Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Igarashi, Sayaka*; Sakamoto, Shigehiro*; Ugata, Takeshi*; Nishida, Akemi; Muramatsu, Ken*; Takada, Tsuyoshi*
Transactions of the 24th International Conference on Structural Mechanics in Reactor Technology (SMiRT-24) (USB Flash Drive), 10 Pages, 2017/08
For the purpose of improving the precision of probabilistic seismic PRA for NPPs, the authors developed the methodology for generating hazard-consistent ground motions based on stochastic fault models which include seismic-source uncertainties by Monte Carlo Simulation. The PRA with HCGMs would require a lot of computer power. The optimization of ground-motions generations is one of the most important subjects for practical application of the PRA method. For optimizing the ground-motions generations, seismic sources for the generations should be selected effectively, and this can be conducted by utilizing optimal seismic index in the hazard analysis. In this study, the method for detecting the optimal seismic intensity index which corresponds with damage probabilities of the target equipment system was developed, and the validity of the proposed method was confirmed for some equipment systems, which has different weak equipment with each other.
Kato, Masato; Komeno, Akira; Uno, Hiroki*; Sugata, Hiromasa*; Nakae, Nobuo; Konashi, Kenji*; Kashimura, Motoaki
Journal of Nuclear Materials, 393(1), p.134 - 140, 2009/08
Times Cited Count:41 Percentile:92.56(Materials Science, Multidisciplinary)In plutonium compounds, the lattice parameter increases due to self-radiation damage by  -decay of plutonium isotopes. The lattice parameter change and its thermal recovery in plutonium and uranium mixed dioxide (MOX) were studied. The lattice parameter for samples of MOX powders and pellets that had been left in the air for up to 32 years was measured. The lattice parameter increased and was saturated at about 0.29%. The change in lattice parameter was formulated as a function of self-radiation dose. Three stages in the thermal recovery of the damage were observed in temperature ranges of below 673K, 673-1073K and above 1073K. The activation energies in each recovery stage were estimated to be 0.12 eV, 0.73 eV and 1.2 eV, respectively, and the corresponding mechanism for each stage was considered to be the recovery of the anion Frenkel defect, the cation Frenkel defect and a defect connected with helium, respectively.
-decay of plutonium isotopes. The lattice parameter change and its thermal recovery in plutonium and uranium mixed dioxide (MOX) were studied. The lattice parameter for samples of MOX powders and pellets that had been left in the air for up to 32 years was measured. The lattice parameter increased and was saturated at about 0.29%. The change in lattice parameter was formulated as a function of self-radiation dose. Three stages in the thermal recovery of the damage were observed in temperature ranges of below 673K, 673-1073K and above 1073K. The activation energies in each recovery stage were estimated to be 0.12 eV, 0.73 eV and 1.2 eV, respectively, and the corresponding mechanism for each stage was considered to be the recovery of the anion Frenkel defect, the cation Frenkel defect and a defect connected with helium, respectively.
Kato, Masato; Morimoto, Kyoichi; Nakamichi, Shinya; Sugata, Hiromasa*; Konashi, Kenji*; Kashimura, Motoaki; Abe, Tomoyuki
Nihon Genshiryoku Gakkai Wabun Rombunshi, 7(4), p.420 - 428, 2008/12
The melting temperatures of MOX for fast reactor fuel were investigated as functions of Pu content, Am content and oxygen-to-metal (O/M) ratio using thermal arrest technique. Rhenium inner was used for the measurement to prevent the reaction between the sample and capsule materials. The solidus temperatures decreased with increasing Pu and Am content and increased with decreasing O/M ratio. It is considered that the maximum temperature in U-Pu-O system varies in hypostoichiometric composition region. The melting temperatures were evaluated by ideal solid solution model in UO -PuO
-PuO -AmO
-AmO -PuO
-PuO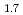 system, and the model was derived for calculating solidus and liquidus temperature. The derived model reproduced the experimental data with
system, and the model was derived for calculating solidus and liquidus temperature. The derived model reproduced the experimental data with  25 K.
25 K.
Kato, Masato; Morimoto, Kyoichi; Sugata, Hiromasa*; Konashi, Kenji*; Kashimura, Motoaki; Abe, Tomoyuki
Journal of Alloys and Compounds, 452(1), p.48 - 53, 2008/03
Times Cited Count:30 Percentile:77.85(Chemistry, Physical)Plutonium and uranium mixed oxide has been developed as a fuel of a fast reactor. The maximum temperature of the fuel pellet is limited within a design criterion to prevent fuel melting. So, the melting points of the mixed oxide have been investigated since the development of fast reactor started. However the measured data are limited. In this work, the melting points of (U1-yPuy)O (y: 0, 0.12, 0.2, 0.3, 0.4) were measured by the thermal arrest method. The evaluated melting point of this study underestimates in case of MOX with high Pu contents of 30% and 40%. The solidus of UO
(y: 0, 0.12, 0.2, 0.3, 0.4) were measured by the thermal arrest method. The evaluated melting point of this study underestimates in case of MOX with high Pu contents of 30% and 40%. The solidus of UO , (Pu
, (Pu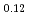 U
U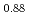 )O
)O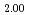 and (Pu
and (Pu U
U )O
)O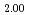 were determined to be 3128K, 3077K and 3052K, respectively. The solidus temperature of hypostoichiometric MOX slightly increased with decreasing O/M.
were determined to be 3128K, 3077K and 3052K, respectively. The solidus temperature of hypostoichiometric MOX slightly increased with decreasing O/M.
