Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
 O
OKondo, Yosuke*; Achouri, N. L.*; Al Falou, H.*; Atar, L.*; Aumann, T.*; Baba, Hidetada*; Boretzky, K.*; Caesar, C.*; Calvet, D.*; Chae, H.*; et al.
Nature, 620(7976), p.965 - 970, 2023/08
Times Cited Count:5 Percentile:92.64(Multidisciplinary Sciences)no abstracts in English
Katsuyama, Jinya; Osakabe, Kazuya*; Uno, Shumpei*; Li, Y.; Yoshimura, Shinobu*
Journal of Pressure Vessel Technology, 142(2), p.021205_1 - 021205_10, 2020/04
Times Cited Count:2 Percentile:15.81(Engineering, Mechanical)no abstracts in English
Katsuyama, Jinya; Uno, Shumpei*; Watanabe, Tadashi*; Li, Y.
Frontiers of Mechanical Engineering, 13(4), p.563 - 570, 2018/12
Times Cited Count:2 Percentile:12.21(Engineering, Mechanical)For the structural integrity assessments on reactor pressure vessels (RPVs) under pressurized thermal shock (PTS) events, thermal hydraulic (TH) behavior of coolant water is one of the most important influence factors. Configuration of plant equipment and their dimensions, and operator action have large influences on TH behavior. In this study, to investigate the influence of operator action on TH behavior during a PTS event, we developed an analysis model for a typical Japanese plant, and performed TH and structural analyses. Two different operator action times were assumed based on the Japanese and US' rules. From the analysis results, it was clarified that differences in operator action times have a significant effect on TH behavior and loading conditions, that is, following the Japanese rule may lead to lower stresses compared to that when following the US rule because earlier operator action caused lower pressure in the RPV.
Lu, K.; Masaki, Koichi; Katsuyama, Jinya; Li, Y.; Uno, Shumpei*
Proceedings of 2018 ASME Pressure Vessels and Piping Conference (PVP 2018), 10 Pages, 2018/07
Li, Y.; Uno, Shumpei*; Masaki, Koichi; Katsuyama, Jinya; Dickson, T.*; Kirk, M.*
Proceedings of 2018 ASME Pressure Vessels and Piping Conference (PVP 2018), 11 Pages, 2018/07
Li, Y.; Uno, Shumpei*; Katsuyama, Jinya; Dickson, T.*; Kirk, M.*
Proceedings of 2017 ASME Pressure Vessels and Piping Conference (PVP 2017) (CD-ROM), 8 Pages, 2017/07
Lu, K.; Katsuyama, Jinya; Uno, Shumpei; Li, Y.
Proceedings of 2017 ASME Pressure Vessels and Piping Conference (PVP 2017) (CD-ROM), 8 Pages, 2017/07
Katsuyama, Jinya; Osakabe, Kazuya*; Uno, Shumpei; Li, Y.; Yoshimura, Shinobu*
Proceedings of 2017 ASME Pressure Vessels and Piping Conference (PVP 2017) (CD-ROM), 9 Pages, 2017/07
A structural integrity assessment methodology based on probabilistic fracture mechanics (PFM) is a rational methodology in evaluating failure frequency of reactor pressure vessels (RPVs) by considering the probabilistic distributions of various influence factors related to the aged degradation. We have developed a PFM analysis code PASCAL to evaluate the failure frequency of RPVs considering the neutron irradiation embrittlement and pressurized thermal shock (PTS) events. We have also developed a guideline on the structural integrity assessment of RPVs based on PFM to improve the applicability of PFM in Japan and to be able to perform the PFM analyses and evaluate through-wall cracking frequency of RPVs. The technical basis for PFM analysis is provided and the latest knowledge is included in the guideline. In this paper, an overview of the guideline and some typical analysis results obtained based on the guideline and Japanese database related to PTS evaluation are presented.
Masaki, Koichi; Miyamoto, Yuhei*; Osakabe, Kazuya*; Uno, Shumpei*; Katsuyama, Jinya; Li, Y.
Proceedings of 2017 ASME Pressure Vessels and Piping Conference (PVP 2017) (CD-ROM), 7 Pages, 2017/07
A probabilistic fracture mechanics (PFM) analysis code PASCAL has been developed by Japan Atomic Energy Agency (JAEA). PASCAL can evaluate failure frequencies of Japanese reactor pressure vessels (RPVs) during pressurized thermal shock (PTS) events based on domestic structural integrity assessment models and data of influence factors. In order to improve the engineering applicability of PFM to Japanese RPVs, we have performed verification of the PASCAL. In general, PFM code consists of many functions such as fracture mechanics evaluation functions, probabilistic evaluation functions including random variables sampling modules and probabilistic evaluation models, and so on. The verification of PFM code is basically difficult because it is impossible to confirm such functions through the comparison with experiments. When a PFM code is applied for evaluating failure frequencies of RPVs, verification methodology of the code should be clarified and it is important that verification results including the region and process of the verification of the code are indicated. In this paper, our activities of verification for PASCAL are presented. We firstly represent the overview and methodology of verification of PFM code, and then, some verification examples are provided. Through the verification activities, the applicability of PASCAL in structural integrity assessments for Japanese RPVs was confirmed with great confidence.
Katsuyama, Jinya; Osakabe, Kazuya*; Uno, Shumpei; Li, Y.
