Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Kajino, Mizuo*; Inomata, Yayoi*; Sato, Keiichi*; Ueda, Hiromasa*; Han, Z.*; An, J.*; Katata, Genki; Deushi, Makoto*; Maki, Takashi*; Oshima, Naga*; et al.
Atmospheric Chemistry and Physics, 12(24), p.11833 - 11856, 2012/12
Times Cited Count:45 Percentile:74.69(Environmental Sciences)A new aerosol chemical transport model, Regional Air Quality Model 2 (RAQM2), was developed to simulate Asian air quality. We implemented a simple version of a modal-moment aerosol dynamics model and achieved completely dynamic solution of a gas-to-particle mass transfer over a wide range of aerosol diameters from 1 nm to super micro m. To consider a variety of atmospheric aerosol properties, a category approach is utilized: aerosols are distributed into 4 categories, Aitken, accumulation, soot aggregates, and coarse mode. A regional-scale simulation was performed for the entire year of 2006, covering Northeast Asian region. Statistical analysis showed the model reproduced the regional-scale transport and transformation of the major inorganic anthropogenic and natural air constituents within factors of 2 to 5. Modeled size distributions of total weight and chemical components were consistent with the observations, indicating simulations of aerosol mixing types were successful.
Katata, Genki; Nagai, Haruyasu; Kajino, Mizuo*; Ueda, Hiromasa*; Hozumi, Yu*
Agricultural and Forest Meteorology, 150(3), p.340 - 353, 2010/03
Times Cited Count:31 Percentile:76.95(Agronomy)The aim of the present study is to evaluate fog deposition on vegetation and its contribution to water and energy balance in arid regions using a detailed land surface model including fog deposition on vegetation under meteorological conditions simulated by a meteorological model. The results of estimated fog deposition indicated that fog deposition provided a more effective water source for plant growth as compared to heavy rainfall in arid areas. Evaporation from leaf surface water eases the plant's water stress via reducing transpiration. Latent heat of evaporation from the leaf surface water and soil causes temperature reduction of soil and leaves during the daytime. Moreover, decreased transpiration rates as a result of increased evaporation from the leaf surface water due to fog deposition, yields an effective water source to be used for photosynthesis for those plants suffering from severe water stress in arid environments.
Katata, Genki; Nagai, Haruyasu; Ueda, Hiromasa*; Agam, N.*; Berliner, P. R.*
Journal of Hydrometeorology, 8(6), p.1307 - 1324, 2007/12
no abstracts in English
Ushigusa, Kenkichi; Seki, Masahiro; Ninomiya, Hiromasa; Norimatsu, Takayoshi*; Kamada, Yutaka; Mori, Masahiro; Okuno, Kiyoshi; Shibanuma, Kiyoshi; Inoue, Takashi; Sakamoto, Keishi; et al.
Genshiryoku Handobukku, p.906 - 1029, 2007/11
no abstracts in English
Katata, Genki; Nagai, Haruyasu; Ueda, Hiromasa*
Proceedings of 4th International Conference on Fog, Fog Collection and Dew, p.33 - 36, 2007/07
Generation of fog along the coastal mountain range in a semi-arid environment is investigated using three-dimensional Mesoscale Model (MM5) simulations. The study focuses on dense fog formed along a west side of the Asir mountains in Saudi Arabia during January 2002. MM5 reproduced tower measurements of cloud water content, wind speed and direction, air temperature, humidity, and solar radiation. Computed profiles of wind speed and direction, air temperature, and humidity also agreed with rawinsonde measurements. Numerical experiments using a one-dimensional model for atmosphere-soil-vegetation interaction (SOLVEG) with fog water deposition process have been performed to evaluate the contribution of fog water deposition to water resource at the area. Meteorological and cloud water at the lowest atmospheric layer from MM5 simulation results were used in the experiments. Fog along the coastal mountain range may be an important water resource for vegetation surviving in the area.
Tamai, Hiroshi; Matsukawa, Makoto; Kurita, Genichi; Hayashi, Nobuhiko; Urata, Kazuhiro*; Miura, Yushi; Kizu, Kaname; Tsuchiya, Katsuhiko; Morioka, Atsuhiko; Kudo, Yusuke; et al.
Plasma Science and Technology, 6(1), p.2141 - 2150, 2004/02
Times Cited Count:2 Percentile:6.49(Physics, Fluids & Plasmas)The dominant issue for the the modification program of JT-60 (JT-60SC) is to demonstrate the steady state reactor relevant plasma operation. Physics design on plasma parameters, operation scenarios, and the plasma control method are investigated for the achievement of high- . Engineering design and the R&D on the superconducting magnet coils, radiation shield, and vacuum vessel are performed. Recent progress in such physics and technology developments is presented.
. Engineering design and the R&D on the superconducting magnet coils, radiation shield, and vacuum vessel are performed. Recent progress in such physics and technology developments is presented.
Ishida, Shinichi; Abe, Katsunori*; Ando, Akira*; Chujo, T.*; Fujii, Tsuneyuki; Fujita, Takaaki; Goto, Seiichi*; Hanada, Kazuaki*; Hatayama, Akiyoshi*; Hino, Tomoaki*; et al.
Nuclear Fusion, 43(7), p.606 - 613, 2003/07
no abstracts in English
Ishida, Shinichi; Abe, Katsunori*; Ando, Akira*; Cho, T.*; Fujii, Tsuneyuki; Fujita, Takaaki; Goto, Seiichi*; Hanada, Kazuaki*; Hatayama, Akiyoshi*; Hino, Tomoaki*; et al.