 -PuO
-PuO system
systemKato, Masato; Morimoto, Kyoichi; Sugata, Hiromasa*; Konashi, Kenji*; Kashimura, Motoaki; Abe, Tomoyuki
Journal of Nuclear Materials, 373(1-3), p.237 - 245, 2008/02
Times Cited Count:60 Percentile:96.13(Materials Science, Multidisciplinary)The melting of plutonium and uranium mixed oxide (MOX) containing Pu of more than 30% was investigated using a tungsten capsule and a rhenium inner capsule. In the conventional measurement of MOX in the tungsten capsule, a liquid phase of tungsten and plutonium oxide appeared in the MOX during melting. This liquid phase was found to have an effect on the measurement of melting point. Therefore the rhenium inner capsule was used to avoid the effect. The solidus and liquidus temperatures in the UO -PuO
-PuO system were decided from the MOX data measured using the rhenium capsule, and the effect of the Am content on the solidus temperature was evaluated. The variation of the solidus and liquidus temperatures in the UO
system were decided from the MOX data measured using the rhenium capsule, and the effect of the Am content on the solidus temperature was evaluated. The variation of the solidus and liquidus temperatures in the UO -PuO
-PuO -AmO
-AmO ternary system was represented to an accuracy of
ternary system was represented to an accuracy of  =
= 9K and
9K and  =
= 16K, respectively, by the ideal solution model.
16K, respectively, by the ideal solution model.
Taniguchi, Naoki; Suzuki, Hiroyuki*; Nakanishi, Tomoaki*; Nakayama, Takenori*; Masugata, Tsuyoshi*; Tateishi, Tsuyoshi*
Zairyo To Kankyo, 56(12), p.576 - 584, 2007/12
The long term hydrogen absorption behavior and the possibility of hydrogen embrittlement were studied for titanium overpack for high level radioactive waste disposal. The results of galvanostatic cathodic polarization tests showed that as the cathodic current density is lowered, the amount of absorbed hydrogen for a constant cathodic charge was increased as well as hydrogen permeated into inside of titanium. The hydrogen absorption ratio for a cathodic current density equivalent to the corrosion rate under anaerobic condition was estimated to nearly 100 percent, and the amount of absorbed hydrogen for 1000 years was evaluated to be 400 ppm. The mechanical property of titanium containing hydrogen depended on not only hydrogen concentration but also hydrogen distribution type. The more hydrogen distribution is uniform, the degree of embrittlement was larger. It was expected that the rupture of titanium overpack with 6 mm thickness would be initiated if the crack size in titanium is over about 2-3 mm under the stress corresponds to yield strength.
Kato, Masato; Morimoto, Kyoichi; Sugata, Hiromasa*; Konashi, Kenji*; Kashimura, Motoaki; Abe, Tomoyuki
Transactions of the American Nuclear Society, 96(1), p.193 - 194, 2007/06
Melting point of a nuclear fuel is one of the important physical properties for its development, because it limits maximum temperature of the fuel during operation. A rhenium inner capsule was used to prevent the reaction with capsule for measuring melting points of MOX. In this work melting points of MOX with 40% and 46%Pu were investigated as a function of an O/M ratio using Re inner, and the effect of the O/M ratio on the melting points was evaluated. The solidus and liquidus temperatures in (Pu U
U )O
)O and (Pu
and (Pu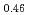 U
U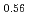 )O
)O were measured by thermal arrest method. It was observed that the melting points in the both samples increased with a decrease of the O/M from 2.00, and their data were 50-100K higher than existing data measured in previous works which were measured with W capsule.
were measured by thermal arrest method. It was observed that the melting points in the both samples increased with a decrease of the O/M from 2.00, and their data were 50-100K higher than existing data measured in previous works which were measured with W capsule.
Taniguchi, Naoki; Suzuki, Hiroyuki*; Yui, Mikazu; Nakanishi, Tomoaki*; Nakayama, Takenori*; Masugata, Tsuyoshi*; Tateishi, Tsuyoshi*
no journal, ,
Titanium (including titanium alloy) is one of the candidate materials of overpacks for geological disposal of high-level radioactive waste, and required long term integrity against the groundwater for more than 1000 years. As the corrosion of titanium occurs, hydrogen is generated since the deep underground environment is originally low oxygen concentration condition. There is a possibility that the titanium overpack will be attackd by the hydrogen embrittlement due to long term hydrogen absorption. In this study, the amount of hydrogen and the possibility of embrittlement were investigated based on the experimental data on the corrosion rate, hydrogen absorption behavior, mechanical proparty of titanium containing hydrogen.