JAEA-Research 2016-022, 40 Pages, 2017/02
For reactor pressure vessels (RPVs) in the light water reactors, the fracture toughness decreases due to the neutron irradiation embrittlement with operating years. In Japan, to prevent RPVs from a nil-ductile fracture, deterministic fracture mechanics methods in accordance with the codes provided by the Japan Electric Association are performed for assessing the structural integrity of RPVs under the pressurized thermal shock (PTS) events by taking the neutron irradiation embrittlement into account. On the other hand, in recent years, probabilistic methodologies for PTS evaluation are introduced into regulations in Europe and the United States. For example, in the United States, a PTS screening criterion related to the reference temperature derived by the probabilistic method is stipulated. If the screening criterion is not satisfied, it is approved to perform the evaluation based on the probabilistic method by calculating numerical index such as through-wall crack frequency (TWCF). To reach the objectives that persons who have knowledge on the fracture mechanics can carry out the PFM analyses and obtain TWCF for a domestic RPVs by referring to this report, we develop the guideline on a structural integrity assessment method based on PFM by reflecting the latest knowledge and expertise.
Uno, Shumpei; Katsuyama, Jinya; Watanabe, Tadashi*; Li, Y.
Proceedings of 2016 ASME Pressure Vessels and Piping Conference (PVP 2016) (Internet), 8 Pages, 2016/07
For structural integrity assessment on reactor pressure vessels (RPVs) of pressurized water reactor during the pressurized thermal shock (PTS) events, thermal history of coolant water and heat transfer coefficient between coolant water and RPV are dominant factors. These values can be determined on the basis of thermal-hydraulics (TH) analyses simulating PTS events and Jackson-Fewster correlation. Using these values, subsequently, loading conditions for structural integrity assessments of RPVs are evaluated by structural analyses. Nowadays, three-dimensional TH and structural analyses are recognized as precise assessment method for structural integrity of RPVs. In this study, we performed the TH and structural analyses using three-dimensional models of cold-leg, downcomer and RPV in order to evaluate loading conditions during a PTS event more accurately. Distributions of temperature of coolant water and heat transfer coefficient on the surface of RPV were calculated by TH analysis. Loading condition evaluation was then performed by using these values and taking the weld residual stress due to weld-overlay cladding and post-weld heat treatment into consideration. From these analyses, we obtained histories and distributions of loading conditions at the reactor core region of RPV. We discussed the conservativeness of current structural integrity assessment method of RPV prescribed in the current codes through the comparison in the loading conditions due to PTS event.
 Ni
NiChiara, C. J.*; Weisshaar, D.*; Janssens, R. V. F.*; Tsunoda, Yusuke*; Otsuka, Takaharu*; Harker, J. L.*; Walters, W. B.*; Recchia, F.*; Albers, M.*; Alcorta, M.*; et al.
Physical Review C, 91(4), p.044309_1 - 044309_10, 2015/04
Times Cited Count:39 Percentile:91.59(Physics, Nuclear)The neutron-rich isotope  Ni was produced by multi-nucleon transfer reactions of
Ni was produced by multi-nucleon transfer reactions of  Zn in the Argonne National Laboratory, and an in-beam
Zn in the Argonne National Laboratory, and an in-beam  -ray experiment were performed using the GRETINA array. The
-ray experiment were performed using the GRETINA array. The 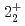 and
and 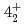 levels of
levels of  Ni were observed for the first time. Those levels are regarded as large deformed states associated with proton excitation from the
Ni were observed for the first time. Those levels are regarded as large deformed states associated with proton excitation from the 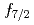 orbit because they cannot be reproduced by a shell-model calculation assuming a small valence space without
orbit because they cannot be reproduced by a shell-model calculation assuming a small valence space without 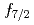 . A theoretical analysis based on the Monte Carlo shell model published in 2014 indicates that those levels corresponds to a prolate deformed band. The present result demonstrates the occurrence of shape coexistence in neutron-rich Ni isotopes other than a known case of
. A theoretical analysis based on the Monte Carlo shell model published in 2014 indicates that those levels corresponds to a prolate deformed band. The present result demonstrates the occurrence of shape coexistence in neutron-rich Ni isotopes other than a known case of  Ni, and confirms the predictive power of the Monte Carlo shell-model calculation.
Ni, and confirms the predictive power of the Monte Carlo shell-model calculation.
Uno, Shumpei; Katsuyama, Jinya; Katsumata, Genshichiro*; Masaki, Koichi*; Osakabe, Kazuya*; Li, Y.
no journal, ,
Assuring the structural integrity of a reactor pressure vessel (RPV) is known as one of the critical issues to maintain the safe long-term operation of a nuclear power plant. Authors have been conducting extensive research on the improvement of structural integrity assessment methods of RPVs. In this paper, we describe some research results obtained from the recent activity including the review on the technical background of the methods and study on probabilistic methods for the applicability to the current code and standard.
Katsuyama, Jinya; Uno, Shumpei; Li, Y.
no journal, ,
no abstracts in English
Masaki, Koichi; Uno, Shumpei*; Katsuyama, Jinya; Li, Y.
no journal, ,
no abstracts in English
Li, Y.; Katsuyama, Jinya; Osakabe, Kazuya*; Uno, Shumpei*
no journal, ,
no abstracts in English
Machida, Masahiko; Uno, Shumpei*; Tanimura, Naoki*; Saito, Kimiaki; Yoshimura, Kazuya
no journal, ,
Air dose rates in urban areas decrease faster in residential areas than in evacuation zones. This suggests that human activities facilitate the reduction. However, since human activities include various factors such as decontamination and road wear caused by traffic, it is difficult to evaluate the effect of human activities by conventional analysis using monitoring data, except for the effect of decontamination. Then, this series of studies aim to evaluate the effects of human activities on the reduction. Among the series presentations, this one focuses on correlations between population dynamics characterized by mobile phone GPS information and ecological half life decays of air dose rates measured by KURAMA over a wide area with long-term monitoring using LASSO scheme.