Nuclear Fusion, 43(7), p.606 - 613, 2003/07
Times Cited Count:33 Percentile:69.14(Physics, Fluids & Plasmas)no abstracts in English
Terada, Hiroaki; Ueda, Hiromasa*; Wang, Z.*
Atmospheric Environment, 36(3), p.503 - 509, 2002/01
Times Cited Count:48 Percentile:70.24(Environmental Sciences)Acid rain and its neutralization by yellow-sand in East Asia was investigated numerically by an Air Quality Prediction Modeling System (AQPMS). AQPMS consists of advection, diffusion, dry and wet deposition, gas- and liquid-phase chemistry. A new deflation module of the yellow-sand was designed to provide explicit information on the dust loading, and linked to the AQPMS. For model validation, the predicted pH values and sulfate- and nitrate-ion levels of precipitation, together with the surface concentrations of gaseous pollutants, were compared with measured values at atmospheric monitoring stations, and a reasonable agreement was obtained. Firstly, trend of the acid rain in East Asia due to the rapid increase of Chinese pollutants emission was investigated, and a remarkably rapid increase of acid rain area was predicted in the period from 1985 to 1995. Secondly, the simulation results of April 1995 exhibited a strong neutralization of the precipitation by the yellow-sand.
Terada, Hiroaki; Ueda, Hiromasa*; Wang, Z.*
Proceedings of 7th International Joint Seminar on the Regional Deposition Processes in the Atmosphere, p.115 - 122, 2001/11
The neutralization of acid rain by yellow-sand in East Asia was investigated numerically by an Air Quality Prediction Modeling System (AQPMS). AQPMS consists of advection, diffusion, dry and wet deposition, gas-phase chemistry and the liquid-phase chemistry. Different from the previous ones for Sahara and Australian deserts, a new deflation module of the yellow-sand was designed here, and this module was linked to the AQPMS. Firstly, for model validation, predicted various values were compared with measured values at atmospheric monitoring stations, and a reasonable agreement was obtained for April 1995. Secondly, a sensitivity experiment about chemical effects of yellow-sand was made and the result of it exhibited a strong neutralization of the precipitation by the yellow-sand. The monthly mean pH values in the northern China showed a remarkable increase of 0.6-1.8 by neutralization effect of the yellow-sand, while the increases in the southern China were less than 0.1. Even in Korea and Japan the yellow-sand caused the increase of the pH value of rain by 0.1-0.2.
Nishio, Satoshi; Ushigusa, Kenkichi; Ueda, Shuzo; Polevoi, A.*; Kurita, Genichi; Tobita, Kenji; Kurihara, Ryoichi; Hu, G.; Okada, Hidetoshi*; Murakami, Yoshiki*; et al.
JAERI-Research 2000-029, 105 Pages, 2000/10
no abstracts in English
Katata, Genki; Nagai, Haruyasu; Ueda, Hiromasa*
no journal, ,
no abstracts in English
Oka, Kiyoshi; Yamashita, Hiromasa*; Nakamura, Tetsuya*; Ueda, Hirohisa*; Chiba, Toshio*
no journal, ,
In fetoscopic laser photocoagulation of placental communicating vessels (FLPC) for twin-to-twin transfusion syndrome (TTTS), there are several technical issues. These include; (1) laser light diffusion that reduces the energy density over the placental surface, (2) unknown distances between the placental surface and laser fiber tip, (3) difficulties in assessing actual flow of the targeted blood vessels, and (4) difficulties in controlling laser light direction for perpendicular irradiation. To settle these problems, we successfully developed a new small composite-type optical fiberscope. In this report, we present our experimental outcomes to assess its clinical availability/feasibility for clinical TTTS laser surgery.
Katata, Genki; Nagai, Haruyasu; Kajino, Mizuo*; Ueda, Hiromasa*
no journal, ,
no abstracts in English
Kajino, Mizuo*; Katata, Genki; Nagai, Haruyasu; Ishikawa, Hirohiko*; Ueda, Hiromasa*
no journal, ,
no abstracts in English
Oka, Kiyoshi; Nakamura, Tetsuya*; Ueda, Hirohisa*; Toriya, Tomoaki*; Tsumanuma, Koji*; Naganawa, Akihiro*; Watanabe, Shinsuke*; Ishiyama, Akihiko*; Yamashita, Hiromasa*; Chiba, Toshio*
no journal, ,
no abstracts in English
Kajino, Mizuo*; Katata, Genki; Hiraki, Takatoshi*; Aikawa, Masahide*; Kobayashi, Tomiki*; Ueda, Hiromasa*
no journal, ,
We numerically evaluated depositional pathways of major air pollutants such as SO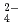 , NH
, NH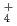 , NO
, NO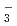 , Cl
, Cl , and Na
, and Na over mountain forest areas in Mt. Rokko in July 1999. A modified WRF model including fog deposition (fog-WRF) and Regional Air Quality Model 2 (RAQM2) was used for simulations. To show the consistency of the model performance, the measured chemical components in fog water were compared with the modeled concentrations. During the simulation period, the persistent southerly wind carried humid air from the Osaka Bay to Mt. Rokko and caused condensation along mountain ridges higher than 400 m in altitude during nights. Simulation results showed that fog deposition was dominant for all depositional components, while dry deposition of nitrate was large due to the high deposition velocity of HNO
over mountain forest areas in Mt. Rokko in July 1999. A modified WRF model including fog deposition (fog-WRF) and Regional Air Quality Model 2 (RAQM2) was used for simulations. To show the consistency of the model performance, the measured chemical components in fog water were compared with the modeled concentrations. During the simulation period, the persistent southerly wind carried humid air from the Osaka Bay to Mt. Rokko and caused condensation along mountain ridges higher than 400 m in altitude during nights. Simulation results showed that fog deposition was dominant for all depositional components, while dry deposition of nitrate was large due to the high deposition velocity of HNO gas.
gas.