p.270 - 275, 2005/08
Borehole log interpretation methods, which are usually used by petroleum exploration companies, are applied for evaluating heterogeneity of deep underground diatomaceous mudstones in the Horonobe area. Natural  ray log and electrical micro image (EMI) log data were used for the log interpretation. Five sedimentary facies, A to E, were established from the EMI log interpretation. Significant correlations between the sedimentary facies, the chemical contents, the natural
ray log and electrical micro image (EMI) log data were used for the log interpretation. Five sedimentary facies, A to E, were established from the EMI log interpretation. Significant correlations between the sedimentary facies, the chemical contents, the natural  ray level, and the electric conductivity in the diatomaceous mudstone were seen. Spatial distribution of the diatomaceous mudstone, in lithology and thickness, was recognized through borehole correlation, which seems to reflect the sedimentary environment change.
ray level, and the electric conductivity in the diatomaceous mudstone were seen. Spatial distribution of the diatomaceous mudstone, in lithology and thickness, was recognized through borehole correlation, which seems to reflect the sedimentary environment change.
Hara, Akio; Tsuji, Takashi*; Hoshi, Kazuyoshi*; Yagi, Masahiko*; Nishimura, Mizue*; Kawada, Koji*; Hou, J.-Y.*
Program and Abstracts, p.65, P. 65, 2005/02
To evaluate heterogeneity of diatomaceous mudstone in Horonobe area, physical properties and lithofacies of sedimentary rocks have been estimated from natural  ray log data and electrical micro imaging (EMI) log data. Spatial distribution of heterogeneity of sedimentary rocks has been discussed by comparison of log data acquired from several boreholes. Five sedimentary facies, A to E, have been established. Sedimentary facies A and B, which can decipher bedding planes clearly in EMI image, have been developed horizontally with low
ray log data and electrical micro imaging (EMI) log data. Spatial distribution of heterogeneity of sedimentary rocks has been discussed by comparison of log data acquired from several boreholes. Five sedimentary facies, A to E, have been established. Sedimentary facies A and B, which can decipher bedding planes clearly in EMI image, have been developed horizontally with low  ray and high SiO
ray and high SiO contents while sedimentary facies D, bedding planes are not clear to decipher, have been developed horizontally with high
contents while sedimentary facies D, bedding planes are not clear to decipher, have been developed horizontally with high  ray and low SiO
ray and low SiO contents. The results of this study support the estimation of Hara (2004) namely the strata which characterized with high
contents. The results of this study support the estimation of Hara (2004) namely the strata which characterized with high  ray have been high Al
ray have been high Al O
O contents and rich in terrigenous sediments such as clay minerals, on the other hand, the strata characterized with low
contents and rich in terrigenous sediments such as clay minerals, on the other hand, the strata characterized with low  ray have high SiO
ray have high SiO contents and rich in diatomaceous fossils. Layered sedimentary facies can correlate between boreholes based on natural
contents and rich in diatomaceous fossils. Layered sedimentary facies can correlate between boreholes based on natural  ray log and EMI log analysis. Sedimentary system and spatial distribution of strata of Horonobe area can estimate from the results of the facies correlation.
ray log and EMI log analysis. Sedimentary system and spatial distribution of strata of Horonobe area can estimate from the results of the facies correlation.
Hoshi, Kazuyoshi*; Hou, J.-Y.*; Kawada, Koji*; Tsuji, Takashi*; Suwabe, Mizue*
JNC TJ8400 2005-009, 67 Pages, 2005/01
Developing a method to evaluate heterogeneity of sedimentary rocks is very important for a site survey and a property test of the site. We studied siliceous shale from wells in the Horonobe area, and developed a sedimentary process modeling software in order to establish a method to evaluate heterogeneity of sedimentary rocks. Well log analysis of Koetoi and Wakkanai Formations revealed variations of porosity, shale content, and amount of erosion. We correlate marker beds, and establish a compaction curve for siliceous shale in the Horonobe area. EMI analysis revealed alternation of thin beds which can not been recognized by naked eyes. Chemical analysis shows that this heterogeneity originates from a variation in diatom and clastic material contents in the rock. We also examined seismic data using GDI method. For sedimentary modeling software, we expanded the sedimentary simulation module, and attached another module to compare the calculated results with actual data. We also attached the module to find the best input parameters. We performed a test run using the geology model we made for Horonobe area.
Hoshi, Kazuyoshi*; Hou, J.-Y.*; Kawada, Koji*; Tsuji, Takashi*; Suwabe, Mizue*
JNC TJ8400 2005-008, 138 Pages, 2005/01
Developing a method to evaluate heterogeneity of sedimentary rocks is very important for a site survey and a property test of the site. We studied siliceous shale from wells in the Horonobe area, and developed a sedimentary process modeling software in order to establish a method to evaluate heterogeneity of sedimentary rocks. Well log analysis of Koetoi and Wakkanai Formations revealed variations of porosity, shale content, and amount of erosion. We correlate marker beds, and establish a compaction curve for siliceous shale in the Horonobe area. EMI analysis revealed alternation of thin beds which can not been recognized by naked eyes. Chemical analysis shows that this heterogeneity originates from a variation in diatom and clastic material contents in the rock. We also examined seismic data using GDI method. For sedimentary modeling software, we expanded the sedimentary simulation module, and attached another module to compare the calculated results with actual data. We also attached the module to find the best input parameters. We performed a test run using the geology model we made for Horonobe area.
Kato, Arata*; Kawada, Koji*; Masui, Yasuhiro*; Tsuji, Takashi*; Suwabe, Mizue*
JNC TJ8400 2003-094, 71 Pages, 2004/02
It is very important to estimate the facies distribution of heterogeneous sedimentary rocks for geological disposal of high level radioactive waste. The heterogeneousness of sedimentary rocks is due to variable distribution of grain size and mineral composition. The objective of this study is to establish the evaluation method for heterogeneous sedimentary rocks based on forward model. In this study, the following items were studied.1.}The sedimentary system for Koetoi and Wakkanai formations in Horonobe area was compiled based on published papers.2.}The cores of HDB-1 were observed mainly from sedimentological view.3.}The facies and compaction property of argillaceous rocks were studied based on physical logs and core analysis data of wells.4.}The structure maps, isochrone maps, isopach maps and restored geological sections were made.5.}The soft wear for sedimentary model to show sedimentary system on a basin scale was developed.
Kato, Arata*; Kawada, Koji*; Masui, Yasuhiro*; Tsuji, Takashi*; Suwabe, Mizue*
JNC TJ8400 2003-093, 178 Pages, 2004/02
It is very important to estimate the facies distribution of heterogeneous sedimentary rocks for geological disposal of high level radioactive waste. The heterogeneousness of sedimentary rocks is due to variable distribution of grain size and mineral composition. The objective of this study is to establish the evaluation method for heterogeneous sedimentary rocks based on forward model. In this study, the following items were studied. 1..The sedimentary system for Koetoi and Wakkanai formations in Horonobe area was compiled based on published papers. 2..The cores of HDB-1 were observed mainly from sedimentological view. 3..The facies and compaction property of argillaceous rocks were studied based on physical logs and core analysis data of wells. 4..The structure maps, isochrone maps, isopach maps and restored geological sections were made. 5..The soft wear for sedimentary model to show sedimentary system on a basin scale was developed.